Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Enzyme Review Mcqs (From The Official Biochemistry Study Guide)
Загружено:
Mrs RehanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Enzyme Review Mcqs (From The Official Biochemistry Study Guide)
Загружено:
Mrs RehanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Enzyme Review MCQs (From the official biochemistry study guide)
1.Enzymes are: a) Proteins b) Chloroplasts c) Genes d) Mitochondria 2. Enzymes are catalysts. They increase the rate of chemical reactions by: a) Raising the activation energy b) Temporarily increasing the temperature c) Covalently binding the substrate d) Lowering the activation energy 3. Enzymes are classified by the: a) Size of the enzyme b) Size of the substrate c) Type of reaction d) Rate of reaction 4. Shown below is a graph describing energy versus reaction coordinate for a catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction. Fill in the blanks with the letter that corresponds to each stage of the graph.
_____ ES _____ S (substrate) _____ P (product) _____ Uncatalyzed reaction 5. The minimum amount of energy necessary for a molecule(s) to react is the: a) Activation energy b) Free energy c) Thermal energy 1
d) Potential energy 6. The state produced when two or more molecules collide with just the right energy and just the right orientation so that a chemical reaction might occur is: a) Catalytic state b) Transition state c) Activation state d) Transient state 7. One of the following statement describing the mechanism of enzyme action is INCORRECT: a) Many enzymes have flexible structures that allow them to enfold their substrate b) The substrate is often distorted when it enters an enzyme-substrate complex c) Amino acid side chains involved in the formation of the active site center are usually close together in the amino acid sequence of the enzyme protein d) Amino acid side chain near the active site center often have a role in the catalytic process 8.Which of the following statement about enzyme catalyzed reaction is NOT TRUE: a) Enzymes form complexes with their substrate b) Enzymes increase the activation energy for chemical reaction c) Many enzymes change shape slightly when substrate binds d) Reactions occur at the active site of enzymes, where a precise quaternary orientation of amino acids is an important feature of catalysis 9. Which of the following does not influence enzyme activity? a) pH b) Temperature c) Product degradation d) Substrate concentration 10. The Michaelis constant Km is: a) Numerically equal to Vmax b) Dependent on the enzyme concentration c) Independent on pH d) Numerically equal to the substrate concentration that gives halfmaximal velocity 11. What effect does temperature have on enzymes? a) Boiling will denature them, as will being too cold b) Boiling will not harm them, but being too cold will denature them c) Boiling and cooling will both reduce the speed of their rate d) Boiling will denature them, but cooling will only slow down their work
12. The Michaelis-Menten equation is Vo=Vmax [S]/(Km+[S]). Fill in the blanks with the letters shown to correctly label each part of the graph
_____ Vmax _____ [S] _____ Vo _____ Point used to determine the Km 13. Which type of reversible enzyme inhibitor binds to the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex? a) Noncompetititive b) Competitive c) Uncompetitive d) None of the above 14. In competitive inhibition, one of the following statement is CORRECT: a) Vmax is increased b) The concentration of active enzyme molecule is unchanged c) The apparent Km is increased d) The apparent Km is decreased 15. Enzyme action can be influenced by the presence of inhibitors. Which of the following statements correctly matches the type of inhibitor with its effect on an enzyme. a) Irreversible and Renders the enzyme permanently inactive b) Competitive and Inhibitor binds only to ES complex, only important when[S] high, Vmax lower, Km lower c) Noncompetitive and Can be overcome with high [S], Vmax unchanged, Km higher d) Uncompetitive and Cannot be overcome with high[S], Vmax lower, but Km unchanged
16. Allosteric enzymes are large, oligomeric proteins that have catalytic sites for binding substrates and regulatory sites that bind effectors. The separate oligomers influence one another; they work cooperatively. This is evidenced by the characteristic rate curves for allosteric enzymes which have: a) Michaelis-Menten kinetics b) Hyperbolic kinetics c) Sigmoidal kinetics d) Regulatory kinetics 17. Some enzymes are first synthesized in an inactive form. These zymogens must undergo proteolytic cleavage to produce the active enzyme. Which of the following statements are true of proteolytic cleavage? a) It is reversible b) It is irreversible c) It is random d) It occurs in the region of zymogen synthesis 18. Increased synthesis of an enzyme is known as: a) Activation b) Inhibition c) Induction d) Repression 19. In the graph below a) Which one of the plot explains the behavior of an allosteric enzyme? b) What is the meaning of cooperativity?
