Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Homework Mechatronic Chapter 7,8,9 (Fatahul Arifin)
Загружено:
Fatahul ArifinАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Homework Mechatronic Chapter 7,8,9 (Fatahul Arifin)
Загружено:
Fatahul ArifinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
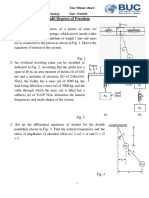
Fatahul Arifin Student Bridging Course National Kaohsiung University Of Applied Science Year 2012/2013 7.
6 Design a pneumatic valve circuit to give sequence A+, followed by B+ and then simultaneously followed by A- and B-. Answer : To solve this problem we can use the diagram movement of cylinder is like table below: Cylinder A
+ + -
Cylinder B
After this table of movement we can draw the figure below.
The equipments are needed: 1. 1 unit compressor 2. 1 unit air-service 3. 2 unit double-acting-cylinder ( A and B)
Homework Chapter 7,8,9 Page 1
4. 2 unit 5/2-way-control-valve with pneumatic actuated 5. 4 unit 3/2-way-control-valve with roller actuated 8.9 Design a mechanical system which can be used to: a. Operate a sequence of micro switches in a timed sequence. b. Move a tool at a steady rate in one direction and then quickly move it back to the beginning of the path. c. Transform a rotation into a linear back-and-forth movement with simple harmonic motion. d. Transform a rotation through some angle into a linear displacement. e. Transform a rotation of a shaft into rotation of another, parallel shaft some distance away. f. Transform a rotation of one shaft into rotation of another close shaft which is at right angles to it. Anwer a. Operate a sequence of micro switches in a timed sequence. The mechanical design for to do this work is camshaft. Camshaft is a shaft that a cam is fixed firmly, or a cam forms an integral part.
b. Move a tool at a steady rate in one direction and then quickly move it back to the beginning of the path. A quick return mechanism such as the one seen below is used where there is a need to convert rotary motion into reciprocating motion. As the disc rotates the black slide moves forwards and backwards. Many machines have this type of mechanism and in the school workshop the best example is the shaping machine.
Homework Chapter 7,8,9
Page 2
c. Transform a rotation into a linear back-and-forth movement with simple harmonic motion. The equipment is an eccentric cam to do this work. It is perfectly circular, but the rotating shaft is off-centre, which affects how it turns. This type of cam produces a smooth, symmetrical rise and fall motion in the follower, which never pauses to dwell.
d. Transform a rotation through some angle into a linear displacement. Rack and pinion is a kind of linear actuator that comprises a pair of gears, which convert rotational motion into linear motion. A circular gear called "the pinion" engages teeth on a linear "gear" bar called "the rack"; rotational motion applied to the pinion causes the rack to move, thereby translating the rotational motion of the pinion into the linear motion of the rack.
e. Transform a rotation of a shaft into rotation of another, parallel shaft some distance away. Belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shaft mechanically. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to spread power efficiently, or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys. In a two pulley system, the belt can either drive the pulleys in the same direction, or the belt can be crossed, so the movement of the shafts is reverse.
Homework Chapter 7,8,9
Page 3
f. Transform a rotation of one shaft into rotation of another close shaft which is at right angles to it. Bevel gears are used to do this work. Bevel gears are most often mounted on shafts that are 90 degrees apart, but can be designed to work at other angles as well. The pitch surface of bevel gears is a cone.
9.4 Suggest possible motors, d.c. or a.c., which can be considered for applications where (a) cheap, constant torque operation is required, (b) high controlled speeds are required, (c) low speed are required, (d) maintenance requirements have to be minimised. Answer: a. D.C. shunt wound
A shunt wound motor has a high-resistance field winding connected in parallel with the armature. It responds to increased load by trying to maintain its speed and this leads to an increase in armature current. This makes it unsuitable for widely-varying loads, which may lead to overheating.
b. Induction motor with inverter
An induction motor is an asynchronous AC motor where power is transferred to the rotor by electromagnetic induction, much like transformer action. An induction motor resembles a rotating transformer, because the stator (stationary part) is essentially the primary side of the transformer and the rotor (rotating part) is the secondary side.
c. d.c. motor
Homework Chapter 7,8,9 Page 4
A DC motor is a mechanically commutated electric motor powered from direct current (DC). The stator is stationary in space by definition and therefore so is its current. The current in the rotor is switched by the commutator to also be stationary in space. This is how the relative angle between the stator and rotor magnetic flux is maintained near 90 degrees, which generates the maximum torque.
d. a.c. motor
An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). It commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stationary stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to the output shaft that is given a torque by the rotating field.
