Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Case Study
Загружено:
Mikko Anthony Pingol AlarconИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Case Study
Загружено:
Mikko Anthony Pingol AlarconАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CASE STUDY
I.
DEMOGRAPHICAL DATA
Name: E.V.E Age: 11 years old Gender: Male Address: Sitio Ibabaw Dulumbayan, Teresa, Rizal Civil Status: Single Date of Birth: Septemr 14, 2001 Place of Birth: Taytay, Rizal Nationality: Filipino Ethnic Group: None Primary Language Spoken: Tagalog Highest Educational Attainment: Grade 4 Occupation: N/A Religious Orientation: Roman Catholic Health Care Financing: Family
A. PRESENT HEALTH HISTORY The patient was admitted last April 16 at around 8:00 pm due to chief complains of vomiting and episodes of loose stools, specifically 5 times. His admitting diagnosis is Acute Gastroenteritis with mild dehydration due to Amoebiasis. According to the patients mother, they went on swimming last April 7 which she thought her son got the infectious agent. Moreover, the patient had been hospitalized for 4 days from now and so he is already in possible discharge. B. PAST HEALTH HISTORY According to the patients mother, E.V.E have had Amoebiasis before when he was still 6 years old and he was also been hospitalized for 3 days due to it. Hindi ko na kasi matandaan kung pano siya nagka-Amoebiasis noon, per siguro dahil sa pagkain, the patients mother verbalized. Also, the patient had pneumonia when he was still on his neonatal period but according to his mother, he was no longer manifesting the condition today. The patient has
complete vaccinations. He usually got colds and fever at approximately 2-3 times a year and over the counter medications is their way of treating it. He had also childhood diseases such as chicken pox and mumps. His chicken pox just happened last May 2012 at lasted for more than a week. He had mumps when he was still on Grade 2. He was breastfed up to 2 years of age as his mother stated. Also, he is not taking any vitamins or supplements. C. FAMILY HEALTH HISTORY GENOGRAM
D.V (-) old age
G.V arthritis D.B (-) DM W.E (-) HPN
L.V (A/W)
L.J.V (A/W)
L.R.E (A/W)
E.R.E (A/W) E.L.E (A/W) E.M.E (DM)
J.E (A/W)
E.E asthma
(Patient) E.V.E
E.J.E (A/W)
The patients father is Edmundo 48 years old and his mother, Leah rose is 39 years old. They are both alive and well with no present illnesses according to the patients mother. He has 4 siblings. The eldest is Junro, 16 years old male, the 2nd is Edrolyn, 15 years old female, who has asthma, the patient is the 3rd child and the youngest is Edmund Jun, 4 years old. All are alive and well aside from her sister who has asthma. The patients grandmother from his mothers side was already deceased and her gradmother has arthritis. E.V.Es mother has 3 siblings, she is the youngest and all of them are alive and well. However, his grandparents from his fathers side were already both deceased. Her grandmother died due to Diabetes Mellitus and his grandfather passed away due to Hypertension. His father has also 3 siblings; he is the eldest and the only male in the family and all of them are all alive and well.
II.
GORDONS FUNCTIONAL HEALTH PATTERNS A. Nutrition
Before Hospitalization: The patient eats 3 times daily. He loves to eat sweets and salty foods. Usually for breakfast, he eats bread and drink milo. For lunch and dinner they often have vegetable dish and sometimes with meat and fish according to the patients mother. Hindi naman sila namimili ng ulam. Kahit anong ihain kinakain naman nila, the patients mother verbalized. In every meal, the patient drinks 2 glasses of water. They seldom eat out on fast foods or restaurants. His sister often cooks food for them as a family. Sometimes he eats junkfoods and soda for snacks. Also, the patient does not have any food allergies noted. In the past 2 days prior to hospital admission, the patient had difficulty eating. He lost appetite and had vomited several times. He only had lugaw each meal time. During the hospitalization: The patients appetite is becoming better compared to 2 days prior his hospitalization according to her mother. He eats a lot more compared to the past 2 days before he was admitted. He usually drinks up to 700ml of water daily. He is not nauseated and doesnt suffer from any gastric upset. However, episodes of vomiting were still noted during the first 2 days of hospitalization. He had several medications; these are as follows, ceftriaxone 500mg TIV q8, Buscupan ampoule TIV, Erceflora 1 tube daily, Paracetamol 7.5ml q4 if with fever, Metronidazole 500mg tablet TID and Zithromax 500mg tablet daily. Norms:Various daily food guides have been developed to help healthy people meet the daily requirements of essential nutrients and to facilitate meal planning. Food group plans emphasize the general types or groups of foods rather than the specific foods, because related foods are similar in composition and often have similar nutrient values. For example, all grains, whether wheat or oats, are significant source of carbohydrate, iron, and the B vitamin thiamine. Daily food guides that are currently used includes Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the Food Guide Pyramids (Source: Fundamentals of Nursing. Kozier and Erb. 2008. Pp 1246.)
Interpretation: The patient usually eats vegetables and is not picky. He also drinks water every time he eats. They do not eat on fast food chains often. So, they prepare their own food; which is better compared to commercially prepared ones. However, as like other kids of his age he loves eating junk foods and sweets for snacks. In the morning he consumes mainly carbohydrates which is good in order to keep him active during the day considering his age where in he is at playful stage.