20. In normal blood, the alkaline phosphatase activity is derived mainly from: a) Bone and small intestine b) Bone and liver c) Small intestine and placenta d) Bone and placenta
21. How many different isoenzymes of normal LDH can be identified by electrophoresis at pH 8.6 a) Two b) Three c) Four d) Five 22. LDH assays are useful in diagnosing diseases of the: a) Heart b) Pancreas c) Liver d) a and c
Вам также может понравиться
- Tutorial 8 - Enzymes and MetabolismДокумент13 страницTutorial 8 - Enzymes and MetabolismSivabalan Sanmugum100% (1)
- A.P. Chapter 8 WebTestДокумент9 страницA.P. Chapter 8 WebTestNick PirainoОценок пока нет
- Edited - Chapter 6 Test BankДокумент18 страницEdited - Chapter 6 Test BankRod De Guzman100% (1)
- Biochem MCqsДокумент42 страницыBiochem MCqsrichard100% (2)
- Questions - Enzymes - Answer KeyДокумент7 страницQuestions - Enzymes - Answer KeyBUG50% (2)
- Enzymes Multiple Choice Revision QuestionsДокумент8 страницEnzymes Multiple Choice Revision QuestionsAli Sajjad50% (2)
- Mcqs Biochemistry IIДокумент36 страницMcqs Biochemistry IIBatool Ashraf100% (1)
- Chapter - 08 - Lipids Membranes-TestДокумент10 страницChapter - 08 - Lipids Membranes-Testendang dian lestariОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Control Questions. Module 1Документ2 страницыBiochemistry Control Questions. Module 1Valeriy MelnykОценок пока нет
- Exam # 1 Chemistry 208, Organic Chemistry I Fall 2016: Your Name: - Laboratory SectionДокумент7 страницExam # 1 Chemistry 208, Organic Chemistry I Fall 2016: Your Name: - Laboratory SectionHieyeОценок пока нет
- CH 22 Test BankДокумент7 страницCH 22 Test BanklolasparkleОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Seventh EditionДокумент24 страницыTest Bank For Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Seventh Editioncosimalocu68xb1Оценок пока нет
- MCQДокумент15 страницMCQSasikala RajendranОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 Biosignaling: Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент3 страницыChapter 12 Biosignaling: Multiple Choice Questionssurankokila50% (4)
- 11 - Biochemistry MCQs Amino Acid & PROTEINSДокумент8 страниц11 - Biochemistry MCQs Amino Acid & PROTEINSMohamed YahiaОценок пока нет
- Ezyme 2Документ3 страницыEzyme 2Nini Besi100% (1)
- Chapter 24 Practice QuestionsДокумент7 страницChapter 24 Practice QuestionsArlene F. Montalbo100% (1)
- Practice TestДокумент13 страницPractice TestYvonne DoОценок пока нет
- 00018Документ92 страницы00018Fernandez-De Ala NicaОценок пока нет
- Biochem HomeworkДокумент13 страницBiochem Homeworkfcukingfranztastik50% (2)
- Final Exam (Practice) KEYДокумент11 страницFinal Exam (Practice) KEYNevenKnezevicОценок пока нет
- Enzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementДокумент19 страницEnzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementArvin DiNozzoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 & 8 Test KeyДокумент3 страницыChapter 6 & 8 Test Keycshining330% (1)
- TRẮC NGHIỆM SHĐCДокумент33 страницыTRẮC NGHIỆM SHĐCsylvester.powell100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Membrane Structure and Function: Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент11 страницChapter 5 Membrane Structure and Function: Multiple Choice QuestionsJohn MixerОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates MCQsДокумент9 страницCarbohydrates MCQsAyesha BatoolОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Review 2Документ14 страницBiochemistry Review 2deelol99Оценок пока нет
