Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Text
Загружено:
Risyane Yoandira AgnesaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Text
Загружено:
Risyane Yoandira AgnesaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
\
218
Chapter 5 Beams
5.5-6
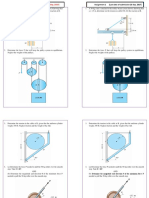
A W12 x 30 of A992 steel has an unbraced length of 10 feet. Using Cb = 1.0, a. Compute Lp and Lr Use the equations in Chapter F of the AISC Specification. Do not use any of the design aids in the Manual. b. Compute the flexural design strength, <j>bMn.
5.5-7 A W18 x 46 is used for a beam with an unbraced length of 10 feet. Using Fy= 50 ksi and Cb = 1, compute the flexural design strength. Use the AISC equations in Chapter F of the Specification. Do not use any of the design aids in the Manual. 5.5-8 A Wl 8 x 71 is used as a beam with an unbraced length of 9 feet. Use Fy = 65 ksi and Cb = 1 and compute the flexural design strength. Compute everything with the equations in Chapter F of the AISC Specification. 5.5-9 The beam shown in Figure P5.5-9 is laterally supported at a, b, and c only. The given loads are factored. Compute Cb for the unbraced segment b-c.
5.5-10 The beam shown in Figure P5.5-10 is laterally supported at the ends and at the concentrated load point. The 3 kip concentrated load is a service live load, and the uniform load is a 6 kip/ft service dead load that includes the weight of the beam. Compute Cb for each unbraced segment.
5.5-11
The beam shown in Figure P5.5-11 has lateral support at a, b, c, and d. Compute Cb for segment b-c.
5.5-12 A W21 x 68 of A992 steel is used as a simply supported beam with a span length of 50 feet. The only load in addition to the beam weight is a uniform live load. If lateral support is provided at 10-foot intervals, what is the maximum service live load, in kips/ft, that can be supported? 5.5-13 The beam shown in Figure P5.5-13 is laterally braced only at the ends. The 30-kip load is a service live load. Use Fy = 50 ksi and determine whether the following shapes are adequate. a. W14x38 b. MCf 8 x 58 (Assume that the load is applied through the shear center so that there is no torsional loading.)
5.5-14 Determine whether a W24 x 104 of A992 steel is adequate for the beam shown in Figure P5.5-14. The uniform load does not include the weight of the beam. Lateral support is provided at A, B, and C.
5.5-15
The beam shown in Figure P5.5-15 is laterally braced at A, B, C, and D. Is a W14 x 132 adequate? Use Fy = 50 ksi.
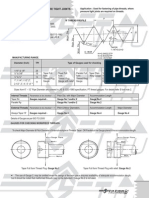
Bending Strength of Noncompact Shapes 5.6-1 A W12 x 65 is used as a simply supported, uniformly loaded beam with a span length of 50 feet and continuous lateral support. The yield stress, Fy, is 50 ksi. If the ratio of live load to dead load is 3, what is the maximum total sendee load, in kips/ft, that can be supported? 5.6-2 A W14 x 99 of A992 steel is used as a beam with lateral support at 10-foot intervals. Assume that Cb= 1.0 and compute the flexural design strength. 5.6-3 A built-up shape consisting of two 3A x 18 flanges and a 3A x 52 web is used as a beam. If A572 Grade 50 steel is used, what is the flexural design strength based on flange local buckling? For width-thickness ratio limits for welded shapes, refer to Table B5.1 in Chapter B of the AISC Specification, "Design Requirements." 5.6-4 A built-up shape consisting of two 1x16 flanges and a /i6 x 40 web is used as a beam with continuous lateral support. If A572 Grade 50 steel is used, what is the flexural design strength? For width-thickness ratio limits for welded shapes, refer to Table B5.1 in Chapter B of the AISC Specification, "Design Requirements."
5
Shear Strength 5.8-1 5.8-2 Compute the shear strength of an M10 x 7.5 of A572 Grade 65 steel. Compute the shear strength of an M12 x 11.8 of A242 steel.