B. Rest and Sleep
Before Hospitalization: The patient has average hours of sleep. He often sleeps at 9:00 pm and wakes up at 8:00am making it up to 11 hours of sleep in total. However, when he has school, the patients mother said that by 8:00 pm he was already asleep and wakes up at 5:00am. At present, because its summer break, there are no classes the patient also takes a nap at noontime. Usually around 1:00 to 3:00pm. E.V.E also mentioned that he is satisfied with his sleeps and does not have any disturbances during his resting period. He does not have any difficulty sleeping. He is refreshed during the day and does not sleepy. During Hospitalization: According to the patient, he does not have any difficulty sleeping in the hospital. He still sleeps at 9:00pm and wakes up at 7 or 8:00am. However, he has slight sleep disturbances as he said, sometimes when the doctors or nurses checks them in the ward he wakes up; also whenever he has to take medications, he has to wake up.
Norms: Most healthy children need 10 to 12 hours of sleep a night to function optimally. (Source: Fundamentals of Nursing 8th edition by Kozier and Erb pp. 1168) Interpretation: The patient has adequate sleep and rest because he has a total of 11 hours of sleep at night and also he mentioned that he also sleeps during noontime. During his hospital admission, he has minimal disturbances which is appropriate because due medications have to be taken within the time prescribed and nurses checking them at the ward from time to time is inevitable and it is on purpose of their stay in the hospital.
Elimination Before Hospitalization: 2 days prior to hospital admission the patient had several episodes of loose bowel movement, 5 times during the day of April 16 to be exact. He described his stools as black and tarry according to his mother. Usually he urinates 3 times a day and the color of the urine is often slightly turbid with no foul odor. Also, he does not have any difficulty urinating.
During Hospitalization: In the first 2 days of hospital admission the patient still have episodes of loose stools though the frequency is decreasing day by day. During the day assessed, he is already for discharge and he had his bowel movement once. He does not have any difficulty moving his bowel and the consistency is not loose anymore. He urinates 4 to 5 times daily and describes the color of his urine as yellowish with no foul smell. Also, he does not have any problems urinating. Norms: Voiding or urination all refer to the process of emptying the urinary bladder. This occurs when the adult bladder contains between 250 and 450 mL of urine. Each person must take 8-10 glasses of water every day. The frequency of defecation is highly individual, varying from several times per day to two or three times per week. Many people believe that regularity means a bowel movement every day. (Source: Fundamentals of Nursing 8th edition by Kozier and Erb pp. 1326 and 1325.)
Interpretation: The patient was able to void without any discomfort as reported by him. From having loose stools, he said that his stools become better than before and that he only moves his bowel once a day already. So, he no longer has problems regarding his bowel movement and urination pattern.
C. Health and Illness The patient describes a healthy individual as a person who is active, playful, happy and does not have any sickness. He stated, Syempre kapag wala kang sakit, nakakapaglaro ka at masaya ka. He said that he likes all vegetables. He is not picky when it comes to food. Para po maging malusog, kelangan kumain ng maraming gulay, the patient verbalized. Norms: Health is a highly individual perception. Many people define and describe health as the following: Being free from symptoms of disease and pain as much as possible Being able to be active and to do what they want or must Being in good spirits most of the time
These characteristics indicate that health is not something that a person achieves suddenly. (Source: Fundamentals of Nursing. Kozier and Erb. 2008. Pp 295).
Interpretation: Observing the patients response, he is right that he should eat a lot because considering his age. He is active and quite playful. Thus, eating a lot will give him energy to sustain in his activities during the day. Parents with school aged children do have a hard time having their child eat vegetables because they prefer processed foods such as hotdogs and sausages but the patient said that he eats vegetables and that he is not picky which is again appropriate in having a proper balanced diet.
Activity/ Exercise The patients daily activities are mainly outside playing with his playmates. He said he plays basketball and other outdoor games. He often goes biking with his playmates around the vicinity of their place during the afternoon. He also plays computer games but not usually because he said his mother does not give him money sometimes to pay in the computer shop.
Norms: Make an activity or exercise for at least 30 minutes. (Fundamentals of Nursing 8th edition by Kozier and Erb pp. 1105) Interpretation: The patient is active, he is outside all day often and so his lifestyle is not sedentary. III. PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT
A. Initial Vital Signs Time: 8:00am Date: April 20, 2013 Temp: 36.0C / Axillary PR: 92 beats/minute= regular; strong RR: 21 cycles/minute= regular;shallow BP: 90/60 mmHg Norms: For the body to function on a cellular level, a core body temperature between 36.5C and 37.7C must be maintained. (Source: Health Assessment in Nursing. Weber and Kelley. Third Edition.)
Pulse rate of adults ranges from 60- 100 beats/minute. A normal adult inspiration lasts 1 to 1.5 seconds and an expiration lasts 2 to 3 seconds. A typical blood pressure for a healthy adult is 120/80. (Source: Fundamentals of Nursing. Kozier and Erb. 2008. ) Interpretation: The patients vital signs are within the normal range and are stable.