- CH 12Документ23 страницыCH 12filippo67% (3)
- BiochemistryДокумент22 страницыBiochemistryChia JoseОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry MCQДокумент24 страницыBiochemistry MCQpoojaОценок пока нет
- Mcqs ProteinsДокумент27 страницMcqs ProteinsMohamed Khalel50% (2)
- Biochemistry Chapter 3Документ5 страницBiochemistry Chapter 3brownhazelОценок пока нет
- 4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IIДокумент3 страницы4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IILinus LiuОценок пока нет
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank CH 3pdfДокумент17 страницLehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank CH 3pdfMcLovin LUОценок пока нет
- Proteins McqsДокумент3 страницыProteins McqsAG Khan100% (1)
- Amino Acids QuestionsДокумент5 страницAmino Acids QuestionsKrishna KumarОценок пока нет
- Biochem QbankДокумент16 страницBiochem Qbank786waqar786Оценок пока нет
- CH 04Документ29 страницCH 04filippoОценок пока нет
- (مكتملة) اسئلة البايو د.ج السمهري (.)Документ10 страниц(مكتملة) اسئلة البايو د.ج السمهري (.)Ozgan SüleymanОценок пока нет
- Glycolysis and Fermentation Worksheet ReviewДокумент3 страницыGlycolysis and Fermentation Worksheet ReviewMastentram WidjajaОценок пока нет
- BCH MCQs1Документ304 страницыBCH MCQs1moxdegr8100% (1)
- Name: Kristine Joy Atos Block: BSN 1-D Practice ProblemsДокумент6 страницName: Kristine Joy Atos Block: BSN 1-D Practice ProblemsJenz Hope Segui Novela100% (3)
- Molecular Cell Biology Lodish 6th Edition Test BankДокумент6 страницMolecular Cell Biology Lodish 6th Edition Test BankCharles BlairОценок пока нет
- 3-Enzymes (2003 - 2010)Документ11 страниц3-Enzymes (2003 - 2010)Asegedech BirhanuОценок пока нет
- Excel 2007 TutorialДокумент5 страницExcel 2007 TutorialromelcarvajalОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент3 страницыBiochemistrysummer168Оценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Question1Документ18 страницCarbohydrate Question1sangram_pharma9145100% (1)
- TestДокумент23 страницыTestParth sarthi Sen guptaОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Page 1 of 12Документ12 страницBiochemistry Page 1 of 12Viviengail GalosОценок пока нет
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank Ch. 10 PDFДокумент8 страницLehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank Ch. 10 PDFTony ChenОценок пока нет
- Biological Chemistry. The Bank of MCQ Test Questions) 2016-2017Документ32 страницыBiological Chemistry. The Bank of MCQ Test Questions) 2016-2017AGM EBОценок пока нет
- Cycle, or The Szent-Györgyi-Krebs CycleДокумент6 страницCycle, or The Szent-Györgyi-Krebs CyclejayrajsenОценок пока нет
- Biochem Post TestДокумент9 страницBiochem Post Testtam meiОценок пока нет
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank Ch. 20 PDFДокумент9 страницLehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank Ch. 20 PDFTony ChenОценок пока нет
- Enzymes MCQsДокумент2 страницыEnzymes MCQsNobody's PerfectОценок пока нет
- Answers Amino Acids PeptidesДокумент6 страницAnswers Amino Acids PeptidesAnna LeeОценок пока нет
- Quiz Lehninger CH 16 FinalДокумент15 страницQuiz Lehninger CH 16 Finalasjdg100% (2)
- Chapter 19 Oxidative Phosphorylation and PhotophosphorylationДокумент8 страницChapter 19 Oxidative Phosphorylation and PhotophosphorylationTony Nguyen33% (3)
