Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Physics 2 F4 Midyr 06
Загружено:
Surendran NagiahОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics 2 F4 Midyr 06
Загружено:
Surendran NagiahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics Paper 2 2006 2 hour SMK BANDAR UTAMA DAMANSARA (4), PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR.
2006 MID YEAR EXAMINATION Physics Form 4 Paper 2 Two hour DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL BEING TOLD 1. This question paper contains 2 sections. 2. Answer all questions in both sections. 3. Diagrams accompanying the questions are meant to give useful information to answering the questions. The diagrams may not be drawn in scale. 4. Write your answer for section A in the space provided after each question. 5. Write your answer for section B on the writing paper
Set by: ______________________ (Pn. Leow Hoay Suan)
Checked by: ________________________ (En. Long Fu Soon)
Parents signature: _______________________
This question paper contains 8 printed pages. [Turn to next page]
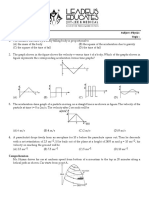
Section A (60%) Answer all questions on the space provided after each question. 1. A student conducted an experiment to investigate the relationship between the acceleration and mass of a trolley when the force is constant. His results are shown on the graph below.
a)
Based on the graph given, what is the relationship between the acceleration and mass of a trolley when the force is constant? (1M)
____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Calculate the gradient of the graph when the mass is 5 kg. Show how you get your answer on the graph. (2M)
c)
Determine the mass of the trolley if its acceleration is 2 cms-2. Show how you get your answer on the graph. (1M)
____________________________________________________________________________________ d) Extrapolate the graph to determine the acceleration of the trolley if its mass is 15 kg. (1M) _______________________________________________________________________________ e) What is the relationship between a and a
1 ? Sketch the graph on the axis below. m
(1M)
1 2. SMK BUD (4) Sport Carnival started at 9.00 a.m. The weather was fine with the wind blowing 2 ms-1 m first event was the 100 m race for class 3. from the north. The temperature on the field was 32 oC. The Shawn was the first to reach the finishing line with a time of 15.0 s. The second event was the short put. Irwan threw a 5 kg short put with a force 100N.
i) Tabulate all physical quantities given above into 2 categories.
(3M)
ii) If Irwan throw the short put at 30 o to the horizontal axis with a force of 100 N. i. Draw and label all the forces acting on the short put as soon as it leaves his palm.
(2M)
ii. Find the resultant force acting on the short put using the graphical method.
(3M)
5m/s y
x iii) The initial velocity of the short put was 5 ms-1 and it took 0.6 s to land. i. Calculate the horizontal distance x when the short put landed. (2M)
ii. Calculate the vertical distance between Irwans palm and the ground, y at the moment it left his palm. (Assume that gravitational acceleration, g = 10 ms-2. (2M)
iv) If Irwan changed the short put with a ping pong ball and threw it he same way as before, do you think it will take the same amount of time to land? Explain your answer. (2M) __________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________
3. The above figure shows a boy sliding down a slide that is smooth. The boy is 40 kg and when he reached P at 20 ms-1 and P is 60 m from ground. After reaching Q, the boy continued moving to R. QR is horizontal and smooth. i) What form of energy does the boy have at P? (1M)
_______________________________________________________________________________ ii) How much energy does he have at P? (2M)
iii) Calculate his velocity at Q.
(2M)
iv) At R, the boy hit a 2kg ball which was hung up by a string from a beam. After the collision, the ball swung up h meter while the boy went down into the pool at 39m/s. i. What is the maximum velocity of the ball after the collision? (2M)
ii. Calculate the value h.
(2M)
iii. What is the important assumption made when you answer d (i)? 4
(1M)
____________________________________________________________________________________ iv. Explain why the end of the slide PQR was placed above the pool? (1M) ____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. John was kicking a stationary 3kg football. His leg hit the ball at 0.2 m/s and his leg and the ball were in contact for 0.02 s. i) Define impulsive force. (2M) ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ii) Calculate the impulsive force acting on Johns leg. (2M)
iii) How much was the impulsive force on the ball?
(1M)
iv) What changes will occur to the impulsive force if John kicked a football that was filled with more air? (1M) _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ v) State an application of impulsive force in our daily lives. (1M)
______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ vi) State a negative effect of large impulsive force in our daily lives. (1M)
_____________________________________________________________________________________ vii) Suggest a way to reduce the negative effect of impulsive force mention in 4 (vi). (1M) ______________________________________________________________________________________
30o T2 Billboard T1
0N 5. A billboard of 100 kg has to be placed 50 m up from the ground. It was lifted up by a crane with a power of 5 kW. Two strong cables were used to keep the billboard in equilibrium. a) What does in equilibrium mean? (2M)
100 1000N
______________________________________________________________________________________ b) How long does the crane take to lift the billboard up 50 m? (2M)
c)
Calculate the tension, T1.
