Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Business Law 1
Загружено:
Pranjit BhuyanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Business Law 1
Загружено:
Pranjit BhuyanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
If there are images in this attachment, they will not be displayed.
Download the original attachment
Page 1 1
UNIT I CONTRACT ACT 1872 WHAT ARE THE ESSENTIALS OF A CONTRACT UNDER THE CONTRACT ACT 1872?
OUTLINE OF CLASS DISCUSSIONS Masoud Zafer School of Business Studies Sharda University Greater Noida January 11, 2011
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Follow up this outline of our class discussions on Essentials of a Contract in conjunction with your class notes, Bare Act, plus any book of your choice from the Suggested Readings list at the bottom of the syllabus. You may discuss your questions on this topic with me in my cubicle in the School of Business Studies Building between 9:30 am and 5:00 pm, except class hours, on working days. You can post your questions, access the transcripts of class discussions, the question bank, syllabus, plus web links to important articles at Sharda Universitys Learning and Management System (LMS). --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
b What are the essentials of a contract?
The essentials are: Offer
+
Acceptance
+
Consideration
+
S 10 components (Consideration, Competent Parties, Free Consent, Lawful Object)
+
Intention to create legal relations Page 2 2
b To create a contract, FIRST create its FOUNDATION:
Offer
+
Acceptance
+
Consideration
b Next, add TWO more essentials to the foundation
They are: -- S 10
-- Intention to create legal relations
b S 10 contains FIVE components of legal enforceability
S 10 says, an agreement will become a contract when it is
8
made for Consideration
8
between Parties
8
who are Competent
8
with their Free Consent
8
for a Lawful Object S 10 or Legal Enforceability require Offer, Acceptance, Consideration to take place - between parties who are
Competent
, i.e. they understand the consequences of their actions (e.g. they are not minors, or of unsound mind ) - with their
Free Consent
, i.e. not through force (e.g. not at the point of a gun ) - for a
Lawful Object
, (e.g. not to sell drugs ) Solve this case Mr. Good Heart buys a brand new latest series Mercedes sports car from a showroom. Same morning he takes out Miss Devious for a joy ride in his new car. That evening Miss Devious invites him to an expensive restaurant for dinner. She orders expensive wines and gets Mr. Good Heart drunk. She then offers to buy his car for Rs10,000. Mr. Good Heart accepts. She gives him the money, and he gives her the car keys and papers. Next morning he realizes what he did in the restaurant. He contacts his lawyer, and Miss Devious contacts hers. Page 3 3 The matter goes to the court of Judge I.M. Sober. Miss Devious lawyer argues there was OFFER, ACCEPTANCE, CONSIDERATION between his client and the Plaintiff. Mr. Good Hearts lawyer argues, Yes there was offer, acceptance, consideration, but it happened when his client was of
unsound mind
. State what Judge I.M. Sober is likely to write in his judgment.
b Intention to create legal relations
In social agreements the presumption is that the parties do not intend to create legal relations.
An agreement to go a restaurant is not a valid agreement under the Act as the law presumes that parties did not intend to create legal relations. In business agreements the presumption is of legal relations where parties intention operates automatically in the background of their agreement. Illustration A offers to sell his LML 150cc scooter to B for Rs4,000, and Bs acceptance of that offer is a valid contract as law presumes that parties intended to create legal relations. If A breaches the contract and puts up his defense that he intended his offer to be a joke, will the court accept that? There were offer, acceptance, consideration + presence of s 10 components + presence of intention to create legal relations Can you explain why A will not succeed in his defense? Can you explain why the law treats contracts, big or small, very seriously?
Summing Up
To fully understand a contract, look up
THREE
sections: i. S 2(h): Definition of Contract Contract = Agreement + Legal Enforceability ii. S 2(e): Definition of Agreement Agreement = Offer + Acceptance (i.e. mutual exchange of promises) Page 4 4 iii. S 10:
FIVE
components of Legal Enforceability An agreement will become a contract when it is:
8
made for Consideration
8
between Parties
8
who are Competent
8
with their Free Consent
8
for a Lawful Object And
NEVER EVER
forget Contracts need not be written and registered. (There are however certain exceptions) Most contracts are in fact oral When you buy bread, butter and coffee, it is a contract.
