Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lab Values
Загружено:
pninthemakinАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lab Values
Загружено:
pninthemakinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
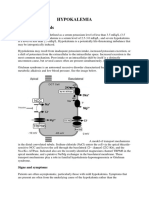
Acetone - < 2.
0 mg/dL Etiologies of high acetone levels - Diabetic ketoacidosis, high-fat diet, low-carbohydrate diet, starvation Albumin - 3.5-5.0 g/dL high albumin levels indicate - Dehydration low albumin levels indicate - Chronic liver disease, malabsorption, malnutrition, nephrotic syndrome Ammonia - 15-45 mcg N/dL 11-32 mol N/L high ammonia levels indicate - severe liver disease high amylase levels indicate - Acute and chronic pancreatitis, mumps (salivary gland disease), perforated ulcers low amylase levels indicate - Acute alcoholism, cirrhosis of liver, extensive destruction of pancreas Bicarbonate - 22-26 mEq/L high bicarbonate levels indicate - Compensated respiratory acidosis, metabolic alkalosis low bicarbonate levels indicate - Compensated respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis b-Type natriuretic peptide (BNP) - <100 mcg/L high BNP levels indicate - Heart failure Bilirubin- Total - 0.2-1.2 mg/dL high bilirubin levels indicate - Biliary obstruction, impaired liver function, hemolytic anemia, pernicious anemia Arterial pH - 7.35-7.45 high aterial pH levels indicate - Alkalosis low arterial pH levels indicate - acidosis PaCO2 - 32-48 mm Hg high PaCO2 levels indicate - Compensated metabolic alkalosis low PaCO2 levels indicate - Compensated metabolic acidosis PaO2 - 80-100 mm Hg High PaO2 levels indicate - Administration of high concentration of oxygen low PaO2 levels indicate - Chronic lung disease, decreased cardiac output Calcium (total) - 9-11 high total calcium levels indicate - Acute osteoporosis, hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D intoxication, multiple myeloma low total calcium levels indicate - Acute pancreatitis, hypoparathyroidism, liver disease, malabsorption syndrome, renal failure, vitamin D deficiency Calcium (ionized) - 4.64-5.28 mg/dL 1.16-1.32 mmol/L Carbon dioxide (CO2) - 23-29 mEq/L high CO2 levels indicate - Compensated respiratory acidosis, metabolic alkalosis Carotene - 10-85 mcg/dL high carotene levels indicate - Cystic fibrosis, hypothyroidism, pancreatic insufficiency low carotene levels indicate - Dietary deficiency, malabsorption disorders Chloride - 96-106 mEq/L high chloride levels indicate - Metabolic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, corticosteroid therapy, uremia
low chloride levels indicate - Addison's disease, diarrhea, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory acidosis, vomiting Cholesterol - <200 mg/dL <5.2 mmol/L high chloesterol levels indicate - Biliary obstruction, hypothyroidism, idiopathic hypercholesterolemia, renal disease, uncontrolled diabetes low choloesterol levels indicate - Extensive liver disease, hyperthyroidism, malnutrition, corticosteroid therapy High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) - Male: >40 mg/dL Female: >50 mg/dL Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) - Recommended: <100 mg/dL Near optimal: 100-129 mg/dL (2.6-3.34 mmol/L) Moderate risk for CAD: 130-159 mg/dL (3.37-4.12 mmol/L) High risk for CAD: >160 mg/dL (>4.14 mmol/L) Cortisol - 8 am: 5-23 mcg/dL8 pm: <10 mcg/dL High cortisol levels indicate - Cushing syndrome, pancreatitis low cortisol levels indicate - Adrenal insufficiency, panhypopituitary states Creatine - 0.2-1.0 mg/dL high creatine levels indicate - Active rheumatoid arthritis, biliary obstruction, hyperthyroidism, renal disorders, severe muscle disease low creatine levels indicate - Diabetes mellitus Creatine kinase (CK) - Male: 20-200 U/L Female: 20-180 U/L high creatine kinase levels indicate - Musculoskeletal injury or disease, myocardial infarction, severe myocarditis, exercise, numerous IM injections CK-MB - <4%-6% of total CK high ck-mb levels