Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pdfa2 1
Загружено:
aizat0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
683 просмотров1 страницаVelocity of an object is changing at different points along a circle. The direction and hence the velocity of the object is always changing. Calculate (a) the acceleration and (b) the total displacement travelled by the object.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
pdfa2_1
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документVelocity of an object is changing at different points along a circle. The direction and hence the velocity of the object is always changing. Calculate (a) the acceleration and (b) the total displacement travelled by the object.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
683 просмотров1 страницаPdfa2 1
Загружено:
aizatVelocity of an object is changing at different points along a circle. The direction and hence the velocity of the object is always changing. Calculate (a) the acceleration and (b) the total displacement travelled by the object.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
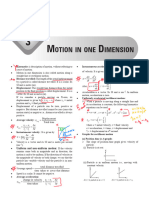
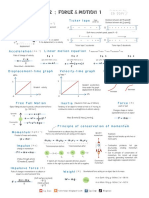
Chapter 2
Transparency
6
Forces And Motion
Linear Motion (I)
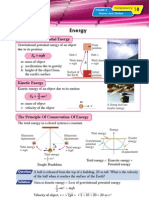
Distance And Displacement Town B
Distance: a scalar quantity. Displacement of town B
Displacement: a vector quantity. from town A = 500 km
Displacement is distance travelled in a
specific direction.
Town A Distance of town B
Speed And Velocity from town A = 620 km
Speed: a scalar quantity.
Velocity: a vector quantity.
An object is moving with a constant speed of 2 m s–1
B in a circle. It has a different velocity at different points
2 m s–1
2 m s–1 along the circle. The direction and hence the velocity
String of the object is always changing.
C A
s
Velocity, v= t
2 m s–1
2 m s–1 where s is the displacement
D
t is the time taken
Acceleration = Rate of change of velocity Equations of Linear Motion with
v–u Uniform Acceleration:
a= t
s=
u–v
2 ( t )
where v is the final velocity v = u + at
u is the initial velocity
s = ut + 1 at 2
t is the time taken 2
v2 = u2 + 2as
Question An object accelerates uniformly along a straight line from a velocity of
5 m s–1 to 25 m s–1 in 4 s. Calculate (a) the acceleration and (b) the total
displacement travelled by the object.
Solution v–u 25 – 5
(a) Acceleration a = t = = 5 m s–2
4
1 1
(b) Total displacement s = ut + at2 = 5 × 4 + × 5 × 42 = 60 m
2 2
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
Вам также может понравиться
- Explain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorОт EverandExplain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorОценок пока нет
- CE Board April 2023 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 5Документ4 страницыCE Board April 2023 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 5Daryl ArizoОценок пока нет
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОт EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Core Concepts Merged Sub SolutionsДокумент5 страницCore Concepts Merged Sub Solutions2pwxanqt8aОценок пока нет
- Note Chapter2 SF017Документ79 страницNote Chapter2 SF017api-3699866100% (3)
- LC 3 - KinematicsДокумент7 страницLC 3 - KinematicsSarah GanganОценок пока нет
- General Physics 1 Week 3Документ5 страницGeneral Physics 1 Week 3Levi AckermanОценок пока нет
- E-Book Chapter 2 and Experiment 2 Dp014Документ35 страницE-Book Chapter 2 and Experiment 2 Dp014nurfarahanii06Оценок пока нет
- AQA Mechanics 1 Revision NotesДокумент9 страницAQA Mechanics 1 Revision NotesEricka AlvarezОценок пока нет
- AQA Mechanics 1 Revision Notes PDFДокумент9 страницAQA Mechanics 1 Revision Notes PDFRishineshОценок пока нет
- STD 9th Science and Technology Chapter Assessment 1 Laws of MotionДокумент3 страницыSTD 9th Science and Technology Chapter Assessment 1 Laws of MotionkhavetodnileshОценок пока нет