9.5 Explain the principle of the brushless d.c. permanent magnet motor Answer : The brushless DC motor is the combination of a permanent excited synchronous motor and a frequency inverter. The inverter has to replace the commutator of a conventional DC motor. Its armature winding corresponds to a three phase winding in delta connection. The commutator acts like a three phase frequency converter. Stator (excitation) and rotor (armature) change places. The commutation of a brushless DC motor depends on the position of the rotor. The angle between the magneto-motive forces of stator and rotor is fixed to 90 o (el.), so the motor produces maximum torque and needs low reactive current - it might be useful to advance commutation by few degrees to compensate the effects of the stray inductance and minimize reactive current. Speed can only be controlled by the the motor voltage. The motor behaves like a DC motor. Unlike the synchronous motor there are no problems with instability at any speed. Because of the PWM frequency inverter, variation of the motor voltage can be achieved easily by changing the duty cycle of the pulse width modulation. Suitable PWM techniques allow regenerative breaking, which increases dynamic and efficiency of the drive. 9.6 Explain the principles of operation of the variable reluctance stepper motor. Answer: Variable reluctance stepper is kind of the stepper motor. With this form the rotor is made of soft steel and is cylindrical with four poles, i.e. fewer poles than on the stator. When an opposite pair of windings has current switched to them, a magnetic field is produced with lines of force which pass from the stator poles through the nearest set of poles on the rotor. Since lines of force can be considered to be rather like elastic thread and always trying to shorten themselves, the rotor will move until the rotor and stator poles line up. This is termed the position of minimum reluctance. This form of stepper generally gives step angles of 7.5o or 15o.
Homework Chapter 7,8,9 Page 5
Вам также может понравиться
- Types of Cams GuideДокумент21 страницаTypes of Cams GuideHarikrishna ShenoyОценок пока нет
- Mechanism Design: Quick Return, Timing ChartsДокумент6 страницMechanism Design: Quick Return, Timing ChartsAsim AshrafОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ2 страницыAssignment 1Diganta Hatibaruah50% (2)
- Unit5-Gear TrainsДокумент18 страницUnit5-Gear TrainsGokulraju RangasamyОценок пока нет
- Brayton CycleДокумент5 страницBrayton CycleDanang Wahdiat Aulia IshaqОценок пока нет
- Scilab FamiliarizationДокумент9 страницScilab FamiliarizationmbmonvilleОценок пока нет
- Cmps QBFFДокумент80 страницCmps QBFFFeliscio Ascione FelicioОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4: Sequantial Control CircuitДокумент7 страницExperiment 4: Sequantial Control CircuitهرمنساڤارودينОценок пока нет
- Automated Guided VehiclesДокумент1 страницаAutomated Guided VehiclesAmey DukleОценок пока нет
- Dot 1Документ5 страницDot 1Thomas Nathaniel AngОценок пока нет
- Sheets (5) Multi DegreeДокумент6 страницSheets (5) Multi DegreeMohamed MosaОценок пока нет
- Power Plant Chapter 2Документ24 страницыPower Plant Chapter 2Harp Yq100% (1)
- Problems Chapter 5 1Документ7 страницProblems Chapter 5 1Siva KumarОценок пока нет
- Circuits1 1 Laboratory Meters and Power SupplyДокумент2 страницыCircuits1 1 Laboratory Meters and Power SupplyJad DimabuyuОценок пока нет
- C16–EE–303 Board Diploma Examination Oct/Nov 2017 Electrical CircuitsДокумент3 страницыC16–EE–303 Board Diploma Examination Oct/Nov 2017 Electrical CircuitsRehaman ShaikОценок пока нет
- Universal MotorДокумент4 страницыUniversal MotorarunОценок пока нет
- Reducing Multiple Subsystems to Single Transfer FunctionsДокумент5 страницReducing Multiple Subsystems to Single Transfer FunctionssreekanthaОценок пока нет
- E. v. v. Ramanamurthy, S. Ramachandran-Design of Transmission Systems-Air Walk Publ. (2015)Документ1 038 страницE. v. v. Ramanamurthy, S. Ramachandran-Design of Transmission Systems-Air Walk Publ. (2015)Anonymous BrraRVdvv383% (18)
- Control McqsДокумент35 страницControl McqsNuman Khan100% (1)