(2M)
d) Calculate the tension, T2.
(2M)
6. A ball was thrown upwards with the initial velocity of 20 m/s from the top of the head of a girl. She is 1.5m tall. i) Calculate the maximum height that the ball can reach above the top of her head. (2M)
ii) Calculate the time taken for the ball to return to the top of the head of the girl.
(2M)
iii) What is the velocity of the ball when it returns to her head?
(1M)
iv) If the girl did not catch the ball in time and it fell to the ground, calculate the velocity of the ball when it touches the ground. (2M)
v) Sketch the speed-time and velocity-time graphs of the ball on the axes below. i. Speed-time ii. Velocity-time
(4M)
Section B (40%) Answer all questions on the writing paper.
0.2m/s
stationary
1. a)
A 50-cent coin, P is placed on a smooth surface of a table. The 3 g coin was pushed and it moved at a velocity of 0.2 ms-1 towards a 20-cent coin, Q. Q is 1 g and stationary. After the collision, P continued to move forward at 0.1 ms-1 while Q moved independently with velocity, v. i) What is momentum? (2M) ii) Name the type of collision involved in this collision. (1M) iii) Calculate the velocity of Q after the collision (2M)
b) The above diagram shows two ice skaters facing each other just before they start a dance routine. The weight of the man and the woman is 60 kg and 45 kg respectively. The man pushes the woman and they move apart. She moves to the left at 20 ms-1 while he moves to the right at a slower velocity. i) Name the Law of Physics involved. ii) Explain the above observation by calculating the velocity of the man. iii) Describe how the same effect is used in launching a rocket. (1M) (3M) (4M)
3m
5m
30o
c)
A 6 kg ball is rolling down through a smooth inclined plane of 30o. The length of the incline plane is 5 m. i) Copy the above diagram and draw all the forces acting on the ball. (3M) ii) Calculate the acceleration of the ball when it is rolling down the plane. (2M) iii) Calculate the work done by the ball when it rolls down from the top to the lowest point of the plane. (2M)
2. Tom and Jerry were running towards Desmond with the same velocity. The masses of Tom and Jerry are 50 kg and 65 kg respectively. Desmond tried to stop the boys. He could stop him very easily. But Tom fell back when he tried to stop Jerry. Based on the observations, a) Describe the physical quantity involved in the above situation. (1M) b) Explain the above situation. (2M) c) Make a suitable inference from the above situation. (2M) d) State an appropriate hypothesis that could be investigated. (2M) e) Using a jigsaw blade, plasticine, G-clamp and other apparatus, describe how you would design an experiment to test your hypothesis. In your description, state the following: (10M) i) Aim of the experiment, ii) Variables involved, iii) List of apparatus and materials used, iv) Arrangement of the apparatus, v) Labeled diagram of the setup of apparatus. vi) The procedure of the experiment, including the method of controlling the manipulated variable and the method of measuring the responding variable, vii) The way you would tabulate the data, viii) The way you would analyse the data. ix) From the experiment, define operationally the period of oscillation of the jigsaw blade. (2M) x) How would the period of oscillation be affected if a longer jigsaw blade is used? (1M) ______________________________________________________________________________________ END OF QUESTION PAPER
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- CH 2 Solutions - Walker PhysicsДокумент32 страницыCH 2 Solutions - Walker PhysicsSadiel Perez70% (10)
- Minds On Physics ....Документ35 страницMinds On Physics ....Matius BiuSarraОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Lab 8 Energy of A Tossed BallДокумент5 страницLab 8 Energy of A Tossed BallvincinugeОценок пока нет
- Electrical Engineer Resume Sample - Advanced OriginalДокумент2 страницыElectrical Engineer Resume Sample - Advanced OriginalMalliga MaganОценок пока нет
- M1 Question Paper January 21Документ24 страницыM1 Question Paper January 21Shere AhmedОценок пока нет
- READ - ME (Font Installation) PDFДокумент1 страницаREAD - ME (Font Installation) PDFSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- Hosts UmbrellaДокумент1 страницаHosts UmbrellaFabsor SoralОценок пока нет
- RARBGДокумент1 страницаRARBGSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- Inti Travels SlidesДокумент10 страницInti Travels SlidesSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- Problem Solving: Developing Life SkillsДокумент25 страницProblem Solving: Developing Life SkillsAakash KambleОценок пока нет