- Motion in One Dimension 2Документ3 страницыMotion in One Dimension 2Naveen KumarОценок пока нет
- Kinematics E 2018Документ52 страницыKinematics E 2018sundararevathyhdОценок пока нет
- Complete JEE MechanicsДокумент384 страницыComplete JEE Mechanicsmohdamaankhan74Оценок пока нет
- 03 - Rotational Motion - Theory & Example Module-2Документ32 страницы03 - Rotational Motion - Theory & Example Module-2Raju SinghОценок пока нет
- PM TB Solutions C02Документ10 страницPM TB Solutions C02Vishwajeet Ujhoodha86% (14)
- 03 - Motion in A Straight Line Super NotesДокумент3 страницы03 - Motion in A Straight Line Super Notesprakashsinghsatya448Оценок пока нет
- T-Ticker Tape Notes - TutorialДокумент4 страницыT-Ticker Tape Notes - TutorialGan Hock KiamОценок пока нет
- AS Level KinematicsДокумент13 страницAS Level Kinematicsaykhan5806Оценок пока нет
- Module 1 (Kinematics) Summary: Scalar Vs VectorДокумент6 страницModule 1 (Kinematics) Summary: Scalar Vs VectorIshaan IngrejiОценок пока нет
- KinematicsДокумент8 страницKinematicsMuhammad QadirОценок пока нет
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Phy Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-3 PDFДокумент46 страницCLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Phy Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-3 PDFsoyelОценок пока нет
- Physics Dynamics - Docx 0Документ16 страницPhysics Dynamics - Docx 0MikeОценок пока нет
- Phy Sci Lesson 8Документ9 страницPhy Sci Lesson 8Raulene MoloОценок пока нет
- Solution-Manual-for-Physics-for-Scientists-and-Engineers-9th-Edition-by-Serway-and-Jewett Ch1-ch2 PDFДокумент65 страницSolution-Manual-for-Physics-for-Scientists-and-Engineers-9th-Edition-by-Serway-and-Jewett Ch1-ch2 PDFCarlo Chua ImperialОценок пока нет
- Chương 2Документ65 страницChương 2Le Nguyen Thu HaОценок пока нет
- Chapter No. 6 Linear MotionДокумент16 страницChapter No. 6 Linear Motionravi maskeОценок пока нет
- Physics Meachanics Lecture NotesДокумент14 страницPhysics Meachanics Lecture Notesjeffersonmanalo787Оценок пока нет
- Motion in A Straight LineДокумент26 страницMotion in A Straight LineLord Siva100% (3)
- Kinematics of Particles: V DT DXДокумент8 страницKinematics of Particles: V DT DXGIYANG BATANОценок пока нет
- Kinematics For PDFДокумент20 страницKinematics For PDFjalanhello71Оценок пока нет
- Studyguide-2 - Force and MotionДокумент50 страницStudyguide-2 - Force and MotionytОценок пока нет
- 4.2 Force and Motion 1Документ19 страниц4.2 Force and Motion 1ammarsyahmiОценок пока нет
- 4.2 Force and MotionДокумент18 страниц4.2 Force and Motionvelavan100% (1)
- Chapter 2Документ10 страницChapter 2HibaОценок пока нет
- Kinematics in One DimensionДокумент31 страницаKinematics in One DimensionShipsGonnaSailОценок пока нет
- Motion in A PlaneДокумент3 страницыMotion in A PlanePilotsaicharan AirbusОценок пока нет
- Dependent Motions - : Dynamics of Rigid BodiesДокумент22 страницыDependent Motions - : Dynamics of Rigid BodiesCllyan ReyesОценок пока нет
- H2 Notes - Tutorial - KinematicsДокумент43 страницыH2 Notes - Tutorial - KinematicsWee Chee LimОценок пока нет
- 2 - Kinematic of MotionДокумент43 страницы2 - Kinematic of MotionJoanne SohОценок пока нет
- Motion in A Straight Line PDFДокумент32 страницыMotion in A Straight Line PDFRohit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6A. AccelerationДокумент61 страницаChapter 6A. AccelerationJulie Jeanne CorderoОценок пока нет
- Sheet - 01 - KinematicsДокумент65 страницSheet - 01 - KinematicsLakshya Pratap SinghОценок пока нет
- Physics Module 1 (Kinematics)Документ5 страницPhysics Module 1 (Kinematics)Nancy AndrawesОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion: A Particle P Travels in Circular Path. It Performs Circular Motion About O With Radius RДокумент38 страницCircular Motion: A Particle P Travels in Circular Path. It Performs Circular Motion About O With Radius ReltytanОценок пока нет
- SHORT NOTES Force and Motion 1Документ1 страницаSHORT NOTES Force and Motion 1YARSHANA A/P SIVAM MoeОценок пока нет
