Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
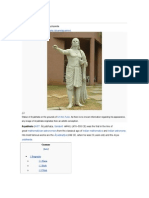
Aryabhata
Загружено:
Minna BobanИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aryabhata
Загружено:
Minna BobanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aryabhata or Aryabhata I (476550 CE) was the first in the line of great mathematicianastronomers from the classical age
of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. His works include the ryabhaya and the Arya-siddhanta. The works of Aryabhata dealt with mainly mathematics and astronomy. He also worked on the approximation for pi.
Works
His major work, Aryabhatiya, a compendium of mathematics and astronomy, was extensively referred to in the Indian mathematical literature and has survived to modern times. The mathematical part of the Aryabhatiya covers arithmetic, algebra, plane trigonometry, and spherical trigonometry. It also contains continued fractions, quadratic equations, sums-ofpower series, and a table of sines.
Mathematics
Place value system and zero
The place-value system was clearly in place in his work. While he did not use a symbol for zero, the French mathematician Georges Ifrah explains that knowledge of zero was implicit in Aryabhata's place-value system as a place holder for the powers of ten with null coefficients[13] However, Aryabhata did not use the Brahmi numerals. Continuing the Sanskritic tradition from Vedic times, he used letters of the alphabet to denote numbers, expressing quantities, such as the table of sines in a mnemonic form.[14]
Approximation of
Aryabhata worked on the approximation for pi ( ), and may have come to the conclusion that is irrational. In the second part of the Aryabhatiyam , he writes:. "Add four to 100, multiply by eight, and then add 62,000. By this rule the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 20,000 can be approached." This implies that the ratio of the circumference to the diameter is ((4 + 100) 8 + 62000)/20000 = 62832/20000 = 3.1416, which is accurate to five significant figures. It is speculated that Aryabhata used the word sanna (approaching), to mean that not only is this an approximation but that the value is incommensurable (or irrational). If this is correct, it is quite a sophisticated insight, because the irrationality of pi was proved in Europe only in 1761 by Lambert.[16]
Trigonometry
Aryabhata gives the area of a triangle as "for a triangle, the result of a perpendicular with the half-side is the area."[17]
Aryabhata discussed the concept of sine in his work by the name of ardha-jya, which literally means "half-chord". Alphabetic code has been used by him to define a set of increments. If we use Aryabhata's table and calculate the value of sin(30) which is 1719/3438 = 0.5; the value is correct. His alphabetic code is commonly known as the Aryabhata cipher.[18]
Aryabhata's work was of great influence in the Indian mathematicall tradition and influenced several neighbouring cultures through translations. His definitions of sine , cosine , versine, and inverse sine influenced the birth of trigonometry. He was also the first to specify sine and versine (1 cos x) tables, in 3.75 intervals from 0 to 90, to an accuracy of 4 decimal places.
Вам также может понравиться
- Contribution of AryabhattaДокумент14 страницContribution of AryabhattaMd yaqub71% (14)
- Contribution of Aryabhatta: in Field of MathemathicsДокумент14 страницContribution of Aryabhatta: in Field of MathemathicsGabbar MiyaОценок пока нет
- About AryabhattaДокумент4 страницыAbout AryabhattaIrfanОценок пока нет
- Mathematicians and Indian MathematicsДокумент8 страницMathematicians and Indian MathematicsyugantarchauhanОценок пока нет
- Contribution of AryabhattaДокумент12 страницContribution of AryabhattaIshpreet Singh Bagga100% (2)
- Indian MathematicianДокумент29 страницIndian Mathematicianrohityd2359Оценок пока нет
- Project:: History of MathematiciansДокумент12 страницProject:: History of MathematiciansMehulОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Project: History of Mathematics With Special Reference To The Contributions of Indian MathematiciansДокумент15 страницMathematics Project: History of Mathematics With Special Reference To The Contributions of Indian MathematiciansRAHUL ROYОценок пока нет
- Aryabhatta and Origin of ZeroДокумент2 страницыAryabhatta and Origin of Zerosrini_srvОценок пока нет
- Aryabhatta Indian Mathematician and His WorksДокумент4 страницыAryabhatta Indian Mathematician and His WorksJaydeepОценок пока нет
