Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
FDI
Загружено:
Juhi KashyapИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
FDI
Загружено:
Juhi KashyapАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A Dissertation Synopsis on
foreign direct investment and its impact on indian economic growth
Faculty of Management Studies, BHU, Varanasi Under the guidance of:
Dr H. P. Mathur Professor FMS-BHU
Submitted By:
Juhi Kashyap MBA-IB (IV Semester) Exam roll no 2011-13 FMS-BHU
Definition of FDI Foreign direct investment (FDI) is investment directly into production in a country by a company located in another country, either by buying a company in the target country or by expanding operations of an existing business in that country. -IMF Types of FDI
1. Horizontal FDI arises when a firm duplicates its home country-based activities at the same value chain stage in a host country through FDI. 2. Platform FDI 3. Vertical FDI takes place when a firm through FDI moves upstream or downstream in different value chains i.e., when firms perform value-adding activities stage by stage in a vertical fashion in a host country
FDI in India The evolution of Indian FDI can broadly be divided into three phases classified on the premises of the initiatives taken to induce foreign investments into the Indian economy:
(a) The first phase, between 1969 and 1991, was marked by the coming into force of the Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Commission (MRTP) in 1969, which imposed restrictions on the size of operations, pricing of products and services of foreign companies. The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) enacted in 1973, limited the extent of foreign equity to 40%, though this limit could be raised to 74% for technology-intensive, export-intensive, and core-sector industries. A selective licensing regime was instituted for technology transfer and royalty payments and applicants were subjected to export obligations.
(b) The second phase, between 1991 and 2000, witnessed the liberalisation of the FDI policy, as part of the Governments economic reforms program. In 1991 as per the Statement on Industrial
Policy, FDI was allowed on the automatic route, up to 51%, in 35 high priority industries. Foreign technical collaboration was also placed under the automatic route, subject to specified limits. In 1996, the automatic approval route for FDI was expanded, from 35 to 111 industries, under four distinct categories (Part Aup to 50%, Part Bup to 51%, Part Cup to 74%, and Part D-up to 100%). A Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB) was constituted to consider cases under the government route.
(c) The third phase, between 2000 till date, has reflected the increasing globalisation of the Indian economy. In the year 2000, a paradigm shift occurred, wherein, except for a negative list, all the remaining activities were placed under the automatic route. Caps were gradually raised in a number of sectors/activities. Some of the initiatives that were taken during this period were that the insurance and defence sectors were opened up to a cap of 26%, the cap for telecom services was increased from 49% to 74% , FDI was allowed up to 51% in single brand retail. The year 2010 saw the continuation of the rationalisation process and all existing regulations on FDI were consolidated into a single document for ease of reference
Modes of receiving Foreign Direct Investment i. Automatic Route FDI up to 100 per cent is allowed under the automatic route in all activities/sectors except where the provisions of the consolidated FDI Policy, paragraph on Entry Routes for Investment issued by the Government of India from time to time, are attracted. FDI in sectors /activities to the extent permitted under the automatic route does not require any prior approval either of the Government or the Reserve Bank of India. ii. Government Route FDI in activities not covered under the automatic route requires prior approval of the Government which are considered by the Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB), Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance. Indian companies having foreign investment approval through FIPB route do not require any further clearance from the Reserve
Bank of India for receiving inward remittance and for the issue of shares to the non-resident investors
Inflows of FDI in India 1991-2010 The data on FDI inflows into the country shows that foreign investors have shown a keen interest in the Indian economy ever since it has been liberalized. An increasing trend of flows can be observed since 1991 with the peak of FDI flows being reached in 2008-09.
Therefore the trend gives support to the fact that as and when the government has taken initiatives to open up and liberalize the economy further, the investors have welcomed the initiative and reciprocated by infusing investments into India. There are various reasons which work in favour of India and increase the level of interest s own in by foreign organizations some of them being its demographics with a young population there is a huge consumer base that is to be tapped, the growing middle class, increased urbanization and awareness, rising disposable incomes.
Recent Issues Related To FDI in India: Union Budget 2012-13: Efforts on for consensus on 51% FDI in multi-brand retail. (March 16, 2012, TIMES OF INDIA) FDI down 33% in Dec to $1.35 bn (March 1, 2012, TIMES OF INDIA) Govt justifies 26% FDI cap in print media (December 21, 2011, TIMES OF INDIA) FDI inflows up 36% in Jan-Oct (January 2, 2012, TIMES OF INDIA) FDI jumps 60% to $1.74bn in November (December 24, 2009, TIMES OF INDIA) The Key Decision Taken By Cabinet (Business Standard, 5 October 2012): Insurance law amendment bill To raise the FDI cap in private insurance to 49% from the existing 26%. Pension fund regulatory and development authority bill To give statutory powers to the interim pension regulator and open the sector to FDI Forward contracts (regulation) amendment bill
To introduce more commodity futures, give more power to forward market commission, Amendment to companies bill, 2011 To make spending on corporate social responsibility a mandatory provision for companies above a threshed
FDI and Economic growth FDI is considered to be the life blood and an important vehicle of for economic development as far as the developing nations are concerned. The important effect of FDI is its contribution to the growth of the economy. FDI has an important impact on countrys trade balance, increasing labour standards and skills, transfer of technology and innovative ideas, skills and the general business climate. FDI also provides opportunity for technological transfer and up gradation, access to global managerial skills and practices ,optimal utilization of human capabilities and natural resources, making industry internationally competiteve,opening up export markets,aceess to international quality goods and services and augmenting employment opportunities
FDI ,determinants and its impact FDI determinants and its impact on an economy can be studied with the help of different variables. These variables are not a exhaustive list and keep on getting updated by research by economist or international organization e.g. IMF, World bank .The following flowchart summarizes different variables that can serve as proxy for determinants and impact of FDI on an economy.