- Dynamics: Prepared By: Engr. Jordan RonquilloДокумент30 страницDynamics: Prepared By: Engr. Jordan RonquilloFrancis Philippe Cruzana CariñoОценок пока нет
- Motion in Two and Three Dimensions: R X I y J Z KДокумент11 страницMotion in Two and Three Dimensions: R X I y J Z KWahyu SipahutarОценок пока нет
- M1 Mei PDFДокумент10 страницM1 Mei PDFOmar HashemОценок пока нет
- Country's Best Online Test PlatformДокумент74 страницыCountry's Best Online Test PlatformSubhrasankar RaychaudhuryОценок пока нет
- Mechanics: Natsci1 - PhysicsДокумент38 страницMechanics: Natsci1 - PhysicsTricia SuperioОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion NotesДокумент7 страницCircular Motion Notesrifu91Оценок пока нет
- Ch2 Motion in Straight LineДокумент56 страницCh2 Motion in Straight Linecvxg5hk5xxОценок пока нет
- Physics: Application of Integration-1: T T T BV V BVT BVTДокумент4 страницыPhysics: Application of Integration-1: T T T BV V BVT BVTShibhaditya DohareОценок пока нет
- Career Point: JEE Main Exam 2016Документ54 страницыCareer Point: JEE Main Exam 2016ashutosh_p29Оценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Motion: Calculating SpeedДокумент37 страницUnit 1 - Motion: Calculating SpeedRamesh Kulkarni100% (1)
- Principles of Dynamics Students Hand OutsДокумент4 страницыPrinciples of Dynamics Students Hand OutsPauline CreoОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - Linear MotionДокумент11 страницTopic 2 - Linear MotionJerome GiovanieОценок пока нет
- Notes On Linear Motion - Physics From 4 Lesson 1Документ7 страницNotes On Linear Motion - Physics From 4 Lesson 1temiОценок пока нет
- Bansal DPPsДокумент315 страницBansal DPPsAgastya SharmaОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Pdfa5 3Документ1 страницаPdfa5 3aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 8Документ1 страницаPdfa4 8aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa5 2Документ1 страницаPdfa5 2aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa5 1Документ1 страницаPdfa5 1aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa5 3Документ1 страницаPdfa5 3aizatОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Pdfa4 7Документ1 страницаPdfa4 7aizatОценок пока нет
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourДокумент1 страницаSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 2Документ1 страницаPdfa4 2aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 6Документ1 страницаPdfa4 6aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 3Документ1 страницаPdfa4 3aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 5Документ1 страницаPdfa4 5aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 7Документ1 страницаPdfa3 7aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 1Документ1 страницаPdfa3 1aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 1Документ1 страницаPdfa4 1aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 5Документ1 страницаPdfa3 5aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 4Документ1 страницаPdfa3 4aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 14Документ1 страницаPdfa2 14aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 6Документ1 страницаPdfa3 6aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 3Документ1 страницаPdfa3 3aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 16Документ1 страницаPdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa3 2Документ1 страницаPdfa3 2aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 15Документ1 страницаPdfa2 15aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 11Документ1 страницаPdfa2 11aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 9Документ1 страницаPdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 12Документ1 страницаPdfa2 12aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 13Документ1 страницаPdfa2 13aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 10Документ1 страницаPdfa2 10aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 8Документ1 страницаPdfa2 8aizatОценок пока нет
