Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bipolar Stepper Motor
Загружено:
dirty_harry1992Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bipolar Stepper Motor
Загружено:
dirty_harry1992Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bipolar Stepper Motor
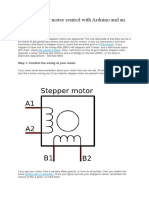
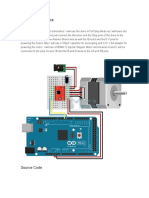
This page shows two examples on how to drive a bipolar stepper motor. These motors can be found in old floppy drives and are easy to control. The one we use has 6 connectors of which one is power (VCC) and the other four are used to drive the motor sending synchronous signals. The first example is the basic code to make the motor spin in one direction. It is aiming those that have no knowledge in how to control stepper motors. The second example is coded in a more complex way, but allows to make the motor spin at different speeds, in both directions, and controlling both from a potentiometer. The prototyping board has been populated with a 10K potentiomenter that we connect to an analog input, and a ULN2003A driver. This chip has a bunch of transistors embedded in a single housing. It allows the connection of devices and components that need much higher current than the ones that the ATMEGA8 from our Arduino board can offer.
Example 1: Simple example
/* Stepper Copal * ------------* * Program to drive a stepper motor coming from a 5'25 disk drive * according to the documentation I found, this stepper: "[...] motor * made by Copal Electronics, with 1.8 degrees per step and 96 ohms * per winding, with center taps brought out to separate leads [...]" * [http://www.cs.uiowa.edu/~jones/step/example.html] * * It is a bipolar stepper motor with 5 wires: * * - red: power connector, I have it at 5V and works fine * - orange and black: coil 1 * - brown and yellow: coil 2 * * (cleft) 2005 DojoDave for K3 * http://www.0j0.org | http://arduino.berlios.de * * @author: David Cuartielles * @date: 20 Oct. 2005 */ int int int int int motorPin1 motorPin2 motorPin3 motorPin4 delayTime = = = = = 8; 9; 10; 11; 500; OUTPUT); OUTPUT); OUTPUT); OUTPUT);
void setup() { pinMode(motorPin1, pinMode(motorPin2, pinMode(motorPin3, pinMode(motorPin4,
} void loop() { digitalWrite(motorPin1, digitalWrite(motorPin2, digitalWrite(motorPin3, digitalWrite(motorPin4, delay(delayTime); digitalWrite(motorPin1, digitalWrite(motorPin2, digitalWrite(motorPin3, digitalWrite(motorPin4, delay(delayTime); digitalWrite(motorPin1, digitalWrite(motorPin2, digitalWrite(motorPin3, digitalWrite(motorPin4, delay(delayTime); digitalWrite(motorPin1, digitalWrite(motorPin2, digitalWrite(motorPin3, digitalWrite(motorPin4, delay(delayTime); } HIGH); LOW); LOW); LOW); LOW); HIGH); LOW); LOW); LOW); LOW); HIGH); LOW); LOW); LOW); LOW); HIGH);
Example 2: Stepper Bipolar Advanced
/* Stepper Bipolar Advanced * -----------------------* * Program to drive a stepper motor coming from a 5'25 disk drive * according to the documentation I found, this stepper: "[...] motor * made by Copal Electronics, with 1.8 degrees per step and 96 ohms * per winding, with center taps brought out to separate leads [...]" * [http://www.cs.uiowa.edu/~jones/step/example.html] * * It is a bipolar stepper motor with 5 wires: * * - red: power connector, I have it at 5V and works fine * - orange and black: coil 1 * - brown and yellow: coil 2 * * (cleft) 2005 DojoDave for K3 * http://www.0j0.org | http://arduino.berlios.de * * @author: David Cuartielles * @date: 20 Oct. 2005 */ int int int int motorPins[] = {8, 9, 10, 11}; count = 0; count2 = 0; delayTime = 500;