- Xhweet Kashu . : Biology Complete Important Mcqs For Medical Entry Test PreparationДокумент47 страницXhweet Kashu . : Biology Complete Important Mcqs For Medical Entry Test PreparationawaisjinnahОценок пока нет
- First Year Medics TestДокумент15 страницFirst Year Medics TestJosephОценок пока нет
- Cell Organelles: DR Amber FarooqДокумент9 страницCell Organelles: DR Amber FarooqMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Plasma Half LifeДокумент6 страницPlasma Half LifeMrs RehanОценок пока нет
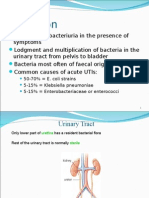
- 50-70% E. Coli Strains 5-15% Klebsiella Pneumoniae 5-15% Enterobacteriaceae or EnterococciДокумент7 страниц50-70% E. Coli Strains 5-15% Klebsiella Pneumoniae 5-15% Enterobacteriaceae or EnterococciMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Presentation 2 EpidemicДокумент79 страницPresentation 2 EpidemicMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidДокумент56 страницNucleotides and Nucleic AcidMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Hypolipidemic Drugs: Maj Kulsoom FarhatДокумент26 страницHypolipidemic Drugs: Maj Kulsoom FarhatMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- CirrhosisДокумент26 страницCirrhosisMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyДокумент14 страницBleeding in Early PregnancyMrs Rehan100% (1)
- Association For Excellence in Medical Education Conference 2015Документ6 страницAssociation For Excellence in Medical Education Conference 2015Mrs RehanОценок пока нет
- J Woodman Normal LabourДокумент16 страницJ Woodman Normal LabourMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Baby Bath Tray: Thermometer JarДокумент1 страницаBaby Bath Tray: Thermometer JarMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Undesired Effects of Drugs Occurring Under Normal Conditions of UseДокумент18 страницAdverse Drug Reactions: Undesired Effects of Drugs Occurring Under Normal Conditions of UseMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Normal Puerperium & PostnatalДокумент38 страницNormal Puerperium & PostnatalMrs Rehan100% (1)
- PedagogyДокумент32 страницыPedagogyMrs Rehan100% (2)
- Innovative Teaching Strategies Pete Dudley and Carol McGuinness MonДокумент8 страницInnovative Teaching Strategies Pete Dudley and Carol McGuinness MonMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Medication TrayДокумент1 страницаMedication TrayMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Community Health Nursing 3 (Ansari Notes)Документ41 страницаCommunity Health Nursing 3 (Ansari Notes)Mrs Rehan80% (5)
- Principles of Effective TeachingДокумент44 страницыPrinciples of Effective TeachingMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Clickers GeneralinfoДокумент1 страницаClickers GeneralinfoMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- AnemiaДокумент2 страницыAnemiaMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Paper - (: Armed Forces Post Graduate Medical Institute Rawalpindi (Session 2005)Документ3 страницыPaper - (: Armed Forces Post Graduate Medical Institute Rawalpindi (Session 2005)Mrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Creating and Maintaining A Sterile FieldДокумент1 страницаCreating and Maintaining A Sterile FieldMrs RehanОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 1 SivertДокумент5 страницProblem Set 1 SivertSivert LundstadОценок пока нет
- Biology Entrance Exam For G11 & G12 From 1995 - 2011Документ60 страницBiology Entrance Exam For G11 & G12 From 1995 - 2011Azure Fikadu100% (1)
- Lab: Effects of PH On Enzyme ActivityДокумент1 страницаLab: Effects of PH On Enzyme ActivitySantosh MiryalaОценок пока нет