- AmdДокумент14 страницAmdObed Andalis100% (1)
- Psychological, Social and Environmental BarriersДокумент12 страницPsychological, Social and Environmental BarrierssaifОценок пока нет
- Ict SS 1Документ37 страницIct SS 1angus ogwucheОценок пока нет
- Altivar Process Ride Through Time - IE04Документ3 страницыAltivar Process Ride Through Time - IE04Goran MladenovicОценок пока нет
- Maths - 2B Imp QuestionsДокумент93 страницыMaths - 2B Imp QuestionsBandaru Chiranjeevi100% (1)
- A Study of Metro Manilas Public Transportation SeДокумент19 страницA Study of Metro Manilas Public Transportation Segundranken08Оценок пока нет
- Paper Test For General PhysicsДокумент2 страницыPaper Test For General PhysicsJerrySemuelОценок пока нет
- Q4 - WEEK 2 - MEASURES OF POSITION For GROUPED DATAДокумент16 страницQ4 - WEEK 2 - MEASURES OF POSITION For GROUPED DATAEllaineeeeОценок пока нет
- Kartveluri Memkvidreoba XIII Khelaia NaziДокумент4 страницыKartveluri Memkvidreoba XIII Khelaia Nazikartvelianheritage XIIIОценок пока нет
- Landscape Products: Technical GuideДокумент124 страницыLandscape Products: Technical Guidegabbo24Оценок пока нет
- 591 Useful Unix Commands PDFДокумент1 страница591 Useful Unix Commands PDFrohit sharmaОценок пока нет
- Ptical Oxygen Sensor: ATA HeetДокумент14 страницPtical Oxygen Sensor: ATA HeetZoran ConstantinescuОценок пока нет
- Ready To Use Therapeutic Food in RwandaДокумент25 страницReady To Use Therapeutic Food in RwandaKABERA RENEОценок пока нет
- UMTS TutorialДокумент84 страницыUMTS Tutorialnale_2100% (1)
- Nicira - It Is Time To Virtualize The NetworkДокумент9 страницNicira - It Is Time To Virtualize The Networkcsp_675491Оценок пока нет
- A Compendium of Blog Posts On Op Amp Design Topics: by Bruce TrumpДокумент37 страницA Compendium of Blog Posts On Op Amp Design Topics: by Bruce TrumpJustine ManningОценок пока нет
- Digital Logic Design Chapter 5Документ28 страницDigital Logic Design Chapter 5Okezaki TemoyoОценок пока нет
- Symbols of Oil Gas PipingДокумент3 страницыSymbols of Oil Gas PipingDelvin Davis M0% (1)
- GusekДокумент177 страницGusekAitorAlbertoBaezОценок пока нет
- Sudhanshu Kumar: ResumeДокумент3 страницыSudhanshu Kumar: ResumePradeepОценок пока нет
- Digital Control System Analysis and Design 4th Edition by Phillips ISBN Solution ManualДокумент46 страницDigital Control System Analysis and Design 4th Edition by Phillips ISBN Solution Manualraymond100% (23)
- Rules of MixtureДокумент37 страницRules of MixtureRahmaF.PuspitaОценок пока нет
- DD210-V 9604sb PDFДокумент4 страницыDD210-V 9604sb PDFBrandon MoralesОценок пока нет
- Price DeterminationДокумент2 страницыPrice DeterminationSikander BehalОценок пока нет
- Testing & Maintenance of Rotating Machines Type Tests, Routine Tests & Special Tests of 1 & 3 Phase Induction MotorsДокумент12 страницTesting & Maintenance of Rotating Machines Type Tests, Routine Tests & Special Tests of 1 & 3 Phase Induction MotorsPKОценок пока нет
- IISER Aptitude Test 17th Sept 2021Документ22 страницыIISER Aptitude Test 17th Sept 2021Muskaan KathuriaОценок пока нет
- Neural-Network-Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Methods For Photovoltaic Systems Operating Under Fast Changing EnvironmentsДокумент12 страницNeural-Network-Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Methods For Photovoltaic Systems Operating Under Fast Changing EnvironmentsAbderrezak BadjiОценок пока нет
- AN000042 SERCOS Troubleshooting Guide - ApplicationNote - En-Us - Revision1Документ14 страницAN000042 SERCOS Troubleshooting Guide - ApplicationNote - En-Us - Revision1uongquocvuОценок пока нет
- Remote Terminal Viewer Software Release Note 1101192-A: © Foxboro Australia 2000 ACN 000 522 26Документ16 страницRemote Terminal Viewer Software Release Note 1101192-A: © Foxboro Australia 2000 ACN 000 522 26Mochamad EffendiОценок пока нет
- Analog Communications-Notes PDFДокумент110 страницAnalog Communications-Notes PDFjyothimunjam100% (1)