Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
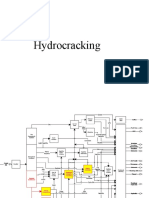
Manufacture of NaphthalenMANUFACTURE OF NAPHTHALENE
Загружено:
Manoj RanjanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Manufacture of NaphthalenMANUFACTURE OF NAPHTHALENE
Загружено:
Manoj RanjanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MANUFACTURE OF NAPHTHALENE
Plant Safety Introduction The significance of Safety & Health in chemical industries has been a vital issue in achieving productivity and an edge in the competitive world. All applicable laws and regulations on environmental protection or plant and industrial safety must be fully complied with. Compliance with all legislation to protect human beings and the environment is one of the companys basic tenets for both legal and ethical reasons. This applies to our products as well as to our processes.
Areas of Concern Dangerous Materials i)Explosives ii) Gases iii) Inflammable Liquids iv) Inflammable Solids v) Oxidising substances vi) Toxic and Infectious substances vii)Radio Active Substances viii)Corrosive Substances ix)Miscellaneous Dangerous Substances Hazards Of Pressure Vessels 1.Leakage or Bursting of Pressure Vessels 2.Design defects 3.Failure of Relief Systems 4.Lack of hydraulic testing. 5. Lack of Proper Instrumentation or Instrumentation Failure 6.Lack of N.D.Tests 7.Corrosion of Vessels. 8. Lack of routine inspections 9. Attempt of Pneumatic testing Hazardous Chemical Reactions Understanding about the behaviours of reactions and adopting precautionary and emergency measures. Hazards of Unit operations Understanding the hazards inherent in each unit operation and adopting precautionary and emergency measures
Heat Transfer
Surface fouling and leakage, Miscalculation in scaling, Mixing of flu
Size Reduction
Dust explosions, Dust release etc.
Flammable Gases, Vapours And Dust Hazards Identification of potential areas, where possibility of flammable mixture are possible. Efforts to avoid hazardous mixtures, by inert gas purging and other methods. Declaring hazard zones and providing flame proof electrical fittings and equipments. Providing Explosion Vents in spaces with possibility of air-vapour mixtures. Explosive meter testing. Providing adequate fire control devices. Providing arrangements to avoid static sparks. Etc.
Health Hazards Identification of potential health hazards. Assessment of levels of physical and chemical health hazards. Control of hazards by various techniques Adequate awareness among the workers. Periodic medical examination of the workers. Personal protection for occasional exposures. Proper hygiene and decontamination facilities. etc.
Entry into Confined Spaces 1.Oxygen Deficiency 2. of Toxic Contamination 3. through Flammable electric
Environment4.Possibility
Electrocutions
equipments5.Possibility of Toxic gas generation during the work 6.Lack of Ventilation 7.Difficulty in welfare monitoring 8.Failure to escape on emergency 9.Combustible Substances
Hazards Due To Corrosion Weakening and falling of structures and sheds. Falling of workers from height due to breaking of raised platforms, hand rails, toe boards, stairs and ladders.
Spills and toxic releases from pipelines due to corrosion. Leakages and bursting of vessels due to corrosion. Corrosion monitoring and control. Testing and inspection of vessels and structures to ensure safety. Hazards Due To Instrument Failures Absence of fail safety instruments. Lack of interlocks and trip systems. Human failures in manual and semi automatic operations. Need for safety analysis of the instrumentation systems
General Safety Rules Smoking is not allowed in any part of the refinery area except in smoking booths. Use of PPE is mandatory in the plant area. Before entering deposit all the matches, lighter or any other spark producing device. Only DCP or CO2 extinguishers are to be used in cause of a fire around electrical equipment. Never enter work area without safety helmet. When dangerous or unsafe condition is observed report to the supervisor or fire and safety division. Job area should be cleaned as soon as job is completed. Always use walkways instead of shortcuts. All stairways, platforms and walkways must be kept clean at all times. Compressed air must not be used except for process and system requirements. Never look directly into the arc produced while welding without proper eye protection. Defective equipment of any kind should not be used. Keep the access to fire fighting equipment free of obstructions as these are required to be used in emergencies. Polyester or nylon clothing should not be worn while on duty as these create hazards of static charge.
