Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Certified AML - KYC Compliance Officer
Загружено:
Ricky MartinОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Certified AML - KYC Compliance Officer
Загружено:
Ricky MartinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer VS-1092
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer
Certificate Code VSVS-1092
Vskills certification in KYC (Know Your Customer) and Anti Money Laundering Operation, is one of the first certifications in this area of banking sector. A Vskills Certified AML/KYC Officer finds employment in banking and banking ancillary firms, security and audit firms, and other small and medium enterprises.
Why should one take this certification?
The certification is aimed at enhancing the quality of compliance with the directions of RBI in combating illegal operations and movement of funds through the use of banking channels. KYC and Anti Money Laundering operations have assumed added importance owing to the security risk that it poses to the country, and also to maintain the financial health of the institutions.
Who will benefit from taking this certification?
KYC and Anti Money Laundering certification is being increasingly taken by a large number of working professionals in banking and finance field. Also, students desirous of entering banking and finance sector, find this certification as a useful addition to their CV.
Test Details:
Duration: 60 minutes No. of questions: 50 Maximum marks: 50, Passing marks: 25 (50%); There is no negative marking in this module.
Fee Structure:
Rs. 2,500/- (Includes all taxes)
www.vskills.in
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer
Table of Content
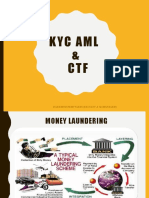
1. Money Laundering
1.1 What is Money Laundering? 1.2 Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PML Act) 1.3 Tainted Money or Dirty Money 1.4 Transfer of funds and washing of Dirty Money 1.5 Global phenomenon
2. Money Laundering: Some Methods used
2.1 Process of Money Laundering: Placement, Layering, Integration 2.2 Methods used in Money Laundering 2.3 Sources of tainted money 2.4 Common techniques employed
3. Legislation and international cooperation
3.1 Legislations in various countries against money laundering 3.2 Financial Action Task Force (FATF) 3.3 Anti Money Laundering measures in India 3.4 Tools required for prevention of Money Laundering
4. Role of correspondent correspondent banking
4.1 Information on Correspondent Bank 4.2 Anti money laundering policies of the correspondent bank
5. Know Your Customer Historical Perspective
5.1 Customer Profile 5.2 KYC Policies and RBI initiative 5.3 Some basic definitions and KYC origination 5.4 Transaction Profile screening 5.5 Organizational Structure in the bank
6. KYC Operating Guidelines
6.1 Customer Identification 6.2 Account opening process 6.3 Accounts of Companies Limited Companies, Proprietorship, Partnerships 6.4 Trusts, fiduciary relations, professional intermediaries 6.5 Joint Accounts 6.6 Suggested safegaurds 6.7 Existing Accounts 6.8 Inoperative Accounts 6.9 Monitoring of Accounts
www.vskills.in
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer
7. Internal Control and structure in banks
7.1 Roles and responsibilities of the Principal Officer 7.2 Roles and responsibilities of the staff 7.3 Roles and responsibilities of Internal Audit and Controls
8. Customer Risk Categorization (CRC)
8.1 Customer Risk 8.2 Need for Customer Risk Categorization 8.3 Customer Acceptance Policy (CAP) 8.4 Customer Identification Procedures 8.5 Customer due diligence
9. Reporting Obligations
9.1 Cash transaction reporting (CTR) 9.2 Counterfeit Currency Reporting (CCR) 9.3 Suspicious Transaction Report (STR)
10. Transaction Monitoring
10.1 Methods of monitoring 10.2 Suspicious transactions 10.3 Name Screening process 10.4 Wire Transfers 10.5 Preservation of records
11. Staff and Customer Awareness
11.1 Training methods 11.2 Assessments 11.3 Records of training 11.4 Importance of creating customer awareness
www.vskills.in
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer
Course Outline
Money Laundering: Laundering: Some Methods Used
Briefly explains the complex web of money laundering operations Various steps involved in money laundering like Placement physically placing bulk cash proceeds, Layering separating the proceeds of criminal activity from their origins, through layers of complex transactions, Integration providing a seemingly legitimate explanation to the illegal proceeds Various methods of money laundering like creating shell companies, front companies, offshore banking accounts, structuring the amounts, and hawala transactions Common sources of money laundering like drug trafficking, tax evasion, organized crime etc Studying the various markets in detail that absorb money laundering money like precious metals etc
Legislation and International International Cooperation