Research methodology
Objectives: To study the trend of FDI in world (1991-2011). To study the trend of FDI in India (1991-2011). To study the impact of FDI on different sector in Indian economy (1991-2011). To study the impact of FDI on economic growth of India via macroeconomic variables.
The study The study was causal in nature.
Tools for Data Collection Data was collected from the official sites of Government of India The period of 1991-2010 was considered for analysis. Tools for Data Analysis Karl Pearson coefficient of correlation.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- BFB Housing Loan Application Form v2016.HmcДокумент2 страницыBFB Housing Loan Application Form v2016.HmcJoy Ramos100% (3)
- Becoming Market SmithДокумент82 страницыBecoming Market SmithTu D.Оценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Kellogg's Financial Statement Case StudyДокумент10 страницKellogg's Financial Statement Case StudyKhoa Huynh67% (6)
- 3 Months Statement. SAUDA 18Документ2 страницы3 Months Statement. SAUDA 18Fikile Eem100% (1)
- 2008.10 The Super Investor Walter Schloss InterviewДокумент4 страницы2008.10 The Super Investor Walter Schloss Interviewadjk97100% (4)
- CaseStudy ExerciseДокумент20 страницCaseStudy ExerciseLinh NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Abm 2 Grade 11 Midterm Exam S.Y. 2019 - 2020Документ2 страницыFundamentals of Abm 2 Grade 11 Midterm Exam S.Y. 2019 - 2020Sheena RobiniolОценок пока нет
- Changing Rooms at Tailor ShopДокумент2 страницыChanging Rooms at Tailor ShopJuhi KashyapОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент4 страницыSWOT AnalysisJuhi KashyapОценок пока нет
- Terrorizmus 5Документ43 страницыTerrorizmus 5Juhi KashyapОценок пока нет
- FDI PolicyДокумент12 страницFDI PolicyJuhi KashyapОценок пока нет
- Balance Sheet of HMC LTD.: (Rs. in Lakhs)Документ2 страницыBalance Sheet of HMC LTD.: (Rs. in Lakhs)Parmar BrijeshОценок пока нет
- Chapter One Extinction of ObligationsДокумент46 страницChapter One Extinction of ObligationsHemen zinahbizuОценок пока нет
- Bio Data - Preyanshi Gupta ACMA OLDДокумент5 страницBio Data - Preyanshi Gupta ACMA OLDPreyanshi GuptaОценок пока нет
- YakДокумент35 страницYakImran PathanОценок пока нет
- # 1 - SalesДокумент29 страниц# 1 - SalesLee TeukОценок пока нет
- FINMAN MIDTERMS StudentsДокумент5 страницFINMAN MIDTERMS StudentsJennifer RasonabeОценок пока нет
- Blackrock Quarterly UpdateДокумент11 страницBlackrock Quarterly UpdateZorrays JunaidОценок пока нет
- Beta Calculation AssignmentДокумент3 страницыBeta Calculation AssignmentAbhishek SinghОценок пока нет
- Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail Limited: Disc - Amt Disc% Item - Name Ean - Code HSN QTY MRP Net - Amt Tax - Rate TaxДокумент2 страницыAditya Birla Fashion and Retail Limited: Disc - Amt Disc% Item - Name Ean - Code HSN QTY MRP Net - Amt Tax - Rate TaxAnirban GhoshОценок пока нет
- Mcit and CWTДокумент5 страницMcit and CWTOlan Dave LachicaОценок пока нет
- LIBOR TransitionДокумент10 страницLIBOR TransitionMahek GoyalОценок пока нет
- Accounting ExercisesДокумент41 страницаAccounting ExercisesKayla MirandaОценок пока нет
- National Pension System (NPS) : Form 101-GSДокумент10 страницNational Pension System (NPS) : Form 101-GSSREERAMULU MADINE0% (1)
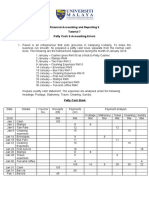
- Tutorial 7 Petty Cash Book QuestionsДокумент3 страницыTutorial 7 Petty Cash Book QuestionsKubenderarubban BalachantharОценок пока нет
- Lower of Cost and Net Realizable ValueДокумент3 страницыLower of Cost and Net Realizable ValueMae Loto100% (1)
- Cibil Report KAILASH CHAND FULARA1564842956149 PDFДокумент3 страницыCibil Report KAILASH CHAND FULARA1564842956149 PDFKaran FularaОценок пока нет
- Vdocuments - MX - Obligations Contracts Memory AidДокумент24 страницыVdocuments - MX - Obligations Contracts Memory AidMarie Lourence AngelesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 The Monetary SystemДокумент3 страницыChapter 16 The Monetary SystemPhuong Vy PhamОценок пока нет
- Mod 2 Income Management-3Документ13 страницMod 2 Income Management-3Shruti b ahujaОценок пока нет
- Brisbane Land ValuationsДокумент8 страницBrisbane Land ValuationsW Martin Canales AyalaОценок пока нет
- PFM 4 DimensionsДокумент10 страницPFM 4 DimensionsSentayehu GebeyehuОценок пока нет
- 2 L-T Financial Management - Financial InstrumentsДокумент54 страницы2 L-T Financial Management - Financial InstrumentsMohammad DwidarОценок пока нет