Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Projectile Motion
Загружено:
ExpertsmindEduАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Projectile Motion
Загружено:
ExpertsmindEduАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics Assignment Help | Projectile Motion |www.expertsmind.
com
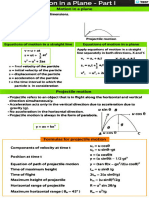
Projectile Motion (Time of Flight, Horizontal Range and Trajectory)
Let P(x, y) present the location of a projectile after a time t from the time of
projection.
At the point O, horizontal part of velocity = u cos and
vertical part of velocity = u sin
Acceleration due to gravity performs vertically downwards. Hence vertical
element of velocity modifies. While horizontal element of velocity remains
constant (u cosu) in the whole motion.
u
ucosu u
R
usi
n
u
O
Time of flight: It is the time taken by the body from the instant it is realized till it strikes a position on the
same horizontal plane as the point of projection.
To calculate time of flight, we can find the time when vertical displacement is zero i.e.
0 = u sinu t
2
gt
2
1
(u sinu gt
2
1
) t = 0 t = 0 or t =
2 usin
g
Thus , Time of flight T =
2usin
g
Range: During this time horizontal element of velocity has taken the particle through a distance x
horizontally
Where, x = u cosu T = u cosu
2 usin
g
=
2
u sin2
g
This distance, we call as range on horizontal plane ,
2
u sin2
R
g
=
R
max
=
g
u
2
for u = 45
For a given velocity same range can be obtained for an angle u and angle (90 u) i.e.
R =
, ,
2
u sin2 90 -
g
=
, ,
2
u sin 180 - 2
g
=
2
u sin2
g
To calculate maximum height, the vertical component of velocity equals to zero, when the particle is at the
highest point from the ground. At that time particle has only horizontal component of velocity i.e. = u cosu
0 = (u sinu)
2
2gH
max
H
max
=
2 2
u sin
2g
The motion of projectile can be analysed through vector notation also for e.g. velocity of projectile (v) at
any time t can be written as
, ,
v ucos i usin gt j = +
Hence, the magnitude of velocity (speed) v at any time is given as ,
v= , , , ,
2 2
ucos usin gt + =
2 2 2
2 sin u g t u gt + (The path of a projectile is called its trajectory)
Trajectory of projectile
y = u sinu t
2
1
2
gt . . . (1) (vertical displacement at any time t)
x = u cosu t . . . (2) (Horizontal displacement at any time t)
Using t =
cos
x
u
We get, y = x tan
2
2 2
2 cos
gx
u
, Which suggest that trajectory of projectile is parabola
Вам также может понравиться
- Mechanics Notes 4Документ15 страницMechanics Notes 4niteshОценок пока нет
- 03 KinematicsДокумент33 страницы03 Kinematicssurya_kotniОценок пока нет
- Projectile MotionДокумент10 страницProjectile Motionpusa123Оценок пока нет
- Motion of ProjectileДокумент7 страницMotion of ProjectileKeyur PatelОценок пока нет
- Physics FormulaДокумент1 страницаPhysics FormulaPedro Jose Guayanay CalvaОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion Constant AccelerationДокумент7 страницProjectile Motion Constant AccelerationIrish MejiaОценок пока нет
- Applied Physics Lab Complex Engineering Activity (Cea) SolutionДокумент4 страницыApplied Physics Lab Complex Engineering Activity (Cea) SolutionAbdul SamadОценок пока нет
- 3Документ1 страница3Atul VermaОценок пока нет
- Kinematics SheetДокумент10 страницKinematics SheetKshitij BansalОценок пока нет
- Important Questions For IAT3 - 17CIV23Документ10 страницImportant Questions For IAT3 - 17CIV23Sreelakshmi GОценок пока нет
- Projectile MotionДокумент10 страницProjectile MotionAmmar IbrahimОценок пока нет
- PROJECTILESДокумент6 страницPROJECTILESJanaka PriyalalОценок пока нет
- PHY1 Mod-08 (Projectile Motion)Документ7 страницPHY1 Mod-08 (Projectile Motion)Shamim ImtiazОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Word DocumentДокумент13 страницNew Microsoft Word DocumentCvm GuptaОценок пока нет
- Mod 7Документ7 страницMod 7S M AkashОценок пока нет
