Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Propulsion Lab 1
Загружено:
Muhammad Ishaq KhanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Propulsion Lab 1
Загружено:
Muhammad Ishaq KhanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
[Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.]
ASSIGNME NT
SPACECRAFT PROPULSION
HOME
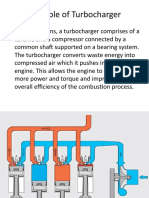
TURBO SHAFT ENGINE
A turboshaft engine is similar in concept to turboprop, but instead of the propeller, the gearbox exits to some other device. The most common use is to power a helicopter rotor. It has the following main components. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Starting Generator Gear box Compressors Combustion Turbine Exhaust
Gear Box There are different gears in this engine. The main function of the gear box is to control the speed of shaft so that stalling and other phenomena does not occur which are harmful for compressor. The gears that are used in this engine are mainly inclined spur gears. The shaft of the main gear is connected to handle which are used to rotate the shaft by hand especially in this engine. Starting Generator A small generator is connected to gear box which are used only for rotation to main shaft at the start. This generator is turn off when engine starts.
Compressors
When the flow enters the engine through the intake of the engine it moves towards the compressor which compress the air so the pressure and density of the air rises. There are two types of compressor used in this engine, one is axial type and other is centrifugal. The air first passes from the axial compressor which works in two stages. First stage is of rotor where the dynamic pressure of air rises while static pressure rises in stator. After passing through axial compressor the air move toward centrifugal compressor where the dynamic pressure rise occur in impeller while total pressure rise occur in diffuser. The main advantage of using centrifugal compressor is for reducing size of engine. Combustion The air directed from diffuser of centrifugal compressor moves towards the combustion chamber where fuel are mixed and are burned by igniter at constant pressure with minimum losses. The temperature of air rises due to which enthalpy rise occur. Turbine Turbine extracts energy from the air and by mean of this energy it run the compressor shaft and also transfers high momentum air toward the exhaust. The turbine works in to three stages in which each stage has the stator and rotor respectively.
Exhaust The high speed air when passes from exhaust give thrust to the engine. A pointed like object is placed in exhaust so that it act as a nozzle.
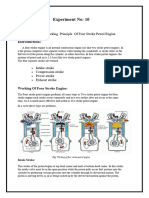
PISTON ENGINE
This is a type of heat Engine that uses reciprocating piston to convert pressure into rotating motion.
Working
The engine that we have studied in laboratory is four stroke engine. It works in following four strokes. 1. 2. 3. 4. Intake stroke Compression stroke Power/ignition stroke Exhaust stroke Intake stroke In this stroke the piston descends from the top of the cylinder to the bottom of the cylinder, increasing the volume of the cylinder. A mixture of fuel and air, or just air in a diesel engine, is forced by atmospheric (or greater) pressure into the cylinder through the intake port. The intake valve(s) then closes. The volume of air/fuel mixture that is drawn into the cylinder, relative to the maximum volume of the cylinder, is called the volumetric efficiency of the engine. Compression stroke In this stroke the mixture of the air and fuel compressed by piston due to which the temperature of the mixture rises. During this stage both the inlet and exhaust valve are closed. Power stroke During this stroke the compressed mixture is ignited by spark plug due to which the air fuel mixture is burned which increase the pressure. The resulting pressure from the combustion of the compressed fuel-air mixture forces the piston back down toward bottom dead Centre. This is the start of the second revolution of the cycle. Exhaust stroke During the exhaust stroke, the piston once again returns to top dead Centre while the exhaust valve is open. This action expels the spent fuel-air mixture through the exhaust valve.
Components of Reciprocating Engine
Almost all of the reciprocating engine are mainly consist of following parts.
Crankcase
Crankcase is the main structure of engine which contain the bearing for crankshaft. It is designed to house crankshaft, camshaft and lubricating oil. The crankshaft must be able to endure multidirectional forces vibration and extreme operating temperature.
Crankshaft
The crankshaft is the part of an engine that translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation. To convert the reciprocating motion into rotation, the crankshaft has "crank throws" or "crankpins", additional bearing surfaces whose axis is offset from that of the crank, to which the "big ends" of the connecting rods from each cylinder attached.
Connecting Rods
Connecting rods connect the piston to crankshaft. It transports the force between the piston and crankshaft.