Protruding nails should be pulled out or bent over. Goggles or shields must be used when working under any circumstances when there are possible eye hazards. All stairways, platforms and walkways must be kept clean at all times. Compressed air must not be used except for process and system requirements. Never look directly into the arc produced while welding without proper eye protection. Defective equipment of any kind should not be used. Keep the access to fire fighting equipment free of obstructions as these are required to be used in emergencies. Polyester or nylon clothing should not be worn while on duty as these create hazards of static charge. Protruding nails should be pulled out or bent over. Goggles or shields must be used when working under any circumstances when there are possible eye hazards. When working around moving machinery the wearing of loose clothing such as lunges, dhoti etc are strictly prohibited. Vehicles of all types must be equipped with approved type of spark arrests and muffler system before entering in the production area. Protective valve caps must be placed on all gas cylinders except when in use. Do not enter into enclosed places without strictly observing the defined precautions. Do not touch hot pipes without wearing suitable protective clothing. Wear ear protection in areas of high noise levels.
Safety Signs
Plant Layout Introduction A plant layout study is an engineering study used to analyze different physical configurations for an manufacturing plant. It is also known as Facilities Planning and Layout. A suitable site must be found for a new project, and the site and equipment layout planned. Provision must be made for the ancillary buildings and services needed for plant operation and for the environmentally acceptable disposal of effluent. Plant layout refers to the arrangement of physical facilities such as machinery, equipment, furniture etc. within the factory building in such a manner so as to have quickest flow of material at the lowest cost and with the least amount of handling in processing the product from the receipt of material to the shipment of the finished product. Factors affecting plant layout While deciding a factory or unit or establishment or store, we should keep the following factors in mind: 1) Location with respect to the market area. 2) Raw material supply. 3) Transport facility. 4) Availability of labour. 5) Availability of utilities: water, fuel, power. 6) Availability of suitable land. 7) Environmental impact and effluent disposal. 8) Local community considerations. 9) Climate. 10) Political and strategic considerations.
Cost Estimation Estimation of total capital investment The total investment I involves :Fixed investment in process area IF Investment in auxiliary services IA Investment in working capital IW i.e. I = IF + IA + IW The approximate cost of various equipments used in the proposed plant are:Equipment No. Cost ( Rs. Lakh)
Gas Stripper
360
Hear Exchanger
300
Reactor
150
Equipment
Nos.
Cost (Rs. Lakh
Furnace
120
Separator
200
Fractionator
350
Miscellaneous
700
Direct Cost Factors
Items
Cost (Rs. Lakh)
Purchased equipment cost
250
Equipment installation
80
Insulation
60
Instrumentation
300
Total Direct Cost = ((Equipment Cost)*(Direct Cost Factor))/100 = (3160*945)/100 = Rs. 20601 Lakh
Indirect Cost Factors
Indirect cost = ((Direct cost)*(Indirect cost factor))/100 = (20601*156)/100 = Rs. 32137.56 Lakh Total fixed investment IF = Total direct cost + Indirect cost = 20601 + 32137.56 = Rs. 52738.56 Lakh
Auxiliary Investment Items such as steam generators, fuel stations & fire protection facilities are commonly stationed outside the process area & serve the system under consideration.