- Motion in 2DДокумент28 страницMotion in 2DnaguОценок пока нет
- Physics Study PaperДокумент6 страницPhysics Study Paperjanine maalaОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motio1Документ13 страницProjectile Motio1Baltazar MarcosОценок пока нет
- NotesДокумент11 страницNotesjyotisahni13Оценок пока нет
- Motion in Two Dimensions: Vidyamandir ClassesДокумент28 страницMotion in Two Dimensions: Vidyamandir ClassesVallabhОценок пока нет
- Motion in 2D Notes Iit JeeДокумент28 страницMotion in 2D Notes Iit JeeSaumya Singh100% (1)
- Mechanics Motion Under Gravity and ProjectilesДокумент11 страницMechanics Motion Under Gravity and ProjectileschidubemofОценок пока нет
- Kinematics BansalДокумент19 страницKinematics BansalBHAAJI000168% (22)
- Projectile Motion: Particular's Page NoДокумент41 страницаProjectile Motion: Particular's Page NoRafsanjaniОценок пока нет
- Math Investigatory ProjectДокумент9 страницMath Investigatory ProjectKavinn100% (1)
- Motion in A Straight LineДокумент15 страницMotion in A Straight LineJyothiОценок пока нет
- KINEMATICSДокумент7 страницKINEMATICSJhane AlvaradoОценок пока нет
- Projectile MotionДокумент5 страницProjectile MotionJasmine Mary Issa QuezonОценок пока нет
- Physics 191 ProjectileДокумент2 страницыPhysics 191 ProjectileAli MoralesОценок пока нет
- Maths ProjectilesДокумент12 страницMaths Projectilesමේනුක සූවින්දОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion2Документ3 страницыProjectile Motion2Anurag MalikОценок пока нет
- Projectile MotionДокумент10 страницProjectile MotionSanОценок пока нет
- Physics Main Focus NotesДокумент103 страницыPhysics Main Focus NotesAswithОценок пока нет
- Focus Area Questions-1Документ53 страницыFocus Area Questions-1AswithОценок пока нет
- Iit Jee StudyДокумент955 страницIit Jee StudyGarlapati Srinivasa Rao88% (17)
- Motion in 2 Dimensions Vidyamandir ClassesДокумент19 страницMotion in 2 Dimensions Vidyamandir ClassesYadav100% (1)
- Projectile Motion (Theory)Документ5 страницProjectile Motion (Theory)Mohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- Phy SS2 Acad Week 2Документ3 страницыPhy SS2 Acad Week 2ohakwekosiОценок пока нет
- Analysis Experiment 103: Projectile Motion. Projectile Motion Is Defined As AДокумент15 страницAnalysis Experiment 103: Projectile Motion. Projectile Motion Is Defined As ARicardo LunaОценок пока нет
- Arihant Kinematics TheoryДокумент8 страницArihant Kinematics TheoryTarun GuptaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Motion in Two DimensionsДокумент25 страницChapter 3 - Motion in Two DimensionsShirah CoolОценок пока нет
- XI P Notes Projectile MotionДокумент33 страницыXI P Notes Projectile Motionsarawalem1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Motion in Straight Line NotesДокумент8 страницChapter 1 Motion in Straight Line Notesaryanbajaj35Оценок пока нет
- Engg Mechcanis Solved University QДокумент31 страницаEngg Mechcanis Solved University Qgod.krish.25Оценок пока нет
- Motion Diagrams:: Interval. V Interval. SДокумент3 страницыMotion Diagrams:: Interval. V Interval. Sruel_galutan100% (1)
- MECHANICS PHYSICS A NOTES 1&2 Dim RevДокумент14 страницMECHANICS PHYSICS A NOTES 1&2 Dim Revokumuenock000Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Motion in Two or Three DimensionsДокумент26 страницLecture 2 Motion in Two or Three Dimensionsa5759761Оценок пока нет
- CH 02Документ23 страницыCH 02Sanjay KumarОценок пока нет
- Distance and DisplacementДокумент15 страницDistance and DisplacementSisay GaromaОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion CPДокумент14 страницProjectile Motion CPPankaj KumarОценок пока нет
- 01 Kinematics Motion in 1D 2DДокумент20 страниц01 Kinematics Motion in 1D 2DSivakumar SarmaОценок пока нет
- Projectile MotionДокумент38 страницProjectile Motionguptaprabhu75% (12)