B. General Appearance
Actual Findings: The patient has a dark even complexion with no presence of hyperpigmentation and lesions on skin. He wears appropriate clothing to situation and weather. His nails on toes are a bit long. Since his hospital admission, he never took a bath just sponge bath. However, he does not have any foul odor. He is conscious, cooperative and coherent. He responds to my questions promptly during the interview. He is also aware of person, place and time. Norms: Color is even without obvious lesions: light to dark beige-pink in lighted skinned client; light tan to dark brown or olive in dark-skinned clients. Dress is appropriate for the occasion and weather. The client is clean and groomed appropriately for occasion. Stains on hands and dirty nails may reflect certain occupations such as mechanic or gardener. Client is cooperative and purposeful in his or her interactions with other. Affect is appropriate for the clients situation. (Source: Health Assessment in Nursing. Weber and Kelley. Third Edition.pp.) Interpretation: In general appearance, the patient looks not properly groomed because he didnt take a bath for days. Nevertheless, he is very cooperative in participating during the interview. His thoughts are appropriate to the situation and he is in a good mood because he knew he is on possible discharge. Thus, the patient is somewhat aware and oriented to person, place and time
C.HEENT Actual Findings: S: The patient stated, Hindi naman po sumasakit ang ulo ko. Malinaw ang mga mata ko. Hindi din po ako bingi, naririnig naman kita ng maayos. O: The patients head is normocephalic, round and symmetrical. His hair is evenly distributed, dyed in brown color. The scalp is lighter in color than the skin color. His face is uniform in color
and temperature with a scar on the forehead. His eyebrows are black in color and aligned; eye lashes are curled outward; the eyelids blink bilateral; pink conjunctiva; the cornea is shiny, transparent and equal in size; pupils are black in color; he can move his eyes without any discomfort. Both ears have the same color with the patients face and aligned to the outer canthus of the eye; pinna moves back when palpated; there is a presence of cerumen on both ears, and it is yellowish in color. He can hear well because he responds to my questions attentively during the interview. His nose is at the center and is symmetrical; uniform in color, and has patent airways. The patient can breathe freely on both nares. The lips is pinkish in color; the teeth are white; no missing teeth and tooth decays noted; the tongue is also pinkish in color as well as the gums, uvula, soft and hard palate. Norms: The skull is round, normocephalic and symmetrical with frontal, parietal, and occipital prominences. Smooth skull contour. Hair is evenly distributed, thick hair, silky, resilient hair, no infection and no infestations. Eyebrows are evenly distributed; skin intact, eyebrows symmetrically aligned, equal movements. Eyelashes are equally distributed and curled slightly outward. Bulbar conjunctiva is transparent, capillaries sometimes evident, sclera appears white. Ears are mobile, Firm, and not tender, Pinna recoils after it is folded. Color same as facial skin, symmetrical, auricle aligned with outer canthus of eye, about 10 degrees from vertical. Nose is symmetric and straight, no discharge or flaring, uniform color. Lips is uniform pink in color. 32 adult teeth; smooth shiny white teeth; pink gums; moist, firm gum texture. Light pink, smooth palate. Lighter pink hard palate and more irregular in texture. Tongue in central position, pink color, no lesions, raised papillae, moves freely with no tenderness. (Source: Health Assessment in Nursing. Weber and Kelley. Third Edition.)
Interpretation: In the HEENT assessment, most of the results are considered to be normal based on the norms. However, the patients hair for instance is not, for the patient admitted he dyed his hair making it brown in color. Though he doesnt have missing tooth or tooth decays, his teeth are not all permanent some are temporary. C. Chest and Back
Actual Findings: S: E.V.E verbalized, Hindi naman po sumasakit ang dibdib ko, pati na din ang likod ko hindi naman nangangalay o sumasakit. Hindi rin ako nahihirapang huminga.
O: The chest is symmetric and expands as he breathes. His respiration is quiet rhythmic, effortless and has 21 cycles in one full minute. The skin is intact and the temperature is even. Norms and Standards: Chest is symmetric. Breasts are not tender when palapated, slightly unequal with no presence of mass and/or lesions. Skin intact and uniform temperature. Full and symmetric chest. Fremitus is heard most clearly at the apex of the lungs. Percussion notes resonate, except over scapula lowest point of resonance is at the diaphragm and vesicular and bronchovesicualr breath sounds. (Source: Fundamentals of Nursing. Kozier and Erb. 2008.)
Interpretation: There are no deviations from normal noted.
D. Abdomen
Actual Findings: S: Hindi na po sumasakit ang aking tyan. Nakakakain ako ng marami at hindi na ko nagsusuka buhat nung isang araw pa. O: The patients abdomen is round, uniform in color with no lesions noted.
Norms: Unblemished skin, uniform color, no lesions, silver-white striae or surgical scars. Flat, rounded or scaphoid. No evidence of liver/spleen enlargement. Symmetric contour. Symmetric movements caused by respiration. Visible peristalsis in very lean client. (Source: Health Assessment in Nursing. Weber and Kelley. Third Edition.) Interpretation: The patients abdomen has no deviation from normal findings noted.
E. Extremities
Actual Findings: S: Hindi naman po masakit at nangangalay ang mga binti at braso ko. O: The patient has smooth coordinated movements; he can move his extremities without any discomfort. His muscle tone is equal in both upper and lower extremities. The skins temperature and color are uniform.
Norms and Standards: Equal size on both sides. No fasciculation/tremors. Joint moves smoothly. Normally firm. Smooth coordinated movement. Equal strength on both sides. No swelling, no tenderness, no nodules. (Source: Health Assessment in Nursing. Weber and Kelley. Third Edition.)
