Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Column Tutorial Answers
Загружено:
berto2008Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Column Tutorial Answers
Загружено:
berto2008Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
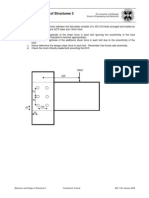
Behaviour and Design of Structures 3 Columns Tutorial Solution
The University of Edinburgh School of Engineering and Electronics
1)
Partial safety factor on load, Partial safety factors on material strength Nominal yield stress Nominal ultimate stress Design load Gross area of tension member Net area of tension member Design resistance
Q 0 2 fu fy Ned= 1.5*150 A= 10*100 Anet= 10*100-(20*10) NRd= min{Afy/m0;0.9Anetfu/m2} = min{275;310}
= 1.5 = 1.0 =1.0 = 275 MPa = 430 MPa = 225 kN = 1000mm2 = 800 mm2
EN1990 NA.A1.2(B) EN1993 NA.2.15
Table 3.1
6.2.3
6.2.3(2) a and b =275kN
NEd /NRd = 0.82
Section OK
2)
Effective length about major axis Effective length about minor axis Design load
Lcr,y=L Lcr,z=0.7L NEd
= 7m = 4.9m =2000kN
NCCI guidance on effective lengths Data given NNCI sizing charts for columns
The column design charts give strengths for columns in multi-storey buildings. It is assumed in these tables that the support conditions are the same for minor and major-axis bending. In effect therefore they give minor axis strengths. Taking Lcr,x and NEd as above try a of 254x254x107UC section of grade S275 steel. =136 cm2 = 17510 cm4 = 5928 cm4 = 1.03
Area of section Second moment of area y-y Second moment of area z-z
Iy Iz h/b=266.7/258.8 E fy
Data from section tables needed later
Modulus of elasticity Yield stress Elastic critical force y-y Elastic critical force z-z Relative slenderness y-y Relative slenderness z-z
= 210 000N/mm2 EN1993 3.2.6(1) = 275 N/mm2 Table 3.1
Ncr,y=2EIy/Lcr,y2= 2210e9*1.7510e-4/72 = 7.3MN Ncr,z=2EIz/Lcr,z2= 2210e9*5.928e-5/4.92 = 5.1MN
y = Af y / N cr , y = (0.0136 * 275) / 7.3 z = Af z / N cr , z = (0.0136 * 275) / 5.1
=0.716 =0.856
Eqn 6.50
Note z could be arrived at slightly more directly using the third term in Eqn. 6.50. Buckling curve for y-y axis is curve b Buckling curve for z-z axis is curve c Table 6.2
Behaviour and Design of Structures 3
Columns Tutorial Solution
MG, January 2009
Behaviour and Design of Structures 3 Columns Tutorial Solution
Imperfection factor for y-y axis Imperfection factor for z-z axis y z
The University of Edinburgh School of Engineering and Electronics
= 0.34 = 0.49
Table 6.1
Therefore minor axis buckling governs (higher z and ) Reduction factor for y-y buckling = 0.68 More detailed assessment of possible using Eqn. 6.49 rather than graphs in Figure. Nb,Rd= Afy/m1=0.68*0.0136*275/1 NEd/Nb,Rd=2/2.5=0.8 = 2.5MN Section OK Figure 6.4
Design buckling resistance
Eqn 6.47 Eqn 6.46
Behaviour and Design of Structures 3
Columns Tutorial Solution
MG, January 2009
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- En 15095-2007+a1 (2008)Документ45 страницEn 15095-2007+a1 (2008)berto2008Оценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Thermodynamics Lab Report - Application of The Perfect Gas Laws in The Determination of Adiabatic Index of AirДокумент9 страницThermodynamics Lab Report - Application of The Perfect Gas Laws in The Determination of Adiabatic Index of Airqiaunus69% (13)
- En 15629 (2008)Документ35 страницEn 15629 (2008)berto2008100% (1)
- En 15620 Steel Static Storage Systems - Adjustable Pallet Racking - Tolerances, Deformations and ClearancesДокумент76 страницEn 15620 Steel Static Storage Systems - Adjustable Pallet Racking - Tolerances, Deformations and ClearancesPaul Costan92% (12)
- Syllabus V To VIII SEM - MECHДокумент22 страницыSyllabus V To VIII SEM - MECHSIETDOC100% (6)
- 7 STEPS TO DEVELOPING AN AGILE MARKETING TEAMДокумент17 страниц7 STEPS TO DEVELOPING AN AGILE MARKETING TEAMberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Worked Examples To Eurocode 2Документ165 страницWorked Examples To Eurocode 2amin6693225097% (30)
- Connection TutorialДокумент1 страницаConnection Tutorialberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Reinforced Concrete Column by Zinab EC2Документ15 страницReinforced Concrete Column by Zinab EC2berto2008Оценок пока нет
- Structrual Concrete Design To Eurocode 2 University of Sheffield Structural Engineering MastersДокумент12 страницStructrual Concrete Design To Eurocode 2 University of Sheffield Structural Engineering Mastersfatabass100% (3)
- Connection Tutorial AnswersДокумент2 страницыConnection Tutorial Answersberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Steel Column Design Eurocode 3Документ2 страницыSteel Column Design Eurocode 3Jonp4ul_MiddletonОценок пока нет
- ConnectionsДокумент38 страницConnectionsberto2008Оценок пока нет
- How To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2Документ104 страницыHow To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2berto2008Оценок пока нет
- Connections Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3Документ1 страницаConnections Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3berto20080% (1)
- Nominal MomentsДокумент2 страницыNominal Momentsberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Simple Column Design ExampleДокумент5 страницSimple Column Design Exampleberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Effective LengthsДокумент8 страницEffective Lengthsberto2008Оценок пока нет
