Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
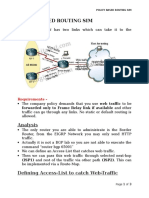
CCNP Route Notes
Загружено:
unikdipОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CCNP Route Notes
Загружено:
unikdipАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CCNP ROUTE Notes
The default-information originate always does not produce a static route in the routing table of the local router on which it is configured but it will generate a default route and advertise it into the ospf domain OSPF FILTERING On the ASBR o Use route-map On the ABR o Area < > filter-list prefix < prefix-list name> [in | out] On any router o Distribute-list < > in [This command will only prevent the filtered route from entering the routing table but the route will still appear in the ospf database] EIGRP considers the load (k2) of an interface only when sending an update for some other reason. The load is a five- minute exponentially weighted average that is updated every five seconds The neighbor command is used in EIGRP to define a neighboring router with which to exchange routing information. EIGRP stops processing multicast packets that come inbound on that interface. It also stop sending multi casts to that interface. No dynamic neighbor can be either discovered or continue to work if already discovered [over a network with more than two routers in the same subnet running EIGRP]. EIGRP exchanges routing information with that neighbor via unicasts whenever this command is used. One difference between DHCPv4 and stateful DHCPv6 is that IPv4 hosts send IP broadcasts to find DHCP servers, whereas IPv6 hosts send IPv6 multicasts. IPv6 multicast addresses have a prefix of FF00::/8, meaning that if the first 8 bits of an address are binary 11111111, or FF in hex. When using link local addresses as the next hop address when configuring IPv6 static routes, the outgoing interface has to be specified in the configuration. Reliable EIGRP packet types Update Query Reply Unreliable EIGRP packet types Ack Hello OSPF Frame Relay Interfaces 1) Physical - Non Broadcast 2) Multipoint subinterfaces - Non Broadcast 3) Point to Point subinterfaces - Point to Point Show ip route ospf | begin IA show ip ospf database | begin Summary Show ip ospf database | include 172.16.4 The maximum number of LSAs learned from other routers can be limited by a router using the max-lsa number OSPF subcommand. When configured, if the router learns more than the configured number of
LSAs from other routers (ignoring those created by the router itself), the router reacts. The first reaction is to issue log messages. The router ignores the event for a time period, after which the router repeats the warning message. This ignore-and-wait strategy can proceed through several iterations, ending when the router closes all neighborships, discards its LSDB, and then starts adding neighbors again. (The ignore time, and the number of times to ignore the event, can be configured with the max-lsa command.) If no DR is required: When sending the first DD message, transition to an Exstart state. The Master/Slave relationship is established in the Exstart state. Then the neighbor is transitioned to the Exchange state The Master is the router with the highest RID Sequence Number begins with 0x80000001 and increments by 1 whenever the LSA changes RouterA#debug ip ospf events OSPF events debugging is on RouterA# 04:43:16: OSPF: Rcv hello from 172.16.1.1 area 0 from Serial0/0 10.1.1.1 04:43:16: OSPF: Mismatched hello parameters from 10.1.1.1 04:43:16: OSPF: Dead R 120 C 10, Hello R 30 C 30 The Dead R is the Dead Timer of the neighbor that in this case is 120 seconds, and the Dead C is the local Dead Timer. When pinging a link local IPv6 address, the outgoing interface will have to be specified because these addresses are are not routed and are not in the routing table. Also note that the full interface name must be specified without spaces. With Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF), layer 3 switching is done in hardware (in an ASIC) instead of by software and the central CPU. It is off by default on all Cisco routers To match a default route with a: 1) Standard ACL, use "access-list x permit 0.0.0.0 2) Extended ACL, use "access-list y permit ip host 0.0.0.0 host 0.0.0.0 3) prefix-list, use "ip prefix-list z permit 0.0.0.0/0 When redistributing IGRP into EIGRP, if they have the same ASN, they redistribute automatically else redistribution needs to be manually configured The redistribute command also tells the router to redistribute connected routes on interfaces enabled with that routing protocol including passive interfaces
Tool command language (tcl) syntax for ping & traceroute Tclsh Foreach address { A.A.A.A $ . . . $ } { ping | trace $address} To quit tcl, use the tclquit command. It takes you straight to privilege mode "Bit bucket" - A term used when a router discards a route that matches the null0 interface of a summary route N/B: for default frame relay networks, Neighbor commands configured on spoke routers will not appear in the running config if the router's OSPF priority has been set to 0 on the interface which would be used to communicate with the designated neighbor. Although you can use the "ip ospf dead-interval minimal hello-multiplier" command on serial links, it would create additional overhead on these slow links and could result in flapping adjacencies if the link begins to experience congestion. Using this command on high-speed serial links would be less of an issue When a router receives an unknown OSPF LSA, it will first of all flood the LSA out all interfaces except the interface it learned that LSA from. This is done before it sends an ACK to the transmitting router of that LSA The metric of an OSPFv3 summary route will be the worst (highest) metric of its subordinate routes Question: what technique should be used on BGP edge routers to prevent a multi- homed AS from becoming a transit system? Answer: Use an outgoing distribution-list to filter all networks not originating from inside the AS