Interpretation: The client can move his extremities without any discomfort. Thus, there are no deviations from normal noted. IV. LABORATORY RESULTS Hematology Examination: Hemoglobin Hematocrit RBC 133gll 0.40 4.79x10/L Ref. Values 125-160 0.38-0.50 4.5-6.2(M) 4.5-5.5(F) Leukocyte Stab Neutrophil Eosinophil Basophil Lymphocyte Monocyte ESR Platelet count Reticulocyte Bleeding Time x10/L x10/L 150-350 5-15 2-4 minutes 0.06 0.84 21.3 x10/L 5-10 0-0.1 0.40-0.60 0.01-0.06 0-0.01 0.20-0.40 0.20-0.40
Clotting Time Clot ret. Time Protime Patient Control % Activity INR APTT Control Secs Secs secs secs %
2-6 minutes
12-14 secs 70-100%
Norms Hematology Result 04.13.07 14.43 x 109/L Result 04.20.07 16.03 x 109/L Normal Values 510 x 109/L
Interpretation Increased Decreased
WBC
Infection Inflammation Trauma
Autoimmune disease Drug toxicity Bone marrow failure aplastic anemia dietary deficiency
Neutrophil
0.01
0.62
0.550.65
stress acute infection
Lymphocytes
0.83
0.31
0.250.35
Chronic infection Viral Infection Mononucleosis
Leukemia Sepsis Immunodeficiency\ diseases
Eosinophils
0.01
0.03
0.020.07
Parasitic infections Allergic reactions
Increased Adrenosteroid production
Leukemia
Hemoglobin
101.1 g/L
110.7 g/L
116-140 g/L
Polycythemia Dehydration COPD
Hemorrhage Anemia Cancer Kidney disease Sickle Cell Anemia
Hematocrit
0.32
0.34
0.350.41
Polycythemia Dehydration COPD
Hemorrhage Anemia Hyperthyroidism Dietary deficiency Hemorrhage Leukemia Pernicious anemia Hemolytic anemia Chemotherapy
Platelet
365 x 109/L
615 x 109/L
150-350 x 109/L
Malignant disorder Polycythemia Rheumatoid Arthritis Iron Deficiency Anemia
RBC
4.76 x 1012/L
5.28
3.0 -5.0x 1012/L
Dehydration Pulmonary fibrosis
Hemorrhage Anemia Dietary deficiency
(Source:http://cdn.nursingcrib.com/wpcontent/uploads/case%20study/labhypertension.p df)
FECALYSIS COLOR: CONSISTENCY: PARASITES: AMOEBA: positive for E. Histolytica cyst. Greenish yellow mucoid
CYST: TROPHOZOITE: PUS CELLS: RBC: OTHERS: 35-40/rpf 3-6/rpf bacteria: many
Norms: Normal Findings Color Consistency brown soft and bulky, small and dry, depending on the diet Parasite Pus Cells Bacteria Red Cells none none none 0-3 (+)infection (-)normal (+)infection (-)normal (+)infection (-)normal normal Interpretation normal normal
(Source: http://healcon.com/health-book/health-condition/fecalysis-norms_AQZ5AGquLGLjKmVjAwRmAmL=.htm)
ELECTROLYTES RESULTS SODIUM POTASSIUM CHLORIDE 136.5 3.6 UNIT mmol/L mmol/L REF. VALUE 135-140 3.5-5.5 98-107
Norms: Normal Findings Sodium 135-145 Interpretation <145 mmol/L: Hypernatremia An excess in sodium levels in the blood in relation to water is called 'hypernatremia'. Causes of hypernatremia may include kidney disease, lack or little water intake or loss of water due to diarrhea and/or vomiting. >135 mmol/L: Hyponatremia A decrease in sodium levels in the blood in relation to water is called 'hyponatremia'. This occurs when there is an increase in the amount of body water in relation to sodium. This occurs with diseases of the liver, kidney, burn victims and those who suffer from congestive heart failure and other conditions. Potassium 3.5-5 <3.5mmol/L: hypokalemia >5 mmol/L: hyperkalemia An abnormal increase in potassium (hyperkalemia) or a decrease in potassium (hypokalemia) can seriously affect the nervous system and increases the chance of arrhythmias. Chloride 98-107 <107 mmol/L: hyperchloremia
Increased chloride levels is 'hyperchloremia'. Elevated levels are seen in diarrhea, some kidney disease and sometimes in overactive parathyroid glands. >98 mmol/L: hypochloremia Decreased chloride levels is 'hypochloremia'. Chloride is normally lost in the urine, sweat and stomach secretions but an excessive loss can happen from heavy sweating, vomiting and adrenal gland or kidney disease. Calcium(ionized) 4.5-5.5 <5.5: hypercalcemia LOW: muscle twitching and cramping seizures varying degrees of depression hair loss cataracts conjunctivitus (inflammation of the mucuos membrane of inner eyelid) >4.5: hypocalcemia HIGH: muscle weakness fatigue abdominal cramps loss of appetite nausea and /or vomiting constipation
possible coma if left untreated Magnesium 1.5-2.5 <2.5: hypermagnesemia >1.5: hypomagnesemia Signs and symptoms associated with abnormal levels: decreased mental function ranging from drowsiness to coma in severe states decreased tendon reflex leading to paralysis Nausea / vomiting hypotension due to dilated blood vessels Phosphate 1.7-2.6 <2.6mmol/L: hyperphosphatemia Causes of increased phosphate leves are due to excess vitamin D, impaired colon motility, hypoparathyroidism, addisons disease and increased intake of phosphate foods >1.7 mmol/L: hypophosphatemia Causes of decreased phosphate are due to malnutrition, excess use of antacids, cushing syndrome, and hyperparathyroidism Signs and Symptoms: Decrease cardiac respiratory function Muscle weakness
Fatigue Confusion Seizures Bone pain
(Source: http://www.mdhealthnetwork.org/Blood-Tests-Electrolytes.htm)
V.
DRUG STUDY
Home Medications
Name
Dosage
Action
Indication
Contraindic ation Ketolide or related allergy.