Items
% of total installed cost
Investment total fixed Auxiliary building Water supply Electric main substation Process waste system Raw material storage Fire protection Roads Sanitary & waste disposal
100 5 2 1.5 1 1 0.7 0.5 0.2
Auxiliary cost (IA) = ((Total fixed investment)*(Auxiliary cost factor))/100 = (52738.56*112.3)/100 = Rs. 59225.4 Lakh Total installed cost = Total fixed investment + Auxiliary cost = 52738.56+59225.4 = Rs. 111963.96 Lakh
Working Capital This is the capital fixed up in the interest of the system in the form of ready cash to meet operating expenses, inventories of raw materials & the products. The working capital may conveniently be assumed as 15% of total investment made in plant. Working capital =111963.96*15/100 = Rs. 16794.59 Lakh Total capital investment = Total installed Cost + Working capital = Rs. 128758.55 Lakh
Estimation of manufacturing cost The manufacturing cost can be divided into three items a) Proportional to total investment b) Anticipated production rate c) Labor requirement
Proportional to total investment This includes the factors which are independent of the production rate & proportional to the fixed investments such as : Maintenance Property tax Insurance Safety expense General services Administrative services
This can be taken as 15% per year of total installed cost i.e. 52738.56*15/100 = Rs. 7910.784 Lakh Anticipated production rate The factors proportional to production rate are : Raw material cost Utilities cost Maintenance cost Chemical, warehouse and shipping
Assuming that the cost proportional to production rate is nearly 60% of the total capital investment. i.e. 128758.55*60/100 = Rs. 77255.13 Lakh Labor Requirement The manufacturing cost proportional to labor might amount to 10% of total manufacturing cost. i.e. (7910.784+ 77255.13)*10/100 = Rs. 8516.59 Lakh
Total Manufacturing cost = 7910.78 + 77255.13 + 8516.59 = Rs. 93682.5Lakh Sale price fixation Rs. 80/Kg. Profitability analysis Total sales income = 80*2000 = Rs. 160000 Lakh Depreciation Using sinking fund method. R = (V-Vs)(i/((1+i)^n-1)) R = Uniform annual payment at the end of each year V = Installed cost of plant Vs = Salvage value of plant after n years n = Life period (Assumed to be 15 years)
i = Annual interest rate (taken as 15%) R = (11963.96-0)(0.15/((1+0.15)^15-1)) = 162296.39*0.021 = Rs. 251.24 Lakh Gross profit Gross profit = Net income from annual sales Annual manufacturing cost = 160000 93682.5 = Rs. 66317.5 Lakh Net profit rate It is defined as the expected annual return on investment after deducting depreciation and taxes. Tax rate is assumed to be 40% Net Profit = Gross profit Depreciation (Gross Profit*Tax rate) = 66317.5 251.24 (66317.5*40/100) = 20795.11 9681.33 = Rs. 39539.26 Lakh
Annual rate of return Annual percent return on the total initial investment after income taxes = (Net profit/Total installed cost)*100 = (39539.26/111963.96)*100 = 35.31% Payout period Payout period = Total installed cost/(Depreciation + Net profit) = 111963.96/(251.24 + 39539.26) = 2.813 years
References Plant Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers Author: Max Peters, Klaus Timmerhaus, Ronald West
Вам также может понравиться
- Coal TarInfoДокумент3 страницыCoal TarInfoNakkolopОценок пока нет
- Karim Benhabib, Pierre Faure, Michel Sardin, Marie-Odile SimonnotДокумент8 страницKarim Benhabib, Pierre Faure, Michel Sardin, Marie-Odile SimonnotAsri GaniОценок пока нет
