Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Session 2 Management Evolution
Загружено:
Samik SinghИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Session 2 Management Evolution
Загружено:
Samik SinghАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Management: An Overview
DEFINITIONS OF MANAGEMENT MANAGERIAL ROLES THE FUNCTIONS OF MANAGERS THE LEVELS OF MANAGEMENT MANAGEMENT SKILLS APPROACHES TO MANAGEMENT
Definitions of Management Koontz and Weiherch Management is a process of designing and maintaining an environment in which individuals work together in groups, efficiently accomplish selected aims. McFafland gives a holistic view on management. Management is a process by which managers create, direct, maintain and operate purposive organizations, through systematic, coordinated cooperative human effort. These definitions when expended have the following implications. The functions of managers include planning, organizing, staffing, leading and controlling. These functions are essential to any kind of organization. It applies to managers at all hierarchical levels. The aim of managers is to increase productivity, effectiveness and efficiency.
Functions of Manager
1. Planning - Decide Mission and objective 2. Organizing Assigning task and allocating resources 3. Staffing Human Resources Management 4. Leading Influencing, motivating and directing people 5. Controlling Comparing performance with standard
Mintzbergs 10 Managerial Roles
Figurehead INTERPERSONAL Performs ceremonial and symbolic duties such as greeting visitors, signing legal documents. Leader Direct and motivate subordinates, training, counseling, and communicating with subordinates. Liaison Maintain information links both inside and outside organization; use mail, phone calls, meets. Monitor Seek and receive information, scan periodicals and reports, maintain personal contacts. Disseminator Forward information to other organization members; send memos and reports, make phone calls. Spokesperson Transmit information to outsiders through speeches, reports, and memos. Entrepreneur Initiate improvement projects, identify new ideas, and delegate idea responsibility to others. Disturbance Take corrective action during disputes or Handler crises; resolve conflicts among subordinates; adapt to environmental crises. Resource Decide who gets resources, scheduling, Allocator budgeting, and setting priorities. Negotiator Represent department during negotiation of union contracts, sales, purchases, and budgets; represent departmental interests.
INFORMATIONAL
DECISIONAL
Level of Management Type of Managers Top Level Managers Middle Level Managers First Level Managers
Managerial Skills
Technical skills:
Required Skills Function Design Skill Planning Human Relation and Conceptual Organizing Skill Technical Skill Directing
Theses skills include the knowledge of and proficiency in activities involving methods, processes and procedures. Human or interpersonal skills: It includes his/her ability to understand other people and interact effectively with them. Conceptual skills: This refers to the ability to think and conceptualize abstract situations. These abilities are required for making complex decisions. Design skills: It enables a manager to handle and solve any kind of unforeseen problems that may crop up in the organization.
Approaches to Management
Characteristic / Contribution Limitation Empirical Or Case Approach Focus on interpersonal behaviour, human Situations are all different. No attempt to relation, leadership, and motivation. Based identify principles. Limited values for on individual psychology. developing management theory Interpersonal Behaviour Approach Focus on interpersonal behaviour human Ignores planning, organizing, and relations, leadership, and motivation. Based controlling. Psychological training is not on individual psychology. enough to become an effective manager. Group Behaviour Approach Emphasis on behaviour of people in Not integrated with management concept, groups. Based on social psychology. The principles, theory and techniques. study of large groups is often called OB Cooperative Social System Approach Concerned with both interpersonal and Too broad a field for the study of group behavioural aspects leading to a management. At the same time it overlook system of cooperation. Expanded concept managerial concepts, principles and includes any cooperative group with clear techniques. purpose. Sociotechnicla System Approach Technical system has great effect on social system (personal attitude, group Emphasis only on blue-collar and lower behaviour). Focus on production, office level office work. Ignore much of other
