Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lesson Notes Earthquakes
Загружено:
mttaibОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lesson Notes Earthquakes
Загружено:
mttaibАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lesson notes Earthquakes
What is an earthquake? An earthquake is a sudden movement of the earths crust, usually along a fault (the dividing line between two parts of the crust). The study of earthquakes is called seismology. Aftershocks are more minor earthquakes that represent the settling down of the plates after an earthquake. What causes earthquakes? Stresses build up along lines of structural weakness until the friction is overcome in a sudden movement. The point at which the stress is released is named the focus (or sometimes the hypocentre), while the point directly above that on the earths surface is the epicentre. The shockwaves released from the earthquake are called seismic waves. These radiate out in all directions, just like throwing a stone in a pond causes ripples on the surface, decreasing in intensity as they spread further from the focus. These stresses tend to built up along plate boundaries, and earthquake patterns are very, very closely relate to them. The different plates result in different earthquakes: Constructive plate boundaries along ocean ridges. Mainly shallow earthquakes. Caused by volcanic activity as magma rises, pushing plates apart. Earthquakes occur below water, so causing little threat to people, although some do occur on land e.g. East African Rift Valley. Destructive plate boundaries involving at least one oceanic plate being subducted the compressing of the subducted oceanic plate causes deep and severe earthquakes in the Benioff Zone which is the area where the plate is being pushed directly underneath the other plate. These plates are the most common cause of tsunami. Collision boundaries (two continental plates colliding) shallow earthquakes over a wide area. Conservative/transform plate boundaries (plates moving past one another, not towards, e.g. San Andreas fault) shallow earthquakes along a narrow zone About 15% of earthquakes occur away from these plate boundaries and are known as intraplate earthquakes. They may be caused by stresses within plates, or by isostatic recoil (the same process that has lead to sea level change in previously glaciated areas) which revives ancient faults that are no longer actually on a plate boundary, e.g. the fault on which Loch Ness sits. What physical factors make the damage from an earthquake increase? Depth of focus - The more shallow the focus deep earthquakes may occur up to 700km below ground level, but those less than 40km deep cause the most damage as the seismic waves as the seismic waves havent dissipated by the time they reach areas of human habitation. Magnitude Earthquakes are measured using the Richter Scale (see below). The stronger the earthquake, the more likely it is to do damage. The Modified Mercalli Scale may also be used. Duration Earthquakes may last a fraction of a second, or may go on for several minutes if you include aftershocks. Distance from epicentre the further away, the less severe the seismic waves (in the same way as depth of focus). Underlying geology softer rocks, muds and clays may cause more damage including liquefaction (see related hazards) Other factors time of day may influence damage to people (night = more deaths as people are asleep and less likely to get out of falling buildings etc.). Quality of buildings, and other human factors, are of course equally important as any physical factors. How are earthquakes measured? A seismometer records the movement of the earth, producing a seismogram or seismograph, which is what we commonly see on TV etc. There are two main scales:
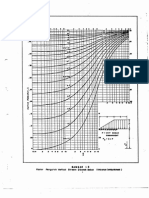
Richter Scale A logarithmic scale ranging from less than 1 (<1) to over 8 (8>) which measures the magnitude of an earthquake as recorded on a seismograph. The worst damage is done between 5 and 8+; under 4 is unlikely even to be felt by humans. Modified Mercalli Scale A 12 point scale describing the physical effects of an earthquake. 1 = earthquake recorded by instruments but felt by very few, up to 12 = total destruction. There are very few earthquakes that reach 12 on this scale.
Вам также может понравиться
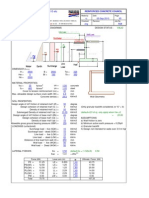
- rcc61 Basement WallДокумент14 страницrcc61 Basement WallmttaibОценок пока нет
- DeMeo THE ORGONE ACCUMULATOR HANDBOOK: Wilhelm Reich's Life Energy Science and Healing Tools For The 21st Century, With Construction PlansДокумент19 страницDeMeo THE ORGONE ACCUMULATOR HANDBOOK: Wilhelm Reich's Life Energy Science and Healing Tools For The 21st Century, With Construction PlansOrgone Biophysical Research Lab53% (15)
- Notes (Scouting) Compass ReadingДокумент5 страницNotes (Scouting) Compass Readinglito77Оценок пока нет
- Excerpt From The Occult and The Curative Powers of Precious Stones by William T FernieДокумент53 страницыExcerpt From The Occult and The Curative Powers of Precious Stones by William T Fernied_rc100% (1)