Several countries have come up with strict legislations to counter money laundering UK has come up with various legislations like Drug Trafficking Offences (1998), Criminal Justice Act (1988), Criminal Justice (Consolidation) (Scotland) Act (1995), Proceeds of Crime (Scotland) Act (1995), Criminal Justice (International Cooperation) Act (1990) USA has consistently come out with various acts , and since 9/11 has taken significant steps like USA Patriot Act 2001 giving substantial powers to law enforcing agencies to prevent cross border flow of funds that look suspicious Basel Principles have also addressed four areas that tackle money laundering i.e. customer identification, compliance with laws, cooperation with law enforcing agencies, adherence to the statement Financial Action Task Force (FATF) was established by G-7 and has come up with recommendations to help uncover money laundering techniques, to introduce counter manners, and to harmonize anti money laundering policies at an international level In India, The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (2002) addresses the problem of money laundering in conjunctions with other laws in existence RBI has also come out with certain guidelines for banks and financial institutions to prevent money laundering Tools are required to study the complex transactions and good software packages are needed along with high quality human resource
Role of Correspondent Banking
Importance of properly examining the correspondent bank with which transactions are happening
www.vskills.in
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer
Gathering all important information about the correspondent bank like other banks management, major business activities, level of KYC and AML norms, etc before extending correspondent facilities to the bank
Know Your Customer: Historical Perspective Perspective
Importance of KYC activities and appreciating the value of KYC processes in ensuring that the banking operations are safe and clean to help clients and bank personnel to conduct business, with comfort and confidence Customer Profile and what is the set of important information that needs to be collected Understanding the global case and countries that are deficient in KYC norms Initiatives taken by the RBI and their impact in the banking business. The RBIs approach has been chiefly to prevent banks from being used by criminal elements to launder money and to help banks know their customers and their financial transactions better Some of the KYC Policies laid down by RBI include Customer Acceptance Policy (CAP), Customer Identification Process, Monitoring of Customer Transactions and Risk Management RBI also suggests close monitoring of transactions like archival of profiles, scrutiny of unusual transactions, audit and compliance functions, reporting and training.
KYC: Operating Guidelines
Various guidelines related to customer identification in opening of accounts, monitoring customer transactions, risk management and other matters related to KYC standards. General operating guidelines for customer identification in opening of accounts as in the case of individuals, companies, partnerships, proprietorships, trusts and foundations Concept of an introducer and who can be an introducer and client accounts opened by professional intermediaries
Internal Control and Structure in bank
Internal control in terms of customer research, monitoring of cash transactions, monitoring remittances, and the parameters used for customer identification Customer research may involve desk research, discussions with customers, periodic calls to customers etc Research on customer may further be extended using softwares of the bank. Internal guidelines for new accounts, cash transactions, large value transfer of funds, monitoring remittances NRI Accounts become important in the light of FEMA, and KYC should be proper
www.vskills.in
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer
Identification parameters need to be established like transactions not consistent with customers usual business, incomplete/non disclosure of data by customer, unusual activity, suspicious fund transfer activity Check on bank employees and their lifestyle, employee discipline and confidentiality of internal control documents Roles and responsibilities of Board of Directors and senior management Appointment of Principal officer along with defining the roles and responsibilities, and formulation of appropriate procedures to prevent Money Laundering Roles and responsibilities of the staff and internal audit/ internal control
Customer Risk Categorization (CRC)
Meaning of Customer risk, and classification of customers in various buckets of risk. Various selection of parameters for risk categorization, determining the risk rating methodology, deciding on type of classification, use of various soft wares for risk categorization, and periodic review of CRC
Reporting Obligations
Under PMLA Act, 2002, certain obligations were cast on banking companies with regards to reporting of certain transactions. Banks are required to make reports of the following types : Cash Transaction Reporting (CTR), Counterfeit Currency Reporting (CCR), Suspicious Transaction Reporting (STR)
Transaction Transaction Monitoring
Transaction Monitoring is critical to AML/KYC efforts. Various methods of monitoring are studied like observation, analysis of exception reports, AML software, looking at suspicious transactions Rules for transaction monitoring and challenges for transaction monitoring Importance of software for transaction monitoring and features available for the software Scope and purpose of name screening and negative lists
Staff and Customer Awareness
Creating staff awareness of AML/KYC and allocating responsibility to top management, defining roles and responsibilities and obligations of staff Need for development appropriate training methods and using regular assessments to gauge performance Maintenance of regular records of training and assessment and why is it important to create customer awareness on AML
