Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bia Writeup
Загружено:
Sadaf KushИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bia Writeup
Загружено:
Sadaf KushАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Overview
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) are a class of electronic meeting systems, a collaboration technology designed to support meetings and group work .[1] GDSS are distinct from computer supported cooperative work (CSCW) technologies as GDSS are more focused on task support, whereas CSCW tools provide general communication support . Group Decision Support Systems are categorized within a time-place paradigm. Different features may be required for synchronous vs asynchronous communication, as well as local vs distant.
Introduction
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) are a class of electronic meeting systems, a collaboration technology designed to support meetings and group work .GDSS are distinct from computer supported cooperative work (CSCW) technologies as GDSS are more focused on task support, whereas CSCW tools provide general communication support. The following are the major characteristics of a Group Decision Support Systems:
Its aim is to support the process of the group decision makers by offering automation of sub processes by using tools of information technology
It is a specially designed information system, not merely a configuration of already-existing system components. It can be designed to address one type of problem or different group-level organizational decisions.
It encourages generation of ideas, resolution of conflicts, and freedom of expression. It contains built-in mechanisms which discourage growth of the negative group behaviors, like groupthink and destructive conflict miscommunication. The first generation of Group Decision Support Systems was designed to support face-to-face meetings in a decision room. Today, support is provided mostly over the Web to virtual groups.
The group can meet at the same time or at different times by using e-mail, sending documents, and reading transaction logs. GDSS is particularly useful as the controversial decisions should be made. Group Decision Support Systems applications require a facilitator when done in one room or a coordinator or leader when done using virtual meetings. GDSS could enhance the decision-making process in several methods or ways.
GDSS vs DSS
GDSS and DSS are computer based information system that may assist decision making processes within a group, company or office. By using GDSS and DSS, the company can speed up decision making process allowing more time for employees to focus on particular issues. Learning and training can be promoted through this system.
GDSS GDSS or Group Decision Support System is a subclass or subcategory of DSS. It is defined as a computer based information system built to support and promotes positive group decision making. GDSS has three important components: software, which consists of the database with management capabilities for group decision making. Another component is the hardware and lastly the people. The latter will include the decision making participants.
DSS Meanwhile, DSS also known as Decision Support System is meant to affect how individuals decide or process decision making. Through the use of DSS, both human capabilities and computer capacities are maximized to result to one great positive decision. The system will provide assistance for the human element and not the sole decision maker. DSS also allows customization of the programs particularly the decision making capabilities to better suit individual needs.
Difference between GDSS and DSS GDSS is a computer based information system that focuses on the group while DSS focuses on an individual for instance, the manager or the supervisor. GDSS and DSS may have similar components in terms of hardware and software structures however, GDSS has a networking
2
technology that is best suited for group discussions or communication. DSS on the other hand, have technologies that are focused for a single user. GDSS maintenance involves a better system reliability and incomprehensible multi-user access compared to DSS because system failures in GDSS will involve a lot of individual. Through these programs or computer based information system, company or individual decision making capacities will be enhanced and hasten. This allows not only good communication system but also a positive outcome within a department, group, or company.
Similarities between GDSS and DSS
Both use models, data and user-friendly software Both are interactive with what-if capabilities Both use internal and external data Both allow the decision maker to take an active role Both have flexible systems Both have graphical output
Advantages of GDSS
Anonymity drive out fear leading to better decisions from a diverse hierarchy of decision makers Parallel Communication eliminate monopolizing providing increased participation, better decisions Automated record keeping no need to take notes, theyre automatically recorded Ability for virtual meetings only need hardware, software and people connected Portability - Can be set up to be portable laptop Global Potential - People can be connected across the world No need for a computer guru although some basic experience is a must
Disadvantages of GDSS
Costinfrastructure costs to provide the hardware and software/room/network connectivity can be very expensive
3
Security especially true when companies rent the facilities for GDSS; also, the facilitator may be a lower-level employee who may leak information to peers
Technical Failure power loss, loss of connectivity, relies heavily on bandwidth and LAN/WAN infrastructure properly setup system should minimize this risk
Keyboarding Skills reduced participation may result due to frustration Training learning curve is present for users, varies by situation Perception of messages lack of verbal communication could lead to misinterpretation
Typical GDSS Process
1) Group Leader (and Facilitator?) select software, develop agenda 2) Participants meet (in decision room/Internet) and are given a task. 3) Participants generate ideas brainstorm anonymously 4) Facilitator organize ideas into categories (different for user-driven software) 5) Discussion and prioritization may involve ranking by some criteria and/or rating to the facilitators scale 6) Repeat Steps 3, 4, 5 as necessary 7) Reach decision 8) Recommend providing feedback on decision and results to all involved
Research
Significant research supports measuring impacts of:
Adapting human factors for these technologies, Facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration, and Promoting effective organizational learning.