When you send your car to a garage for repairs, it is a contract. Do you write these contracts, or register them? Test your knowledge Distinguish between: Social agreement Business agreement ___________________________
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Beginner Guide To Drawing AnimeДокумент14 страницBeginner Guide To Drawing AnimeCharles Lacuna75% (4)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Apollo Parachute Landing SystemДокумент28 страницThe Apollo Parachute Landing SystemBob Andrepont100% (2)
- Hamlet Test ReviewДокумент3 страницыHamlet Test ReviewAnonymous 1iZ7ooCLkj100% (2)
- NIVEA Umbrella BrandingДокумент28 страницNIVEA Umbrella BrandingAnamikaSenguptaОценок пока нет
- Arne Langaskens - HerbalistДокумент3 страницыArne Langaskens - HerbalistFilipОценок пока нет
- Dipu MedicalДокумент1 страницаDipu MedicalPranjit BhuyanОценок пока нет
- TZBT LRQCMG ONg DwoДокумент6 страницTZBT LRQCMG ONg DwoPranjit BhuyanОценок пока нет
- How To CrackДокумент1 страницаHow To CrackPranjit BhuyanОценок пока нет
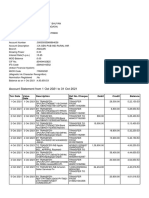
- Account Statement From 1 Nov 2021 To 30 Nov 2021: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceДокумент4 страницыAccount Statement From 1 Nov 2021 To 30 Nov 2021: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalancePranjit BhuyanОценок пока нет
- Equity and Hybrid InstrumentsДокумент75 страницEquity and Hybrid InstrumentsPranjit BhuyanОценок пока нет
- DiversificationДокумент2 страницыDiversificationPranjit BhuyanОценок пока нет
- Investment ManagementДокумент38 страницInvestment ManagementPranjit BhuyanОценок пока нет
- Management Information SystemДокумент98 страницManagement Information SystemPranjit BhuyanОценок пока нет
- Econ 281 Chapter02Документ86 страницEcon 281 Chapter02Elon MuskОценок пока нет
- Short StoriesДокумент20 страницShort StoriesPatrick Paul AlvaradoОценок пока нет
- Human Rights in The Secondary SchoolДокумент57 страницHuman Rights in The Secondary SchoolJacaОценок пока нет
- Research Papers Harvard Business SchoolДокумент8 страницResearch Papers Harvard Business Schoolyquyxsund100% (1)
- 0015020KAI LimДокумент22 страницы0015020KAI LimJoshua CurtisОценок пока нет
- MGMT S-2000 Harvard University Summer School Principles of Finance Summer, 2016Документ14 страницMGMT S-2000 Harvard University Summer School Principles of Finance Summer, 2016David MorganОценок пока нет
- Art CriticismДокумент3 страницыArt CriticismVallerie ServanoОценок пока нет
- Member, National Gender Resource Pool Philippine Commission On WomenДокумент66 страницMember, National Gender Resource Pool Philippine Commission On WomenMonika LangngagОценок пока нет
- Peer Pressure and Academic Performance 1Документ38 страницPeer Pressure and Academic Performance 1alnoel oleroОценок пока нет
- Distribution Optimization With The Transportation Method: Risna Kartika, Nuryanti Taufik, Marlina Nur LestariДокумент9 страницDistribution Optimization With The Transportation Method: Risna Kartika, Nuryanti Taufik, Marlina Nur Lestariferdyanta_sitepuОценок пока нет
- Highway MidtermsДокумент108 страницHighway MidtermsAnghelo AlyenaОценок пока нет
- Infographic Group Output GROUP 2Документ2 страницыInfographic Group Output GROUP 2Arlene Culagbang GuitguitinОценок пока нет
- Burger 2005Документ7 страницBurger 2005Stefania PDОценок пока нет
- Ernest Renan What Is Nation PDFДокумент2 страницыErnest Renan What Is Nation PDFJohnny0% (1)
- Ukg HHW 2023Документ11 страницUkg HHW 2023Janakiram YarlagaddaОценок пока нет
- Running Head: Mental Illness As A Cause of Homelessness 1Документ12 страницRunning Head: Mental Illness As A Cause of Homelessness 1api-286680238Оценок пока нет
- NASA: 45607main NNBE Interim Report1 12-20-02Документ91 страницаNASA: 45607main NNBE Interim Report1 12-20-02NASAdocumentsОценок пока нет
- A Copmanion To Love Druga KnjigaДокумент237 страницA Copmanion To Love Druga KnjigaSer YandeОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Loan Repayment Performance: in Case of Awash Bank in Sikela BranchДокумент9 страницAssessment of Loan Repayment Performance: in Case of Awash Bank in Sikela Branchbundesa buzo100% (1)
- The Cornerstones of TestingДокумент7 страницThe Cornerstones of TestingOmar Khalid Shohag100% (3)
- Gravity & MagneticДокумент13 страницGravity & MagneticBunny Leal100% (1)
- Multiple Effect EvaporatorДокумент4 страницыMultiple Effect EvaporatorKusmakarОценок пока нет
- SPM Bahasa Inggeris PAPER 1 - NOTES 2020Документ11 страницSPM Bahasa Inggeris PAPER 1 - NOTES 2020MaryОценок пока нет
- Thesis RadioactivityДокумент13 страницThesis RadioactivitysaanvicodingОценок пока нет
- Libro de Social Studies PDFДокумент76 страницLibro de Social Studies PDFNoheОценок пока нет