operations, and other areas with close managerial knowledge. relationship between technical system and people. Decision Theory Approach Focus on the making of decisions, person or groups making decisions, and the There is more to managing than making decision making process. Some theorists decision. The focus is at the same time too use decision-making as a springboard to narrow and too wide. study all enterprise activities. Systems Approach Systems concepts have broad applicability. Systems have boundaries, but they also Analyses of the interrelatedness of system interact with the external environment i.e. and subsystems as well as the interactions organizations are open system. Recognizes of organizations with their external importance of studying interrelatedness of environment, can hardly be considered a planning, organizing, and controlling in an new approach to management organization as well as the many Subsystems. Mathematical Or Management Science Approach Managing is seen as mathematical Preoccupation with mathematical models. processes, concepts, symbols and models. Many aspects in managing cannot be Looks at magt. As a purely logical process, modeled. Mathematics is a useful tool, but expressed in mathematical symbols and hardly a school or an approach to relationships. management Contingency or Situational Approach Managerial practice depends on Managers have long realized that there is circumstances. Contingency theory no one best way to do things. Difficulty in recognizes the influence of given solution determining all relevant contingency on organizational behaviour patterns. factors and showing their relationship Managerial Roles Approach Based on observation of five chief Sample was very small, some important executive and ten managerial roles managerial activities are left Mc Kinseys 7-S Framework Strategy, Structure, Systems, Style, Staff, Terms used are not precise and topics are Shared values, Skills not discuss in depth Operational Approach Draws together concept, principles, techniques and knowledge from other fields According to coordination is a essence of and managerial approach. Distinguishes management and a separate function. managerial and non managerial functions
Evolution of Management Thought
Approaches
Early Approach
Main Aspects
Major Contribution
Classical Approach
IR in Europe in mid 1700 Robert Owen Broader inquiry into the Charles Babbage nature of management Andrew Ure Charles Dupin Henry R. Towne Frederick W. Taylor, Scientific Management Frank and Lillian Gilbreth, Henry Gantt Bureaucratic Management Administrative Management Group Influence Hawthorne Studies Max Weber Henri Fayol Mary Parker Follet Elton Mayo Abraham Maslow Douglas Mc Gregor Chris Argyris
Behavioural Maslows needs theory Approach Theory of X and Y Model I V/s Model II Quantitative Management Science Approach Operation Management Management Information System Modern Approach The System Theory Contingency Theory Emerging Approach Theory Z and TQM
Emerged during world war II The army brought together managers, government officials and scientists to help in deploy its resources more effectively and efficiently.
Looking at an Organization as a whole Based on input, output and process Based on Situational Theory William Ouchi: Combination of American And Japanese style of magt.
Name Robert Owen Charles Babbage Andrew Ure
Education/main study British Entrepreneur British Professor of Mathematics, Father of modern computing British Academician
Contribution Silent monitor` Standard working hours Mechanical Calculator Analytical engine
The philosophy of Manufacturing Charles Dupin French Engineer Influenced Henry Fayol Henry R. Towne President of Yale and Towne F.W. Taylor was influenced manufacturing by him company Frederick Father of Scientific Referred problem of Winslow Taylor, Management Soldiering Frank Gilbreth Father of motion study therbligs (17 motions), bricklaying study Lillian Gilbreth Wife of Frank Gilbreth The philosophy of Earn 22 honorary degree management -her Ph D work Henry Gantt Associate of Taylor at Midvale Gantt Chart, task and bonus & Bethlehem Steel system Henri Fayol Father of Administrative and Identify Business Operation, General Gave fourteen Management principles of management Max Weber Father of Bureaucratic Observe nepotism, identify Management the characteristic of ideal bureaucracy Mary She understood the Function of group in the Parker Follet significance of workplace, introduced terms human element in power with and power over, power sharing, integration organization. Elton Mayo Father of Human Relation 1. Illumination experiments Approach, in 1924 2. Relay assembly test room started study at 3. Interview Phase Western Electrics 4. Bank wiring observation Hawthorne plant