In the 1980s, a commercial joint venture between IBM and the U.S. Department of Defense created a new form of software as a solution to improve the decision alignment between various branches of the armed forces. This first commercial (DOS-based) technology was developed by behavioral scientist Dr. Jerry Wagner and was called VisionQuest. In the 1990's while at the University of Texas, Austin campus, Dr. Wagner secured venture capital funding to develop new GDSS software, this time with the end goal of leveraging the Internet (which was becoming mainstream by now). The new technology was WebIQ and is now called WIQ (by ynSyte).[1] Academic work on Group Decision Support Systems was largely led in the 1980s and 1990s by the University of Minnesota (the SAMM System) and the University of Arizona (PLEXSYS, later renamed GroupSystems). The Arizona research software was spun off as Ventana Corporation (now known as GroupSystems Inc.). The University of Arizona researchers report both benefits and costs for their electronic meeting system.[2] The benefits, or process gains, from using a GDSS (over more traditional group techniques) are:
More precise communication; Synergy: members are empowered to build on ideas of others; More objective evaluation of ideas; Stimulation of individuals to increase participation; Learning: group members imitate and learn from successful behaviors of others.
The costs, or process losses, from using a GDSS (instead of more traditional group techniques) are:
More free riding; More information overload; More flaming; Slower feedback; Fewer information cues; Incomplete use of information.
However, the researchers found that GDSS over traditional group techniques limited or reduced the following process losses:
Less attention blocking Less conformance pressure Less airtime fragmentation Less attenuation blocking Less socializing Less individual domination
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Arduino Based Heart Rate Monitor ProjectДокумент7 страницArduino Based Heart Rate Monitor ProjectMaged Alqubati100% (1)
- Gas Reservoir Engineering Application ToolkitДокумент20 страницGas Reservoir Engineering Application Toolkitnishant41288100% (1)
- On Chip Networks - Second EditionДокумент212 страницOn Chip Networks - Second EditionAditya Nair100% (3)
- 5 Entrepreneurial Leadership CharacteristicsДокумент2 страницы5 Entrepreneurial Leadership CharacteristicsSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- BLE Prinicipal OA in Matter Oft:: DelhiДокумент52 страницыBLE Prinicipal OA in Matter Oft:: DelhiSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Financing and Developing PACSДокумент3 страницыFinancing and Developing PACSSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Delhi Development Authority Recruitment Cell: Commissioner (Personnel)Документ1 страницаDelhi Development Authority Recruitment Cell: Commissioner (Personnel)Sadaf KushОценок пока нет
- IGNOU 32nd ConvocationДокумент1 страницаIGNOU 32nd ConvocationSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Awarded To Manmohan Singh: Indira Gandhi Prize For Peace, Disarmament and DevelopmentДокумент1 страницаAwarded To Manmohan Singh: Indira Gandhi Prize For Peace, Disarmament and DevelopmentSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- New RRs - Group-CДокумент36 страницNew RRs - Group-CSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Tentative Work Schedule Event Tentative Dates Our TaskДокумент1 страницаTentative Work Schedule Event Tentative Dates Our TaskSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Bba Mom SyllabusДокумент86 страницBba Mom SyllabusSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- ESBD Financial MarketsДокумент1 страницаESBD Financial MarketsSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Objectives For Chapter 8 Price Floors and Ceilings: "Black Market" and "Gray Market"Документ8 страницObjectives For Chapter 8 Price Floors and Ceilings: "Black Market" and "Gray Market"Sadaf KushОценок пока нет