- Machine Elements L2Документ31 страницаMachine Elements L2Julie Ann D. GaboОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1Документ3 страницыExperiment 1Ben RileyОценок пока нет
- Psoc Textbook by SivanagarajuДокумент925 страницPsoc Textbook by SivanagarajuBhanu BkvОценок пока нет
- Kom Unit 1Документ5 страницKom Unit 1M.ThirunavukkarasuОценок пока нет
- EENG492 Extended Assignment Spring 2019-2020 - v4Документ4 страницыEENG492 Extended Assignment Spring 2019-2020 - v4Jamil NahraОценок пока нет
- Assignment of Control EngineeringДокумент1 страницаAssignment of Control EngineeringahmadОценок пока нет
- Short Questions ECDДокумент7 страницShort Questions ECDNanda Kishore RayОценок пока нет
- f2. Heisler-Grober ChartsДокумент3 страницыf2. Heisler-Grober Chartssyazwani ridzuan100% (1)
- Torsional Vibration HandoutsДокумент3 страницыTorsional Vibration HandoutsjaycobsmillanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ11 страницChapter 3bernabasОценок пока нет
- AUTO400 Homework Assignment 1 SOLUTIONДокумент16 страницAUTO400 Homework Assignment 1 SOLUTIONVinoliaEdwin100% (1)
- 2 Flywheel PDFДокумент10 страниц2 Flywheel PDFMohammed Safuvan KazhungilОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2 PSMДокумент4 страницыAssignment 2 PSMrazu1234Оценок пока нет
- Assignment No.: 2 (Topic Name: Rolling Contact BearingДокумент1 страницаAssignment No.: 2 (Topic Name: Rolling Contact BearingJai Sharma0% (1)
- Introduction to Kinematics of MachinesДокумент3 страницыIntroduction to Kinematics of MachinesEmmanuelRomaresОценок пока нет
- Southern Luzon State University: College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentДокумент8 страницSouthern Luzon State University: College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentRosalyОценок пока нет
- Design of Robot-Centered CellДокумент7 страницDesign of Robot-Centered CellRachnaОценок пока нет
- Marks: 0.00 User Answer Sheet Rank: 7: Report QuestionДокумент17 страницMarks: 0.00 User Answer Sheet Rank: 7: Report Questionchandrachurom5538100% (1)
- SHEET 1 SolutionДокумент9 страницSHEET 1 Solution171148 171148Оценок пока нет
- Magenetic Chip Collector New 2Документ27 страницMagenetic Chip Collector New 2Hemasundar Reddy JolluОценок пока нет
- BMEF17M001 ICE Assignment 2Документ9 страницBMEF17M001 ICE Assignment 2Muhammad Javed IqbalОценок пока нет
- Automatic pneumatic jack designДокумент5 страницAutomatic pneumatic jack designSaravanan ViswakarmaОценок пока нет
- Frog Leg WindingДокумент9 страницFrog Leg WindingAbhijeet RedekarОценок пока нет
- 11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Документ22 страницы11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Bakkiya Raj100% (1)
- Chapter 15 PDFДокумент31 страницаChapter 15 PDFAmirulHanif AlyahyaОценок пока нет
- EET306 Tutorial 3 2018 SolutionДокумент11 страницEET306 Tutorial 3 2018 SolutionShang Divina EbradaОценок пока нет
- Online Lab - Me Lab1 Expt 2 Area MeasurementДокумент5 страницOnline Lab - Me Lab1 Expt 2 Area MeasurementDessa GuditoОценок пока нет
- Assignment (Electric Power Utilization EE16105)Документ4 страницыAssignment (Electric Power Utilization EE16105)Prasenjit DeyОценок пока нет
- Three Phase Induction Motor Interview Questions 2 1Документ24 страницыThree Phase Induction Motor Interview Questions 2 1Kulshresth Joshi100% (1)
- Induction Motor Electric BrakingДокумент12 страницInduction Motor Electric Brakingmastanamma.Y100% (1)
- Bevel GearsДокумент22 страницыBevel GearsNisarg MistryОценок пока нет
- Substation Solved ProblemsДокумент50 страницSubstation Solved ProblemsEli m. paredesОценок пока нет
- Module 6 Reciprocating COMPRESSORДокумент30 страницModule 6 Reciprocating COMPRESSORSylvesterОценок пока нет
- Me 313b Fluid Machineries Module Week 10 13 PDF FreeДокумент60 страницMe 313b Fluid Machineries Module Week 10 13 PDF FreeChris TopherОценок пока нет
- UNIT-1 DC Machines: ConstructionДокумент54 страницыUNIT-1 DC Machines: ConstructionT.ThilagamaniОценок пока нет
- A. Flat Belt & Pulleys: Unit I Design of Transmission Systems For Flexible ElementsДокумент3 страницыA. Flat Belt & Pulleys: Unit I Design of Transmission Systems For Flexible ElementsVijaya Prabhu KumarasamyОценок пока нет