Abraham Maslow
A Brandies University Psychologist
Douglas Mc Gregor Chris Argyris William Ouchi
1.Needs never completely fulfilled 2. We try to fulfill needs 3. Need occur in hierarchical manner Developed two assumption Theory X and Theory Y about human behaviour Yale University Professor Model I and Model II Management Expert Theory Z America + Japan
Name Robert Owen Charles Babbage Andrew Ure Charles Dupin Henry R. Towne
Wrong Contribution Influenced Henry Fayol The philosophy of Manufacturing Fourteen principles of management Silent monitor The philosophy of management Father of modern computing
Right Contribution
Frederick Winslow Taylor, Frank Gilbreth Father of Scientific Management Lillian Gilbreth Influenced F.W. Taylor Henry Gantt Henri Fayol Max Weber Mary Parker Follet Elton Mayo Abraham Maslow Douglas Mc Gregor Chris Argyris William Ouchi Peter Drucker Henry therbligs
Hawthorne Illumination experiments Model I and Model II America + Japan =Z Challenge the traditional assumption about the people 10 Managerial roles Characteristic of ideal bureaucracy
Do the right thing Doing the thing rightly power with and power over, power sharing,
Needs never completely Task and bonus system
Mintz berg
Robert H. Kalz Four kind of skills
Frederick Winslow Taylor: Essence or Principles of Scientific Management 1. Need for developing a scientific way of performing each job
Вам также может понравиться
- Handbook for Strategic HR - Section 2: Consulting and Partnership SkillsОт EverandHandbook for Strategic HR - Section 2: Consulting and Partnership SkillsОценок пока нет
- Handbook for Strategic HR - Section 3: Use of Self as an Instrument of ChangeОт EverandHandbook for Strategic HR - Section 3: Use of Self as an Instrument of ChangeОценок пока нет
- Understanding The Manager's JobДокумент42 страницыUnderstanding The Manager's JobFaheem JuttОценок пока нет
- TM-2223 AVEVA Marine (12.1) HVAC RevДокумент150 страницTM-2223 AVEVA Marine (12.1) HVAC Revprash28091981Оценок пока нет
- Organization and Management of Physical Education and HealthДокумент5 страницOrganization and Management of Physical Education and HealthAnne Santos Rojo33% (3)
- Theories of ManagementДокумент9 страницTheories of Managementbaby100% (1)
- Product ResearchДокумент10 страницProduct ResearchkgtandonОценок пока нет
- Management and Organisational Behaviour PDFДокумент86 страницManagement and Organisational Behaviour PDFMadhuri Devi100% (1)
- Management Theories PDFДокумент27 страницManagement Theories PDFRaja RamanОценок пока нет
- LabManual - Test and Reliability - v1 - 1Документ28 страницLabManual - Test and Reliability - v1 - 1Pedro Henrique KöhlerОценок пока нет
- Elements of User Experience by Jesse James GarrettДокумент73 страницыElements of User Experience by Jesse James GarrettIdyawati Hussein83% (6)
- Management Handout Cha 1 - 5Документ70 страницManagement Handout Cha 1 - 5momra100% (6)
- PrefaceДокумент2 страницыPrefaceKhaledMostafaОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Management ThoughtДокумент6 страницEvolution of Management ThoughtRyhanul Islam91% (34)
- Management and Organisational BehaviourДокумент86 страницManagement and Organisational BehaviourRaunak KumarОценок пока нет
- Library ManagementДокумент237 страницLibrary ManagementeducationdoctorОценок пока нет
- It - Intro To Human Computer Interaction - EditedДокумент19 страницIt - Intro To Human Computer Interaction - Editedmaribeth riveraОценок пока нет
- Construction Project Management Getting It Right First Time 293 PDFДокумент293 страницыConstruction Project Management Getting It Right First Time 293 PDFbakbakОценок пока нет
- Erco. Lighting For MuseumsДокумент9 страницErco. Lighting For MuseumsjapaОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Management Thought IntroductionДокумент6 страницEvolution of Management Thought IntroductionamoghvkiniОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Management Thoughts NewДокумент34 страницыEvaluation of Management Thoughts NewtharakadesilvaОценок пока нет