- Aryabhata The ElderДокумент5 страницAryabhata The Elderapi-240974857Оценок пока нет
- Math Education PowerPoint Template With PiДокумент11 страницMath Education PowerPoint Template With PiPraveen SinghОценок пока нет
- Mathematician: Submitted By: Nimisha PaulДокумент40 страницMathematician: Submitted By: Nimisha PaulNITHIYA PAUL 1847244Оценок пока нет
- The Art of TrigonometryДокумент3 страницыThe Art of Trigonometryapi-231202726Оценок пока нет
- AryabhataДокумент3 страницыAryabhataash1234Оценок пока нет
- Aryabhata: The Great Indian MathematicianДокумент5 страницAryabhata: The Great Indian MathematiciansuyovjОценок пока нет
- Aryabhata The Elder: Born: DiedДокумент5 страницAryabhata The Elder: Born: Diedvenugopal_nayrОценок пока нет
- Indian Contribution To SNTДокумент10 страницIndian Contribution To SNTRex RegioОценок пока нет
- Indian Civilization MathematicsДокумент12 страницIndian Civilization MathematicsAmarpreet KaurОценок пока нет
- Indian 2Документ8 страницIndian 2Amarpreet KaurОценок пока нет
- Indian Mathematics and Numeral SystemДокумент2 страницыIndian Mathematics and Numeral Systemdarkforestmine2005Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Math of Medieval India123Документ33 страницыIntroduction To Math of Medieval India123Riza Mae BayoОценок пока нет
- Digital AlbumДокумент59 страницDigital AlbumMeenu TomyОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Word DocumentДокумент4 страницыNew Microsoft Word DocumentVishwa GuptaОценок пока нет
- Ganita ("Mathematics") Kala-Kriya ("Time Calculations") Gola ("Sphere")Документ6 страницGanita ("Mathematics") Kala-Kriya ("Time Calculations") Gola ("Sphere")Ujjwal BagraniaОценок пока нет
- Appy Athematics AyДокумент13 страницAppy Athematics Aytrushnadhar111Оценок пока нет
- BAB 10 PERKEMBANGAN MATEMATIKA HINDU - Id.enДокумент5 страницBAB 10 PERKEMBANGAN MATEMATIKA HINDU - Id.ensulys SimanjuntakОценок пока нет
- AryabhattaДокумент12 страницAryabhattaChhaya SinghОценок пока нет
- History of Mathemati CS: Felisilda, Angelou Watson Bsed-1A (Math)Документ52 страницыHistory of Mathemati CS: Felisilda, Angelou Watson Bsed-1A (Math)Angelou FelisildaОценок пока нет
- Geniuses in MathematicsДокумент11 страницGeniuses in MathematicsCricatics with RSNОценок пока нет
- AryabhataДокумент10 страницAryabhataKhoba AnkushОценок пока нет
- Brahmagupta: Life and WorkДокумент26 страницBrahmagupta: Life and WorkMukhilan PariОценок пока нет
- Biography: Aryabhata (IAST: Āryabhaṭa; Sanskrit: आयरभटः) (476-550 CE) was the first in theДокумент7 страницBiography: Aryabhata (IAST: Āryabhaṭa; Sanskrit: आयरभटः) (476-550 CE) was the first in theshabaan786Оценок пока нет
- Aryabhata: S-1F - by Pratham P. ChopraДокумент15 страницAryabhata: S-1F - by Pratham P. ChopraPratham ChopraОценок пока нет
- About AryabhattaДокумент11 страницAbout AryabhattaLuke SkywalkerОценок пока нет
- Biography: Āryabha Īya SiddhantaДокумент9 страницBiography: Āryabha Īya Siddhantasaikripa121Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics "History of MathemeticiansДокумент30 страницMathematics "History of MathemeticiansDHAОценок пока нет
- Aryabhata: For Other Uses, SeeДокумент10 страницAryabhata: For Other Uses, SeeGeorge NcОценок пока нет
- Brahma GuptaДокумент11 страницBrahma GuptaJohn rey OrtiagaОценок пока нет
- Āryabha Īya Siddhanta: Āryabha A) or Aryabhata IДокумент1 страницаĀryabha Īya Siddhanta: Āryabha A) or Aryabhata IMd ZahiruddinОценок пока нет
- Maths ArticleДокумент12 страницMaths ArticleprathibhaОценок пока нет
- AryabhattaДокумент15 страницAryabhattaNikhil KapoorОценок пока нет
- Biography OF BHASKARACHARYAДокумент3 страницыBiography OF BHASKARACHARYAakshay dhoreОценок пока нет
- AryabhattaДокумент14 страницAryabhattaimsukhОценок пока нет
- AryabhattaДокумент1 страницаAryabhattapink_key711Оценок пока нет
- Aryabhatta: The Famous MathematicianДокумент18 страницAryabhatta: The Famous MathematicianNandkishor PalОценок пока нет
- Mathematician: Aryabhatta - Facts About The Great Indian Astronomer &Документ20 страницMathematician: Aryabhatta - Facts About The Great Indian Astronomer &dillip88Оценок пока нет
- BhaskaracharyaДокумент12 страницBhaskaracharyawabab26275Оценок пока нет
- AryabhataДокумент7 страницAryabhatadevashish12388Оценок пока нет
- Aryabhatta-The Great Indian Mathematician and Astrologer: Born: 476 A.D. Died: 550 A Brief IntroductionДокумент10 страницAryabhatta-The Great Indian Mathematician and Astrologer: Born: 476 A.D. Died: 550 A Brief IntroductionPoonia AnuОценок пока нет
- Ancient EgyptДокумент5 страницAncient Egyptarchesy9Оценок пока нет