Side Effects
Generic: Azithromy cin Brand name: Zithromax Drug Class: Macrolide antibiotic
500 mg/1 tab OD for 3 days
Azithromyc in is an antibiotic (macrolidetype) used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.Th is antibiotic treats only bacterial infections. It will not work for viral infections (e.g., common cold, flu). Metronidaz
Indicated for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptibl e strains of the designate d microorga nisms.
GI upset, abdominal pain, rash, chest pain; hepatotoxicit y, allergy (eg, angioedema, cholestatic jaundice), C. difficile associated diarrhea.
Nursing Responsibilitie s Inform patient not to share medications Do not take drug with food or antacids Take antacids 2h before or after taking the drug Direct sunlight (UV) exposure should be minimized during therapy with drug or patient might use sunblock Report immediately if onset of diarrhea occurs
Generic:
500 mg 1
Acute
History of
GI
Take full
Metronida zole Brand name: Flagyl Drug Class: Antiinfectives, Antiprotozoals
tab for 7 days
ole is converted to reduction products that interact with DNA to cause destruction of helical DNA structure and strand leading to a protein synthesis inhibition and cell death in susceptible organisms. It is effective against a wide range of organisms including E. histolytica, T. vaginalis, Giardia, anaerobes e.g. Bacterioide s sp, Fusobacter ium sp, Clostridium sp, Peptococc us sp and Peptostrep tococcus sp, and moderately active against Gardnerell
infection with susceptibl e anaerobic bacteria Acute intestinal amebiasis Amebic liver abscess Trichomon iasis (acute and partners of patients with acute infection) Preoperati ve, intraoperat ive, postoperat ive prophylaxi s for patients undergoin g colorectal surgery Topical application : Treatment of inflammat ory papules, pustules, and erythema of rosacea
hypersensit ivity to metronidaz ole or other nitroimidaz ole derivatives. Pregnancy (1st trimester) and lactation.
disturbances Furred tongue, glossitis, and stomatitis due to overgrowth of Candida. Weakness, dizziness, ataxia, headache, drowsiness, insomnia, changes in mood or mental state. Numbness or tingling in the extremities, epileptic form seizures (high doses or prolonged treatment). Transient leucopenia and thrombocyto penia. Hypersensiti vity reactions. Urethral discomfort and darkening of urine. Raised liver enzyme values, cholestatic hepatitis, jaundice. Thrombophle bitis (IV).
course of drug therapy; take the drug with food if GI upset occurs. Do not drink alcohol (beverages or preparations containing alcohol, cough syrups); severe reactions may occur. Your urine may be a darker color than usual; this is expected. Refrain from sexual intercourse during treatment for trichomoniasis , unless partner wears a condom. Apply the topical preparation by cleansing the area and then rubbing a thin film into the affected area. Avoid contact with the eyes. Cosmetics may be applied to the area after application. You may experience these side effects: Dry mouth with strange
a sp and Campyloba cter sp.
metallic taste (frequent mouth care, sucking sugarless candies may help); nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (eat frequent small meals). Report severe GI upset, dizziness, unusual fatigue or weakness, fever, chills. Acute diarrhea with duration of 14 days due to infection, drugs or poisons. Chronic or persistent diarrhea with duration of >14 days. Not for use in immunoco mpromised patients (cancer patients on chemother apy, patients takingimmu nosuppres sant meds) No known side effects Shake drug well before administration Administer drug within 30 minutes after opening Dilute drug with sweetened milk or fruit juice Administer per orem Monitor patient for any unusual effects from drug
Generic: Bacillus Clausii Brand name: Erceflora Drug class: Antidiarrh eals
1 vial of 2 billion/ 5 ml suspensi on
Contribute s to the recovery of the intestinal microbial flora altered during the course of microbialdi sorders of diverse origin. It produces various vitamins, particularly group B vitamins thus contributin gto correction of vitamin disorders caused by antibiotics & chemother apeutic agents.
Promotesn ormalizatio n of intestinal flora.
VI.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
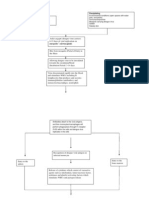
Infective cysts are ingested through water or food contaminated with infected feces. The cysts travel through the digestive track until the small intestine. There, excystation occurs, forming a motile trophozoite. It then travels to the large intestine and colon. Here the infection can follow either of two phases: pathogenic and non-pathogenic. In the pathogenic phase, the virulent trophozoite invades the gut, intestinal lumen, and sometimes the mucosa. Here they kill epithelial cells, neutrophils, and lymphocytes. In the process, they destroy tissues and cells, and produce colitis. Occasionally they manage to enter the capillaries, where they can be transported to the liver, lungs, or the brain. Once in those organs, the parasite can cause abscesses. The abscesses may subsequently burst, releasing many trophozoites which can re-enter the lumen. After feeding, the trophozoites extrude all
ingested material and binary fission occurs. They round up and form cysts, where they areresistant to the environment. The cysts pass through the digestive system and are contained in the feces. In feces, they can live anywhere from2-5 weeks, waiting for a new host. In the non-pathogenic phase, the trophozoites feed on bacteria and detritus from the outer lining of the gut. They do not invade the membrane, and do not form ulcers or abscesses. After feeding, they round up and form cysts, as in the pathogenic phase. (Source: http://nursingcrib.com/case-study/amoebiasis-amebiasis-amoebic-dysentery-casestudy/)
VII.