- FGC Group LLC - Consulting & Engineering - Products - Thermal Processing Equipment - Activated Carbon Plant PDFДокумент3 страницыFGC Group LLC - Consulting & Engineering - Products - Thermal Processing Equipment - Activated Carbon Plant PDFCleverSeyramKetekuОценок пока нет
- Oxidation of Organic Compounds: Medium Effects in Radical ReactionsОт EverandOxidation of Organic Compounds: Medium Effects in Radical ReactionsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Utilization of Fly Ash and Rice Husk Ash As A Supplement To Concrete Materials - A Critical ReviewДокумент9 страницUtilization of Fly Ash and Rice Husk Ash As A Supplement To Concrete Materials - A Critical Reviewijetrm journalОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Production From The Low-TemperatureДокумент8 страницHydrogen Production From The Low-TemperatureAndres Acosta100% (1)
- 19.-Pyrolysis FurnaceДокумент5 страниц19.-Pyrolysis FurnaceWilfredo PastranaОценок пока нет
- Monohydric Alcohols Their Ethers and Esters Sulphur Analogues Nitrogen Derivatives Organometallic Compounds: A Modern Comprehensive TreatiseОт EverandMonohydric Alcohols Their Ethers and Esters Sulphur Analogues Nitrogen Derivatives Organometallic Compounds: A Modern Comprehensive TreatiseОценок пока нет
- Urea 6Документ28 страницUrea 6Pragati Kshatriya100% (1)
- 4 - Watkinson - Coke Formation - F - FoulingДокумент8 страниц4 - Watkinson - Coke Formation - F - Foulingeragorn100% (1)
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Oxbow Calcining LLCДокумент4 страницыMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Oxbow Calcining LLCFinka Pertama PutriОценок пока нет
- Aspek Keselamatan Pada Aplikasi Reaktor Nuklir Suhu Tinggi Untuk Proses Steam Reforming Gas AlamДокумент9 страницAspek Keselamatan Pada Aplikasi Reaktor Nuklir Suhu Tinggi Untuk Proses Steam Reforming Gas AlamhasmiatiОценок пока нет
- KeithwrightДокумент37 страницKeithwrightSumit GuptaОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Studies of Ketazine Formation PDFДокумент6 страницKinetic Studies of Ketazine Formation PDFkamesh_che009100% (1)
- Coke CVДокумент4 страницыCoke CVAshutosh MishraОценок пока нет
- Drive Failure and Interruption in SCP Machines of Battery 567, Coke PlantДокумент37 страницDrive Failure and Interruption in SCP Machines of Battery 567, Coke Plantnarendramaharana39Оценок пока нет
- Strat Up Process PlantДокумент383 страницыStrat Up Process PlantGeorge Van Bommel50% (2)
- Coke Oven Life Prolongation - A Multidisciplinary ApproachДокумент31 страницаCoke Oven Life Prolongation - A Multidisciplinary ApproachJorge MadiasОценок пока нет
- CHMT 2009 Week 5 Coal PropertiesДокумент38 страницCHMT 2009 Week 5 Coal PropertiesTiisetso MokwaneОценок пока нет
- Hatch and Northern Graphite PaperДокумент6 страницHatch and Northern Graphite PaperNarayana Murthy GadiОценок пока нет
- Cement Industry Environmental Consortium: Carbon Capture and Reuse ProjectДокумент27 страницCement Industry Environmental Consortium: Carbon Capture and Reuse ProjectHala RiadОценок пока нет
- Waste Water - Coke PlantДокумент13 страницWaste Water - Coke PlantSejla Becirovic Cehajic100% (1)
- Unit IvДокумент21 страницаUnit IvadityarajchikkalaОценок пока нет
- Fly Ash Journal PDFДокумент10 страницFly Ash Journal PDFMagendranОценок пока нет
- Cement manufacturing emissions guidelinesДокумент4 страницыCement manufacturing emissions guidelinesSambhu YadavОценок пока нет