- Allosteric EnzymeДокумент22 страницыAllosteric EnzymeAhmed ImranОценок пока нет
- FBE Merged - MidsemДокумент276 страницFBE Merged - MidsemAnusha DesaiОценок пока нет
- Btech Syllabus Mechanical 2018 Draft1Документ130 страницBtech Syllabus Mechanical 2018 Draft1axat patelОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionДокумент31 страницаEnzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionCathrine CruzОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Review Worksheet: Name: . DateДокумент4 страницыEnzymes Review Worksheet: Name: . Dateapi-233187566100% (1)
- The Biotechnological Utilization of Cheese Whey: A ReviewДокумент11 страницThe Biotechnological Utilization of Cheese Whey: A ReviewEduar Moreno LondoñoОценок пока нет
- Biotechnology Reports: Swati B. Jadhav, Neha Shah, Ankit Rathi, Vic Rathi, Abhijit RathiДокумент9 страницBiotechnology Reports: Swati B. Jadhav, Neha Shah, Ankit Rathi, Vic Rathi, Abhijit RathiishfaqqqОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Assays and KineticsДокумент12 страницEnzyme Assays and KineticsKNTОценок пока нет
- 2004 - Se1 Current Models For Starch SynthesisДокумент8 страниц2004 - Se1 Current Models For Starch SynthesisAnand KhotОценок пока нет
- CDDS ClassificationДокумент63 страницыCDDS ClassificationAna MacoveiОценок пока нет
- Xu Princeton 0181D 10615Документ175 страницXu Princeton 0181D 10615Sailendra MeherОценок пока нет
- Biology Paper 3 Experiment - Activity Enzyme Affected by TemperatureДокумент18 страницBiology Paper 3 Experiment - Activity Enzyme Affected by TemperaturePau Siew LingОценок пока нет
- C-Bacterial Metabolism-Springer-Verlag New York (1986)Документ370 страницC-Bacterial Metabolism-Springer-Verlag New York (1986)xuantra100% (1)
- Function of Ingridients AIBДокумент18 страницFunction of Ingridients AIBJaved Khan Nadir Khan100% (1)
- Drug Intereaction in Treatment Cancer PDFДокумент195 страницDrug Intereaction in Treatment Cancer PDFRijantono Franciscus MariaОценок пока нет
- Derivations OF: Enzyme Kinetics (I)Документ20 страницDerivations OF: Enzyme Kinetics (I)Sabari Krishnan B B100% (1)
- 4HB0 02 MSC 201603021 PDFДокумент14 страниц4HB0 02 MSC 201603021 PDFJoseph LAU [11D]Оценок пока нет
- Biotechnology Eligibility Test (BET) For DBT-JRF Award (2009-10)Документ18 страницBiotechnology Eligibility Test (BET) For DBT-JRF Award (2009-10)Nandakumar HaorongbamОценок пока нет
- Cell ImmobilДокумент34 страницыCell ImmobilVikas GuptaОценок пока нет
- The SimplyRaw Living Foods Detox Manual (PDFDrive)Документ307 страницThe SimplyRaw Living Foods Detox Manual (PDFDrive)Ksenija Medic100% (1)
- Organic Compounds in Living Things: PropertiesДокумент96 страницOrganic Compounds in Living Things: PropertiesTUĞRUL ERGÜLОценок пока нет
- B-Complex Vitamins Role in Energy ReleaseДокумент5 страницB-Complex Vitamins Role in Energy ReleaseEno WijayantiОценок пока нет
- 424 MicrobiologyДокумент72 страницы424 MicrobiologyVignesh ReddyОценок пока нет
- Cellular Responses To Stress and Noxious StimuliДокумент12 страницCellular Responses To Stress and Noxious StimulialaboudimuhammadОценок пока нет
- Answer To Exam Practice CHP 5 PDFДокумент5 страницAnswer To Exam Practice CHP 5 PDF[4D06] CHAU PAK YU [4D06] 周柏宇Оценок пока нет
- 7 PorteinsДокумент13 страниц7 PorteinsbalaeОценок пока нет
- Biology 8461/1H: Paper 1 Higher TierДокумент21 страницаBiology 8461/1H: Paper 1 Higher TierSaul CombesОценок пока нет