PRIORITIZED LIST OF PROBLEMS Cues Rationale
Nursing Diagnoses
Readiness for enhanced S: Gusto ko na pong maligo pero -to assist client in maintaining sabi ng nanay ko sa bahay na self-care responsibility for planning and lang daw namin kase uuwi na achieving self-care goals/general well naman daw kami. being -to support client in making healhrelated decisions and pursuit of selfcare practices that promote helth to foster self-esteem and support positive self-concept. -to encourage communication among those who are involved in clients health promotion. -to provide accurate and relevant information future needs. -to maintain general health and regarding current and
physical well being -to remain free of preventable
complications -to control feelings of anxiety and help patient manage the situation
Risk for Infection
Risk factors: Immunosuppression Antibiotic Therapy Increased environmental exposure to pathogens Insufficient knowledge to avoid exposure to pathogens
-to identify etiology/precipitating factors -to note signs and symptoms of sepsis -to demonstrate behaviors or lifestyle changes to prevent development of infection -to avoid reoccurrences of the condition
Risk
for
deficient
fluid Risk factors: Excessive losses through normal routes (e.g Diarrhea) Oral fluid intake of 6 glasses per day -to identify risk factors and appropriate interventions -to demonstrate behaviors or lifestyle changes to prevent development of fluid volume deficit
volume
(Source: NANDA 11th edition)
REFERENCES: Weber and Kelly: Health Assessment in Nursing 3rd Edition Kozier and Erb (2008): Fundamentals of Nursing 8th Edition) Doenges, Moorhouse and Murr: Nurses Pocket Guide 11th edition Source:http://cdn.nursingcrib.com/wpcontent/uploads/case%20study/labhypertension.pdf Source:http://healcon.com/health-book/health-condition/fecalysis-norms_ AQZ5AGquLGLjKmVjAwRmAmL.htm Source: http://www.mdhealthnetwork.org/Blood-Tests-Electrolytes.htm Source: http://nursingcrib.com/case-study/amoebiasis-amebiasis-amoebic-dysentery-casestudy/
VIII.
NURSING CARE PLAN
Nursing Diagnosis Readiness for enhanced selfcare
Analysis
Goal and Objectives Goal: After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the client will be able to maintain responsibility in achieving proper self-care Objectives: After 30 minutes of nursing intervention, the clients condition will be monitored
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
Subjective: The patient verbalized, Gusto ko na pong maligo pero sabi ng nanay ko sa bahay na lang daw namin kase uuwi na naman daw kami.
Goal was met as evidenced by healing of the skin rashes as evidenced by visual disappearance of the rashes and a rate of 0 in itchiness from a scale of 1-10. Administer medications as ordered Vital signs taken and recorded Performed initial thorough assessment Discuss to the client the importance of maintaining To promote faster healing To note any changes in the vital signs To obtain baseline data To promote maintenanc e of good proper
After 5 minutes of nursing intervention, the client will be able to identify the importance of
maintaining good proper hygiene
good proper hygiene Provide ways to the client on how to achieve good proper hygiene Initiate daily bathing and good grooming Promote handwashing before and after eating and voiding
hygiene
After 10 minutes of nursing interventions, the client will be able to demonstrate ways in achieving proper hygiene
To help the client learn ways on how to achieve good proper hygiene To promote comfort
To remove dirt and prevent contaminati on and transmissio n of microorgani sms To prevent transmissio n of microorgani sms into the body To prevent re-
Encourage client to keep nails clean and short
After 15 minutes of nursing
Assist patient in developing
intervention, the client will be able to participate in prevention measures and treatment program
programs for preventive care
occurence of the condition and further complicatio ns To avoid ingestion of infectious agents
Encourage client to avoid consumption of such food and water if in doubt of its preparation Instruct the clients guardian to report in cases of vomiting and diarrhea Inform the medications to be taken at home and its specific considerations Promote the importance of compliance to home
To monitor signs and symptoms of Amoebiasis
To promote timely healing
To enhance effect of treatment program
medications Inform the clients guardian the importance of follow up visits Encourage client that maintaining good proper hygiene is a key role in health promotion Offer support To promote commitment , optimizing better outcomes To enhance understandi ng and cooperation
In another 10 minutes of nursing interventions, the client will be able to show willingness to participate in health promotion
To reduce anxiety and boost selfesteem
Вам также может понравиться
- GordonsДокумент3 страницыGordonsKevin Gonzales DiamosОценок пока нет
- Pattern Before Present Interpretation AnalysisДокумент8 страницPattern Before Present Interpretation AnalysisJorelyn FriasОценок пока нет
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedДокумент5 страницAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangОценок пока нет
- NCP LeprosyДокумент3 страницыNCP LeprosyJane MinОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Документ6 страницIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.Оценок пока нет
- Learning Feedback g2Документ8 страницLearning Feedback g2Darwin DaveОценок пока нет
- A Family Case Study of Real FamilyДокумент43 страницыA Family Case Study of Real Familyneo quarto0% (1)