Piston
Piston move up and down in the cylinder. It draw air/fuel mixture into cylinder and drive the crankshaft on downward stroke. It also compress the air fuel mixture on upward stoke. Piston rings fit into grooves on the side and form the seal between the side and cylinder wall. The ring are designed with a gape which is forced closed when the piston is inserted into cylinder to form a spring loaded seal. The main function of piston ring is to prevent combustion gases from escaping the cylinder
Вам также может понравиться
- ICE Engineering IДокумент16 страницICE Engineering Izhafran1513Оценок пока нет
- Asi Unit 3Документ21 страницаAsi Unit 3Raja RamОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion Engine: 1-Four-Stroke IC EngineДокумент21 страницаInternal Combustion Engine: 1-Four-Stroke IC EngineZahid HussainОценок пока нет
- Diesel Engine: Heavy VehiclesДокумент33 страницыDiesel Engine: Heavy VehiclesAvinash GangadharanОценок пока нет
- Ic EngineДокумент27 страницIc EngineSRL MECHОценок пока нет
- Lect 2Документ13 страницLect 2khalid mustafaОценок пока нет
- 2-Four and Two Stroke EnginesДокумент27 страниц2-Four and Two Stroke EnginesAHMADОценок пока нет
- AE 1356 Propulsion Lab ManualДокумент22 страницыAE 1356 Propulsion Lab ManualVasthadu Vasu KannahОценок пока нет
- LecturesДокумент142 страницыLecturesMuhammad RazaОценок пока нет
- Types of EnginesДокумент24 страницыTypes of EnginesTimothy Del ValleОценок пока нет
- EMEg 5221 Chapter 12 13 14Документ51 страницаEMEg 5221 Chapter 12 13 14Yoseph MershaОценок пока нет
- Description: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerДокумент16 страницDescription: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerNazrul Aizat ZunaidiОценок пока нет
- Types of EnginesДокумент24 страницыTypes of Enginestshuxi30Оценок пока нет
- ICE (Internal Combustion Engine)Документ22 страницыICE (Internal Combustion Engine)johnlloydsantossssОценок пока нет
- Gasoline EngineДокумент6 страницGasoline EngineJonan TutaanОценок пока нет
- Basic Piston Engine PrinciplesДокумент8 страницBasic Piston Engine PrinciplesAhmad Dayan Ma'shumОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion Engine: Chapter Learning ObjectivesДокумент17 страницInternal Combustion Engine: Chapter Learning ObjectivesRahul KhatriОценок пока нет
- Turbo NotesДокумент18 страницTurbo NotescleousОценок пока нет
- How Turbocharger WorksДокумент1 страницаHow Turbocharger WorksCurtler PaquibotОценок пока нет
- Module 2Документ21 страницаModule 2NithinОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1Документ9 страницExperiment 1Mehar HamzaОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion EnginesДокумент32 страницыInternal Combustion Enginespramodkb_cusatОценок пока нет
- Technical Description (Eport)Документ4 страницыTechnical Description (Eport)api-284962336100% (1)
- Assign#1 Thermo Lab. 2019p-ME-18Документ8 страницAssign#1 Thermo Lab. 2019p-ME-18Abdul Rasheed GhaziОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Internal Combustion Engines.: Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics ME 1052Документ7 страницIntroduction To Internal Combustion Engines.: Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics ME 1052Supun AmarasingheОценок пока нет
- Jet EnginesДокумент3 страницыJet EnginesYemaneDibetaОценок пока нет
- Piston EngineДокумент6 страницPiston EngineanandОценок пока нет
- 03 Principle of TurbochargerДокумент19 страниц03 Principle of TurbochargerSky RОценок пока нет
- 1.FSAE Turbocharger Design and ImplementationДокумент27 страниц1.FSAE Turbocharger Design and ImplementationJoy NagОценок пока нет
- Section 6 TRESДокумент2 страницыSection 6 TRESAndrès MendozaОценок пока нет
- AE 2306 Propulsion Lab ManualДокумент22 страницыAE 2306 Propulsion Lab Manualmurjass85Оценок пока нет