indicate - Acute myocardial infarction Creatinine - 0.6-1.3 mg/dL high creatinine levels indicate - Severe renal disease Ferritin - 10-250 ng/mL 10-250 mcg/L low ferritin levels indicate - Iron-deficiency anemia Folate (folic acid) - 5-16 ng/mL 11-36 nmol/L high folate levels indicate - Hypothyroidism low folate levels indicate - Alcoholism, hemolytic anemia, inadequate diet, malabsorption syndrome, megaloblastic anemia Glucose (fasting) - 70-99 mg/dL 3.9-5.5 mmol/L high glucose levels are present in - Acute stress, Cushing disease, diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, pancreatic insufficiency low glucose levels are present in - Addison's disease, hepatic disease, hypothyroidism, insulin overdosage, pancreatic tumor, pituitary hypofunction
Insulin (fasting) - 4-24 U/mL 29-172 pmol/L high fasting insulin levels indicate - Acromegaly, adenoma of pancreatic islet cells, untreated mild case of type 2 diabetes low fasting insulin levels indicate - Inadequately treated type 1 diabetes mellitus Iron, total - 50-175 mcg/dL 9.0-31.3 mol/L high iron levels indicate - Excessive RBC destruction low iron levels indicate - Iron-deficiency anemia, anemia of chronic disease Iron-binding capacity - 250-425 mcg/dL 44.8-76.1 mol/L high levels of iron binding capacity indicate - Iron-deficient state, polycythemia low levels of iron binding capacity indicate - Cancer, chronic infections, pernicious anemia Lactic acid (L-Lactate) - 6.3-22.5 mcg/dL 0.7-2.5 mmol/L high lactic acid levels indicate - Acidosis, heart failure, shock Lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) - 140-280 U/L 0.83-2.5 kat/L high Lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) levels indicate - Heart failure, hemolytic disorders, hepatitis, metastatic cancer of liver, myocardial infarction, pernicious anemia, pulmonary embolus, skeletal muscle damage Lipase - 31-186 U/L 0.5-3.2 kat/L high lipase levels indicate - Acute pancreatitis, hepatic disorders, perforated peptic ulcer Magnesium - 1.5-2.5 mEq/L 0.75-1.25 mmol/L high magnesium levels indicate - Addison's disease, hypothyroidism, renal failure low magnesium levels indicate - Chronic alcoholism, severe malabsorption Osmolality - 275-295 high osmolarity indicates - Chronic renal disease, diabetes mellitus low osmolarity indicates - Addison's disease, diuretic therapy Oxygen saturation (arterial) (SaO2) - >95% Phosphatase, acid - 0-0.6 U/L high levels of Phosphatase, acid - Advanced Paget's disease, cancer of prostate, hyperparathyroidism Phosphatase, alkaline - 38-126 U/L 0.65-2.14 kat/L high levels of Phosphatase, alkaline indicate - Bone diseases, marked hyperparathyroidism, obstruction of biliary system, rickets low levels of Phosphatase, alkaline indicate - Excessive vitamin D ingestion, hypothyroidism Phosphorus (phosphate) - 2.4-4.4 mg/dL 0.78-1.42 mmol/L high Phosphorus levels indicate - Healing fractures, hypoparathyroidism, renal disease, vitamin D intoxication
low Phosphorus levels indicate - Diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency Potassium - 3.5-5.0 mEq/L High Potassium levels indicate - Addison's disease, diabetic ketosis, massive tissue destruction, renal failure low Potassium levels indicate - Cushing syndrome, diarrhea (severe), diuretic therapy, gastrointestinal fistula, pyloric obstruction, starvation, vomiting Sodium - 135-145 mEq/L high sodium levels may be present in - Dehydration, impaired renal function, primary aldoster-onism, corticosteroid therapy low sodium levels may be present in - Addison's disease, diabetic ketoacidosis, diuretic therapy, excessive loss from GI tract, excessive perspiration, water intoxication
Вам также может понравиться
- Native Indian Fighting TechniquesДокумент15 страницNative Indian Fighting TechniquesRobert Rippey67% (3)
- Interpretation of Lab TestsДокумент29 страницInterpretation of Lab TestsRitesh Singh100% (6)
- Petition For Certiorari Under Rule 65 SampleДокумент9 страницPetition For Certiorari Under Rule 65 SampleCha50% (2)