int val = 0; void setup() { pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); for (count = 0; count < 4; count++) { pinMode(motorPins[count], OUTPUT); } } void moveForward() { if ((count2 == 0) || (count2 == 1)) { count2 = 16; } count2>>=1; for (count = 3; count >= 0; count--) { digitalWrite(motorPins[count], count2>>count&0x01); } delay(delayTime); } void moveBackward() { if ((count2 == 0) || (count2 == 1)) { count2 = 16; } count2>>=1; for (count = 3; count >= 0; count--) { digitalWrite(motorPins[3 - count], count2>>count&0x01); } delay(delayTime); } void loop() { val = analogRead(0); if (val > 540) { // move faster the higher the value from the potentiometer delayTime = 2048 - 1024 * val / 512 + 1; moveForward(); } else if (val < 480) { // move faster the lower the value from the potentiometer delayTime = 1024 * val / 512 + 1; moveBackward(); } else { delayTime = 1024; } }
Вам также может понравиться
- Connect Motor Controller Pins To Arduino Digital PinsДокумент6 страницConnect Motor Controller Pins To Arduino Digital PinsMuhammadAkbarAsisОценок пока нет
- Step 1: Specification, Motor DriverДокумент8 страницStep 1: Specification, Motor DriverAfriОценок пока нет
- C Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemОт EverandC Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemОценок пока нет
- ArduinoДокумент156 страницArduinoMike Gomez91% (23)
- Easy To Build CNC Mill Stepper Motor and Driver CircuitsДокумент11 страницEasy To Build CNC Mill Stepper Motor and Driver CircuitsAhida Butik100% (1)
- EASA Exam - Module 04 ElectronicsДокумент115 страницEASA Exam - Module 04 Electronicsbika100% (1)
- Build A Simple PLC Using ArduinoДокумент7 страницBuild A Simple PLC Using ArduinoFredy Peñafiel Paz100% (2)
- Global User GuideДокумент107 страницGlobal User GuideManny MendozaОценок пока нет
- FPGA With Touch ScreenДокумент23 страницыFPGA With Touch ScreenCharawut MasukОценок пока нет
- CCS ExampleДокумент28 страницCCS Exampletuane07100% (3)
- STM32 Tutorial 04 - I2C Module (Pca9685) Using HAL (And FreeRTOS)Документ6 страницSTM32 Tutorial 04 - I2C Module (Pca9685) Using HAL (And FreeRTOS)Quocdt Ngoc100% (1)
- ESP8266 - Independent Study - mr945 PDFДокумент49 страницESP8266 - Independent Study - mr945 PDFsaravananОценок пока нет
- Capstone Project 1Документ47 страницCapstone Project 1priyanka allaka100% (3)
- Mitsumi M42sp-4np Pluged To ArduinoДокумент4 страницыMitsumi M42sp-4np Pluged To ArduinoFedorTashkinОценок пока нет
- Connect Motor Controller Pins To Arduino Digital PinsДокумент5 страницConnect Motor Controller Pins To Arduino Digital PinsMuhammadAkbarAsisОценок пока нет
- Connect Motor Controller Pins To Arduino Digital PinsДокумент5 страницConnect Motor Controller Pins To Arduino Digital PinsMuhammadAkbarAsis100% (1)
- 20IE10051 RITIK Tuesday HW4Документ10 страниц20IE10051 RITIK Tuesday HW4ritikОценок пока нет
- Micro-Controllers Post Lab 7: ObjectiveДокумент2 страницыMicro-Controllers Post Lab 7: ObjectiveSyed Zain AbbasОценок пока нет
- Transforming Your AVR Microcontroller To The I2C or TWI Slave I - O Expander Project - ErmicroblogДокумент18 страницTransforming Your AVR Microcontroller To The I2C or TWI Slave I - O Expander Project - Ermicroblogمحمد الد ين الفجرОценок пока нет
- Keypad - I2C.cpp - Bloco de NotasДокумент2 страницыKeypad - I2C.cpp - Bloco de NotasJackson FerreiraОценок пока нет
- Iot Record111Документ53 страницыIot Record111Mohammed ShahidОценок пока нет
- Testing Pic Code For I2C Master - Slave CommunicationДокумент15 страницTesting Pic Code For I2C Master - Slave CommunicationJavier Corimaya33% (3)
- Eastern Mediterranean UniversityДокумент24 страницыEastern Mediterranean UniversityMpu KatanaОценок пока нет
- 8 Channel 5V 10a Relay ModuleДокумент7 страниц8 Channel 5V 10a Relay ModuleArnaudОценок пока нет
