Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Tolerancias Lineales GBT1804
Загружено:
monkey1929Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tolerancias Lineales GBT1804
Загружено:
monkey1929Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
National Standard of the Peoples Republic of China General tolerance GB/T 1804-92 Tolerance for linear dimensions without
individual tolerance indications replaces GB 1804-79 This standard adopts the part Tolerance for linear dimensions without individual tolerance indications of international standard ISO 2768-1: 1989 General tolerance Part I: Tolerances for linear and angular dimensions without individual tolerance indications. 1. Theme content and scope This standard specifies the general tolerance grad and limit deviation for linear tolerance. This standard is applicable to metal cutting dimensions and general pressing dimensions. Dimensions of nonmetal material and other process manufacturing method can refer to this standard. The limit deviation specified in this standard is applied to non fit dimensions. 2. General tolerance concept General tolerance refers to the tolerance which can be guaranteed in the workshop under the normal manufacturing conditions. The dimensions with general tolerance need not mark limit deviation. 3. General tolerance for linear dimensions 3.1. Normally the general tolerance for linear dimensions specifies four tolerance grades. Limit deviation value of linear dimension please see Table 1; limit deviation of fillet radius and chamfer height dimensions please see Table 2. 3.2. In order to specify the linear dimensions without individual tolerance indications, the workshop general manufacturing accuracy should be considered; take the tolerance grade specified in this standard, and the detail is specified in related technical document or standard. Table 1 Limit Deviation Value of Linear Dimension
Tolerance grade f(fine) ccoarse Dimension sections 0.5~3 0.05 0.2 >3~6 0.05 0.1 0.3 0.5 >6~30 0.1 0.2 0.5 1 >30~12 0 0.15 0.3 0.8 1.5 >120~4 00 0.2 0.5 1.2 2.5 >400~1 000 0.3 0.8 2 4 >1000~ 2000 0.5 1.2 3 6 >2000~ 4000 2 4 8
mm
m medium 0.1 v most coarse
Approved by China State Bureau of Technical Supervision Feb. 09, 1992
Implemented on Oct. 01, 1992
PDF "pdfFactory Pro" www.fineprint.com.cn
GB/T 1804-92
Table 2 Limit Deviation Value of Fillet Radius and Chamfer Height
Tolerance grade f (fine) mmedium ccoarse V most coarse 0.4 1 2 4 Dimension sections 0.5~3 0.2 >3~6 0.5 >6~30 1 >30 2
mm
Note: Meaning of fillet radius and chamfer height please see national standard GB 6403.4 (Part fillet and chamfer). 4. Express method of linear dimension general tolerance The standard code and tolerance grade code should be marked if the general tolerance specifies in this standard are used in drawing, technical document or standard. For example, to select medium grade, it can be expressed as: GB 1804-m
PDF "pdfFactory Pro" www.fineprint.com.cn
GB/T 1804-92
Annex A Concept and function of linear dimension general tolerance (Informative) A1. General review A1.1 Dimension, shape of part feature or position requirement of all the features is decided by their function. There are no features without function requirements. So, all the features expressed on the drawing of one part should have tolerance requirements. A1.2 Give general tolerance to the features which have no function special requirements. A1.3 General tolerance can be applied on the geometric element linear dimension, angular dimension, shape and position etc.. A1.4 The general tolerance of feature need not mark on the drawing individually; there should be a general explanation on drawing, technical document or standard. A2 Concept of linear dimension general tolerance A2.1 Linear dimension general tolerance refers to the tolerance can be guaranteed under the normal process conditions with the machine normally manufacturing abilities. It represents the economic manufacturing accuracy under the normal maintain and operation. A2.2 Linear dimension general tolerance mainly is applicable to the low accuracy fits dimension. When the tolerance allowed by the function is equal or bigger than general tolerance, take the general tolerance. Except for one feature is allowed to have one tolerance which is bigger than general tolerance, and this tolerance is more economic than the general tolerance ( for example, the depth of blind hole for assembly), mark the corresponding limit deviation behind of this dimension. A2.3 The dimension adopts the general tolerance need not to be inspected normally if the normal workshop accuracy is guaranteed. A2.4 If one surface will have two different manufacturing processes (for example cutting and casting), take the bigger one of the linear dimension general tolerance between them according to the stipulation. A3 Function of general tolerance Using general tolerances leads to the following advantages: a) Drawings are easier to read and thus communication is made more effective to the user of the drawing; b) The design draughtsman saves time by avoiding de-tailed tolerance calculations as it is sufficient only to know that the function allows a tolerance greater than or equal to the general tolerance; c) The drawing readily indicates which feature can be produced by normal process capability, which also assists quality engineering by reducing inspection levels; d) those dimensions remaining, which have individually indicated tolerances,
PDF "pdfFactory Pro" www.fineprint.com.cn
GB/T 1804-92
will, for the most part, be those control-ling features for which the function requires relatively small tolerances and which therefore may require special effort in the production - this will be helpful for production planning and will assist quality control services in their analysis of inspection requirements; e) To avoid the unnecessary dispute between supplying and requisitioning parties because the general tolerance requirement is confirmed on the drawing which can help both parties to reach a manufacturing and sales contract.