www.vskills.in
Certified AML/KYC Compliance Officer
Sample Questions
1. Money Laundering refers to ____________.
A. Tansfer of assets/cash from one account to another B. Conversion of illegal money through banking channels C. Conversion of cash into gold for hoarding D. Conversion of assets into cash to avoid income tax
2. In case of societies, the important document to be verified is ____________.
A. Copy of bye laws B. Certificate given by ROC C. Certificate given by the Local Authorities D. No document is to be verified in case of societies, as societies are exempted by Registrar
3. PAN (Permanent Account Number) is compulsory for Fixed Deposits, Remittances like DDs/TTs/RTCs, etc ____________.
A. if the amount exceeds Rs.10,000 B. if the amount exceeds Rs.25,000 C. if the amount exceeds Rs 50,000 D. no such limit is fixed by income tax authorities
4. Dormant/ in operative account means ____________.
A. No debits/credits in account for a certain period B. Dead Account without any operation for long C. No debit entries, but certain credit entries for a certain period D. Fixed asset account of the bank
5. While opening an account of a Public Limited company, which of the following is a must? must?
A. Introduction by a customer known to the banker B. Certificate of incorporation/Certificate of commencement of business C. Introduction by ROC D. None of the above
Answer: 1 (B), 2 (A (A), 3 (C (C), 4 (A (A), 5 (B (B)
www.vskills.in
Вам также может понравиться
- Anti Money Laundering Training Program 2016Документ27 страницAnti Money Laundering Training Program 2016Peter Goldmann100% (1)
- Wood Magazine 137 2001Документ69 страницWood Magazine 137 2001cgsharp100% (1)
- Aml Training - SuperrrДокумент56 страницAml Training - SuperrrAdina LazarОценок пока нет
- AML-KYC-Sample Questions by MuruganДокумент67 страницAML-KYC-Sample Questions by Muruganpetre86% (56)
- AML and KYCДокумент36 страницAML and KYCSamaksh Kumar100% (1)
- AML KYC Low PDFДокумент8 страницAML KYC Low PDFMani KsnОценок пока нет
- KYC & AML HandbookДокумент60 страницKYC & AML HandbookUmair Khan Niazi100% (1)
- Aml PWCДокумент8 страницAml PWCVarun NakraОценок пока нет
- Kyc N AmlДокумент53 страницыKyc N Amlrakesh kumar yadav100% (1)
- Know Your CustomerДокумент75 страницKnow Your Customerkomal chavan100% (2)
- KYC Guide-1Документ65 страницKYC Guide-1Avishadhana100% (1)
- KYC-AML POLICYApprovedto24.01.2017 PDFДокумент75 страницKYC-AML POLICYApprovedto24.01.2017 PDFchandrasekaranraj100% (1)
- En ISO 1874-1 - Nylon PA 6 NaturalДокумент14 страницEn ISO 1874-1 - Nylon PA 6 NaturalGiovanniDamicoPereira100% (2)
- Certified Purchase ManagerДокумент13 страницCertified Purchase ManagerRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Anti Money LaunderingДокумент111 страницAnti Money LaunderingFaria Hossain100% (1)
- Aml Monitoring System RisksДокумент16 страницAml Monitoring System RisksrajsalgyanОценок пока нет
- AMLCFT Training Module 2021 v2Документ79 страницAMLCFT Training Module 2021 v2pibg skbk2100% (1)
- Aml KycДокумент5 страницAml KycRaja MumtazaliОценок пока нет
- E Book - Aml-Kyc and ComplianceДокумент638 страницE Book - Aml-Kyc and ComplianceGanesh Ramaiyer100% (1)
- Kyc Aml CFTДокумент201 страницаKyc Aml CFTkunal tyagi100% (2)
- Compliance/KYC/AML OfficerДокумент2 страницыCompliance/KYC/AML Officerapi-78410889Оценок пока нет
- Aml KycДокумент71 страницаAml KycLuminiţa Flintaşu0% (1)
- Oracle MantasДокумент31 страницаOracle Mantascrejoc100% (1)