- Gear and Its Train NumericalДокумент3 страницыGear and Its Train NumericalSubidha PaudelОценок пока нет
- MD ShaftДокумент18 страницMD Shaftiftikhar ahmedОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3 19BME069Документ14 страницTutorial 3 19BME06920BME005 INAM SABRIОценок пока нет
- Double Acting Hacksaw Machine Using Scotch Yoke MechanismДокумент32 страницыDouble Acting Hacksaw Machine Using Scotch Yoke Mechanismbalaji67% (12)
- MEMS Trends No.10 2012.04Документ36 страницMEMS Trends No.10 2012.04Fatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Cited Form International Seminar Teori and ApplicationДокумент4 страницыCited Form International Seminar Teori and ApplicationFatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Modeling of Advanced Alkaline Electrolyzers A System Simulation ApproachДокумент13 страницModeling of Advanced Alkaline Electrolyzers A System Simulation ApproachFatahul Arifin100% (2)
- Ch1 PaperSearching 20130928Документ11 страницCh1 PaperSearching 20130928Fatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- MEMS Trends No.9 2012.01Документ40 страницMEMS Trends No.9 2012.01Fatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Homework Chapter 4 and 6Документ3 страницыHomework Chapter 4 and 6Fatahul Arifin100% (1)
- ctm99 2Документ9 страницctm99 2Fatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- LECT11 - 212216 Coefisien AlfaДокумент33 страницыLECT11 - 212216 Coefisien AlfaFatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- ThermocoupleДокумент12 страницThermocoupleFatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Progam Variabel VB 6Документ8 страницProgam Variabel VB 6Fatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Progam Variabel VB 6Документ8 страницProgam Variabel VB 6Fatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Lean ManufacturingДокумент12 страницLean ManufacturingFatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- 5 Axis MachiningДокумент5 страниц5 Axis MachiningFatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Simple Calculator Program CodeДокумент6 страницSimple Calculator Program CodeFatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Presentation 1Документ2 страницыPresentation 1Fatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Prospect of Solar Oven in IndonesiaДокумент4 страницыProspect of Solar Oven in IndonesiaFatahul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Bristol R92JДокумент3 страницыBristol R92JGerson RomeroОценок пока нет
- Fault Current Selection Circuit Breaker Substation LayoutДокумент69 страницFault Current Selection Circuit Breaker Substation LayoutSon NonОценок пока нет
- Conext SW Using Lithium Ion and Advanced Batteries - EngДокумент2 страницыConext SW Using Lithium Ion and Advanced Batteries - EngElectroventica ElectroventicaОценок пока нет
- Info Iec61869-5 (Ed1.0) BДокумент15 страницInfo Iec61869-5 (Ed1.0) Bmido211250% (2)
- CH8-Auxiliary Power Supply PDFДокумент10 страницCH8-Auxiliary Power Supply PDFJuvencio MolinaОценок пока нет
- User Manual: Product Type: Switching Power Supply Model Name: HG2, HP2, PSM, PSLДокумент17 страницUser Manual: Product Type: Switching Power Supply Model Name: HG2, HP2, PSM, PSLotrupon melliОценок пока нет
- Bst100 User ManualДокумент27 страницBst100 User Manualpepsi_bozic100% (1)
- Lab 8: D A AC C: Iode S Lipper IrcuitДокумент8 страницLab 8: D A AC C: Iode S Lipper IrcuitMuhammad Nauman ZakkiОценок пока нет
- Transmission Surge Arrester SpecificationДокумент13 страницTransmission Surge Arrester SpecificationAWОценок пока нет
- Insulation Co OrdinationДокумент4 страницыInsulation Co OrdinationVasudha SinghОценок пока нет
- Operator's Manual: G Design 1000 Through 3000 Amp. SizesДокумент12 страницOperator's Manual: G Design 1000 Through 3000 Amp. SizesJosé David Barrios PadrónОценок пока нет
- Dt109a / Dt107a / Dt106a / Dt105a / Dt104a Auto-Tune Pid Temperature ControllerДокумент4 страницыDt109a / Dt107a / Dt106a / Dt105a / Dt104a Auto-Tune Pid Temperature Controlleralaa suhailОценок пока нет
- MFM376 SERIES ORDER CODE INFORMATION SAFETY PRECAUTIONSДокумент4 страницыMFM376 SERIES ORDER CODE INFORMATION SAFETY PRECAUTIONSRofikОценок пока нет
