Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ALM DNA Structure Sp'13 Name
Загружено:
Brian BradyАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ALM DNA Structure Sp'13 Name
Загружено:
Brian BradyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name:
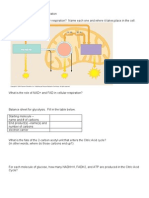
Bio2 Active Learning Module DNA Structure 1. In the last unit, we learned that the monomers of nucleic acids are called nucleotides. Label the following components of the nucleotide (figure on left): 1. Ribose sugar, 2. Nitrogenous base, 3. Phosphate.
2. In the figure to the right, label the same nucleotide components on nucleotides on both sides of the double helix. 3. Which two components make up the backbone of the the DNA polymer? 4. Why is the DNA sequence ACTG not the same as GTCA? 5. Fill in the complementary nucleotide sequence on this imcomplete double helix:
5-ACTGGCAT-3
3-TG
6.
Refer
to
question
5.
What
is
the
primary
sequence
of
the
top
strand?
7.
Refer
to
question
5.
What
is
the
primary
sequence
of
the
bottom
strand?
8.
What
does
the
term
anti-parallel
orientation
mean?
Name: Bio2 Active Learning Module DNA Replication/Mitosis 1. Consider the replication bubble that is partially drawn out for you. Complete the figure by adding the following features: a. Finish labeling the 5 and 3 ends of the parental DNA strands b. Add the leading strand to the left half of the bubble c. Add the lagging strand to the left half of the bubble d. Label the ends of the leading and lagging daughter strands with 5 or 3 e. DNA polymerase f. Helicase g. Origin of replication h. DNA ligase
2. What does the term semi-conservative replication mean?
3. On the back of the page, draw a line separating the page in half. Draw cartoon mitosis (as we did in class), labeling the representative stages and major events that occur during each of these stages.
Name: Bio2 Active Learning Module Meiosis 1. On the back of the paper, draw two chromosomes, one duplicated, the other non- duplicated. Labeling the parts: 1. Sister chromatids, 2. Centromere 2. What is the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete? 3. What is the difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes? 4. Define homologous chromosomes. 5. On the back of the paper, draw out the steps in cartoon meiosis. Label each stage of meiosis, describing the major events that occur. 6. Using your completed mitosis and meiosis cartoons, complete the table below, comparing these two processes: MITOSIS MEIOSIS Number of chromosomal duplications Number of cell divisions Number of chromosomes in daughter cells How chromosomes line up during metaphase Genetic relationship of daughter cells to parent cell Which kind of cell? 7. Refer to the cartoon of the gamete below. In the cartoon gamete, there is a tetrad (homologous pair of chromosomes) aligned with each other. Show how crossing over can swap out part of the chromosome. Draw your result in the empty gamete.
A
A a
a
B B b b
Name: Bio2 Active Learning Module Meiosis 8. During which stage of meiosis does crossing over occur? 9. What is the Principle of Independent Assortment in your own words? 10. Give definitions for the following chromosomal alterations in your own words. 11. A male individual has suffers from a relatively rare (~1 out of 600 males) genetic condition in which they possess 47 chromosomes including TWO X chromosomes and ONE Y chromosome. Individuals with this disorder have feminized features, are typically sterile, and may have reduced IQ. Propose a mechanism by which this may have occurred.
Вам также может понравиться
- ALM Evolutionary ForcesДокумент2 страницыALM Evolutionary ForcesBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- ALM Evolutionary ForcesДокумент2 страницыALM Evolutionary ForcesBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- ALM Transcription TranslationДокумент3 страницыALM Transcription TranslationBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- Molecular Biology LectureДокумент43 страницыMolecular Biology LectureBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- ALM Photosynthesis and RespirationДокумент4 страницыALM Photosynthesis and RespirationBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- Genetics Bio101 LectureДокумент41 страницаGenetics Bio101 LectureBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- DNA Replication Mitosis Meiosis Sp'13Документ39 страницDNA Replication Mitosis Meiosis Sp'13Brian BradyОценок пока нет
- Evolution Lecture F'12Документ56 страницEvolution Lecture F'12Brian BradyОценок пока нет
- ALM GeneticsДокумент2 страницыALM GeneticsBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- Genetics Bio101 LectureДокумент41 страницаGenetics Bio101 LectureBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- ALM The Working Cell F'12Документ3 страницыALM The Working Cell F'12Brian BradyОценок пока нет
