Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pdfa4 8
Загружено:
aizatИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pdfa4 8
Загружено:
aizatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 4
Transparency
36
Heat
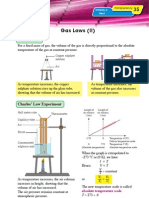
Gas Laws (III)
Pressure Law
For a fixed mass of gas, the pressure of the gas is directly proportional to the absolute
temperature of the gas at constant volume.
Closed metal
container As the gas is heated, the average velocity of its
molecules increases. The rate of collisions of
Gas molecules
the gas molecules with the wall of the container
increases and hence the pressure increases.
Bourdon
Pressure Law Experiment gauge
Glass Thermometer
Air pressure Air pressure
p (Pa) p (Pa)
tube
Ice
Air
Water Stirrer
bath
−273 0 Temperature θ (ºC)
Celsius temperature scale
0 273 Temperature T (K)
(Absolute temperature) Absolute temperature scale
As the temperature of the gas increases, its pressure also increases. The pressure of the
gas is measured by using a Bourdon gauge. When the graph is extrapolated to −273 ºC
or (0 K), we have p
p ∝ T or T = constant
p1 p
= 2
T1 T2
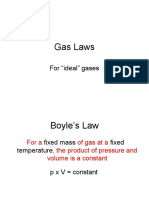
Ideal Gas Laws Ideal Gas Law
Formula
pV ∝ T Boyleʼs Charlesʼs
Law Law
Equation of state:
pV
= constant
T p1 p2 p2
p1V1 pV V1 Vʹ V2
= 2 2
T1 T2 T1 T1 T2
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
Вам также может понравиться
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Mass Transfer Operations 1: List of Books Information of CrystallizationДокумент13 страницMass Transfer Operations 1: List of Books Information of CrystallizationZaid MansuriОценок пока нет
- 4.4 Gas LawДокумент23 страницы4.4 Gas LawkhodijahaminОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws ProblemsДокумент46 страницGas Laws ProblemsIris LeuterioОценок пока нет
- Science Quarter 4 ReviewerДокумент8 страницScience Quarter 4 Reviewercali annaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MatterДокумент9 страницChapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MattergnkstarОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws / Gases BehaviourДокумент35 страницGas Laws / Gases Behaviour9338-Anmol KatharОценок пока нет
- Chem0861 GasLawProblemsДокумент3 страницыChem0861 GasLawProblemsHavenОценок пока нет
- Volume Molar GasДокумент13 страницVolume Molar GasSagung DyahОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirДокумент22 страницыGas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirIrwan M. IskoberОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 7Документ1 страницаPdfa4 7aizatОценок пока нет
- GAS LAWS Markup PDFДокумент30 страницGAS LAWS Markup PDFIsmaОценок пока нет
- Ch. 12 - Gases: II. The Gas Laws Boyles Charles Gay-LussacДокумент22 страницыCh. 12 - Gases: II. The Gas Laws Boyles Charles Gay-LussacEmmie Denisse ApistarОценок пока нет
- States of Matter PDFДокумент42 страницыStates of Matter PDFSiddharth DhurandharОценок пока нет
- 05 States of Matter Formula Sheets QuizrrДокумент9 страниц05 States of Matter Formula Sheets QuizrrArush GuptaОценок пока нет
- 12 Gas Laws PVT CombinedДокумент60 страниц12 Gas Laws PVT CombinedcrystaljanelletabsingОценок пока нет
- S.4 Heat Notes Gayaza High School PDFДокумент14 страницS.4 Heat Notes Gayaza High School PDFKayanja JonathanОценок пока нет
- AC Instruments Systems - Part 1 Jan 22, 2021Документ45 страницAC Instruments Systems - Part 1 Jan 22, 2021Ron McIntyreОценок пока нет
- Gas LawsДокумент63 страницыGas LawsJay-mee Claire V. DioОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws: For "Ideal" GasesДокумент27 страницGas Laws: For "Ideal" GasesHiwetОценок пока нет
- Atmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionДокумент4 страницыAtmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionjenduekieОценок пока нет
- Gas LawsДокумент27 страницGas LawsRizky HermawanОценок пока нет
- 05 States of Matter Formula Sheets QuizrrДокумент10 страниц05 States of Matter Formula Sheets QuizrrIshita AgarwalОценок пока нет
- CHM 221Документ12 страницCHM 221Necherem MissionОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 Gases: 10.4 Temperature and Volume (Charles' Law) 10.5 Temperature and Pressure (Gay-Lussac's Law)Документ16 страницChapter 10 Gases: 10.4 Temperature and Volume (Charles' Law) 10.5 Temperature and Pressure (Gay-Lussac's Law)olongkodokОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 5.1 GasДокумент18 страницCHAPTER 5.1 GasZARITH SOFHIA BINTI MD KHARODIN KM-PelajarОценок пока нет
- Gas LawsДокумент66 страницGas LawsLorilieОценок пока нет
- Chapter 03 - States of Matter - ModuleДокумент33 страницыChapter 03 - States of Matter - ModulePriya MishraОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirДокумент22 страницыGas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirKevin SimanjorangОценок пока нет
- 11th Chemistry Chapter 4 PDF Notes - Unlocked - OCRДокумент27 страниц11th Chemistry Chapter 4 PDF Notes - Unlocked - OCRamirbadshahОценок пока нет
- States of Matter Formula Sheet @cbseinfiniteДокумент8 страницStates of Matter Formula Sheet @cbseinfiniteSulveОценок пока нет
- Silo - Tips - Chapter 5 The Gaseous StateДокумент18 страницSilo - Tips - Chapter 5 The Gaseous StateJerich Ivan PaalisboОценок пока нет
- States of Matter PDFДокумент42 страницыStates of Matter PDFSarthak GuptaОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Документ47 страницTopic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Joshua LaBordeОценок пока нет
- Student CH 13 GasesДокумент51 страницаStudent CH 13 GasesMichael MaglaqueОценок пока нет
- C4-State of MatterДокумент171 страницаC4-State of MatterLan FazlanОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirДокумент24 страницыGas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirShandy ManabatОценок пока нет
- YI-DiUCh9D V7o NДокумент25 страницYI-DiUCh9D V7o NAyca UgurluОценок пока нет
- Note Chapter13 19 20Документ51 страницаNote Chapter13 19 20Nursyafiqa IdwaniОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11ThermalProperties PDFДокумент12 страницChapter 11ThermalProperties PDFzeus292122Оценок пока нет
- Behaviour of GasesДокумент30 страницBehaviour of GasesRaveendra MungaraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ8 страницChapter 2J.K HomerОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws - F3Документ17 страницGas Laws - F3Kiama GitahiОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of GasesДокумент66 страницKinetic Theory of GasesDr. Sushil Kumar SharmaОценок пока нет
- G10 Science Q4 - Week 1-2-Constant Temp of GasДокумент34 страницыG10 Science Q4 - Week 1-2-Constant Temp of GasMelissa Ganituen-BautistaОценок пока нет
- Gaseous StateДокумент45 страницGaseous StateRajesh Das50% (2)
- Student CH 13 GasesДокумент51 страницаStudent CH 13 GasesFernando Hernández VenegasОценок пока нет
- Gas Law: Ref: Basic Chemistry, TimberlakeДокумент22 страницыGas Law: Ref: Basic Chemistry, TimberlakeSofeaОценок пока нет
- 7 ThermalДокумент69 страниц7 ThermalKingsonОценок пока нет
- Gas LawsДокумент31 страницаGas Lawsapi-546066323Оценок пока нет
- 5.1 GasДокумент72 страницы5.1 GasP YОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws PPTДокумент41 страницаGas Laws PPTIsabelle OdenbachОценок пока нет
- 12stem B - Week9Документ2 страницы12stem B - Week9Franz SorianoОценок пока нет
- M1-5B - Kinetic Theory-Gas LawsДокумент19 страницM1-5B - Kinetic Theory-Gas LawsestherОценок пока нет
- 3.99 Gas LawsДокумент18 страниц3.99 Gas LawscecilialaventineОценок пока нет
- States of Matter by Rakshita SinghДокумент14 страницStates of Matter by Rakshita SinghFarzana ShaikОценок пока нет
- Volume and Temperature Relationship of A Gas - Charles' Law - Pass My ExamsPass My ExamsДокумент4 страницыVolume and Temperature Relationship of A Gas - Charles' Law - Pass My ExamsPass My ExamsDorwinNeroОценок пока нет
- 10 GasesДокумент7 страниц10 GasesKkkОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 GasesДокумент30 страницChapter 13 GasesGwen100% (1)
- STD 9 - Chemistry - Study of Gas LawsДокумент5 страницSTD 9 - Chemistry - Study of Gas LawsRamchandra MurthyОценок пока нет
- Worked Problems in Heat, Thermodynamics and Kinetic Theory for Physics Students: The Commonwealth and International Library: Physics DivisionОт EverandWorked Problems in Heat, Thermodynamics and Kinetic Theory for Physics Students: The Commonwealth and International Library: Physics DivisionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Pdfa5 1Документ1 страницаPdfa5 1aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa5 3Документ1 страницаPdfa5 3aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa5 3Документ1 страницаPdfa5 3aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa5 2Документ1 страницаPdfa5 2aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 1Документ1 страницаPdfa4 1aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 5Документ1 страницаPdfa4 5aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 7Документ1 страницаPdfa4 7aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 3Документ1 страницаPdfa4 3aizatОценок пока нет