- S - G S, D: T Regorios Chool WarkaДокумент2 страницыS - G S, D: T Regorios Chool WarkaSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- The Horror of 16/12: Via BingДокумент34 страницыThe Horror of 16/12: Via BingSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Business Behaving Badly - CartelsДокумент17 страницBusiness Behaving Badly - CartelsSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Poverty in India: Concepts, Measurement and TrendsДокумент8 страницPoverty in India: Concepts, Measurement and TrendsSadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Business Environment: Presented byДокумент22 страницыBusiness Environment: Presented bySadaf KushОценок пока нет
- Making A Quick Water Material in 3ds Max.: by Gerardo I. RamirezДокумент3 страницыMaking A Quick Water Material in 3ds Max.: by Gerardo I. Ramirezpalanisamy744Оценок пока нет
- DD Vstor40 LP x64 ptbUI2C3AДокумент6 страницDD Vstor40 LP x64 ptbUI2C3AwilsonnascОценок пока нет
- Surpac ReportingДокумент4 страницыSurpac ReportingDelfidelfi SatuОценок пока нет
- Koyo DL205 Power CalculationДокумент2 страницыKoyo DL205 Power CalculationiedmondОценок пока нет
- Siko Product OverviewДокумент20 страницSiko Product OverviewMECING LTDAОценок пока нет
- 2019 MUSE Conference - Educational Presentations - Rev May 2 2019Документ81 страница2019 MUSE Conference - Educational Presentations - Rev May 2 2019Michele LambertОценок пока нет
- Tutorial-3 With SolutionsДокумент3 страницыTutorial-3 With SolutionsSandesh RSОценок пока нет
- Sca-Library Acquisition ProgramДокумент9 страницSca-Library Acquisition ProgramCindy Basilio PinedaОценок пока нет
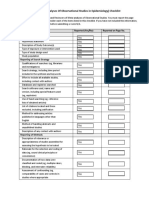
- MOOSE (Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) ChecklistДокумент2 страницыMOOSE (Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) ChecklistNesru Ahmed AkkichuОценок пока нет
- JDSU TrueSpeed Automated RFC-6349 TCP TestingДокумент36 страницJDSU TrueSpeed Automated RFC-6349 TCP TestingTakisОценок пока нет
- EAS6800+ High Quality Composite Video Encoder/Synchronizer and Analog Audio DemultiplexerДокумент90 страницEAS6800+ High Quality Composite Video Encoder/Synchronizer and Analog Audio DemultiplexerTechne PhobosОценок пока нет
- HP Pavilion & G42 Notebook As 011112Документ1 страницаHP Pavilion & G42 Notebook As 011112Syahril Adzim Md RejabОценок пока нет
- DS FT232HДокумент57 страницDS FT232HplwrlvzxaocrejwruoОценок пока нет
- Edc 4 UnitДокумент26 страницEdc 4 UnitAnonymous 6Ts3r7dwОценок пока нет
- Inv 27113Документ2 страницыInv 27113joakim KiambaОценок пока нет
- Igcse Ict Lessonplan 1Документ3 страницыIgcse Ict Lessonplan 1Chaima Ahmed GaidОценок пока нет
- Accurate Real Time Altitude Estimation PDFДокумент5 страницAccurate Real Time Altitude Estimation PDFMartin Manullang100% (1)
- AvPvT CCG CardlistДокумент5 страницAvPvT CCG CardlistDavid de VisserОценок пока нет
- Sub-GHz Wi-SUN Introduction v2.0Документ37 страницSub-GHz Wi-SUN Introduction v2.0Xiong ChwОценок пока нет
- Sony wx-850bt 900bt 900btm Ver.1.1Документ62 страницыSony wx-850bt 900bt 900btm Ver.1.1Zsolt CsalótzkyОценок пока нет
- Design of ExperimentsДокумент5 страницDesign of ExperimentsPhelelaniОценок пока нет
- CORBA Developer's Guide With XMLДокумент295 страницCORBA Developer's Guide With XMLDmitry SosnitskyОценок пока нет
- ZXDU68 B451 V6.0R20M02 DC Power System Quick Installation GuideДокумент7 страницZXDU68 B451 V6.0R20M02 DC Power System Quick Installation GuideVictor ArticaОценок пока нет
- Irfiz 34 NДокумент8 страницIrfiz 34 NBase de DatosОценок пока нет
- HP Moonshot Provisiong Manager User GuideДокумент44 страницыHP Moonshot Provisiong Manager User GuideBalasubramanian ReguramanОценок пока нет
- Treacy WiersemaДокумент7 страницTreacy WiersemaRiya BlanciaОценок пока нет
- WSDL Reading, A Beginner's GuideДокумент18 страницWSDL Reading, A Beginner's GuidePVParameswaranОценок пока нет