- Lab Workup: Practical Nursing Mohawk College 2014Документ2 страницыLab Workup: Practical Nursing Mohawk College 2014Pawel PietruszczakОценок пока нет
- Lab Values Cheat SheetДокумент8 страницLab Values Cheat SheetNaman NamanОценок пока нет
- Stop Absorbing Other People's EmotionsДокумент5 страницStop Absorbing Other People's EmotionsMarielle MaikОценок пока нет
- Interpretation of Lab Test ProfilesДокумент15 страницInterpretation of Lab Test ProfilesNicole Alexandra KhoОценок пока нет
- Blood ChemistryДокумент3 страницыBlood ChemistryHal Theodore Maranian BallotaОценок пока нет
- Baba Ifa Karade - The Handbook of Yoruba Religious ConceptsДокумент142 страницыBaba Ifa Karade - The Handbook of Yoruba Religious ConceptsNiger Morie Rocha Silva100% (2)
- Solo-Play Adventure PDFДокумент4 страницыSolo-Play Adventure PDFКарен ЗакарянОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Result and InterpretationДокумент11 страницLaboratory Result and Interpretationtzuquino Emz100% (1)
- Laboratory Data InterpretationДокумент24 страницыLaboratory Data InterpretationDanish KamalОценок пока нет
- Blood Chemistry Tests and Logy Reference ValuesДокумент4 страницыBlood Chemistry Tests and Logy Reference ValuesMarggie SalaoОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Laboratory TestsДокумент6 страницDiagnostic Laboratory TestsKiana Mae Wong Diwag100% (1)
- Diagnostic TestsДокумент3 страницыDiagnostic Testsapi-251516913100% (1)
- Original Copy Business Permit Application Form BPLOs PDFДокумент2 страницыOriginal Copy Business Permit Application Form BPLOs PDFNicole Canarias100% (1)
- Hospital DietsДокумент1 страницаHospital DietsAnne Julia AgustinОценок пока нет
- ValuesДокумент19 страницValuescabrerahazel100% (1)
- Laboratory ValuesДокумент12 страницLaboratory ValuesJaney Co100% (2)
- People V. Garcia-CristobalДокумент2 страницыPeople V. Garcia-CristobalCarl AlonzoОценок пока нет
- Is CODE MINIMUM STEEL - What Is The Maximum Percentage of Reinforcement That Can Be Provided For A RCC StructureДокумент9 страницIs CODE MINIMUM STEEL - What Is The Maximum Percentage of Reinforcement That Can Be Provided For A RCC StructureKENNY0% (3)
- Administrative Order No. 125-2007Документ7 страницAdministrative Order No. 125-2007neri roseОценок пока нет
- Clinical Chemistry Board ReviewДокумент14 страницClinical Chemistry Board ReviewWellaBaylasОценок пока нет
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionОт EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionОценок пока нет
- Themes VignettesДокумент6 страницThemes Vignettesapi-327029938Оценок пока нет
- HypokalemiaДокумент40 страницHypokalemiaNadila Putri100% (1)
- General Principles of Law Recognised by Civilised StatesДокумент7 страницGeneral Principles of Law Recognised by Civilised StatesSangeeta SinghОценок пока нет
- Edward Keller vs. COB Group, G.R. No. L-68097, January 16, 1986Документ3 страницыEdward Keller vs. COB Group, G.R. No. L-68097, January 16, 1986LilianОценок пока нет
- The Command Theory by John Austin and Its Legal Implications On Philippine JurisprudenceДокумент15 страницThe Command Theory by John Austin and Its Legal Implications On Philippine JurisprudenceAnne Lorraine DioknoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology ESRDДокумент9 страницPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoОценок пока нет
- Test Normal Values Higher Value Lower Value NotesДокумент6 страницTest Normal Values Higher Value Lower Value Notesjetri0905Оценок пока нет
- Blood InvestigationДокумент2 страницыBlood Investigationali jasimОценок пока нет
- Lood Chemistry Tests and Haematology Reference ValuesДокумент6 страницLood Chemistry Tests and Haematology Reference ValuesJeshwinder KaurОценок пока нет
- Lab Normal Value Comments: AlbuminДокумент4 страницыLab Normal Value Comments: AlbumindelantarzОценок пока нет
- Lab Value Activity For MNT IДокумент4 страницыLab Value Activity For MNT IAnonymous U3GOK360Оценок пока нет