- NCCI Simplified LT-Buckling Calcs 2upДокумент5 страницNCCI Simplified LT-Buckling Calcs 2upberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Connection Tutorial AnswersДокумент2 страницыConnection Tutorial Answersberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Columns Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3Документ1 страницаColumns Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3berto2008Оценок пока нет
- ConnectionsДокумент38 страницConnectionsberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Effective Lengths - 2upДокумент4 страницыEffective Lengths - 2upberto2008Оценок пока нет
- SIMPLIFIED BENDING RESISTANCE CHECK ACCORDING TO EUROCODEДокумент22 страницыSIMPLIFIED BENDING RESISTANCE CHECK ACCORDING TO EUROCODEberto2008Оценок пока нет
- LT Buckling Beam Design - Simple Method - 2upДокумент5 страницLT Buckling Beam Design - Simple Method - 2upberto2008Оценок пока нет
- ColumnsДокумент28 страницColumnsberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Column Sizing Chart PDFДокумент7 страницColumn Sizing Chart PDFberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Steel Beam DesignДокумент39 страницSteel Beam Designberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Steel Beams TutorialДокумент1 страницаSteel Beams Tutorialberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Design Charts For Non-Composite Beams 2upДокумент3 страницыDesign Charts For Non-Composite Beams 2upberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Design Charts For Composite Beams 2upДокумент3 страницыDesign Charts For Composite Beams 2upberto2008Оценок пока нет
- Science 8 Module 5Документ8 страницScience 8 Module 5Farhana MacaalinОценок пока нет
- Class XI Physics DPP Set (25) - Previous Chaps + SHMДокумент14 страницClass XI Physics DPP Set (25) - Previous Chaps + SHMNilabha Das100% (1)
- TIMBERДокумент13 страницTIMBERAbigail FababaerОценок пока нет
- Air Crew Radiation Exposure - An OverviewДокумент8 страницAir Crew Radiation Exposure - An OverviewStarxteelОценок пока нет
- ANSYS Workshop 2Документ45 страницANSYS Workshop 2toshugoОценок пока нет
- PMRE 6006 WT Assignments Oct 2017Документ2 страницыPMRE 6006 WT Assignments Oct 2017Noor HasanОценок пока нет
- B. Real GasesДокумент57 страницB. Real GasesRayanna WardОценок пока нет
- Phase DiagramДокумент13 страницPhase DiagramJayzl Lastrella CastanedaОценок пока нет
- Electrical ProperitiesДокумент66 страницElectrical ProperitiesGabito EssienОценок пока нет
- Food PolymersДокумент8 страницFood PolymersfitsnjОценок пока нет
- Gomes, GabrielДокумент12 страницGomes, GabrielVálter LúcioОценок пока нет
- Introduction to CSAMT: A Guide to Controlled Source Audio-Frequency MagnetotelluricsДокумент4 страницыIntroduction to CSAMT: A Guide to Controlled Source Audio-Frequency MagnetotelluricsAndy KurniyantoОценок пока нет
- Cold Facts Buyers Guide (2017) PDFДокумент41 страницаCold Facts Buyers Guide (2017) PDFBinh Thanh LeОценок пока нет
- Nuratherm PIR TDSДокумент2 страницыNuratherm PIR TDSNathan BlythОценок пока нет
- Final Year Project Presentation: Lokmanya Tilak College of EngineeringДокумент20 страницFinal Year Project Presentation: Lokmanya Tilak College of EngineeringOnkar BhosaleОценок пока нет
- Rock properties affecting conical pick performance and comparison of experimental and theoretical cutting resultsДокумент38 страницRock properties affecting conical pick performance and comparison of experimental and theoretical cutting resultsFranceth Castellanos BallesterosОценок пока нет
- Masterflow: Cementitious High Strength Non-Shrink Precision GroutДокумент3 страницыMasterflow: Cementitious High Strength Non-Shrink Precision GroutAydın VarolОценок пока нет
- Module 17 Cat A (Jan 18)Документ2 страницыModule 17 Cat A (Jan 18)Shaheed ChirayinkeezhuОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ12 страницLecture 2Sima KumariОценок пока нет
- Dhio Corporate Brochure 2023 FordistributionДокумент12 страницDhio Corporate Brochure 2023 FordistributionsrashmiiiscОценок пока нет
- Nanocomposix Guidelines For Zeta Potential Analysis of Nanoparticles PDFДокумент6 страницNanocomposix Guidelines For Zeta Potential Analysis of Nanoparticles PDFGOWTHAM GUPTHAОценок пока нет
- Boilers & FurnacesДокумент88 страницBoilers & Furnacesnrnak0% (1)
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0702 FDДокумент49 страницCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0702 FDKim balugayОценок пока нет
- RRB JE Civil Engineering MCQs BookДокумент40 страницRRB JE Civil Engineering MCQs Bookpruthviraj kadupuОценок пока нет
- Cu-ETP: C11000 Industrial RolledДокумент4 страницыCu-ETP: C11000 Industrial Rolledsrsivaraman81Оценок пока нет
- Bearing Angle Model For Bond of Reinforcing Bars To ConcreteДокумент4 страницыBearing Angle Model For Bond of Reinforcing Bars To ConcreteRicardo EscobarОценок пока нет
- Anti Reflective Coating PhotoresistДокумент7 страницAnti Reflective Coating PhotoresistsaipramodОценок пока нет
- The Optimal Design of Pressure Swing Adsorption SystemsДокумент27 страницThe Optimal Design of Pressure Swing Adsorption SystemsBich Lien PhamОценок пока нет