- Kinematics PDFДокумент33 страницыKinematics PDFVudugundla KodandapaniОценок пока нет
- Aakash 1 DДокумент8 страницAakash 1 DNavin RaiОценок пока нет
- Solved Electricity Numerical For Class 10Документ8 страницSolved Electricity Numerical For Class 10Shweta DixitОценок пока нет
- Science Reviewer 4TH QRTRДокумент18 страницScience Reviewer 4TH QRTRAlex LovesmangoesОценок пока нет
- Types of PendulumДокумент5 страницTypes of PendulumExpertsmindEdu100% (2)
- Physics Assignment Help - Work Done in Displacement of A Body inДокумент1 страницаPhysics Assignment Help - Work Done in Displacement of A Body inExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Variable MassДокумент3 страницыVariable MassExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Work Done Against GravityДокумент3 страницыWork Done Against GravityExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Uniform and Non - Uniform Circular MotionДокумент4 страницыUniform and Non - Uniform Circular MotionExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Work Done by A ForceДокумент2 страницыWork Done by A ForceExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Relation Between G and GДокумент3 страницыRelation Between G and GExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Physics Assignment Help - Simple Harmonic Motion in Spring-MassДокумент1 страницаPhysics Assignment Help - Simple Harmonic Motion in Spring-MassExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- TorqueДокумент1 страницаTorqueExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Rotational Work and EnergyДокумент1 страницаRotational Work and EnergyExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Satellite and Planetary MotionДокумент5 страницSatellite and Planetary MotionExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Physics Assignment Help - Kinetic Energy of A Rigid Body: K I N e T I C E N e R G y o F A R I G I D B o D yДокумент1 страницаPhysics Assignment Help - Kinetic Energy of A Rigid Body: K I N e T I C E N e R G y o F A R I G I D B o D yExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Simple Harmonic MotionДокумент6 страницSimple Harmonic MotionExpertsmindEdu100% (1)
- Physics Assignment Help - Relation Between Linear and AngularДокумент1 страницаPhysics Assignment Help - Relation Between Linear and AngularExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Motion in A Vertical CircleДокумент2 страницыMotion in A Vertical CircleExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Physics Assignment Help - Oscillation of Liquid Column in A UДокумент1 страницаPhysics Assignment Help - Oscillation of Liquid Column in A UExpertsmindEdu100% (2)
- PowerДокумент2 страницыPowerExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Motion of Centre of MassДокумент2 страницыMotion of Centre of MassExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Newton's Laws of MotionДокумент2 страницыNewton's Laws of MotionExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Newton's Law of Universal GravitationДокумент2 страницыNewton's Law of Universal GravitationExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Moment of InertiaДокумент2 страницыMoment of InertiaExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Law of Conservation of Mechanical EnergyДокумент1 страницаLaw of Conservation of Mechanical EnergyExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Motion in Two DimensionsДокумент2 страницыMotion in Two DimensionsExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Oblique CollisionДокумент1 страницаOblique CollisionExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Kinematics and DynamicsДокумент2 страницыKinematics and DynamicsExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Kepler's LawsДокумент1 страницаKepler's LawsExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Gravitational PotentialДокумент2 страницыGravitational PotentialExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Gravitational Field IntensityДокумент2 страницыGravitational Field IntensityExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Gravitational Potential EnergyДокумент3 страницыGravitational Potential EnergyExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Marblevator, Wave: InstructablesДокумент29 страницMarblevator, Wave: InstructablesGCОценок пока нет