- Branch Banking CompleteДокумент195 страницBranch Banking Completesohail merchantОценок пока нет
- FRM Part 1 Study Plan May 2017Документ3 страницыFRM Part 1 Study Plan May 2017msreya100% (1)
- DOP Guidelines AML KYC For MTSS and Forex13112018Документ19 страницDOP Guidelines AML KYC For MTSS and Forex13112018DEBADITYA CHAKRABORTYОценок пока нет
- Certified IT Support ProfessionalДокумент14 страницCertified IT Support ProfessionalRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Operational Risk in PaymentДокумент36 страницOperational Risk in PaymentFlaviub23Оценок пока нет
- AML LearningДокумент23 страницыAML Learningstvo49100% (1)
- New Iibf Aml& Kyc 2018 Border PDFДокумент128 страницNew Iibf Aml& Kyc 2018 Border PDFSandeepYadavОценок пока нет
- Certified Wealth ManagerДокумент10 страницCertified Wealth ManagerRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- AML KYC Final - Ver2Документ30 страницAML KYC Final - Ver2gayatri_bksОценок пока нет
- KYC AML CFT Procedure ManualДокумент74 страницыKYC AML CFT Procedure ManualVipul Jain100% (7)
- MONEY LAUNDERING Documentation - EditedДокумент13 страницMONEY LAUNDERING Documentation - EditedAkanksha GuptaОценок пока нет
- AML Compliance or Compliance Officer or KYC or AML or BSA or ComДокумент4 страницыAML Compliance or Compliance Officer or KYC or AML or BSA or Comapi-79303276Оценок пока нет
- Aml Final ReportДокумент98 страницAml Final ReportHadi Sumartono100% (1)
- Aml Kyc NotesДокумент12 страницAml Kyc Notesabhi_33Оценок пока нет
- Aml& Kyc 2020 PDFДокумент130 страницAml& Kyc 2020 PDFRaja Reddy Medagam75% (4)
- Training Material For AML-KYC - PDF RoomДокумент30 страницTraining Material For AML-KYC - PDF RoomAkshay RastogiОценок пока нет
- Question Paper On KYCДокумент9 страницQuestion Paper On KYCNaresh JoshiОценок пока нет
- Fsa Aml SystemsДокумент5 страницFsa Aml SystemsSam 1980Оценок пока нет
- KYC ProjectДокумент40 страницKYC Projectanon_292134566100% (2)
- Aml& Kyc PDFДокумент133 страницыAml& Kyc PDFmayur kulkarniОценок пока нет
- AML KYC Mock Test - Practice TestsДокумент16 страницAML KYC Mock Test - Practice Testsdev100% (1)
- SAP FICO NotesДокумент39 страницSAP FICO NotesShivaniОценок пока нет
- Certified Credit Officer CourseДокумент8 страницCertified Credit Officer CourseAbhishek Kaushik100% (2)
- AML Risk ManagementДокумент7 страницAML Risk ManagementGodsonОценок пока нет
- IIBF Certificate Examination in Trade Finance Details 1Документ10 страницIIBF Certificate Examination in Trade Finance Details 1abhay0% (1)
- KYC, AML and Compliance Basic Module (New)Документ15 страницKYC, AML and Compliance Basic Module (New)Vijay ChallaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: The Recording Process: Questions and AnswersДокумент16 страницChapter 2: The Recording Process: Questions and AnswersKarim KhaledОценок пока нет
- Kyc - AmlДокумент7 страницKyc - AmlAmit GiriОценок пока нет
- KYC AmlДокумент44 страницыKYC Amlakshay2orionОценок пока нет
- KYC NormsДокумент38 страницKYC Normsdranita@yahoo.com100% (2)
- AML and KYCДокумент34 страницыAML and KYCKanika Dhingra0% (1)
- Maharashtra Industries Directory PDFДокумент2 страницыMaharashtra Industries Directory PDFmanisha50% (2)
- Aml Kyc Notice PDFДокумент4 страницыAml Kyc Notice PDFabhishek50% (2)
- Aml & KycДокумент3 страницыAml & KycPallavi Pai Prabhu0% (1)
- KYC & AML Booklet - July 2009Документ169 страницKYC & AML Booklet - July 2009Vriti Bohra0% (1)