- TQMДокумент9 страницTQMCharlotte AvalonОценок пока нет
- Principles of Management: by Prof. Raghavendran.VДокумент44 страницыPrinciples of Management: by Prof. Raghavendran.VPingali ShashiОценок пока нет
- Principles and Practices of Management Unit IДокумент30 страницPrinciples and Practices of Management Unit IshwetabatraОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Management Science GPДокумент32 страницыIntroduction To Management Science GPGuru PrasadОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Management TheoriesДокумент54 страницыChapter 2 Management TheoriesAnish PoudelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ46 страницChapter 1bahmud mohammedОценок пока нет
- Short Notes of Principle of Management (MGT 301) : Lesson-1Документ18 страницShort Notes of Principle of Management (MGT 301) : Lesson-1asad ImranОценок пока нет
- CM1, CU 1, WK 1-Introduction To Leadership and ManagementДокумент16 страницCM1, CU 1, WK 1-Introduction To Leadership and ManagementMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareОценок пока нет
- Ch01 mgt162Документ21 страницаCh01 mgt162aleef aleefОценок пока нет
- ThoghtДокумент73 страницыThoghtwondimu getachewОценок пока нет
- What Is Management?Документ22 страницыWhat Is Management?pawanshrestha1Оценок пока нет
- Evolution of Management TheoriesДокумент18 страницEvolution of Management TheoriesKirstine Valerie MandalonesОценок пока нет
- MGT503Документ32 страницыMGT503Qamar NangrajОценок пока нет
- After Reading This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToДокумент27 страницAfter Reading This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToGaurav PatniОценок пока нет
- Mc&ob-All-Merged UnitsДокумент74 страницыMc&ob-All-Merged UnitsAnuj YadavОценок пока нет
- Mcob Unit 1Документ21 страницаMcob Unit 1Anuj YadavОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts of ManagementДокумент30 страницBasic Concepts of ManagementMark SorianoОценок пока нет
- Effective Class NotesДокумент28 страницEffective Class NotesElton Gil Toriaga MendozaОценок пока нет
- Organization and Mngt. 12 Modules QRTR 1Документ15 страницOrganization and Mngt. 12 Modules QRTR 1remely marcosОценок пока нет
- Ch02-Evolution & ThoughtДокумент49 страницCh02-Evolution & ThoughtAmirul HaffizОценок пока нет
- ESM 520 Lecture 1 NewДокумент63 страницыESM 520 Lecture 1 Newkhawla2789Оценок пока нет
- MNGДокумент5 страницMNGaamirsubhan4321Оценок пока нет
- Management and Leadership Theories EditedДокумент36 страницManagement and Leadership Theories EditedAudelio CerezoОценок пока нет
- RM. ManegementДокумент130 страницRM. ManegementMuhammad Akhlaq KhanОценок пока нет
- ABM 7 Module 3rd Quarter 2Документ38 страницABM 7 Module 3rd Quarter 2Pacito Sto TomasОценок пока нет
- Principles of Management: Vinod Basupattad-JSS-DVH-IMSRДокумент46 страницPrinciples of Management: Vinod Basupattad-JSS-DVH-IMSRkalpalisaacОценок пока нет
- AnswersДокумент4 страницыAnswersAngelie UmambacОценок пока нет
- ENT117 - MU1 - Introduction To Human Resource ManagementДокумент26 страницENT117 - MU1 - Introduction To Human Resource ManagementSamYeol ParkОценок пока нет
- Topic 2Документ34 страницыTopic 2api-3824226100% (1)
- MG 2351 Principles of ManagementДокумент75 страницMG 2351 Principles of Managementmurjass85Оценок пока нет
- Chapter I PPT Engineering Management Lesson 1.1 1.2Документ19 страницChapter I PPT Engineering Management Lesson 1.1 1.2Anne Clarisse DionisioОценок пока нет
- ME Module 1Документ104 страницыME Module 1vinod kumarОценок пока нет
- Business StudiesДокумент5 страницBusiness StudiesJibcomОценок пока нет
- GDM MFДокумент267 страницGDM MFsam rosОценок пока нет
- Syllabus 07 08 Mba Sem I MTPДокумент3 страницыSyllabus 07 08 Mba Sem I MTPChaitanya DevОценок пока нет
- mgt503 Notes 1to22 LessonДокумент24 страницыmgt503 Notes 1to22 LessonAyesha MughalОценок пока нет
- ManagmentДокумент33 страницыManagmentayan khanОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 TheoriesДокумент69 страницLesson 3 TheoriesJhensczy Hazel Maye AlbaОценок пока нет
- Management and Behavioral ProcessДокумент164 страницыManagement and Behavioral ProcessRaghavendra Kaladi0% (1)
- Chapter 1 BДокумент6 страницChapter 1 BDolly MehtaОценок пока нет
- Introduction Management Theory, Management and SocietyДокумент30 страницIntroduction Management Theory, Management and SocietyvishalgoreОценок пока нет