- Energy Saving Denox - Catalysts: Ruedi Frey, Hitachi Zosen Inova, ZürichДокумент30 страницEnergy Saving Denox - Catalysts: Ruedi Frey, Hitachi Zosen Inova, Zürichnay denОценок пока нет
- Indian Oil Cooperation LTD (Assam Oil Division Digboi Refinery)Документ64 страницыIndian Oil Cooperation LTD (Assam Oil Division Digboi Refinery)NingSeng SingphoОценок пока нет
- FirstДокумент6 страницFirstreddyОценок пока нет
- Preparation of Catalysts II: Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous CatalystsОт EverandPreparation of Catalysts II: Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous CatalystsОценок пока нет
- CO2 Capture Over K2CO3 MgO Al2O3 Dry Sorbent in A Fluidized BedДокумент8 страницCO2 Capture Over K2CO3 MgO Al2O3 Dry Sorbent in A Fluidized BedFarah Talib Al-sudaniОценок пока нет
- Cement: Dr. Prashant Mehta Assistant Professor, National Law University, JodhpurДокумент26 страницCement: Dr. Prashant Mehta Assistant Professor, National Law University, Jodhpurtesfayregs gebretsadikОценок пока нет
- HydrocrackingДокумент33 страницыHydrocrackingNikita SeleznevОценок пока нет
- Polymer Composite Systems in Pipeline Repair: Design, Manufacture, Application, and Environmental ImpactsОт EverandPolymer Composite Systems in Pipeline Repair: Design, Manufacture, Application, and Environmental ImpactsSanjay Mavinkere RangappaОценок пока нет
- Water Quality Control Technology For Thermal Power PlantsДокумент7 страницWater Quality Control Technology For Thermal Power PlantsGiovanniStirelliОценок пока нет
- Successful Design of Catalysts: Future Requirements and DevelopmentОт EverandSuccessful Design of Catalysts: Future Requirements and DevelopmentОценок пока нет
- IOCL Summer Training Presentation on Barauni RefineryДокумент16 страницIOCL Summer Training Presentation on Barauni Refineryamish umar0% (1)
- ECUST PresentДокумент35 страницECUST Presentupruss63Оценок пока нет
- Benefits of Platinum-Rhodium Catalyst in Nitric Acid ProductionДокумент5 страницBenefits of Platinum-Rhodium Catalyst in Nitric Acid ProductionBorith pangОценок пока нет
- State of the Art in Steel Mill Dust RecyclingДокумент6 страницState of the Art in Steel Mill Dust RecyclingCeyhun TatarОценок пока нет
- 30 Full Turnkey CapabilitiesДокумент12 страниц30 Full Turnkey CapabilitiesMahazan Ab. GhaniОценок пока нет
- SOP for Safe Quenching of Pyrophoric SubstancesДокумент5 страницSOP for Safe Quenching of Pyrophoric Substancesdhavalesh1Оценок пока нет
- Components of Coal AshДокумент4 страницыComponents of Coal AshDulguun BayОценок пока нет
- Energy and Mass Balance of Incinerator PDFДокумент11 страницEnergy and Mass Balance of Incinerator PDFdrop shipОценок пока нет
- Team 3Документ21 страницаTeam 3lux0008Оценок пока нет
- Henry's Law Constants Publishedl VersionДокумент10 страницHenry's Law Constants Publishedl VersionGuerrero OmarОценок пока нет
- CO2 SMR White Paper - Shell Catalysts & TechnologiesДокумент12 страницCO2 SMR White Paper - Shell Catalysts & Technologiespierre-françois Le BouilleОценок пока нет
- Coal Gasification: HistoryДокумент3 страницыCoal Gasification: HistoryTalha Jamil MalikОценок пока нет
- Classification of PetrochemicalsДокумент5 страницClassification of PetrochemicalsMarvin Paras0% (1)
- Coking and Thermal ProcessesДокумент8 страницCoking and Thermal ProcessesWulandariОценок пока нет
- Cdi - AliДокумент34 страницыCdi - AliNKSОценок пока нет