The BGP Synchronization Rule - Do not use or internally advertise a route until the route is learned from a source other than BGP The redistribution command tells the router to take not only routes learned by the source routing protocol but also connected routes on interfaces enabled wit that routing protocol - including passive interfaces. i.e. 1) All routes in the routing table learned by the source 2) All connected routes of interfaces on which the source routing protocol was enabled Delay is configured in tens-of-microseconds Bandwidth is configured in kilobits per second The OSPF Type-E2 metric is simply the metric value listed in the type 5 LSA
To defeat the RIP-OSPF domain loop problem using AD, just configure the AD for OSPF external routes to be higher than the AD of RIP on the same router.
When configuring per-router AD, the IP address of the neighboring router as referenced in the distance command in OSPF configuration will be compared to the RID of router that owns the Type-5 LSA With regards to RIP and EIGRP, the IP address referenced is that of the neighboring router that advertises the route RIPv2 does not allow summarizing to a mask length that is less than the class full network prefix. To get around the " ip summary-address rip" command issue, create a static route to summarize the routes then redistribute the route using the " redistribute static" command. NOTE: this is not a limitation of RIPv2 but a Cisco IOS implementation issue You might need to issue the " clear ip route* " command on the route you wish to see changes in its routing table when using RIPv2 The administrative distance for a specific routing protocol is locally significant. Using route-maps with PBR, you have two match options to use 1) Match IP address [ ] 2) Match length [min max] When a route-map (with the permit action) matches a packet, the set command defines the action to be taken. The 4 set command options are 1) Set ip next-hop [address 1, address 2........] 2) Set ip default next-hop [....., ....,.........] 3) Set interface [ interface-type interface-number,...........] 4) Set default interface [ interface-type interface-number,...........] N/B: 1) the next-hop IP has to be in the same connected subnet 2) with the default keyword used, the IOS applies the normal destination-based logic first (excluding default routes) To make the IOS process locally generated traffic using PBR logic, the " ip local policy route-map [ ]" global config command should be used
16-Bit ASN Assignment Categories 0 Reserved 1 - 64,495 Assigned by IANA for public use 64,496 - 64,511 Reserved for use in documentation 64,512 - 65,534 Private Use 65,535 Reserved
BGP Operation 1) Only advertise the best route in any BGP update 2) Do not advertise iBGP-learned routes to iBGP peers By default, when a router advertises a route using eBGP, the advertising router lists its own updatesource IP address as the next-hop address of the route. However when advertising a route to an iBGP peer, the advertising router does not change the next-hop IP address. The "neighbor [A.A.A.A] next-hop self" command changes the default iBGP next-hop behavior
Redistribution of BGP routes into an IGP is generally not recommended. This redistribution requires a relatively large amount of memory and a relatively large amount of processing by the IGP with the much larger number of routes to process. Redistributing the number of routes in the full Internet BGP table could crash the IGP routing protocols. The synchronization features tells a BGP router the following: Do not consider an iBGP-learned route as best unless the exact prefix was learned via an IGP and is currently in the IP routing table. Therefore, if you must redistribute eBGP learned routes into an Enterprise IGP, turn synchronization on. This will prevent routing loops Synchronization is applied to the entire BGP process and is "off" by default. Various ways of clearing a BGP neighborship include 1) Reloading the router 2) Administratively disabling and re-enabling the BGP neighborship using the neighbor shutdown and no neighbor shutdown commands 3) Various favors of the ip BGP clear exec command N/B: The "clear ip bgp <neighbor-Id> soft in" command only works if the "soft reconfiguration inbound" keyword is added to the "neighbor <neighbor-id> "command This command causes the router to retain the received BGP updates from that neighbor The newer version of this command (without the "soft in" keyword), doesn't require "soft reconfiguration". It uses the "route refresh" feature (this allows a BGP router to ask its neighbor to resend its full BGP update To use the "show ip bgp neighbor received routes" command, soft reconfiguration inbound has to be configured BGP uses the AS_Path PA as its primary loop prevention tool To display the RID, use the "show ip bgp nlri" exec command The weight can be set using 1) route-map 2) "neighbor A.A.A.A weight" command ( does not use an "in" or " out" direction because weight can only be set on input) Best BGP route tiebreaker Step 9) Oldest (longest known) eBGP route (skip this step if there is no current best path) Step 10) lowest neighbor BGP RID Step 11) lowest neighbor IP address As it turns out, because Updates received from eBGP peers do not include the Local_Pref PA, IOS lists a null value for Local_Pref for eBGP-learned routes by default. However, Updates from iBGP peers do include the Local_Pref. Note that both the "show ip bgp longer-prefixes" commands briefer output, and the show "ip bgp A.A.A.A/B" commands more verbose output, both identify the Local_Pref value. However, the longer command output does not list the Weight value.