___________________ Additional explanation: This standard was proposed by National Tolerance and Fits Standardization Technical Commission. This standard is under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Machinery Industry P.R China. This standard is drafted by Standardization Institute of Ministry of Machinery Industry P.R China. This standard is drafted by Li Xiaopei and Yu Hanqing. Standardization Institute of Ministry of Machinery Industry was entrusted to have the right of interpretation of this standard .
PDF "pdfFactory Pro" www.fineprint.com.cn
Вам также может понравиться
- Is 2102Документ8 страницIs 2102Sowmen Chakroborty100% (1)
- IS.2102 General ToleranceДокумент5 страницIS.2102 General Tolerancekamalkraj4002100% (1)
- Esbm5a-B 1n261-s Aa RSWДокумент37 страницEsbm5a-B 1n261-s Aa RSWChandrajeet Shelke50% (2)
- Iso 68-1 PDF - Google SearchДокумент2 страницыIso 68-1 PDF - Google SearchDeniz Tuncbilek0% (1)
- GBT 1299-2014 Tool and Mould SteelsДокумент68 страницGBT 1299-2014 Tool and Mould SteelsPhong Tong100% (1)
- Iso 642-1999Документ24 страницыIso 642-1999jerfmos100% (3)
- Calculation of Load Capacity of Shafts and Axles: German Standard October 2000Документ16 страницCalculation of Load Capacity of Shafts and Axles: German Standard October 2000Karthik Vaidhyanathan100% (1)
- Methods For'Measuring Case Depth of Steel: Indian StandardДокумент7 страницMethods For'Measuring Case Depth of Steel: Indian Standardsingaravelan narayanasamyОценок пока нет
- Name Engineering Standard Number: Cummins ConfidentialДокумент18 страницName Engineering Standard Number: Cummins ConfidentialshankarОценок пока нет
- Iso 15330 en PDFДокумент6 страницIso 15330 en PDFScube engineersОценок пока нет
- Ti Spec ANSI B1.8 1988 Contents PDFДокумент2 страницыTi Spec ANSI B1.8 1988 Contents PDFDanang PrasetioОценок пока нет
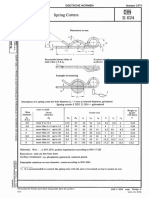
- DIN 11024 - Spring Cotters PDFДокумент1 страницаDIN 11024 - Spring Cotters PDFthisisjineshОценок пока нет
- Din 13-1Документ4 страницыDin 13-1Sankha Dasgupta100% (3)
- 18-1600 enДокумент13 страниц18-1600 enCaique de Oliveira100% (1)
- International Standard: Hexagon Regular Nuts (Style 1) - Product Grades A and BДокумент14 страницInternational Standard: Hexagon Regular Nuts (Style 1) - Product Grades A and BUdit Kumar SarkarОценок пока нет
- Is 513 PDFДокумент13 страницIs 513 PDFManeesh Bangale100% (5)
- File 20200313 224143 Jis-G-4305-2012Документ50 страницFile 20200313 224143 Jis-G-4305-2012tad69550% (2)
- Din 6930-2Документ1 страницаDin 6930-2murniОценок пока нет
- Is 1977Документ11 страницIs 1977rahulmechdceОценок пока нет
- JIS-standard G3113 PDFДокумент11 страницJIS-standard G3113 PDFMahesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Iso 10683Документ7 страницIso 10683Permeshwara Nand BhattОценок пока нет
- Tolerance of Position (TOP) - 1Документ34 страницыTolerance of Position (TOP) - 1maddy_scribdОценок пока нет
- BS 6615 Iso 8062-CT7Документ2 страницыBS 6615 Iso 8062-CT7Purushothama Nanje GowdaОценок пока нет
- Macroetch Testing of Consumable Electrode Remelted Steel Bars and BilletsДокумент15 страницMacroetch Testing of Consumable Electrode Remelted Steel Bars and BilletsJosé de Paula Moreira0% (1)