- Renewable Energy Resources: Introduction & Economic Analysis of A Gasification PlantДокумент36 страницRenewable Energy Resources: Introduction & Economic Analysis of A Gasification PlantfaizanОценок пока нет
- 1097 2301 Univar E Detergents Nordic Brochure 4Документ12 страниц1097 2301 Univar E Detergents Nordic Brochure 4troity100% (2)
- Aits Open Test Jee Paper 1Документ19 страницAits Open Test Jee Paper 1Viny GОценок пока нет
- Dosing PumpsДокумент2 страницыDosing PumpsSherlockОценок пока нет
- Calculations of Elastic Moduli of Polymer Crystals." II. TeryleneДокумент11 страницCalculations of Elastic Moduli of Polymer Crystals." II. Teryleneapi-3733260Оценок пока нет
- Solid, Liquid, Gas Explanation TextДокумент2 страницыSolid, Liquid, Gas Explanation Textnettexts100% (1)
- Separation NotesДокумент3 страницыSeparation NotesMeetaDeviОценок пока нет
- Differential Thermal Analysis (Dta)Документ21 страницаDifferential Thermal Analysis (Dta)Shaise Jacob100% (6)
- Rucofin GWG 200: Composition UsesДокумент2 страницыRucofin GWG 200: Composition UsesConsultora2Оценок пока нет
- Precipitation-Hardening Bolting (UNS N07718) For High Temperature ServiceДокумент4 страницыPrecipitation-Hardening Bolting (UNS N07718) For High Temperature ServiceJose Anisio SilvaОценок пока нет
- APL - Emulsifiers Products ListДокумент2 страницыAPL - Emulsifiers Products Listshreeket3953Оценок пока нет
- 02-1 Sampling Challenges in Laterite - Waheed AhmadДокумент31 страница02-1 Sampling Challenges in Laterite - Waheed AhmadDinanОценок пока нет
- Primus Operation FS6 To FS23Документ50 страницPrimus Operation FS6 To FS23Arun George50% (2)
- BC34.1 E9 Determination of Acid Value of FatsДокумент3 страницыBC34.1 E9 Determination of Acid Value of FatsGlenn Vincent Tumimbang96% (26)
- Prediction of Adhesion from Lewis Acid Base MeasurementsДокумент6 страницPrediction of Adhesion from Lewis Acid Base MeasurementsGabriel MendivilОценок пока нет
- Sudharshan Seneviratne 1995Документ41 страницаSudharshan Seneviratne 1995darshanieratnawalliОценок пока нет
- GSAP - Shell HelixДокумент16 страницGSAP - Shell HelixJoseph Rubyanto SudrajadОценок пока нет
- Hotel FireДокумент94 страницыHotel FireCoara OvidiuОценок пока нет
- Thread: Threads RequirementДокумент17 страницThread: Threads RequirementVarun GuptaОценок пока нет
- نرخ نامه1Документ7 страницنرخ نامه1Farhad KaweshОценок пока нет
- 01 Well Cementing - Day 1 PDFДокумент131 страница01 Well Cementing - Day 1 PDFام فاطمة البطاط100% (1)
- Tds 071 Rev 05 Residhere Am 140 SДокумент1 страницаTds 071 Rev 05 Residhere Am 140 Sاحمد عدنانОценок пока нет
- RNA, DNA Transcription and RNA TranslationДокумент5 страницRNA, DNA Transcription and RNA TranslationHassan AljaberiОценок пока нет
- Toksikologi PDFДокумент134 страницыToksikologi PDFPurwani Ni NyomanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 MassMicroДокумент25 страницLecture 2 MassMicroPelin KınıkОценок пока нет
- Iffco ProjectДокумент113 страницIffco ProjectShefali ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Physics 107 Problem 10.2 Madelung Constant NaClДокумент12 страницPhysics 107 Problem 10.2 Madelung Constant NaClJay Sharma75% (4)
- Cirp MSDSДокумент2 страницыCirp MSDSsharemw100% (2)
- All about the Properties and Uses of Common StonesДокумент41 страницаAll about the Properties and Uses of Common StonesBhavya MewadaОценок пока нет
- ISO 17746-2016 Steel Wire Rope Net Panels and RollsДокумент24 страницыISO 17746-2016 Steel Wire Rope Net Panels and RollsOctavian Miclescu100% (1)