- 10A DC Motor Driver ManualДокумент16 страниц10A DC Motor Driver ManualthysmjbОценок пока нет
- Arduino Bipolar Stepper Motor Control - Imple ProjectsДокумент9 страницArduino Bipolar Stepper Motor Control - Imple ProjectsSssОценок пока нет
- I2c EEPROM FULL CODEДокумент24 страницыI2c EEPROM FULL CODESumathi AnandОценок пока нет
- This Is Arduino Code To Control 28BYjДокумент3 страницыThis Is Arduino Code To Control 28BYjRejaul KarimОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 6Документ12 страницLab Report 6Rama AliОценок пока нет
- Bai Thuc Hanh KTVXLДокумент71 страницаBai Thuc Hanh KTVXLHương LanОценок пока нет
- Address Able LatchДокумент9 страницAddress Able Latchjnanesh1987Оценок пока нет
- 20soece11004 Krupa Bhalani Iot Experiment - 1Документ5 страниц20soece11004 Krupa Bhalani Iot Experiment - 1kbhalani288Оценок пока нет
- IOT PracticalДокумент10 страницIOT PracticalParmar ManthanОценок пока нет
- A Quick and Dirty Function Generator ELP 305: Design and System LaboratoryДокумент6 страницA Quick and Dirty Function Generator ELP 305: Design and System LaboratorySamarthОценок пока нет
- 03 Circuit Schematics An4988Документ3 страницы03 Circuit Schematics An4988Adam Mamani100% (1)
- CD4067 Multiplexer Used To Control LEDs Code, Circuits, & ConstructionДокумент3 страницыCD4067 Multiplexer Used To Control LEDs Code, Circuits, & ConstructionAndreaZannoОценок пока нет
- ES Lab FileДокумент37 страницES Lab FileMøhït JáñgírОценок пока нет
- MikroElektronika - View Topic - EnC28J60 and PIC18F4550 Ethernet CommunicationДокумент7 страницMikroElektronika - View Topic - EnC28J60 and PIC18F4550 Ethernet CommunicationDanh_IS4Оценок пока нет
- Exp 04Документ6 страницExp 04ZAHID HOSSAINОценок пока нет
- Turtle KitДокумент51 страницаTurtle KitInstituto La Católica HuánucoОценок пока нет
- BEE-9D ESD Lab 1Документ4 страницыBEE-9D ESD Lab 1Saad NadeemОценок пока нет
- Digital LabДокумент61 страницаDigital LabShanmugaraja PОценок пока нет
- Control Lab3 ReportДокумент14 страницControl Lab3 ReportSai Susrush KadiyalaОценок пока нет
- Lab ManualДокумент78 страницLab Manualgurusandhya11Оценок пока нет
- ECE 2003 ManualДокумент79 страницECE 2003 Manualannambaka satishОценок пока нет
- Traffic LightДокумент19 страницTraffic LightDianne ParОценок пока нет
- WWW Ermicro ComДокумент19 страницWWW Ermicro ComDinosaurio1990Оценок пока нет
- Ard1 - Using 7-Segment and PWMДокумент8 страницArd1 - Using 7-Segment and PWMaliОценок пока нет
- #1 Blink An LEDДокумент23 страницы#1 Blink An LEDclaire cabatoОценок пока нет
- IoT Basics and Smart Sensors - EXP 3Документ8 страницIoT Basics and Smart Sensors - EXP 3swapnilsghadge1807Оценок пока нет
- An Arduino Library To Control The 28BYJ-48 Stepper Motor - CodeProjectДокумент9 страницAn Arduino Library To Control The 28BYJ-48 Stepper Motor - CodeProjectshokaxОценок пока нет
- 1 2 3 MergedДокумент38 страниц1 2 3 MergedthesoulmatecreationОценок пока нет
- Hindustan College of Science and Technology Farah, MathuraДокумент34 страницыHindustan College of Science and Technology Farah, MathuraK.D. computerОценок пока нет
- High Stepping Automatic Coil WinderДокумент7 страницHigh Stepping Automatic Coil WinderradovanovdОценок пока нет
- K179. Unipolar Steppermotor Driver: Five, Six or Eight Wires. Five-Wire Motors Have The TwoДокумент2 страницыK179. Unipolar Steppermotor Driver: Five, Six or Eight Wires. Five-Wire Motors Have The TwoducchungОценок пока нет
- NV5001 PDFДокумент34 страницыNV5001 PDFdhakadpradeepОценок пока нет
- Experiment No 1 GLCDДокумент18 страницExperiment No 1 GLCDDakshata WaghОценок пока нет
- ECPC Assignment 2 - With AnsДокумент4 страницыECPC Assignment 2 - With AnsYashwin.v YashuОценок пока нет