- Indian Institute of Banking & Finance: Certificate Examination in Anti-Money Laundering & Know Your CustomerДокумент6 страницIndian Institute of Banking & Finance: Certificate Examination in Anti-Money Laundering & Know Your CustomerKarthik TrОценок пока нет
- Definition of Money LaunderingДокумент3 страницыDefinition of Money LaunderingAnubhav Srivastava100% (1)
- Details & Time Table of AML & KYC - IIBF ExaminationДокумент1 страницаDetails & Time Table of AML & KYC - IIBF Examinationupasana rajОценок пока нет
- Question AMLДокумент13 страницQuestion AMLdabloo_3sepОценок пока нет
- Kyc & AmlДокумент43 страницыKyc & AmlBabli PattanaikОценок пока нет
- Bcsbi PDFДокумент284 страницыBcsbi PDFsimerjotkaur100% (3)
- Kyc & AmlДокумент3 страницыKyc & Amlbhupendersingh00950% (2)
- AML KYC Low 032013 1Документ8 страницAML KYC Low 032013 1Michelle AndrewОценок пока нет
- Legal AspectsДокумент38 страницLegal AspectsAravind JayanОценок пока нет
- Main Project PDFДокумент56 страницMain Project PDFNaira Puneet BhatiaОценок пока нет
- Kyc and AmlДокумент6 страницKyc and AmlPriyanka DhingraОценок пока нет
- Certified Wordpress Developer - BrochureДокумент7 страницCertified Wordpress Developer - BrochureRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Vskills CertificationДокумент8 страницVskills CertificationRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Equity Research CertificationДокумент9 страницEquity Research CertificationVskills CertificationОценок пока нет
- Vskills Certified Iphone Apps Developer - BrochureДокумент7 страницVskills Certified Iphone Apps Developer - BrochureRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Vskills Certified Router Support Professional - BrochureДокумент12 страницVskills Certified Router Support Professional - BrochureRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Android Apps Developer VS-1044Документ9 страницCertified Android Apps Developer VS-1044Ricky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Basic Network Support Professional - BrochureДокумент14 страницCertified Basic Network Support Professional - BrochureRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Technical AnalystДокумент9 страницCertified Technical AnalystRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Business AccountantДокумент11 страницCertified Business AccountantRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified HTML5 DeveloperДокумент12 страницCertified HTML5 DeveloperRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified ASP - Net ProgrammerДокумент17 страницCertified ASP - Net ProgrammerRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Software Testing ProfessionalДокумент12 страницCertified Software Testing ProfessionalRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified HTML DesignerДокумент14 страницCertified HTML DesignerRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified CSS DesignerДокумент13 страницCertified CSS DesignerRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Equity Research CertificationДокумент9 страницEquity Research CertificationVskills CertificationОценок пока нет
- Certified Tally 9.0 ProfessionalДокумент8 страницCertified Tally 9.0 ProfessionalRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Hedge Fund ManagerДокумент8 страницCertified Hedge Fund ManagerRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Foreign Exchange Professional BrochureДокумент15 страницCertified Foreign Exchange Professional BrochureNarender RanaОценок пока нет