The routing table manager (RTM) decides which of all the best routes will be included in its routing table eBGP - 20 iBGP - 200 IGPs - various ADs The "show ip bgp rib-failure" command list one line for each best route the RTM didn't place in the routing table (adjust the various default ADs to influence which route is placed in the routing table) Assuming ISPA is preferred, Only when the AS_Path (before prepending) is at least the number of ASNs added shorter through ISPB can the ISPB path be chosen. Note: When using AS_Path prepending, do not prepend just any ASN. BGP still uses the AS_Path for loop avoidance, so using an ASN already in the AS_Path, like the ASN of the most recently added ASN (for example, ASN 3 in this case), or the local ASN (for example, ASN 11 in this case), makes the most sense. Although presented here as a tool for influencing outbound routes, As_Path prepending can also be used to influence the inbound routes as well. Weight is local for each router Local Preference is advertised to all iBGP peers within the same AS ( by design, this can be set on eBGP peers. They will then advertise the Local_Pref in iBGP updates) The "neighbor x.x.x.x remove-private-as" removes private ASNs from outbound bgp updates bound for the specified neighbor BGP updates can also be filtered based on the AS_Path using: "ip as-path access-list < > [deny|permit] { }" "neighbor x.x.x.x filter-list <as-path access-list number> [out|in]" N/B: for the as-path access-lists, " deny^100$" ; ^ means that the AS Pathetic must begin with the given AS $ means that the path must end with the given AS Find out which represents "contains" Therefore, ^100$ means that the as access-list will match only updates sourced from AS 100 . (Period) denotes a wildcard * stands for repetition Therefore "permit .*" permits any value not matched by the deny access list ( assuming the deny portion came before it) BGP If u decide to use a network from say the ISP as your default route within the enterprise, the "ip defaultnetwork" command works well on the enterprise boarder router only with remotely-learned classful networks. It should not be used with classless networks. An alternative to using the ip default-network command is issuing the neighbor X.X.X.X default-originate configuration on the ISP router. NOTE: By default, the MED is compared only when the route is being received from the same neighboring AS, although advertised by different border routers. The nondefault behavior of comparing the MED regardless of the AS advertising the route can be activated using the bgp always-compare- med command, however, the results of this command have to be carefully considered. NOTE: Because the MED is an optional attribute, it might not be present in BGP updates. RFC 4271 requires that a missing MED is equivalent to having the MED set to 0. However, a missing MED can also
be considered to be the worst possible MED, which is activated using the bgp bestpath med missing- asworst command. The use of route reflectors is an alternative to using a full mesh internal BGP. The "neighbor x.x.x.x route-reflector-client" which is configured on the route reflector server, reflects or advertises BGP updates received from its x.x.x.x iBGP peer to other iBGP peers within the ASN The link local addresses for the respective IPv6 tunnels are derived as follows: 1) Manually configured - FF80::/96 with tunnel source IPv4 address 2) GRE - IPv6 eui-64 rule using lowest numbered interface's MAC address 3) Auto 6to4 - FF80::/96 with the tunnel's IPv4 source address 4) ISATAP - FF80::/64 with the embedded IPv4 address in the IPv4 address formed using the modified eui-64 BGP next-hop of 0.0.0.0; 1) The network was locally originated via redistribution of IGP