- Saej 356 V 002Документ7 страницSaej 356 V 002Evandro Luis GomesОценок пока нет
- Hex Socket Head Screws Is 2269Документ17 страницHex Socket Head Screws Is 2269Rajasekaran MuruganОценок пока нет
- Iso 286-2Документ55 страницIso 286-2Alexander Zuñiga Valbuena100% (2)
- High-Carbon Anti-Friction Bearing Steel: Standard Specification ForДокумент4 страницыHigh-Carbon Anti-Friction Bearing Steel: Standard Specification ForTriveni Forge QCОценок пока нет
- Iso 6157-1-1988Документ12 страницIso 6157-1-1988Djaffar SalahouiОценок пока нет
- Is 1079 - 2009Документ10 страницIs 1079 - 2009Shradha SinghaniaОценок пока нет
- .250 .031 R Collar, An876 (Proper Dash No.) Silver Solder To TubeДокумент3 страницы.250 .031 R Collar, An876 (Proper Dash No.) Silver Solder To TubeAnonymous 1CBdStCXUОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of The VDA 238-100 Tight Radius Bending Test Using Digital Image Correlation Strain MeasurementДокумент9 страницEvaluation of The VDA 238-100 Tight Radius Bending Test Using Digital Image Correlation Strain MeasurementR JОценок пока нет
- Keyway DIN 6885 - Parallel Metric Keys and Keyway DimensionsДокумент2 страницыKeyway DIN 6885 - Parallel Metric Keys and Keyway DimensionsHenrique MarquesОценок пока нет
- External Metric ISO Thread Table Chart Sizes M20 - M55Документ8 страницExternal Metric ISO Thread Table Chart Sizes M20 - M55dilipОценок пока нет
- Din 13-51Документ1 страницаDin 13-51anks_raОценок пока нет
- Astm A276 PDFДокумент7 страницAstm A276 PDFJhon Edison Posada MuñozОценок пока нет
- EN8 Steel: BS970: 1955 EN8, BS970/PD970: 1970 OnwardsДокумент1 страницаEN8 Steel: BS970: 1955 EN8, BS970/PD970: 1970 Onwardsgowtham_venkat_4Оценок пока нет
- Ford Worldwide Fastener Standard: Printed Copies Are UncontrolledДокумент7 страницFord Worldwide Fastener Standard: Printed Copies Are Uncontrolledferhat aydoganОценок пока нет
- Iso 9717 2010 en FR - PDF Phosphate CoatingДокумент11 страницIso 9717 2010 en FR - PDF Phosphate CoatingGANESH AОценок пока нет
- Asme B1.12-1987 (2018)Документ74 страницыAsme B1.12-1987 (2018)vijay pawar100% (1)
- CNH Spec MAT4030 - Gas CarburizationДокумент12 страницCNH Spec MAT4030 - Gas CarburizationJoe Scopelite100% (1)
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: GM Global Fastening CatalogДокумент107 страницWorldwide Engineering Standards: GM Global Fastening Catalogaldairlopes100% (1)
- Is 11158 1984 ISO 7083 1983 Proportions and Dimensions of Symbols For Geometrical Tolerancing Used in Technical DrawingsДокумент10 страницIs 11158 1984 ISO 7083 1983 Proportions and Dimensions of Symbols For Geometrical Tolerancing Used in Technical DrawingsleovenuОценок пока нет
- Din 13Документ1 страницаDin 13dedosimoesОценок пока нет
- AGMA Standards ListДокумент1 страницаAGMA Standards ListMauro MLRОценок пока нет
- 16906Документ12 страниц16906Ashish DubeyОценок пока нет
- Astm B633 98Документ5 страницAstm B633 98onkar290967% (3)
- Geometric Dimensioning AND Tolerancing (GD & T) : Prepared by Jignesh PatelДокумент13 страницGeometric Dimensioning AND Tolerancing (GD & T) : Prepared by Jignesh PatelunendratОценок пока нет
- GMW 14057-2012Документ11 страницGMW 14057-2012JUAN CARLOS MURILLO LARROTAОценок пока нет