- Appendicitis Case StudyДокумент35 страницAppendicitis Case StudyWilliam Soneja CalapiniОценок пока нет
- GORDON'SДокумент6 страницGORDON'SSkyla FiestaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Disturbed Body Image Ineffective DenialДокумент6 страницNursing Care Plan: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Disturbed Body Image Ineffective DenialBrix ValdrizОценок пока нет
- Nursing Process NUTRITIONДокумент82 страницыNursing Process NUTRITIONNoci M. FrenkОценок пока нет
- NCP Bernal Imbalanced Nutrition pt2Документ2 страницыNCP Bernal Imbalanced Nutrition pt2Maria CabangonОценок пока нет
- 4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Документ11 страниц4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Sheda BondОценок пока нет
- Final Gordon'SFunctionalHealthДокумент4 страницыFinal Gordon'SFunctionalHealthNecesario BanaagОценок пока нет
- NCP EsrdДокумент2 страницыNCP EsrdAziil LiizaОценок пока нет
- Student Nurses' Community Nursing Care PlanДокумент3 страницыStudent Nurses' Community Nursing Care PlanMussaib MushtaqОценок пока нет
- Gordons 11 Functional Pattern Final Colon CAДокумент3 страницыGordons 11 Functional Pattern Final Colon CAFrancez Anne GuanzonОценок пока нет
- NCP TetanusДокумент2 страницыNCP TetanusSugar Capule - Manuel0% (1)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Albano, Bautista, Cimatu, Purificacion, SieteralesДокумент84 страницыDiabetic Ketoacidosis: Albano, Bautista, Cimatu, Purificacion, SieteralesSyd BautistaОценок пока нет
- DM - Case Pres 1aДокумент59 страницDM - Case Pres 1abon clayОценок пока нет
- Gordons Health PatternsДокумент2 страницыGordons Health PatternsLaurence ZernaОценок пока нет
- NCP Imbalanced NutritionДокумент7 страницNCP Imbalanced NutritionNora VarshavskiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - MCNДокумент2 страницыChapter 6 - MCNPrincess Queenie OlarteОценок пока нет
- Gordon's Functional Health PatternДокумент5 страницGordon's Functional Health PatternnerlynОценок пока нет
- Case Study 1 (Pneumonia)Документ13 страницCase Study 1 (Pneumonia)Kate EscotonОценок пока нет
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsДокумент2 страницыImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsSundaraBharathiОценок пока нет
- Activity IntoleranceДокумент4 страницыActivity IntoleranceShermane Criszen F. SallanОценок пока нет
- Module 12Документ12 страницModule 12mirai desuОценок пока нет
- NCM 114 - NCPДокумент3 страницыNCM 114 - NCPReysiela Mae ValinoОценок пока нет
- History of Past IllnessДокумент4 страницыHistory of Past IllnessKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Health HistoryДокумент2 страницыHealth HistoryFaisaliah UngkakayОценок пока нет
- CASE STUDY PheumoniaДокумент5 страницCASE STUDY PheumoniaEdelweiss Marie CayetanoОценок пока нет
- SeizuresДокумент2 страницыSeizureskaythe08Оценок пока нет
- NCP RiskДокумент2 страницыNCP RiskNorries Jonell CaballarОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of Uremic SyndromeДокумент11 страницNursing Care of Uremic Syndromeyoedha_banditozz50% (2)
- Case AnalysisДокумент25 страницCase AnalysisGerly LagutingОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleДокумент8 страницNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiОценок пока нет
- Discharge Planning: By: Chin V. UlamДокумент2 страницыDischarge Planning: By: Chin V. UlamChin Villanueva UlamОценок пока нет
- Health EducationДокумент5 страницHealth EducationMichellin Lara VergaraОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Special ChildrenДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Special Childrenharas_dcsaisОценок пока нет
- General Description of Client: A. Nursing Health HistoryДокумент3 страницыGeneral Description of Client: A. Nursing Health HistoryDianneОценок пока нет
- Acute Gastroenteritis With Severe DehydrationДокумент22 страницыAcute Gastroenteritis With Severe DehydrationCess Dunwan100% (1)
- NCP Risk InfectionДокумент1 страницаNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiОценок пока нет
- Ambeguia Elijah - BulSU-OP-CON-23F10-Assessment-Data-Base - Part1Документ11 страницAmbeguia Elijah - BulSU-OP-CON-23F10-Assessment-Data-Base - Part1Ambeguia ElijahОценок пока нет
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Документ6 страницDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogОценок пока нет
- Nursing History and Gordon'sДокумент2 страницыNursing History and Gordon'sCarlo bersamiraОценок пока нет
- GordonДокумент6 страницGordonKristine Joy EbordeОценок пока нет
- SJMC.x-prioritized Nursing ProblemsДокумент8 страницSJMC.x-prioritized Nursing ProblemsKatherine_Chyr_9112Оценок пока нет
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanДокумент3 страницыCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- A Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanДокумент1 страницаA Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanJulius Caesar ColladoОценок пока нет
- Geria Rle Week 6 Pain 1Документ1 страницаGeria Rle Week 6 Pain 1Maica LectanaОценок пока нет
- Gordon'S Functional Health Patterns Illness Scientific Rationale Before CurrentДокумент3 страницыGordon'S Functional Health Patterns Illness Scientific Rationale Before CurrentGen Rodriguez100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug StudyLorraine Tuesday BuenviajeОценок пока нет
- GeriaДокумент2 страницыGeriaJackRolunaBernalesОценок пока нет
- APOLONIO, JC - Natural Theory - Thomas AquinasДокумент3 страницыAPOLONIO, JC - Natural Theory - Thomas AquinasJustin ApolonioОценок пока нет
- Case StudyДокумент17 страницCase StudyNikko DioОценок пока нет