- ACR, Albumin-To-Creatinine Ratio AER, Albumin ExcretionДокумент18 страницACR, Albumin-To-Creatinine Ratio AER, Albumin ExcretionBening IrhamnaОценок пока нет
- Renal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi SharmaДокумент36 страницRenal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi Sharmanidhi261987Оценок пока нет
- Uric Acid Fluid Conventional SI UnitsДокумент3 страницыUric Acid Fluid Conventional SI UnitsSk Saklin MustakОценок пока нет
- Acute Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: DR Yemane G (MD, Assis. Prof. EMCC)Документ63 страницыAcute Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: DR Yemane G (MD, Assis. Prof. EMCC)yared getachewОценок пока нет
- Acidosis and Alkalosis EditedДокумент39 страницAcidosis and Alkalosis EditedShirmagne ManugasОценок пока нет
- 27) HypokalemiaДокумент29 страниц27) HypokalemiaMariam AntonyОценок пока нет
- Dr. Erwin Christianto - Nutrisi Pada Penyakit GinjalДокумент39 страницDr. Erwin Christianto - Nutrisi Pada Penyakit GinjalWorldhealthОценок пока нет
- AmilazaДокумент9 страницAmilazaCraciun Tatiana100% (1)
- Guidelines For The Management Of: Kurdistan Higher Council For Medical SpecialtiesДокумент6 страницGuidelines For The Management Of: Kurdistan Higher Council For Medical SpecialtiesCik JaaОценок пока нет
- List of Recommended DietsДокумент1 страницаList of Recommended DietsFetz FitzgeraldОценок пока нет
- Hypokalemia CausesДокумент12 страницHypokalemia CausesEsther RefuncionОценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Sumit Kumar, MD, MPH Presbyterian Hospital, Dallas, TXДокумент47 страницChronic Kidney Disease: Sumit Kumar, MD, MPH Presbyterian Hospital, Dallas, TXAnn Michelle TarrobagoОценок пока нет
- Dietetic Treatment: Dr. Sumbul FatmaДокумент25 страницDietetic Treatment: Dr. Sumbul FatmasahrОценок пока нет
- Hospital Diets: Disorder/Condition Recommended DietДокумент2 страницыHospital Diets: Disorder/Condition Recommended DietAilene Ponce FillonОценок пока нет
- Health Disorders & DietДокумент120 страницHealth Disorders & DietHannaniah Gabriel AmanteОценок пока нет
- PATIENT WITH ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION - PPTX Diabetes EmergenciecyДокумент45 страницPATIENT WITH ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION - PPTX Diabetes Emergenciecysembakarani thevagumaranОценок пока нет
- L V Laboratory Test Reference Range Comments Conventional Units SI Units Chem-7Документ2 страницыL V Laboratory Test Reference Range Comments Conventional Units SI Units Chem-7Jenna DantОценок пока нет
- Hospital Diets: Disorder/Condition Recommended DietДокумент2 страницыHospital Diets: Disorder/Condition Recommended DietVin BitzОценок пока нет
- Basic Metabolic PanelДокумент11 страницBasic Metabolic PanelLaurenОценок пока нет
- Function Maintain Homeostatic Balance With Respect To Fluids, Electrolytes, and Organic SolutesДокумент8 страницFunction Maintain Homeostatic Balance With Respect To Fluids, Electrolytes, and Organic SolutesNikki SalivioОценок пока нет
- Chronic Renal FailureДокумент14 страницChronic Renal FailurevaliamnisaОценок пока нет
- A1c (Hba1c) Diabetes TDK Terkontrol DGN Baik 8%Документ2 страницыA1c (Hba1c) Diabetes TDK Terkontrol DGN Baik 8%mirantiОценок пока нет
- Kidney DiseasesДокумент45 страницKidney DiseasesSai ViswasОценок пока нет
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Документ39 страницMedical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2016Steven FongОценок пока нет
- ART'S DKA TXДокумент6 страницART'S DKA TXphat lippОценок пока нет
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2021Документ39 страницMedical Nutrition Therapy For Renal Disease 2021Oktaviani Karo SekaliОценок пока нет
- Normal Range Disturbance Most Common Causes Signs and Symptoms Sodium 135-145 Meq/LДокумент2 страницыNormal Range Disturbance Most Common Causes Signs and Symptoms Sodium 135-145 Meq/Lharrytan81Оценок пока нет