- The Basics of Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingДокумент9 страницThe Basics of Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingKishanОценок пока нет
- GD&T Basics (Level-1)Документ85 страницGD&T Basics (Level-1)Thiyagu rajОценок пока нет
- App E - Dim RulesДокумент4 страницыApp E - Dim RulesIbadurrahman KahfiОценок пока нет
- 1.0 General: Drafting ManualДокумент8 страниц1.0 General: Drafting ManualMubashar Khalil Hashmi100% (1)
- Geometrical Dimenstioning and ToleranceДокумент82 страницыGeometrical Dimenstioning and ToleranceSreedhar PugalendhiОценок пока нет
- Homework 2Документ2 страницыHomework 2asp9924Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To GD&T?Документ11 страницIntroduction To GD&T?AravindОценок пока нет
- MBN10231 Eng+2008-09Документ12 страницMBN10231 Eng+2008-09gültekin gökОценок пока нет
- GD&TДокумент17 страницGD&TAtharva AnchalwarОценок пока нет
- GD&T PDFДокумент49 страницGD&T PDFnupurvinodОценок пока нет
- GD&TДокумент11 страницGD&TrakshithmpОценок пока нет
- SAE J 673-1993 Automotive Safety Glasses PDFДокумент9 страницSAE J 673-1993 Automotive Safety Glasses PDFmonkey1929100% (1)
- Catalogo Aimco ViejoДокумент116 страницCatalogo Aimco Viejomonkey1929Оценок пока нет
- 3M 5386Документ2 страницы3M 5386monkey1929Оценок пока нет
- Guide To US Plastic AssemblyДокумент118 страницGuide To US Plastic AssemblyrenebbОценок пока нет
- Next Engine 3D Scanner InstructionsДокумент3 страницыNext Engine 3D Scanner Instructionsmonkey1929Оценок пока нет
- RapidWorks Whats NewДокумент55 страницRapidWorks Whats Newmonkey1929Оценок пока нет
- Politica Automotriz 2000-2009Документ7 страницPolitica Automotriz 2000-2009monkey1929Оценок пока нет
- Ferrous Materials Metallurgy I: Contents: STD - Jisf 2008 V.1Документ30 страницFerrous Materials Metallurgy I: Contents: STD - Jisf 2008 V.1monkey1929Оценок пока нет
- Catia V5 Tutorial Work BookДокумент17 страницCatia V5 Tutorial Work Bookavaakayi100% (2)
- 93-0011 RevbДокумент6 страниц93-0011 Revbmonkey1929Оценок пока нет
- Nextengine 3D Scanning Tutorial: PartsДокумент36 страницNextengine 3D Scanning Tutorial: Partsgad30Оценок пока нет
- Muhamad Hazrul Hakimin Abu Shaari PDFДокумент24 страницыMuhamad Hazrul Hakimin Abu Shaari PDFShwetha BhatОценок пока нет
- Next Engine 3D Scanner InstructionsДокумент3 страницыNext Engine 3D Scanner Instructionsmonkey1929Оценок пока нет
- Tolerancias Lineales GBT1804Документ4 страницыTolerancias Lineales GBT1804monkey1929Оценок пока нет
- Tolerancias Lineales GBT1804Документ4 страницыTolerancias Lineales GBT1804monkey1929Оценок пока нет
- List of Tyre Pyrolysis Oil Companies in IndiaДокумент2 страницыList of Tyre Pyrolysis Oil Companies in IndiaHaneesh ReddyОценок пока нет
- Examiners' Report Principal Examiner Feedback January 2018Документ7 страницExaminers' Report Principal Examiner Feedback January 2018WandaОценок пока нет
- 50+ MATLAB Projects For Engineering StudentsДокумент5 страниц50+ MATLAB Projects For Engineering StudentsaamyaОценок пока нет
- Alderamin On The Sky - Volume 7Документ311 страницAlderamin On The Sky - Volume 7Pedro SilvaОценок пока нет
- Samsung Galaxy Watch 5 Pro User ManualДокумент131 страницаSamsung Galaxy Watch 5 Pro User Manualzyron100% (1)
- Motorola Talkabout T82 PDFДокумент184 страницыMotorola Talkabout T82 PDFAlex TamayoОценок пока нет