- The Working Cell Sp'12 Reduced SizeДокумент44 страницыThe Working Cell Sp'12 Reduced SizeBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- Study Guide For RCC Bio1 Lab MidtermДокумент1 страницаStudy Guide For RCC Bio1 Lab MidtermBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- Respiration Lecture F'12Документ36 страницRespiration Lecture F'12Brian BradyОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis: - I. Bottom Line of PhotosynthesisДокумент21 страницаPhotosynthesis: - I. Bottom Line of PhotosynthesisBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- ALM Origin of Life and Tour of Cell F'12Документ3 страницыALM Origin of Life and Tour of Cell F'12Brian BradyОценок пока нет
- ALM Introduction Atoms Molecules Water PHДокумент5 страницALM Introduction Atoms Molecules Water PHBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- ALM BiochemistryДокумент4 страницыALM BiochemistryBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- Bio 100:101 Introduction Lecture Sp'13Документ22 страницыBio 100:101 Introduction Lecture Sp'13Brian BradyОценок пока нет
- Macromolecules LectureДокумент51 страницаMacromolecules LectureBrian BradyОценок пока нет
- Cell Theory and Tour of Cell Sp'13Документ44 страницыCell Theory and Tour of Cell Sp'13Brian BradyОценок пока нет
- Lecture Atoms Molecules Water PH Sp'13Документ24 страницыLecture Atoms Molecules Water PH Sp'13Brian BradyОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Golden Age of Greek Culture and the Origins of GeneticsДокумент9 страницGolden Age of Greek Culture and the Origins of GeneticsKAYLE NICOLE ILIJAYОценок пока нет
- The Significance of MeiosisДокумент5 страницThe Significance of MeiosisKaren CasternoboОценок пока нет
- Amoeba Sisters - MeiosisДокумент2 страницыAmoeba Sisters - MeiosisCourtlynn RodgersОценок пока нет
- 11.4 - Reproduction IB BiologyДокумент3 страницы11.4 - Reproduction IB BiologyannehindenbergОценок пока нет
- CBSE-12 Biology Solved Paper-2023Документ18 страницCBSE-12 Biology Solved Paper-2023Vaibhav ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Cell Division, Mitosis, and MeiosisДокумент15 страницCell Division, Mitosis, and MeiosisanisnazihahОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsДокумент32 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of Farm Animalsufaysa gensaОценок пока нет
- Apomixis Molecular Life of PlantsДокумент3 страницыApomixis Molecular Life of Plantspedro antonioОценок пока нет
- Biology Module 5 NotesДокумент17 страницBiology Module 5 NotesKatie BellОценок пока нет
- Kanha: Important InstructionsДокумент24 страницыKanha: Important InstructionsHARIKRISHNA PRASAD R KОценок пока нет
- Testis Physiology-Overview and Histology: January 2018Документ13 страницTestis Physiology-Overview and Histology: January 2018Sephendra LutfiОценок пока нет
- Instructions: Grade 10 Life Sciences November Paper 2Документ14 страницInstructions: Grade 10 Life Sciences November Paper 2JustinCase1991Оценок пока нет
- First Trial Exam - Biologi (SMK Kwong Hua)Документ23 страницыFirst Trial Exam - Biologi (SMK Kwong Hua)anakiuОценок пока нет
- Agricultural Sciences P1 Nov 2015 Memo EngДокумент9 страницAgricultural Sciences P1 Nov 2015 Memo EngAbubakr IsmailОценок пока нет
- Pierce, Genetics: A Conceptual Approach, 5e: Chapter 8 NotesДокумент18 страницPierce, Genetics: A Conceptual Approach, 5e: Chapter 8 NotesHannah BroussardОценок пока нет
- Mcqs Biology IxДокумент34 страницыMcqs Biology IxMysteious RuneОценок пока нет
- Lycopodium Habit and Morphology GuideДокумент73 страницыLycopodium Habit and Morphology GuideAnjaliОценок пока нет
- TEXT READINGS Chapter - 16Документ6 страницTEXT READINGS Chapter - 16tanusehdev17Оценок пока нет
- GB - 1st Quarter - wk3 - PDFДокумент20 страницGB - 1st Quarter - wk3 - PDFHeaven LeighОценок пока нет
- Perfect BONUS: Bacteria and Microbiology ReviewДокумент47 страницPerfect BONUS: Bacteria and Microbiology ReviewJack KayatОценок пока нет
- Biology Form 4Документ13 страницBiology Form 4Arvinth Guna SegaranОценок пока нет
- Class XII Biology Practical 2022-23Документ23 страницыClass XII Biology Practical 2022-23karishmaОценок пока нет
- Induction and Verification of Triploidy in FishДокумент2 страницыInduction and Verification of Triploidy in FishRoger PilonОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Cells, Development, Biodiversity and ConservationДокумент47 страницUnit 2 Cells, Development, Biodiversity and ConservationEllane leeОценок пока нет
- Cell DivisionДокумент4 страницыCell DivisionMhariane MabborangОценок пока нет
- Klinefelter SyndromeДокумент21 страницаKlinefelter SyndromeClaire GuanteroОценок пока нет
- Paper Pet ProjectДокумент27 страницPaper Pet Projectapi-406104878Оценок пока нет
- Botany Document Section A Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент14 страницBotany Document Section A Multiple Choice QuestionsSiddhartha ShakyaОценок пока нет
- Path 171Документ118 страницPath 171manirathina100% (1)