into BGP or 2) A network or aggregate command in BGP configuration When configuring tunnels, IPv4 addresses are not needed on tunnel interfaces ISATAP uses modified eui-64; 0000:5EFE in the 5 & 6 quartet DHCP Config ip dhcp pool [pool-name] network x.x.x.x <mask> default-router y.y.y.y ip dhcp exclude-address z.z.z.z (assuming the default gateway-y.y.y.y is in this range. dns-server a.a.a.a b.b.b.b IPsec tunnels do not support IGPs. Alternatives that do include 1) GRE 2) Group Encrypted Transport (GET) 3) Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) 4) Virtual Tunnel Interface - same as GRE but does not use a 4 byte header For a given prefix/length, OSPF always prefers an E1 route over an E2 route OSI networking layer addressing is implemented by using two types of hierarchical address 1) Network Service Access Point (NSAP) 2) Network Entity Titles (NET)
Вам также может понравиться
- Catálogo de Peças TR 6180 J PDFДокумент652 страницыCatálogo de Peças TR 6180 J PDFBarra Nova Ferreira80% (15)
- Azure WVD - Design Document - 20210601 v0.03Документ42 страницыAzure WVD - Design Document - 20210601 v0.03RASHMI RОценок пока нет
- 210-S637UUT-200FH-HA - Baylor MotorsGenerators Instruction and Service Manual PDFДокумент49 страниц210-S637UUT-200FH-HA - Baylor MotorsGenerators Instruction and Service Manual PDFCarlos Antonio Fontalvo Carrascal100% (4)
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsОт EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsОценок пока нет
- Cobit 5Документ3 страницыCobit 5Marco Putra WibawaОценок пока нет
- The China Continental Scientific Drilling Project CCSD-1 Well Drilling Engineering and Construction PDFДокумент375 страницThe China Continental Scientific Drilling Project CCSD-1 Well Drilling Engineering and Construction PDF杨建政Оценок пока нет
- CCNP ROUTE Notes - UpdatedДокумент4 страницыCCNP ROUTE Notes - Updatedclassic317Оценок пока нет
- Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSОт EverandVersatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSОценок пока нет
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesОт EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesОценок пока нет
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsОт EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsОценок пока нет
- Module 8 - Policy Based Routing: ISP/IXP Networking Workshop LabДокумент15 страницModule 8 - Policy Based Routing: ISP/IXP Networking Workshop LabmaracyberstationОценок пока нет
- Policy Based Routing SIM (Formatted)Документ3 страницыPolicy Based Routing SIM (Formatted)Gossan AnicetОценок пока нет
- Ccna 1) What Is An IP Address?Документ15 страницCcna 1) What Is An IP Address?pankaj_subhedarОценок пока нет
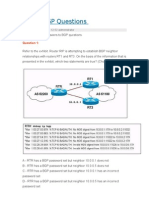
- OSPF QuestionsДокумент31 страницаOSPF QuestionsArvind KumarОценок пока нет
- Cisco HSRP TroubleshootingДокумент52 страницыCisco HSRP TroubleshootingSivakonalarao MandalapuОценок пока нет
- 6.-Policy Based Routing (PBR)Документ11 страниц6.-Policy Based Routing (PBR)jaiimeandres100% (1)
- Network Engineer Interview QuestionsДокумент8 страницNetwork Engineer Interview Questionsnatrix029Оценок пока нет
- Implement Vrf-Lite: Lab TopologyДокумент18 страницImplement Vrf-Lite: Lab TopologycciersmanОценок пока нет
- Notes To CcieДокумент42 страницыNotes To CcieLeon DobrzinskyОценок пока нет
- Menog4 Isis TutorialДокумент80 страницMenog4 Isis TutorialarunascarletОценок пока нет
- 2.10-InterVLAN Routing PDFДокумент14 страниц2.10-InterVLAN Routing PDFYureka MindsetОценок пока нет
- VTP Interview Questions and Answers (VLAN Trunking Protocol) - Networker InterviewДокумент2 страницыVTP Interview Questions and Answers (VLAN Trunking Protocol) - Networker InterviewBhanu SainiОценок пока нет