- Management TheoriesДокумент31 страницаManagement TheoriesShreya BansalОценок пока нет
- Meppt1 PDFДокумент104 страницыMeppt1 PDFAjaykumar KumarОценок пока нет
- History and Evolution of Management ThoughtДокумент36 страницHistory and Evolution of Management ThoughtRohan ViswanathОценок пока нет
- Behavioral Approach To ManagementДокумент2 страницыBehavioral Approach To ManagementLouise Joseph Peralta100% (1)
- DST School of Thoughts in ManagementДокумент9 страницDST School of Thoughts in ManagementKartika NairОценок пока нет
- Management ScienceДокумент141 страницаManagement ScienceassamОценок пока нет
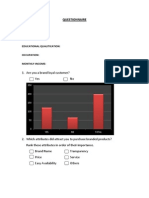
- QuestionnaireДокумент5 страницQuestionnaireSamik SinghОценок пока нет
- Advertising Regulation in India: Assignment OnДокумент12 страницAdvertising Regulation in India: Assignment OnSamik SinghОценок пока нет
- India's Urban Poor Need 40 MN Houses, 500 Health Centres: ASSOCHAM ReportДокумент2 страницыIndia's Urban Poor Need 40 MN Houses, 500 Health Centres: ASSOCHAM ReportSamik SinghОценок пока нет
- Born or Made?: Dilemmas of Destiny and DevelopmentДокумент14 страницBorn or Made?: Dilemmas of Destiny and DevelopmentSamik SinghОценок пока нет
- Questionnaire: - (Adaption and Acceptability of Internet Banking)Документ2 страницыQuestionnaire: - (Adaption and Acceptability of Internet Banking)Samik SinghОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)Документ23 страницыIntroduction To Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)cvithy999Оценок пока нет
- Formula Lincoln ProgramДокумент60 страницFormula Lincoln ProgramLuizОценок пока нет
- Thesis Schedule Thesis 2018-19: - Climate ConsiderationsДокумент3 страницыThesis Schedule Thesis 2018-19: - Climate ConsiderationssalmanОценок пока нет
- CSC2073 - Lecture 30 (Software Design Principles - I)Документ30 страницCSC2073 - Lecture 30 (Software Design Principles - I)Ch UmerОценок пока нет
- Vernacular DesignДокумент15 страницVernacular DesignscribdbangkokОценок пока нет
- Construction and Engineering Management: Engr. AlbertsaludДокумент13 страницConstruction and Engineering Management: Engr. AlbertsaludemmaОценок пока нет
- Practical Research 1 DLL January 20 24 2020Документ4 страницыPractical Research 1 DLL January 20 24 2020Dearla BitoonОценок пока нет
- Putrajaya Campus Final Examination Timetable For Semester 1 20172018Документ5 страницPutrajaya Campus Final Examination Timetable For Semester 1 20172018Shangkaran RadakrishnanОценок пока нет
- Kerala University B.tech 2008 Scheme Syllabus For 1&2 SemДокумент4 страницыKerala University B.tech 2008 Scheme Syllabus For 1&2 Semjoyasams100% (1)
- ME136P 2 Engineering Materials Processess and TestingДокумент10 страницME136P 2 Engineering Materials Processess and TestingJeffersonTalanОценок пока нет
- Sram Programmable Fpgas: Configuration Memory CellsДокумент2 страницыSram Programmable Fpgas: Configuration Memory Cellsyasar saleemОценок пока нет
- NMA Full Degree Prospectus 2019 PDFДокумент58 страницNMA Full Degree Prospectus 2019 PDFShehzad KhanОценок пока нет
- Architecture Design Presentation - Banquet Hall and Villa at Kekunadura, MataraДокумент17 страницArchitecture Design Presentation - Banquet Hall and Villa at Kekunadura, MataraMANJULA KALHARA DE SILVA ARCHITECTSОценок пока нет
- Construction and Working of Input and Output Devices Input DevicesДокумент24 страницыConstruction and Working of Input and Output Devices Input DevicesMazhar SandhuОценок пока нет
- Module - 5 Introduction To VHDL 5.1: ObjectivesДокумент14 страницModule - 5 Introduction To VHDL 5.1: Objectivesabhilash gowdaОценок пока нет
- Verdi: Automated Debug SystemДокумент8 страницVerdi: Automated Debug Systemali abdelslam AbdelalimОценок пока нет
- Knowledge Management in Manufacturing SectorДокумент22 страницыKnowledge Management in Manufacturing SectorVaishnavi PreranaОценок пока нет
- Floor Plan 01 Section 1-1 03: Detail 01Документ1 страницаFloor Plan 01 Section 1-1 03: Detail 01Hung NguyentheОценок пока нет
- Cultivating Next-GEN Designers: The Systematic Transfer of KnowledgeДокумент10 страницCultivating Next-GEN Designers: The Systematic Transfer of KnowledgeGokilaVijayalakshmiОценок пока нет
- English Courses UpvДокумент110 страницEnglish Courses UpvAnonymous U7slfmBWHbОценок пока нет
- Principles of TeachingДокумент12 страницPrinciples of TeachingJM INOCENTE CALANAOОценок пока нет
- 212 1.user Manual Part 2 918925Документ49 страниц212 1.user Manual Part 2 918925willian rochaОценок пока нет