- Certified Treasury Markets ProfessionalДокумент9 страницCertified Treasury Markets ProfessionalRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Commercial BankerДокумент13 страницCertified Commercial BankerRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified Merger and Acquisition AnalystДокумент12 страницCertified Merger and Acquisition AnalystRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Vskills Certified Compensation and Benefits Manager - BrochureДокумент11 страницVskills Certified Compensation and Benefits Manager - BrochureRickyОценок пока нет
- Certified Logistics and Supply Chain Management ProfessionalДокумент12 страницCertified Logistics and Supply Chain Management ProfessionalRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Certified International Logistics Management ProfessionalДокумент10 страницCertified International Logistics Management ProfessionalRicky MartinОценок пока нет
- Performance Appraisal Manager CertificationДокумент10 страницPerformance Appraisal Manager CertificationVskills CertificationОценок пока нет
- Certified Human Resources Manager - BrochureДокумент6 страницCertified Human Resources Manager - BrochureRickyОценок пока нет
- Rev.1 - Conciliation of RevenuessДокумент101 страницаRev.1 - Conciliation of RevenuessMirandaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 17Документ7 страницChapter 17Le QuangОценок пока нет
- Draft SubmissionДокумент8 страницDraft SubmissionEthan HuntОценок пока нет
- Basic Questions IIДокумент8 страницBasic Questions IImohan yadavОценок пока нет
- Segmenting Global MarketsДокумент12 страницSegmenting Global MarketsJenny YadvОценок пока нет
- OD328636244353646100Документ3 страницыOD328636244353646100ankit ojhaОценок пока нет
- Rolex Explorer 40mm 224270 Unworn 2023 New Release For $10,215 For Sale From A Trusted Seller On Chrono24Документ1 страницаRolex Explorer 40mm 224270 Unworn 2023 New Release For $10,215 For Sale From A Trusted Seller On Chrono24j9f2wvwbrhОценок пока нет
- Cambridge O Level: ACCOUNTING 7707/22Документ20 страницCambridge O Level: ACCOUNTING 7707/22shujaitbukhariОценок пока нет
- Book TocДокумент7 страницBook TocAli FarooqОценок пока нет
- Occupation 3Документ14 страницOccupation 3api-306711329Оценок пока нет
- A-FLY Quotation For Schindler Parts-20170815-142636703Документ2 страницыA-FLY Quotation For Schindler Parts-20170815-142636703habibullaОценок пока нет
- Breach of ContractДокумент2 страницыBreach of ContractKarishmaОценок пока нет
- NTA - Part 3 - LazadaДокумент9 страницNTA - Part 3 - LazadaHoàng Minh TrangОценок пока нет
- SukritiДокумент11 страницSukritiFoodie InsaaanОценок пока нет
- Amul Taste of IndiaДокумент18 страницAmul Taste of Indiatamil maniОценок пока нет
- Profit and LossДокумент8 страницProfit and Losschitos100% (1)
- Capital Budgeting Decision Criteria: 2002, Prentice Hall, IncДокумент59 страницCapital Budgeting Decision Criteria: 2002, Prentice Hall, IncMarselinus Aditya Hartanto TjungadiОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Open Innovation in New Product Development ProcessДокумент6 страницThe Impact of Open Innovation in New Product Development Process5joanОценок пока нет
- Anil Sharma ResumeДокумент4 страницыAnil Sharma ResumeAnnil SharmaОценок пока нет
- Prac2 ReviewerДокумент12 страницPrac2 ReviewerRay Jhon Ortiz0% (1)
- Mareng AdvancedДокумент33 страницыMareng AdvancedJose LeónОценок пока нет
- Certificat Iso 9001-Romana PDFДокумент1 страницаCertificat Iso 9001-Romana PDFAmy VinehouseОценок пока нет
- MoaДокумент5 страницMoaRaghvirОценок пока нет