- MathmaticianДокумент10 страницMathmaticianMonika MathurОценок пока нет
- Contribution of INDIAN Mathematicians in Field of MathematicsДокумент3 страницыContribution of INDIAN Mathematicians in Field of MathematicsVikas ChauhanОценок пока нет
- SridharaacharyaДокумент4 страницыSridharaacharyapsaisruthi1100% (1)
- MathemathicsДокумент4 страницыMathemathicsJosué ArmasОценок пока нет
- Maths in Focus, Margaret Grove - PrelimsДокумент13 страницMaths in Focus, Margaret Grove - PrelimsSam Scheding45% (11)
- Trigonometry 20-2 Lesson 1Документ2 страницыTrigonometry 20-2 Lesson 1api-535278422Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics Rank Booster CourseДокумент2 страницыMathematics Rank Booster CourseabhayОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Functions & Identities - SolutionsДокумент3 страницыTrigonometric Functions & Identities - SolutionswolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Design Creative & Thinking Lab (CSP116)Документ14 страницDesign Creative & Thinking Lab (CSP116)puyishОценок пока нет
- Ess at 12 CN StuДокумент11 страницEss at 12 CN Stujsmith012xОценок пока нет
- Bansal Classes Maths DPP - Grade 12Документ133 страницыBansal Classes Maths DPP - Grade 12mohit24031986100% (4)
- TRIGONOMETRYДокумент61 страницаTRIGONOMETRYMapurisa TriciahОценок пока нет
- Formulæ For Calculating Muslim Prayer Times-And Three Types of SundialДокумент4 страницыFormulæ For Calculating Muslim Prayer Times-And Three Types of SundialChristopher EllisОценок пока нет
- Dobot Blockly WorkbookДокумент180 страницDobot Blockly Workbooktemporal temporalОценок пока нет
- Classical Mechanics NotesДокумент54 страницыClassical Mechanics NotesAmichai LevyОценок пока нет
- Sinusoids LectureДокумент51 страницаSinusoids LecturegumptionsОценок пока нет
- Trigonometry: Trigonometric RatioДокумент11 страницTrigonometry: Trigonometric RatioVishwjeet SinghОценок пока нет
- Eqs Formula Language Reference: 19 June 2012Документ21 страницаEqs Formula Language Reference: 19 June 2012chuff6675Оценок пока нет
- Chap Er 12 ReviewДокумент2 страницыChap Er 12 Reviewmhrdd222Оценок пока нет
- Curriculum Map - Math 10Документ10 страницCurriculum Map - Math 10api-456913177Оценок пока нет
- As 91259Документ3 страницыAs 91259Jojo DeProProОценок пока нет
- 10 Algebra PDFДокумент493 страницы10 Algebra PDFFuad_Khafizov_5342Оценок пока нет
- Final ReportДокумент15 страницFinal ReportdhruvikОценок пока нет
- Power System Harmonic Analysis (Jos Arrillaga Bruce Smith, Neville Watson & Alan Wood)Документ382 страницыPower System Harmonic Analysis (Jos Arrillaga Bruce Smith, Neville Watson & Alan Wood)Angel Pm90% (10)
- Chapter 7 TestДокумент7 страницChapter 7 TestHyelin Song20% (5)
- The Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) Algorithm: James R. NagelДокумент7 страницThe Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) Algorithm: James R. NagelSadie WilliamsonОценок пока нет
- GCDkit ManualДокумент175 страницGCDkit ManualRheza FirmansyahОценок пока нет
- IGSCE Revision NotesДокумент95 страницIGSCE Revision NotesBonulala67% (3)
- Calculus CHAPTER 4Документ29 страницCalculus CHAPTER 4PrivilegeОценок пока нет
- EAMCET Engineering Information BrochureДокумент23 страницыEAMCET Engineering Information BrochureAnweshaBoseОценок пока нет
- One and Two Meter Tangent Screen Instructions 012307Документ2 страницыOne and Two Meter Tangent Screen Instructions 012307Doc AaryanОценок пока нет
- Fergus Sir 2021 m2 Free Mock (E)Документ36 страницFergus Sir 2021 m2 Free Mock (E)Cheung Tsz ShunОценок пока нет
- N5 Mathematics Revised 2Документ32 страницыN5 Mathematics Revised 2Anesu MasirahaОценок пока нет
- 30-C-1 - Maths (Standard)Документ23 страницы30-C-1 - Maths (Standard)Sagar TiwariОценок пока нет
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)От EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Оценок пока нет
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsОт EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.От EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeОт EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeОт EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersОт EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormОт EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryОт EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingОт EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldОт EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (80)
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)От EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Оценок пока нет