- Aero Engine - 1504714592213Документ75 страницAero Engine - 1504714592213raviОценок пока нет
- Below Is An Overview of The Fuel System Intake OperationДокумент8 страницBelow Is An Overview of The Fuel System Intake OperationchigauОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ29 страницLecture 2khalid mustafaОценок пока нет
- Lab ReportДокумент7 страницLab Reportshah_gen89Оценок пока нет
- Engine:: Engine Is The Heart of Aircraft. It Is The Machine Used To Drive The AircraftДокумент13 страницEngine:: Engine Is The Heart of Aircraft. It Is The Machine Used To Drive The Aircraftanup312Оценок пока нет
- Engine Part IДокумент39 страницEngine Part Iaashish koiralaОценок пока нет
- Hemi EngineДокумент23 страницыHemi EngineGunja GopalОценок пока нет
- GAS Turbine PresentationfdhtdgdffffffffffffffffffffffffffДокумент266 страницGAS Turbine Presentationfdhtdgdffffffffffffffffffffffffffjeromejoe100% (1)
- Gas Turbine For Power Generation: Dates Back To 1939Документ6 страницGas Turbine For Power Generation: Dates Back To 1939Wakwkaka JssjaaОценок пока нет
- SUCTION STROKE Suction StrokeДокумент5 страницSUCTION STROKE Suction Strokeashok pradhanОценок пока нет
- 4 Stroke Petrol EngineДокумент9 страниц4 Stroke Petrol EngineZahid MughalОценок пока нет
- 1 - Internal Combustion EngineДокумент6 страниц1 - Internal Combustion EngineCamia Empleo100% (1)
- IC EnginesДокумент8 страницIC EnginesNo MIОценок пока нет
- BCMEДокумент9 страницBCMEVenkateshwaran VenkyОценок пока нет
- Experiment No 09Документ3 страницыExperiment No 0920MCE 01 Mehwish KhanОценок пока нет
- Stroke and CyclesДокумент6 страницStroke and Cyclesjohn connoОценок пока нет
- Lovely Professional Unversity: Term PaperДокумент15 страницLovely Professional Unversity: Term PaperShekhar TomarОценок пока нет
- JET ENGINE FundamentalsДокумент18 страницJET ENGINE FundamentalsHareesha N GОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion EngineДокумент46 страницInternal Combustion EngineJoseph Rebanal AlmanzaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 Supercharging TurbochargingДокумент33 страницыChapter 12 Supercharging Turbochargingdesie yalewОценок пока нет
- GAS Turbine PresentationДокумент266 страницGAS Turbine Presentationagiba100% (6)
- Aircraft Systems: PowerplantДокумент4 страницыAircraft Systems: PowerplantHanz EspirituОценок пока нет
- THERMO BS II NotesДокумент8 страницTHERMO BS II Notesm.waseemОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Lab ReportДокумент49 страницThermodynamics Lab Reportjawad60% (5)
- Turbochargers in Diesel EnginesДокумент6 страницTurbochargers in Diesel EnginesSrini VasanОценок пока нет
- Basic's of Aircraft EnginesДокумент5 страницBasic's of Aircraft Enginesvenu991Оценок пока нет
- Turbocharger and SuperchargerДокумент65 страницTurbocharger and Superchargerzia malikОценок пока нет
- Divergence Thrust Loss Calculations For Convergent-Divergent Nozzles: Extensions To The Classical CaseДокумент18 страницDivergence Thrust Loss Calculations For Convergent-Divergent Nozzles: Extensions To The Classical CaseMuhammad Ishaq KhanОценок пока нет
- B 9fuel200313 w21Документ70 страницB 9fuel200313 w21Muhammad Ishaq KhanОценок пока нет
- Staging and Ascent Trajectory: CVA 2011summer SchoolДокумент32 страницыStaging and Ascent Trajectory: CVA 2011summer SchoolMuhammad Ishaq KhanОценок пока нет
- Two-Dimensional Heat Transfer: 3/28/2013 ES 312 - Energy Transfer Fundamentals 116Документ17 страницTwo-Dimensional Heat Transfer: 3/28/2013 ES 312 - Energy Transfer Fundamentals 116Muhammad Ishaq KhanОценок пока нет
- Aircraft RotorcraftДокумент26 страницAircraft Rotorcraftmoj33Оценок пока нет
- Federal Register / Vol. 76, No. 53 / Friday, March 18, 2011 / Rules and RegulationsДокумент2 страницыFederal Register / Vol. 76, No. 53 / Friday, March 18, 2011 / Rules and RegulationsMuhammad Ishaq KhanОценок пока нет