- Stripper EZ-range US v3 Web-1Документ2 страницыStripper EZ-range US v3 Web-1irwin kurniadiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 MPLS OAM Configuration Commands ...................................................................... 1-1Документ27 страницChapter 1 MPLS OAM Configuration Commands ...................................................................... 1-1Randy DookheranОценок пока нет
- The First-Fourth Books of The HitopadésaДокумент116 страницThe First-Fourth Books of The HitopadésaMiguel RosaОценок пока нет
- PP in Ii 001Документ15 страницPP in Ii 001Dav EipОценок пока нет
- Framework For A Digital Twin in Manufacturing Scope and RequirementsДокумент3 страницыFramework For A Digital Twin in Manufacturing Scope and RequirementsJoão Vitor100% (1)
- Exposition Text Exercise ZenowskyДокумент8 страницExposition Text Exercise ZenowskyZenowsky Wira Efrata SianturiОценок пока нет
- C7 On-Highway Engine Electrical System: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsДокумент2 страницыC7 On-Highway Engine Electrical System: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsFeDe Aavina Glez100% (3)
- Strategic Cost AnalysisДокумент24 страницыStrategic Cost AnalysisBusiness Expert Press100% (10)
- (English (Auto-Generated) ) Intraday Trading On Nifty (2nd September, 2021) 8 Lakhs Profit Shreyas Bandi Trade Ideas Live (DownSub - Com)Документ41 страница(English (Auto-Generated) ) Intraday Trading On Nifty (2nd September, 2021) 8 Lakhs Profit Shreyas Bandi Trade Ideas Live (DownSub - Com)YaaroОценок пока нет
- Fiitjee All India Test Series: Concept Recapitulation Test - Iv JEE (Advanced) - 2019Документ13 страницFiitjee All India Test Series: Concept Recapitulation Test - Iv JEE (Advanced) - 2019Raj KumarОценок пока нет
- ZTE V4 RNC Commissioning and Integration TrainingДокумент2 страницыZTE V4 RNC Commissioning and Integration TrainingBeena SinghОценок пока нет
- NCR Supplier PPAP Training PresentationДокумент166 страницNCR Supplier PPAP Training PresentationRajeev ChadhaОценок пока нет
- IPE SakibBhaiMagicChothaДокумент55 страницIPE SakibBhaiMagicChothaTousif SadmanОценок пока нет
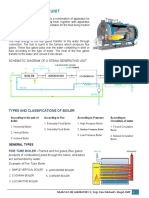
- MLAB 3 - BoilerДокумент3 страницыMLAB 3 - BoilerReden LopezОценок пока нет
- PreNav - Pitch - Customers Wind SiДокумент20 страницPreNav - Pitch - Customers Wind SiKaterinaLiОценок пока нет
- 2021 3 AbstractsДокумент168 страниц2021 3 AbstractsLong An ĐỗОценок пока нет
- SOL-Logarithm, Surds and IndicesДокумент12 страницSOL-Logarithm, Surds and Indicesdevli falduОценок пока нет
- COCCIMORPHДокумент13 страницCOCCIMORPHmiminОценок пока нет
- Centralized PurchasingДокумент2 страницыCentralized PurchasingbiyyamobulreddyОценок пока нет
- Palmiye Leaflet 2015 enДокумент4 страницыPalmiye Leaflet 2015 ensaraju_felixОценок пока нет
- Permeability Estimation PDFДокумент10 страницPermeability Estimation PDFEdison Javier Acevedo ArismendiОценок пока нет
- FMS 427 BusinessPolicy1Документ279 страницFMS 427 BusinessPolicy1Adeniyi Adedolapo OLanrewajuОценок пока нет
- Statistical MethodsДокумент77 страницStatistical MethodsGuruKPO100% (1)
- Mech Syllabus R-2017 - 1Документ110 страницMech Syllabus R-2017 - 1goujjОценок пока нет