- Note c2305Документ1 страницаNote c2305Surendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- EE108 TC Company Registration Form J16Документ2 страницыEE108 TC Company Registration Form J16Surendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- 1 Units and Sig DigitsДокумент20 страниц1 Units and Sig DigitsSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- Chapter3 DesignДокумент13 страницChapter3 DesignSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- EE101 Tutorial-6 AnswerДокумент7 страницEE101 Tutorial-6 AnswerSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- 2 ForcesДокумент20 страниц2 ForcesSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- JADUAL TUGASdДокумент1 страницаJADUAL TUGASdSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- SMS CuteДокумент5 страницSMS CuteSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- Elemen 2Документ1 страницаElemen 2Surendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- ACADEMIC CALENDAR 2014 - Student: January February March AprilДокумент3 страницыACADEMIC CALENDAR 2014 - Student: January February March AprilSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- 1mca Education Loan SchemeДокумент3 страницы1mca Education Loan SchemeSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- GamedataДокумент1 страницаGamedataedenamiriambutОценок пока нет
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightДокумент593 страницыHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- (Malaysians Only) : Postgraduate Programmes Fee ScheduleДокумент2 страницы(Malaysians Only) : Postgraduate Programmes Fee ScheduleSurendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- Elemen 2Документ1 страницаElemen 2Surendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- Elemen 2Документ1 страницаElemen 2Surendran NagiahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Motion - ObjДокумент3 страницыChapter 8 - Motion - ObjShubh tiwari TiwariОценок пока нет
- Work Energy and Power1Документ13 страницWork Energy and Power1E guruОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 3 - 2023ProjectileMotion 2Документ46 страницChapter - 3 - 2023ProjectileMotion 2문용준Оценок пока нет
- EAMCET 2015 - EngineeringДокумент26 страницEAMCET 2015 - EngineeringNeepur Garg100% (1)
- Lecture Note 03.2 Reponse Specturm AnalysisДокумент8 страницLecture Note 03.2 Reponse Specturm AnalysisPrasanna AbeysekaraОценок пока нет
- Energy and Momentum Conceptual SurveyДокумент12 страницEnergy and Momentum Conceptual SurveyMenna GalalОценок пока нет
- Early Warning in South Asia Constarints and ImplecationsДокумент43 страницыEarly Warning in South Asia Constarints and Implecationsquaidian06Оценок пока нет
- Physics 10th Edition Cutnell Solutions Manual 1Документ36 страницPhysics 10th Edition Cutnell Solutions Manual 1marchowardwacfrpgzxn100% (27)
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Practice CpoДокумент6 страницPotential and Kinetic Energy Practice Cpoapi-319102793Оценок пока нет
- 11 Physic SolutionДокумент330 страниц11 Physic Solutioncrazy about readingОценок пока нет
- Force Motion O-Level-Physics-Notes-by-Sir-Abdul-Hakeem-Updated-2019Документ19 страницForce Motion O-Level-Physics-Notes-by-Sir-Abdul-Hakeem-Updated-2019Naveed KHANОценок пока нет
- Kinematic Characterization of Lacrosse Shooting Motions of The Dominant and Non-Dominant Side: 1940 Board #226 May 29, 3Документ2 страницыKinematic Characterization of Lacrosse Shooting Motions of The Dominant and Non-Dominant Side: 1940 Board #226 May 29, 3paulОценок пока нет
- Daily Practice Sheet 1-15Документ24 страницыDaily Practice Sheet 1-15kraken monsterОценок пока нет
- Energy, Impulse and MomentumДокумент23 страницыEnergy, Impulse and MomentumAhmad Shah100% (2)
- Classical Mechanics NotesДокумент54 страницыClassical Mechanics NotesAmichai LevyОценок пока нет
- AIM-Sample Paper-02Документ15 страницAIM-Sample Paper-02Bala ChinnappaОценок пока нет
- Speed, Velocity & Acceleration - QuizizzДокумент5 страницSpeed, Velocity & Acceleration - QuizizzNilar LwinОценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент84 страницыSciencejhemakshОценок пока нет
- Illustrated Parts Catalogue: Ed. 4 Rev. 3 - November, 2018Документ2 страницыIllustrated Parts Catalogue: Ed. 4 Rev. 3 - November, 2018Andrii KlishchevskyiОценок пока нет
- Keep 317Документ30 страницKeep 317nellai kumarОценок пока нет
- MainДокумент45 страницMainapi-534925017Оценок пока нет
- Kinematics TestДокумент13 страницKinematics TestJason YuОценок пока нет
- Foundation Maths-Exam Paper-June 2014 - Final FPBДокумент7 страницFoundation Maths-Exam Paper-June 2014 - Final FPBpappadut50% (2)
- Differential Calculus: Solved Problems in Time RatesДокумент10 страницDifferential Calculus: Solved Problems in Time RatesDennis Dale71% (7)
- 1A MotionДокумент70 страниц1A MotionLiang LuОценок пока нет
- Dynamics ch1Документ104 страницыDynamics ch1Miguel A. ChávezОценок пока нет