- 3310 Chapter 2Документ88 страниц3310 Chapter 2Muhammad Ishaq KhanОценок пока нет
- 2 Torsion SMДокумент27 страниц2 Torsion SMMuhammad Ishaq KhanОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer NotesДокумент364 страницыHeat Transfer NotesSrihari Managoli100% (5)
- Modeling FlightДокумент202 страницыModeling Flightaeroprince100% (3)
- PAKISTAN (2) : Mr. Tahir MuhammadДокумент12 страницPAKISTAN (2) : Mr. Tahir MuhammadMuhammad Ishaq KhanОценок пока нет
- EagleBurgmann H7N ENДокумент5 страницEagleBurgmann H7N ENlamtony2013Оценок пока нет
- Surface TensisonДокумент28 страницSurface TensisonJAWAD AHMAD BURTОценок пока нет
- Merged DocumentДокумент28 страницMerged DocumentJamirah Maha ShahinurОценок пока нет
- Intermed Products: International CatalogueДокумент12 страницIntermed Products: International CatalogueRicardo Bonetti TadenОценок пока нет
- C-L-X® Type MC-HL (XHHW-2)Документ3 страницыC-L-X® Type MC-HL (XHHW-2)Xin LiОценок пока нет
- A 2Документ3 страницыA 2John Kevin NocheОценок пока нет
- Fame and FortuneДокумент8 страницFame and FortuneNguyễn Đình Tuấn ĐạtОценок пока нет
- Technical Bulletin: ConditionДокумент11 страницTechnical Bulletin: ConditionFrancoОценок пока нет
- Optimal Control Development System For ElectricalДокумент7 страницOptimal Control Development System For ElectricalCRISTIAN CAMILO MORALES SOLISОценок пока нет
- 3rd QuarterДокумент14 страниц3rd QuarterZula DapugoОценок пока нет
- Solar Water Heater MOU LaodiceaДокумент2 страницыSolar Water Heater MOU LaodiceaZeeshan YasinОценок пока нет
- Autodesk 3ds Max SkillsДокумент18 страницAutodesk 3ds Max SkillsJuan UrdanetaОценок пока нет
- 120-21 TM RF HandbookДокумент164 страницы120-21 TM RF HandbookbaymanОценок пока нет
- International Journal of Agricultural ExtensionДокумент6 страницInternational Journal of Agricultural Extensionacasushi ginzagaОценок пока нет
- Bollard Pull Calculations For Towing OperationsДокумент8 страницBollard Pull Calculations For Towing OperationsDiegoОценок пока нет
- Position, Velocity and AccelerationДокумент12 страницPosition, Velocity and Accelerationpeter vuОценок пока нет
- 1.vedantu - Class 3 To 5 - BrochureДокумент1 страница1.vedantu - Class 3 To 5 - BrochureDeepak SharmaОценок пока нет
- Activity Diagram Airline Reservation System PDFДокумент4 страницыActivity Diagram Airline Reservation System PDFAnonymous zSn6IALuabОценок пока нет
- Bistable Relays RXMVB 2, RXMVB 4: FeaturesДокумент4 страницыBistable Relays RXMVB 2, RXMVB 4: FeaturesGabriel Maxo PapagalloОценок пока нет
- Drone Survival GuideДокумент2 страницыDrone Survival GuidevthiseasОценок пока нет
- Design of Electrical Machines NotesДокумент24 страницыDesign of Electrical Machines Notesmadhes14Оценок пока нет
- Bài Tập Bổ Trợ Nâng Cao Tiếng Anh 7-8-9 Chương Trình Mới (1) -Trang-292-433Документ142 страницыBài Tập Bổ Trợ Nâng Cao Tiếng Anh 7-8-9 Chương Trình Mới (1) -Trang-292-433Nguyễn Lâm ThươngОценок пока нет
- ISMR B-School BrochureДокумент28 страницISMR B-School Brochurerahul kantОценок пока нет
- Brushless MotorsДокумент20 страницBrushless Motorsbwatkins6Оценок пока нет
- Development of Mmlps in India: Western DFC Eastern DFCДокумент2 страницыDevelopment of Mmlps in India: Western DFC Eastern DFCsdfg100% (2)
- Pro Tester ManualДокумент49 страницPro Tester ManualRobson AlencarОценок пока нет
- Datasheet Double Solenoid Valve DMV 12Документ7 страницDatasheet Double Solenoid Valve DMV 12flatron445Оценок пока нет
- Solutions Tutorial 6Документ9 страницSolutions Tutorial 6Nur Aqilah Abdullah HashimОценок пока нет
- SVC200Документ5 страницSVC200fransiskus_ricky3329Оценок пока нет
- ReflectionДокумент1 страницаReflectionHeaven GuzmanОценок пока нет