- Health Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismДокумент25 страницHealth Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismKim DajaoОценок пока нет
- Reflection On Feeding Elderly ClientsДокумент2 страницыReflection On Feeding Elderly ClientsLaydee GiaAmОценок пока нет
- Complications in PregnancyДокумент36 страницComplications in PregnancyJADE PATEGAОценок пока нет
- Reflection Paper (A Vow To Cherish)Документ1 страницаReflection Paper (A Vow To Cherish)Mikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Case in DutyДокумент1 страницаCase in DutyMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Health Teaching Plan 1Документ5 страницHealth Teaching Plan 1Mikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Reflection-A Vow To CherishДокумент2 страницыReflection-A Vow To CherishMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon0% (1)
- Date Time Client's Printed Name With Signature Clinical InstructorДокумент1 страницаDate Time Client's Printed Name With Signature Clinical InstructorMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Hyperthermia NCPДокумент1 страницаHyperthermia NCPMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Pharma Long Quiz - KeyДокумент3 страницыPharma Long Quiz - KeyMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Page 18Документ1 страницаPage 18Mikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- NPI Feb2,7 And8Документ14 страницNPI Feb2,7 And8Mikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- MSE Ko PoДокумент2 страницыMSE Ko PoMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Schematic Diagram: Precipitating PredisposingДокумент4 страницыSchematic Diagram: Precipitating PredisposingMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- VI. Laboratory Results Date Laboratory Procedure Component Normal Finding Actual Findings Interpretation and Analysis 04/18/2013Документ3 страницыVI. Laboratory Results Date Laboratory Procedure Component Normal Finding Actual Findings Interpretation and Analysis 04/18/2013Mikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Ncp3rdrot DocxsДокумент4 страницыNcp3rdrot DocxsMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconОценок пока нет
- Cargo ManagementДокумент45 страницCargo ManagementShubham Chaurasia75% (8)
- TM-8000 HD Manual PDFДокумент37 страницTM-8000 HD Manual PDFRoxana BirtumОценок пока нет
- CapstoneДокумент23 страницыCapstoneA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonОценок пока нет
- 41z S4hana2021 Set-Up en XXДокумент46 страниц41z S4hana2021 Set-Up en XXHussain MulthazimОценок пока нет
- Process Costing Exercises Series 1Документ23 страницыProcess Costing Exercises Series 1sarahbeeОценок пока нет
- Ensemble Averaging (Machine Learning)Документ3 страницыEnsemble Averaging (Machine Learning)emma698Оценок пока нет
- 4 Force & ExtensionДокумент13 страниц4 Force & ExtensionSelwah Hj AkipОценок пока нет
- OurCatholicFaith PowerPoint Chapter1Документ21 страницаOurCatholicFaith PowerPoint Chapter1VinОценок пока нет
- IV. Network Modeling, Simple SystemДокумент16 страницIV. Network Modeling, Simple SystemJaya BayuОценок пока нет
- Effects of Climate ChangeДокумент3 страницыEffects of Climate Changejiofjij100% (1)
- The Passion For Cacti and Other Succulents: June 2017Документ140 страницThe Passion For Cacti and Other Succulents: June 2017golf2010Оценок пока нет
- Math COT 3Документ18 страницMath COT 3Icy Mae SenadosОценок пока нет
- Table Equivalent Schedule 40 Steel PipeДокумент1 страницаTable Equivalent Schedule 40 Steel PipeorisОценок пока нет
- Awakened Citizen Programme-Report-class VII-2014Документ4 страницыAwakened Citizen Programme-Report-class VII-2014bhsgeneral r m saraswathi50% (4)
- Someone Who Believes in YouДокумент1 страницаSomeone Who Believes in YouMANOLO C. LUCENECIOОценок пока нет
- Tesla Coil ProjectДокумент8 страницTesla Coil ProjectShivam singhОценок пока нет
- Tugas Dikumpulkan Pada Hari Sabtu, 11 April 2020. Apabila Email Bermasalah Dapat Mengirimkan Via WA PribadiДокумент4 страницыTugas Dikumpulkan Pada Hari Sabtu, 11 April 2020. Apabila Email Bermasalah Dapat Mengirimkan Via WA PribadiFebry SugiantaraОценок пока нет
- Rekomendasi AnimeДокумент11 страницRekomendasi Animeosvaldo manurungОценок пока нет
- Bulacan Agricultural State College: Lesson Plan in Science 4 Life Cycle of Humans, Animals and PlantsДокумент6 страницBulacan Agricultural State College: Lesson Plan in Science 4 Life Cycle of Humans, Animals and PlantsHarmonica PellazarОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Vitae - RadikaДокумент3 страницыCurriculum Vitae - RadikaradikahendryОценок пока нет
- The Acceptability of Rubber Tree Sap (A As An Alternative Roof SealantДокумент7 страницThe Acceptability of Rubber Tree Sap (A As An Alternative Roof SealantHannilyn Caldeo100% (2)
- Pediatric EmergenciesДокумент47 страницPediatric EmergenciesahmedОценок пока нет
- De Vault 1996Документ22 страницыDe Vault 1996Harumi OOОценок пока нет
- PPT DIARHEA IN CHILDRENДокумент31 страницаPPT DIARHEA IN CHILDRENRifka AnisaОценок пока нет
- PIX4D Simply PowerfulДокумент43 страницыPIX4D Simply PowerfulJUAN BAQUEROОценок пока нет
- Save Water SpeechДокумент4 страницыSave Water SpeechHari Prakash Shukla0% (1)
- Dual Op Amp and Voltage Reference Ap4310/AДокумент12 страницDual Op Amp and Voltage Reference Ap4310/AМихаил ЯненкоОценок пока нет
- Bảng giá FLUKEДокумент18 страницBảng giá FLUKEVăn Long NguyênОценок пока нет
- Anxiety Disorders - Causes, Types, Symptoms, & TreatmentsДокумент5 страницAnxiety Disorders - Causes, Types, Symptoms, & Treatmentsrehaan662Оценок пока нет
- Flow Chart - QCДокумент2 страницыFlow Chart - QCKarthikeyan Shanmugavel100% (1)