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourДокумент1 страницаSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 13Документ1 страницаPdfa2 13aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 6Документ1 страницаPdfa4 6aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa4 2Документ1 страницаPdfa4 2aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 16Документ1 страницаPdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa3 6Документ1 страницаPdfa3 6aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 7Документ1 страницаPdfa3 7aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 2Документ1 страницаPdfa3 2aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 3Документ1 страницаPdfa3 3aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 4Документ1 страницаPdfa3 4aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 15Документ1 страницаPdfa2 15aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 14Документ1 страницаPdfa2 14aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 1Документ1 страницаPdfa3 1aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa3 5Документ1 страницаPdfa3 5aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 12Документ1 страницаPdfa2 12aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 11Документ1 страницаPdfa2 11aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 10Документ1 страницаPdfa2 10aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 8Документ1 страницаPdfa2 8aizatОценок пока нет
- Pdfa2 9Документ1 страницаPdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Vol 31 PhotochemistryДокумент69 страницVol 31 PhotochemistryRicardo Gamboa CastellanosОценок пока нет
- Exp 3Документ6 страницExp 3ohhiОценок пока нет
- BlowersДокумент58 страницBlowersmahmad61100% (1)
- Reading Material Lecture 04Документ12 страницReading Material Lecture 04Muqeem MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Interactions Between PVC and Binary or Ternary Blends of Plasticizers. Part I. PVC/plasticizer CompatibilityДокумент14 страницInteractions Between PVC and Binary or Ternary Blends of Plasticizers. Part I. PVC/plasticizer CompatibilityJose CastroОценок пока нет
- Fournier1977 Geotermometer & Mixing PDFДокумент10 страницFournier1977 Geotermometer & Mixing PDFAnonymous FdickkSXcОценок пока нет
- Cape Physics U1 P1 2013Документ11 страницCape Physics U1 P1 2013C.Оценок пока нет
- Background Information For Ni ComplexДокумент3 страницыBackground Information For Ni ComplexKira NguyenОценок пока нет
- Oxygen USPДокумент2 страницыOxygen USPMartha Lucia Roa FonsecaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5 Numerical Solar ThermalДокумент14 страницLecture 5 Numerical Solar ThermalKanzul EmanОценок пока нет
- Amine Value 1Документ4 страницыAmine Value 1mahmoud bdourОценок пока нет
- Liquid Penetrantion Test: Greated byДокумент25 страницLiquid Penetrantion Test: Greated byشمس الضحىОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Fluid Mechanics 1St Edition by Hibbeler Isbn 0132777622 9780132777629 Full Chapter PDFДокумент30 страницSolution Manual For Fluid Mechanics 1St Edition by Hibbeler Isbn 0132777622 9780132777629 Full Chapter PDFscott.fischer352100% (9)
- HMT Unit 4Документ21 страницаHMT Unit 4Muthuvel MОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE ™: Combined ScienceДокумент11 страницCambridge IGCSE ™: Combined ScienceAhmed Jomaa Salem0% (1)
- Final05 PDFДокумент7 страницFinal05 PDFRam chandraОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Lab 1Документ4 страницыChemistry Lab 1Call Mi BlacksОценок пока нет
- LeaP Science G5 Week3 Q3Документ5 страницLeaP Science G5 Week3 Q3archie monrealОценок пока нет
- MT036 Emulsion CipacДокумент3 страницыMT036 Emulsion CipacAntony Vilca Vergaray100% (3)
- Binary ORC (Organic Rankine Cycles) Power Plants For The Exploitation of Medium-Low Temperature Geothermal Sources - Part B Techno-Economic OptimizationДокумент12 страницBinary ORC (Organic Rankine Cycles) Power Plants For The Exploitation of Medium-Low Temperature Geothermal Sources - Part B Techno-Economic OptimizationJoao Minho100% (1)
- Q2 Science 9 - Module 1Документ27 страницQ2 Science 9 - Module 1Reynalyn asoyОценок пока нет
- CHM IA - FinalДокумент14 страницCHM IA - FinalMatthew BondОценок пока нет
- Experiment 8 Synthesis of An Azo Dye - The Coupling Reaction of Benzenediazonium Ion With Naphthalen-2-OlДокумент9 страницExperiment 8 Synthesis of An Azo Dye - The Coupling Reaction of Benzenediazonium Ion With Naphthalen-2-OlShivam SinghОценок пока нет
- Jamb-chemistry-syllabus-by-Studentmajor.com-convertedДокумент4 страницыJamb-chemistry-syllabus-by-Studentmajor.com-convertedEtefia EtefiaОценок пока нет
- Chemical ReactionsДокумент11 страницChemical Reactionsapi-272822216Оценок пока нет
- (Isao Ando) Annual Reports On NMR Spectroscopy, Vo (BookFi)Документ337 страниц(Isao Ando) Annual Reports On NMR Spectroscopy, Vo (BookFi)Rogério SiqueiraОценок пока нет
- Cardanol, A Bio-Based Building Block For New Sustainable and Functional MaterialsДокумент198 страницCardanol, A Bio-Based Building Block For New Sustainable and Functional MaterialsHa LeeОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen ProductionДокумент11 страницHydrogen ProductionRichard AlexanderОценок пока нет