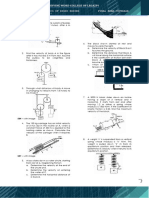
5.8-3 The beam shown in Figure P5.8-3 is a W16 x 31 of A992 steel and has continuous lateral support. The two concentrated loads are service live loads. Neglect the weight of the beam and determine whether the beam is adequate.
5.8-4 The cantilever beam shown in Figure P5.8-4 is a W16 x 45 of A992 steel. There is no lateral support other than at the fixed end. Use an unbraced length equal to the span length and determine whether the beam is adequate. The uniform load is a service dead load that includes the beam weight, and the concentrated load is a service live load.
Design 5.10-1 Use A992 steel and select a W-shape for the following beam: Simply supported with a span length of 30 feet Laterally braced only at the ends
Service dead load = 0.75 kips/ft The service live load consists of a 34-kip concentrated load at the center of the span.
There is no limit on the deflection. 5.10-2 Use A992 steel and select the most economical W-shape for each ol the cases listed. The loads shown in Figure P5.10-2 are service loads. The beam weight is not included. Do not check deflection. a. The beam has continuous lateral support. b. Lateral support is provided at the ends and at the concentrated load.
5.10-3 The beam shown in Figure P5.10-3 has lateral support only at the ends. The uniform load is a superimposed dead load, and the concentrated load is a live load. Use A992 steel and select a W-shape. The live load deflection must not exceed L/360.
' 5.10-4 The given beam is laterally supported at the ends and at the Vi points (points 1, 2, 3, and 4). The concentrated load is a service live load. Use Fy = 50 ksi and select a W-shape. Do not check deflections.
5.10-5 The beam shown in Figure P5.10-5 has lateral support at the ends only. The concentrated loads are live loads. Use A992 steel and select a shape. Do not check deflections. Use Cb - 1.0 (this is conservative).
5.10-6 The beam shown in Figure P5.10-6 is part of a roof system. Assume that there is partial lateral support equivalent to bracing at the ends and at midspan. The loading consists of 170 lb/ft dead load (not including the weight of the beam). 100 lb/ft roof live load, 280 lb/ft snow load, and 180 lb/ft wind load acting upward. The dead, live, and snow loads are gravity loads and always act downward, whereas the wind load on the roof will always act upward. Use A572 Grade 50 steel and select a shape. The total deflection must not exceed L/180.
Floor and Roof Framing Systems 5.11-1 Use Fy = 50 ksi and select a shape for a typical floor beam AB. Assume that the floor slab provides continuous lateral support. The maximum permissible live load deflection is L/180. The service dead loads consist of a 5-inch-thick reinforced concrete
Вам также может понравиться
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsОт EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsОценок пока нет
- StrucTheor FormulasДокумент3 страницыStrucTheor FormulasMJ Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- HAU Structural Loads LessonДокумент14 страницHAU Structural Loads Lessoncutie4everrОценок пока нет
- Short Bond Paper Landscape: Score Statics-Rb RubricДокумент6 страницShort Bond Paper Landscape: Score Statics-Rb RubricxVlad LedesmaОценок пока нет
- Strain and StressДокумент9 страницStrain and StressCharlene Anne Austria VillarozaОценок пока нет