- Product Datasheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Ns800N, 50 Ka at 415 Vac, Micrologic 2.0 E Trip Unit, 800 A, Fixed, 3 Poles 3DДокумент3 страницыProduct Datasheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Ns800N, 50 Ka at 415 Vac, Micrologic 2.0 E Trip Unit, 800 A, Fixed, 3 Poles 3Dahmed elsheikhОценок пока нет
- Swinburne's Test of DC Machine - Electrical4uДокумент7 страницSwinburne's Test of DC Machine - Electrical4uM Kumar Marimuthu0% (1)
- DM-311 EZ Digital MultimeterДокумент34 страницыDM-311 EZ Digital MultimeterdonsterthemonsterОценок пока нет
- PLL 2138 PDFДокумент208 страницPLL 2138 PDFRaj KumarОценок пока нет
- EeeДокумент13 страницEeesiddharthОценок пока нет
- Side Airbag Sensor Diagnostic CheckДокумент5 страницSide Airbag Sensor Diagnostic Check81968Оценок пока нет
- Fiksna Kompenzacija TransformatorДокумент3 страницыFiksna Kompenzacija Transformatorts45306Оценок пока нет
- Exp2 - Single Phase Uncontrolled RectifierДокумент25 страницExp2 - Single Phase Uncontrolled RectifierAaaa DdddОценок пока нет
- Com Statement (HT APFC22 - 02)Документ2 страницыCom Statement (HT APFC22 - 02)SOUMENОценок пока нет
- Cost DataДокумент7 страницCost DataMohanta AmritОценок пока нет
- P245 - As BuiltДокумент27 страницP245 - As BuiltMaría Ester Tobar TapiaОценок пока нет
- 400A 4-Pole Transfer SwitchДокумент3 страницы400A 4-Pole Transfer Switchbachir oussamaОценок пока нет
- EIM 4 Lesson 4 TransformerДокумент40 страницEIM 4 Lesson 4 TransformerVictor RosalesОценок пока нет
- CS-Datasheet-TOPHiKu6 - CS6W-T v1.6 F45 EN 560-580WДокумент2 страницыCS-Datasheet-TOPHiKu6 - CS6W-T v1.6 F45 EN 560-580WHoàng TuấnОценок пока нет
- Thesis On Solar Power ProjectДокумент86 страницThesis On Solar Power Projectshrey2694% (36)
- Emerson DCSДокумент27 страницEmerson DCSSrikar Reddy GummadiОценок пока нет
- Digital Earth Resistance Tester: AC V DC VДокумент2 страницыDigital Earth Resistance Tester: AC V DC VVincent LinzieОценок пока нет
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignОт EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (137)
- The Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastОт EverandThe Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (76)
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsОт EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsОценок пока нет
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataОт EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (22)
- Transmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualОт EverandTransmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (10)
- Climate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingОт EverandClimate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingОценок пока нет
- Pile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbОт EverandPile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (15)
- Building Support Structures, 2nd Ed., Analysis and Design with SAP2000 SoftwareОт EverandBuilding Support Structures, 2nd Ed., Analysis and Design with SAP2000 SoftwareРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (15)
- Green Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsОт EverandGreen Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsОценок пока нет
- Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresОт EverandAdvanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- Piezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation EngineeringОт EverandPiezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation EngineeringОценок пока нет
- Pipeline Planning and Construction Field ManualОт EverandPipeline Planning and Construction Field ManualРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsОт EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (16)
- Matrix Methods for Advanced Structural AnalysisОт EverandMatrix Methods for Advanced Structural AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Natural Ventilation of Buildings: Theory, Measurement and DesignОт EverandNatural Ventilation of Buildings: Theory, Measurement and DesignОценок пока нет
- Concrete Structures: Repair, Rehabilitation and StrengtheningОт EverandConcrete Structures: Repair, Rehabilitation and StrengtheningОценок пока нет