- Chronic Renal FailureДокумент3 страницыChronic Renal FailureJashine DajayОценок пока нет
- Dictionary of Blood TestsДокумент6 страницDictionary of Blood Teststvland1098Оценок пока нет
- Hospital Diet For Different DiseasesДокумент2 страницыHospital Diet For Different DiseasesJekka Ann Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Renal Nutrition TherapyДокумент2 страницыRenal Nutrition TherapyEdsylaine BumatayОценок пока нет
- Renal Nutrition TherapyДокумент2 страницыRenal Nutrition TherapyEdsylaine BumatayОценок пока нет
- RINJUДокумент35 страницRINJUதீபன்குமார் கதிரேசன்100% (1)
- CKD PDFДокумент26 страницCKD PDFNogra CarlОценок пока нет
- Week 1 PHAR401F16-CKD-1-Intro (160822) - BBДокумент34 страницыWeek 1 PHAR401F16-CKD-1-Intro (160822) - BBoxyc0n999Оценок пока нет
- CVD HTN Case Study AssignmentДокумент7 страницCVD HTN Case Study Assignmentapi-353723892Оценок пока нет
- Hypo Kale MiaДокумент34 страницыHypo Kale MiaSyafniYuliaSistriОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ2 страницыChapter 7pninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ2 страницыChapter 5pninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ2 страницыChapter 4pninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ2 страницыChapter 6pninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8Документ2 страницыChapter 8pninthemakinОценок пока нет
- PP Drug Classes and IndicationsДокумент67 страницPP Drug Classes and IndicationspninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Polly List of Lab ValuesДокумент1 страницаPolly List of Lab ValuespninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Blood Gas ValuesДокумент9 страницBlood Gas ValuespninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Heart ValvesДокумент1 страницаAnatomy of The Heart ValvespninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Electrical Heart Conduction PathwayДокумент1 страницаElectrical Heart Conduction PathwaypninthemakinОценок пока нет
- Coronary CirculationДокумент1 страницаCoronary CirculationpninthemakinОценок пока нет
- West Bengal Police Recruitment Board: Application Form For The Post of Si/Lsi of Excise 2018Документ2 страницыWest Bengal Police Recruitment Board: Application Form For The Post of Si/Lsi of Excise 2018Ridan DasОценок пока нет
- Smun BG PDFДокумент17 страницSmun BG PDFBaber Bilal MalikОценок пока нет
- United States Ex Rel. Willie Richardson v. Daniel McMann Warden, Clinton Prison, Dannemora, New York, 408 F.2d 48, 2d Cir. (1969)Документ8 страницUnited States Ex Rel. Willie Richardson v. Daniel McMann Warden, Clinton Prison, Dannemora, New York, 408 F.2d 48, 2d Cir. (1969)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Independence From FactionДокумент26 страницIndependence From FactionAllison HymasОценок пока нет
- Modern FamilyДокумент4 страницыModern FamilyLuciana Gossmann100% (1)
- Script - The RunawayДокумент9 страницScript - The Runawayapi-461261491Оценок пока нет
- Thesis 2Документ61 страницаThesis 2Sarita MaesoОценок пока нет
- Current Affairs Jan-Dec 2020.Документ545 страницCurrent Affairs Jan-Dec 2020.Shubham ranjanОценок пока нет
- Cultural Revolution CommonLitДокумент7 страницCultural Revolution CommonLitCheeseit 67Оценок пока нет
- Lectue 20 Session 2Документ43 страницыLectue 20 Session 2Shahzadi HiraОценок пока нет
- Case DigestДокумент22 страницыCase DigestKimОценок пока нет
- NV School Law Artifact 3Документ4 страницыNV School Law Artifact 3api-317392531Оценок пока нет
- KorschДокумент32 страницыKorschbayan.rihawi95Оценок пока нет
- Contract Agreement Between HRL and SJ - SMEC - EGC 15 March 2021Документ31 страницаContract Agreement Between HRL and SJ - SMEC - EGC 15 March 2021Arshad MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Assignment Insurance LawДокумент5 страницAssignment Insurance LawJetheo100% (1)
- Marcin PassiveДокумент3 страницыMarcin PassiveBarry ParkerОценок пока нет
- Stay Particular JTO - 21march2020Документ18 страницStay Particular JTO - 21march2020Vikrant PathakОценок пока нет