- Solved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Документ1 страницаSolved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Cristian A. GarridoОценок пока нет
- Module-1 Home-Eval 1Документ9 страницModule-1 Home-Eval 1Michael James ll BanawisОценок пока нет
- Ce0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignДокумент40 страницCe0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignjerichoОценок пока нет
- Engg Mechanics QuestionnaireДокумент15 страницEngg Mechanics Questionnaireacurvz2005Оценок пока нет
- Irregular Section of Beams Reinforced For TensionДокумент26 страницIrregular Section of Beams Reinforced For TensionMadelyn Escaner MorilloОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Flexural Design - (Part 5)Документ35 страницChapter 4 Flexural Design - (Part 5)Raja AliОценок пока нет
- FA NO. 7 (Problem Set)Документ2 страницыFA NO. 7 (Problem Set)Peter Adrian Ngo100% (1)
- Plate 1Документ2 страницыPlate 1Dawnald Fortin PepitoОценок пока нет
- Mathalino - Double Integration MethodДокумент38 страницMathalino - Double Integration Methodanjibee100% (1)
- Ce182P-2 Ce Project 1 1 QTR SY2019-2020 July 2019 Structural Engineering Cluster F.A.A.UyДокумент4 страницыCe182P-2 Ce Project 1 1 QTR SY2019-2020 July 2019 Structural Engineering Cluster F.A.A.UyemmaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Weight Volume RelationshipsДокумент88 страницChapter 3 Weight Volume RelationshipsJeannieMayDelfinОценок пока нет
- Network Diagram Project PlanningДокумент8 страницNetwork Diagram Project PlanningKlent Evran JalecoОценок пока нет
- Bicol University CE 420C Flowchart Analysis and Design of RC StructuresДокумент23 страницыBicol University CE 420C Flowchart Analysis and Design of RC StructuresSam Barotilla100% (1)
- PERMEABILITYДокумент26 страницPERMEABILITYChristian Felix MapilesОценок пока нет
- Outline of Topics: Resultant Moments. These Are The Stress Resultants (Also Called Membrane ForcesДокумент16 страницOutline of Topics: Resultant Moments. These Are The Stress Resultants (Also Called Membrane ForcesJosiah FloresОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Network - Homework Question 01 (By Ankit Sir)Документ7 страницFundamentals of Network - Homework Question 01 (By Ankit Sir)Adarsh RathoreОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersДокумент56 страницChapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersRami DemachkiОценок пока нет
- Design of Beam For TorsionДокумент14 страницDesign of Beam For TorsionmehrdadОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6.0 - Analysis and Design For TorsionДокумент22 страницыLecture 6.0 - Analysis and Design For TorsionRonnie BarreraОценок пока нет
- Deflection of Trusses by The Virtual Work MethodДокумент19 страницDeflection of Trusses by The Virtual Work MethodTin VillalbaОценок пока нет
- Prismoidal Formula 2Документ11 страницPrismoidal Formula 2anggaxkusumaОценок пока нет
- 2-CE 305 MOD 2 Singly RCFДокумент10 страниц2-CE 305 MOD 2 Singly RCFLester Khiets RoaОценок пока нет
- P5 3B Bernardo KathryneДокумент5 страницP5 3B Bernardo KathryneKATHRYNE BERNARDOОценок пока нет
- MCQs in Engineering Mathematics Part 10Документ12 страницMCQs in Engineering Mathematics Part 10Richster LofrancoОценок пока нет
- Holy Angel University midterm exam for concrete structuresДокумент4 страницыHoly Angel University midterm exam for concrete structuresAngelito AngelesОценок пока нет
- Ce Reviewer DesignДокумент18 страницCe Reviewer Designeleonor0% (1)