- CCIE Notes From ExperienceДокумент27 страницCCIE Notes From Experienceapi-3817990Оценок пока нет
- Policy Based RoutingДокумент16 страницPolicy Based RoutingAgbo Sunday ChukwuemekaОценок пока нет
- MPLS Configuration Tutorial Step by StepДокумент17 страницMPLS Configuration Tutorial Step by StepJeffrey GirardОценок пока нет
- Cisco BGPДокумент82 страницыCisco BGPMohit KumarОценок пока нет
- Advance EigrpДокумент42 страницыAdvance EigrpashdesantisОценок пока нет
- BGP ReportДокумент85 страницBGP ReportathaiОценок пока нет
- OSPF Route Filtering DemystifiedДокумент25 страницOSPF Route Filtering Demystifiedbedjo123Оценок пока нет
- Ospf NotesДокумент5 страницOspf Notesdhdeore81Оценок пока нет
- BGP Advanced Lab PDFДокумент8 страницBGP Advanced Lab PDFDwi UtomoОценок пока нет
- Top 90+ CCIE OSPF Interview Questions (UPDATED) 2018Документ8 страницTop 90+ CCIE OSPF Interview Questions (UPDATED) 2018Larry TembuОценок пока нет
- Routing Process PictureДокумент1 страницаRouting Process Picturelefreak1979Оценок пока нет
- How Do Prefix List WorkДокумент18 страницHow Do Prefix List WorkYusuf MahmoudОценок пока нет
- EIGRP MindmapДокумент1 страницаEIGRP MindmapJason RobinsonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4/module 3 EigrpДокумент29 страницChapter 4/module 3 EigrpArad RezaОценок пока нет
- BGP QuestionsДокумент8 страницBGP Questionsstorm2010Оценок пока нет
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) - Port 179: Gateway Protocols (IGP's)Документ32 страницыBGP (Border Gateway Protocol) - Port 179: Gateway Protocols (IGP's)Nitesh MulukОценок пока нет
- CCNP1 - Mod 6 OSPF Labs PDFДокумент79 страницCCNP1 - Mod 6 OSPF Labs PDFngangaОценок пока нет
- Lab 2 - Mpls Te - Mpls and Application Lab Assignments - ThuanДокумент27 страницLab 2 - Mpls Te - Mpls and Application Lab Assignments - ThuanalexvnptОценок пока нет
- CCIE RS Quick Review Kit Ver2 Vol1 PDFДокумент40 страницCCIE RS Quick Review Kit Ver2 Vol1 PDFDinh Truong CongОценок пока нет
- Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0Документ24 страницыAdvanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0Thomas PSОценок пока нет
- BGP Community: Lab TopologyДокумент6 страницBGP Community: Lab TopologyNguyễn Đức KiênОценок пока нет
- 6 Network AssuranceДокумент31 страница6 Network AssuranceKv142 KvОценок пока нет
- OSPF - Quick Referce IsmailДокумент6 страницOSPF - Quick Referce IsmailSai Kyaw HtikeОценок пока нет
- The CISCO IP Routing Process: White PaperДокумент18 страницThe CISCO IP Routing Process: White PapersoennekerОценок пока нет
- BGPДокумент10 страницBGPyasser23Оценок пока нет
- Yasser Auda CCIEv5 WorkbookДокумент26 страницYasser Auda CCIEv5 WorkbookphamvanhaОценок пока нет
- CCNP Routing&Switching ProgramДокумент2 страницыCCNP Routing&Switching ProgramClaudian PaduraruОценок пока нет
- Yasser Auda CCIEv5 IPv4 Multicast Study Guide PDFДокумент50 страницYasser Auda CCIEv5 IPv4 Multicast Study Guide PDFsheraz35Оценок пока нет
- CCNP Interview QuestionsДокумент4 страницыCCNP Interview QuestionsNaeem ShahzadОценок пока нет
- OSPF Deep DiveДокумент149 страницOSPF Deep DiveNirmal KumarОценок пока нет
- Ccie Rs NoteДокумент60 страницCcie Rs NoteVeeji SwamyОценок пока нет
- 11.advanced OSPF Topics Part IIДокумент10 страниц11.advanced OSPF Topics Part IIjosephjoОценок пока нет
- Switch Final Exam CCNP 6Документ12 страницSwitch Final Exam CCNP 6Tuấn Linh100% (2)
- BGP CommunityДокумент20 страницBGP CommunityRANJITHОценок пока нет
- Basic BGP Notes in ShortДокумент12 страницBasic BGP Notes in Shortparveen_1974Оценок пока нет
- Routing Basic Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент8 страницRouting Basic Interview Questions and AnswersLokesh ShanjeevОценок пока нет
- EIGRPДокумент90 страницEIGRPТијана Илић100% (1)