- C Chains APIДокумент1 страницаC Chains APILuisSilvaОценок пока нет
- Bircosir - NW 150: Stability and DiversityДокумент5 страницBircosir - NW 150: Stability and Diversityjagath2005ukОценок пока нет
- flowIT FTBGDW-16Документ1 страницаflowIT FTBGDW-16technicalsupportОценок пока нет
- Wa5471ab SeriesДокумент41 страницаWa5471ab SeriesJahangir JinguОценок пока нет
- Dbatu Scheme - New & OldДокумент9 страницDbatu Scheme - New & OldDeepak BhopeОценок пока нет
- ME3252 Chapter 2 NotesДокумент5 страницME3252 Chapter 2 NotesAsffaq MuhdОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент7 страницThermodynamicsRaj BoligorОценок пока нет
- Manual de Peças Manipulador Telescopico 1200SJP 1350SJPДокумент460 страницManual de Peças Manipulador Telescopico 1200SJP 1350SJPAlessandro de OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Omega PTFE Needle Valve - FVLT100Документ1 страницаOmega PTFE Needle Valve - FVLT100XavierОценок пока нет
- Spare Parts Catalogue: AXLE 138670 REF: 138670Документ10 страницSpare Parts Catalogue: AXLE 138670 REF: 138670avant comercialОценок пока нет
- L2C1 MEC420 1D Kinematics of Particle FS2 PDFДокумент30 страницL2C1 MEC420 1D Kinematics of Particle FS2 PDFMuhammad Danial Hakim Bin JohariОценок пока нет
- Altronic Agv5 Operating Manual Gas Fuel Valve Form Agv5 Om 8-03Документ12 страницAltronic Agv5 Operating Manual Gas Fuel Valve Form Agv5 Om 8-03SMcОценок пока нет
- Flower Duet in G Voices OnlyДокумент80 страницFlower Duet in G Voices Onlym1d0r1Оценок пока нет
- Cummins QSK 23 Fuel Shutoff ValveДокумент8 страницCummins QSK 23 Fuel Shutoff ValvePedro Schembri100% (1)
- Mapex AN0320SN PDFДокумент1 страницаMapex AN0320SN PDFDiegoTierradentroОценок пока нет
- Smaw PDFДокумент10 страницSmaw PDFArizapatazoОценок пока нет
- Cpmpression Member Design: 4.1 Introductory ConceptsДокумент40 страницCpmpression Member Design: 4.1 Introductory ConceptssaadkhalisОценок пока нет
- Speed Torque Gear Ratios Motor Vehicles Internal Combustion Engine Rotational Speed TorqueДокумент45 страницSpeed Torque Gear Ratios Motor Vehicles Internal Combustion Engine Rotational Speed TorqueAkshay SinghОценок пока нет
- PET 332 E Production Engineering & Surface FacilitiesДокумент13 страницPET 332 E Production Engineering & Surface Facilities000Оценок пока нет
- SOM 2-2 (Students Note)Документ15 страницSOM 2-2 (Students Note)HasmitthaОценок пока нет
- Fiitjee: Answers, Hints & SolutionsДокумент10 страницFiitjee: Answers, Hints & SolutionsZayanmalikОценок пока нет
- Setra 400 Class - 415 416 Euro 5 ManualДокумент620 страницSetra 400 Class - 415 416 Euro 5 ManualAshley Cardwell100% (3)
- Types of PendulumsДокумент10 страницTypes of PendulumsAdrian Arasu100% (1)
- UGC-01 sCHEDULEДокумент6 страницUGC-01 sCHEDULELingesh SivaОценок пока нет
- 1 - Firewater Piping Spec - DIДокумент2 страницы1 - Firewater Piping Spec - DISuezie Iella100% (1)
- NDT Ultrasonic Phased Array Examination (NDT Examen de Ultrasonido Arreglo de Fases)Документ2 страницыNDT Ultrasonic Phased Array Examination (NDT Examen de Ultrasonido Arreglo de Fases)reyserОценок пока нет
- WEG Alternadores Sincronos Linha Ag10 12638144 Manual Portugues BRДокумент139 страницWEG Alternadores Sincronos Linha Ag10 12638144 Manual Portugues BRAntonio Monteiro100% (1)
- sl2019 685Документ3 страницыsl2019 685avm4343Оценок пока нет
- Refractory Equipment GAODETECДокумент9 страницRefractory Equipment GAODETECorangel anayaОценок пока нет