- CE133P-2 Structural Design ExamДокумент6 страницCE133P-2 Structural Design ExamChian CerezoОценок пока нет
- CENG 196 Problem Set Midterms 2Документ2 страницыCENG 196 Problem Set Midterms 2Arc Mayenard Beltran100% (1)
- CE414 Hydraulics Course OutlineДокумент1 страницаCE414 Hydraulics Course OutlineJohn Taylor BernasОценок пока нет
- Mock Board Exams Geotech & HydraulicsДокумент2 страницыMock Board Exams Geotech & Hydraulicsguian domanОценок пока нет
- Sas 1 - 7Документ50 страницSas 1 - 7jaira.masuangatОценок пока нет
- Assessement Task 2 - Fluid Flows in PipeДокумент3 страницыAssessement Task 2 - Fluid Flows in Pipeacurvz2005100% (1)
- Universal College Steel Design GuideДокумент43 страницыUniversal College Steel Design GuideFritz LuzonОценок пока нет
- Asdsingment 1Документ2 страницыAsdsingment 1drjbjpОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Serviceability PDFДокумент45 страницChapter 6 - Serviceability PDFJhe TaguinesОценок пока нет
- CE Reference: Working Stress Analysis For Concrete BeamsДокумент5 страницCE Reference: Working Stress Analysis For Concrete BeamsYamil Camilo Bastidas ArciniegasОценок пока нет
- Eccentric Welded ConnectionsДокумент35 страницEccentric Welded ConnectionsDavid ReyesОценок пока нет
- Module 3 and 5 PDFДокумент55 страницModule 3 and 5 PDFSaptadip SahaОценок пока нет
- EQUAKEДокумент64 страницыEQUAKERouvelle TanyagОценок пока нет
- Highway and Railroad Engineering: Compound CurvesДокумент9 страницHighway and Railroad Engineering: Compound CurvesDirect XОценок пока нет
- Reinforced Concrete Design Problems With Solution Under NSCP 2015 JEDR ManuscriptДокумент40 страницReinforced Concrete Design Problems With Solution Under NSCP 2015 JEDR ManuscriptMark Bastien LizertiguezОценок пока нет
- Instructional Materials Principles of Reinforced Conrete Cien 30183Документ251 страницаInstructional Materials Principles of Reinforced Conrete Cien 30183Aichelle Ann BersabeОценок пока нет
- BeamДокумент20 страницBeamarno assassinОценок пока нет
- Seismic Load: Prepared By: Placio, Princess AngelДокумент21 страницаSeismic Load: Prepared By: Placio, Princess AngelRuf FethОценок пока нет
- Combined Footing DesignДокумент4 страницыCombined Footing DesignAJОценок пока нет
- CE Syllabus Primer Soil MechanicsДокумент7 страницCE Syllabus Primer Soil MechanicsHatsuieeОценок пока нет
- C1609-Flex Test For GFRCДокумент9 страницC1609-Flex Test For GFRCBrinder DhanoaОценок пока нет
- V0L2 PDFДокумент4 страницыV0L2 PDFJohannie Nina ClaridadОценок пока нет
- SAB2223 Mechanics of Materials and Structures: Topic 1 Stress and StrainДокумент120 страницSAB2223 Mechanics of Materials and Structures: Topic 1 Stress and StrainTsalach100% (1)
- Statics FundamentalsДокумент142 страницыStatics FundamentalsDean Ackles100% (1)
- Steel ReviewerДокумент4 страницыSteel ReviewerGlenn SeoОценок пока нет
- Steel Problem Set FinalДокумент27 страницSteel Problem Set FinalJupissa EspinosaОценок пока нет
- Steel Beam Design and Analysis QuestionsДокумент27 страницSteel Beam Design and Analysis QuestionsJayChristian Quimson100% (1)
- steel-reviewerДокумент11 страницsteel-reviewerKyla AbordoОценок пока нет
- ASTM C1609 - C1609M - 19a Standard Test Method For Flexural Performance of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (Using Beam With Third-Point Loading)Документ5 страницASTM C1609 - C1609M - 19a Standard Test Method For Flexural Performance of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (Using Beam With Third-Point Loading)ming_zhu10Оценок пока нет