- ARM STM32F107 Development Board ManualДокумент66 страницARM STM32F107 Development Board ManualTiago AveiroОценок пока нет
- XSIM Telemetry Data To MotorsДокумент10 страницXSIM Telemetry Data To MotorsperrociegoОценок пока нет
- Display "Hello World"message Using Internal UARTДокумент16 страницDisplay "Hello World"message Using Internal UARTAkshathaОценок пока нет
- Ramakrishna Mission Shilpamandira: IR Remote Mains SwitchingДокумент29 страницRamakrishna Mission Shilpamandira: IR Remote Mains SwitchingDebabrata AdakОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Gedit EditorДокумент51 страницаIntroduction To The Gedit Editortonitt100% (1)
- CV ExampleДокумент1 страницаCV ExampleIgor SavchukОценок пока нет
- AN00153 Programming OTP Memory Via SPI Boot 1.0.2rc1Документ12 страницAN00153 Programming OTP Memory Via SPI Boot 1.0.2rc1Dimitris DimitriadisОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Computer: Chapter OneДокумент33 страницыIntroduction To Computer: Chapter OneYaregal ChalachewОценок пока нет
- ECAD Question BankДокумент5 страницECAD Question Bank20BF1A04M6 sumanthОценок пока нет
- Imag Diagramas 4Документ1 страницаImag Diagramas 4BG Jluis100% (1)
- Part 1. Video1Документ2 страницыPart 1. Video1Andr AzevedoОценок пока нет
- Ebook Electrical Engineering Principlesand Applications 6Th Edition Hambley Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент68 страницEbook Electrical Engineering Principlesand Applications 6Th Edition Hambley Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFbonnieusefullygllin100% (11)
- ONYXSWORKДокумент4 страницыONYXSWORKMuhammad Azizi SubariОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Parallel Quick and Merge Sort Algorithms On Architecture With Shared MemoryДокумент6 страницComparison of Parallel Quick and Merge Sort Algorithms On Architecture With Shared Memoryemir8galloОценок пока нет
- Computer Systems Unit 2 - Fill The BlanksДокумент7 страницComputer Systems Unit 2 - Fill The BlanksDavidoffОценок пока нет
- Xiner-Xnf15n60t C379741Документ1 страницаXiner-Xnf15n60t C379741Imran AslamОценок пока нет
- WCF Guidance For WP F DevelopersДокумент66 страницWCF Guidance For WP F DevelopersrayanmoussaОценок пока нет
- Eurosens DDS User Manual en v2 00 2Документ57 страницEurosens DDS User Manual en v2 00 2joseph wamweaОценок пока нет
- AWS Storage OverviewДокумент22 страницыAWS Storage OverviewGustavo Adolfo Gamboa CruzОценок пока нет
- JVM JRE JDK Program Exe FlowДокумент6 страницJVM JRE JDK Program Exe Flowshubham gajbhiyeОценок пока нет
- Networks of Workstations: (Distributed Memory)Документ19 страницNetworks of Workstations: (Distributed Memory)aliha ghaffarОценок пока нет
- Beginner Guide Mimic Training Kit Nordbo RoboticsДокумент15 страницBeginner Guide Mimic Training Kit Nordbo RoboticsCaio AlvesОценок пока нет
- Ali Omar CVДокумент3 страницыAli Omar CVlooool1984100% (5)
- LogcatДокумент197 страницLogcatAdheShenzaОценок пока нет
- A System For Speed and Torque Control of DC Motors With Application To Small Snake RobotsДокумент6 страницA System For Speed and Torque Control of DC Motors With Application To Small Snake RobotsASOCIACION ATECUBOОценок пока нет
- Csla4 AllbooksДокумент1 017 страницCsla4 AllbooksJoseph RiccardoОценок пока нет
- Programming Practices QuestionsДокумент29 страницProgramming Practices QuestionsBoby RathourОценок пока нет
- Eee312 ContentДокумент2 страницыEee312 Contentjames deepbreatheОценок пока нет
- System Tools and Documentation TechniquesДокумент4 страницыSystem Tools and Documentation TechniquesVenice DatoОценок пока нет
- 6 Data Storage and QueryingДокумент58 страниц6 Data Storage and Queryingfdghj100% (1)