- Narbik NocДокумент23 страницыNarbik Nocobee1234Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF TopologyДокумент24 страницыChapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF TopologyErid RocaОценок пока нет
- Q5 - BGPДокумент13 страницQ5 - BGPtuan anhОценок пока нет
- CCNP Job Interview Questions & Answers - Fahad KhanДокумент5 страницCCNP Job Interview Questions & Answers - Fahad KhanGold SunriseОценок пока нет
- CCNP Route (642-902)Документ12 страницCCNP Route (642-902)Mashiur NayanОценок пока нет
- OSPF Part3 - CheatSheet ATech (Waqas Karim)Документ1 страницаOSPF Part3 - CheatSheet ATech (Waqas Karim)Waqas Karim100% (1)
- The Ultimate Guide To Youtube AdvertisingДокумент54 страницыThe Ultimate Guide To Youtube Advertisingsumit-7Оценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To Linux: 1.2 Linux Evolution and Popular Operating SystemsДокумент11 страницCHAPTER 1 - Introduction To Linux: 1.2 Linux Evolution and Popular Operating SystemsSofОценок пока нет
- Assessment Submission Sheet: Australian Ideal CollegeДокумент18 страницAssessment Submission Sheet: Australian Ideal CollegeBishal GaneshОценок пока нет
- Alberta Apprenticeship and Industry Training: Trade Entrance RequirementsДокумент1 страницаAlberta Apprenticeship and Industry Training: Trade Entrance RequirementsRamsés IIОценок пока нет
- DLC3 CalyaДокумент4 страницыDLC3 Calyakurnia wanОценок пока нет
- Sewer Line LayoutДокумент1 страницаSewer Line LayoutJing ReyesОценок пока нет
- AAU On Tele BirrДокумент72 страницыAAU On Tele BirrNatinael AbebeОценок пока нет
- Accessories - 700-HC RelaysДокумент1 страницаAccessories - 700-HC RelaysArif KhanОценок пока нет
- Queueing Theory: Queueing Theory Is The Mathematical Study of Waiting Lines, orДокумент12 страницQueueing Theory: Queueing Theory Is The Mathematical Study of Waiting Lines, orGabrielОценок пока нет
- Banlga Text To Bangla Sign Language Parvez For ConferenceДокумент6 страницBanlga Text To Bangla Sign Language Parvez For ConferenceDr. Muhammad Aminur RahamanОценок пока нет
- Ptest 2022Документ3 страницыPtest 2022Shubham Singh YadavОценок пока нет
- L3H CAS - PresoДокумент140 страницL3H CAS - PresoPablo RestrepoОценок пока нет
- Nuevo Documento de TextoДокумент1 страницаNuevo Documento de TextoGuillermo Cabrera ContreraОценок пока нет
- Fms - Flexible Manufacturing SystemsДокумент47 страницFms - Flexible Manufacturing SystemsYashwanth ReddyОценок пока нет
- B. SC - ElectronicsДокумент55 страницB. SC - Electronicsjerushi karuОценок пока нет
- Carrier Aggregation (5G RAN6.1 - 02)Документ199 страницCarrier Aggregation (5G RAN6.1 - 02)VVL1959Оценок пока нет
- Egypt Update Jan 2023Документ4 страницыEgypt Update Jan 2023rohandev1001Оценок пока нет
- Operator Manual: WarningДокумент12 страницOperator Manual: WarningMohamed FazilОценок пока нет
- US460Документ5 страницUS460bbОценок пока нет
- Amphibious House A Novel Practice As A Flood MitigДокумент13 страницAmphibious House A Novel Practice As A Flood MitigPearlОценок пока нет
- TU8000 TV: Product HighlightsДокумент6 страницTU8000 TV: Product HighlightsEdwinОценок пока нет
- See Results About: Mining SimulatorДокумент1 страницаSee Results About: Mining Simulatorrafael_moraes_11Оценок пока нет
- Additive ManufacturingДокумент13 страницAdditive ManufacturingPrajwal ChatraОценок пока нет
- Computer Training Institute: Project Report ofДокумент9 страницComputer Training Institute: Project Report ofEMMANUEL TV INDIAОценок пока нет
- Infineon-CE222306 - PSoC - 4 - I2C - Communication - With - Serial - Communication - Block - (SCB) - Code Example-V03 - 00-ENДокумент10 страницInfineon-CE222306 - PSoC - 4 - I2C - Communication - With - Serial - Communication - Block - (SCB) - Code Example-V03 - 00-ENPiyush Kumar SahooОценок пока нет