- Selection of MotorsДокумент16 страницSelection of Motorsmithun46Оценок пока нет
- Dyn Tutorial 5.1 PDFДокумент3 страницыDyn Tutorial 5.1 PDFTareq SammarОценок пока нет
- Terminal Blocks ABBДокумент36 страницTerminal Blocks ABBalishaikh12Оценок пока нет
- An Insight of Compacted Graphite Iron (Cgi) Characteristics and Its Production A ReviewДокумент18 страницAn Insight of Compacted Graphite Iron (Cgi) Characteristics and Its Production A ReviewMiguel BrionesОценок пока нет
- Axial Piston Pump Lecture 8Документ12 страницAxial Piston Pump Lecture 8ssbudzОценок пока нет
- Technical Description MPPUДокумент10 страницTechnical Description MPPUNinaОценок пока нет
- PC2000-8 Shop ManualДокумент1 348 страницPC2000-8 Shop ManualPeetОценок пока нет
- Válvula Relief RD-10A-25WL IB6B9 (Data Sheet)Документ1 страницаVálvula Relief RD-10A-25WL IB6B9 (Data Sheet)Arturo Valencia LaureanoОценок пока нет
- Manufacturing Range Thread GaugesДокумент2 страницыManufacturing Range Thread GaugesKarthik RajanОценок пока нет
- PMDC Motor Guide: Everything You Need to KnowДокумент7 страницPMDC Motor Guide: Everything You Need to KnowJesse Jones Seraspe100% (1)
- Design Criteria For Exposed Hydro Penstocks - Gordon1978 PDFДокумент12 страницDesign Criteria For Exposed Hydro Penstocks - Gordon1978 PDFDavid DelgadoОценок пока нет
- 2019 - Uniflair Room Cooling BrochureДокумент92 страницы2019 - Uniflair Room Cooling BrochureJeff100% (2)
- Hyster j2 2 3 5xnДокумент12 страницHyster j2 2 3 5xnBraveBoy JalloОценок пока нет
- FEA Answers by Professor GuruprasadДокумент146 страницFEA Answers by Professor GuruprasadManendra SaiОценок пока нет
- A Mechanical Engineer S Handbook by ONGC PDFДокумент303 страницыA Mechanical Engineer S Handbook by ONGC PDFshujad77Оценок пока нет
- Lect 5 - Mechanism DescriptionДокумент15 страницLect 5 - Mechanism Descriptionjackie delos santosОценок пока нет
- LEKX6306 Torque CurvesДокумент11 страницLEKX6306 Torque Curvesmijael1393100% (1)
- Section A: Service Manual - 506C, 506CHL, 508C LoadallsДокумент8 страницSection A: Service Manual - 506C, 506CHL, 508C Loadallsmauricio carmona67% (3)
- Dynamics Final Exam CoverageДокумент6 страницDynamics Final Exam CoverageRhona BASKIÑASОценок пока нет
- Grindex Lista de PartesДокумент28 страницGrindex Lista de PartesMarco Antonio Cerna HaroОценок пока нет
- Steel and Cast Iron Bar Compression ProblemДокумент26 страницSteel and Cast Iron Bar Compression ProblemLarete PaoloОценок пока нет
- DESIGN CRITERIA AND LOADING PARAMETERSДокумент6 страницDESIGN CRITERIA AND LOADING PARAMETERSVhorn TiuОценок пока нет
- Sectional Properties of Rolled Steel Joists (Ref: Is: 808 - 1989 & Is: 12778 - 2004)Документ49 страницSectional Properties of Rolled Steel Joists (Ref: Is: 808 - 1989 & Is: 12778 - 2004)rohitnrgОценок пока нет
- Soil Strength Testing With The Merrick FlexometerДокумент95 страницSoil Strength Testing With The Merrick Flexometerd080310Оценок пока нет
- Gears PresentationДокумент33 страницыGears PresentationNaveen YadavОценок пока нет
- CDM816DⅢ配件图册 (2015第1版第1次)Документ188 страницCDM816DⅢ配件图册 (2015第1版第1次)Mohammadazmy Sobursyakur0% (1)
- Low Pressure Pumps: Installation and Start-Up InstructionДокумент12 страницLow Pressure Pumps: Installation and Start-Up InstructionsmithworkОценок пока нет
- Questions Old 2066 & 2068 NTC Level - 7 (Elx & Comm)Документ5 страницQuestions Old 2066 & 2068 NTC Level - 7 (Elx & Comm)Prashant McFc AdhikaryОценок пока нет