- BBC Knowledge - April 2016 SGДокумент100 страницBBC Knowledge - April 2016 SGSenia Dzwoneczek Žarković100% (2)
- Retaining Wall DesignДокумент10 страницRetaining Wall DesignklynchelleОценок пока нет
- Seismology: Earthquake Kinematics and DynamicsДокумент29 страницSeismology: Earthquake Kinematics and DynamicsJam Allana QuismundoОценок пока нет
- Extraterrestrial CommunicationДокумент39 страницExtraterrestrial CommunicationpsamiaoueОценок пока нет
- Assam Basin IntroductionДокумент6 страницAssam Basin IntroductionrijindiОценок пока нет
- Sun Rise-SetДокумент24 страницыSun Rise-Setsri78100% (3)
- Arudha LagnaДокумент13 страницArudha Lagnaic_manojupadhyay100% (9)
- Marana Karaka Avastha of PlanetsДокумент4 страницыMarana Karaka Avastha of PlanetstechkasambaОценок пока нет
- Journey To The Centre of The EarthДокумент4 страницыJourney To The Centre of The EarthMystique Carrera100% (1)
- The Earth-Shaking Facts about Earthquakes with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceОт EverandThe Earth-Shaking Facts about Earthquakes with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceОценок пока нет
- Causes of EarthquakesДокумент8 страницCauses of Earthquakesdumea paulОценок пока нет
- Unit II: Earthquake Disaster MitigationДокумент106 страницUnit II: Earthquake Disaster Mitigationgdevi80Оценок пока нет
- Earthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Документ15 страницEarthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Ar Shubham JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Grade 10 Science Summary From BookДокумент3 страницыGrade 10 Science Summary From BookRyzhenSanchez-Infante80% (20)
- Final S. Places and Landscapes in A Changing WorldДокумент9 страницFinal S. Places and Landscapes in A Changing WorldRazel G. Taquiso80% (10)
- EarthquakeДокумент38 страницEarthquakevccgyugu jbuuОценок пока нет
- Earthquakes - Chapter 3Документ6 страницEarthquakes - Chapter 3ellahbrackenОценок пока нет
- EARTHQUAKE Final OutputДокумент33 страницыEARTHQUAKE Final OutputHazel BersabalОценок пока нет
- Lec 4 EarthquakeДокумент35 страницLec 4 EarthquakeASHISH PANDEY100% (1)
- Unit 4 DMДокумент14 страницUnit 4 DMAman SinghОценок пока нет
- DisastersДокумент8 страницDisastersjaninepenelope07Оценок пока нет
- Engineering Geography: EarthquakeДокумент23 страницыEngineering Geography: EarthquakeDaljeet SidhuОценок пока нет
- 1-131 Introduction To Seismology PDFДокумент31 страница1-131 Introduction To Seismology PDFAbdalrahim Al Rantisi100% (2)
- EarthquakeДокумент28 страницEarthquakeBhupendra SoniОценок пока нет
- Earthquake Reviewer PDFДокумент6 страницEarthquake Reviewer PDFJomar LampitokОценок пока нет
- Earthquke PresentationДокумент34 страницыEarthquke PresentationKenny CantilaОценок пока нет
- Earth Quakes and Dams-3Документ16 страницEarth Quakes and Dams-3Vitalis KinyuaОценок пока нет
- Causes of EarthquakeДокумент15 страницCauses of EarthquakeAaron de GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Plate Tectonics Power PointДокумент25 страницPlate Tectonics Power PointLory Grace TorresОценок пока нет
- Lec # 1Документ43 страницыLec # 1Rajpoot WritesОценок пока нет
- EarthquakeДокумент10 страницEarthquakeBakhtyir muhamadОценок пока нет
- Classification of EarthquakesДокумент7 страницClassification of EarthquakesMainak ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Chapter Four: Earth QuakeДокумент37 страницChapter Four: Earth QuakeYomif BokuОценок пока нет
- Grade Eight EarthquakeДокумент55 страницGrade Eight EarthquakeCirille AgpaoaОценок пока нет
- Earthquake, Volcano and TsunamiДокумент64 страницыEarthquake, Volcano and TsunamiumzzОценок пока нет
- Earthquake Resistant Design AR 17-92Документ59 страницEarthquake Resistant Design AR 17-92Vivin N VОценок пока нет
- Types of EarthquakesДокумент6 страницTypes of EarthquakesMarvin EstebanОценок пока нет
- Endogenic ProcessesДокумент50 страницEndogenic Processesedena delos santosОценок пока нет
- Earthquake: Types of Earthquake and CausesДокумент9 страницEarthquake: Types of Earthquake and CausesArindam BhowmickОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Nature of Earthquake Ground MotionДокумент28 страницLecture 2 Nature of Earthquake Ground MotionJomar LampitokОценок пока нет
- 13 EarthquakesДокумент50 страниц13 EarthquakesAman Deep SinghОценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarter Science 8Документ15 страниц2nd Quarter Science 8John Ryan PiolОценок пока нет
- Causes of Earthquakes: The Surface of The Earth Is Divided Into Pieces Called "Tectonic Plates"Документ5 страницCauses of Earthquakes: The Surface of The Earth Is Divided Into Pieces Called "Tectonic Plates"rranbir07Оценок пока нет
- Earthquake: 1. Volcanic ActivitiesДокумент2 страницыEarthquake: 1. Volcanic ActivitiesNoellhaJeanetteGabeLiwagonОценок пока нет
- Lecture9 EarthquakesДокумент9 страницLecture9 EarthquakesAllen Ray Lopez SaclagОценок пока нет
- Earthquake: Naturally Occurring EarthquakesДокумент13 страницEarthquake: Naturally Occurring EarthquakesYogesh ShirodkarОценок пока нет
- Earth QuakeДокумент12 страницEarth QuakeNATNAEL ZEWDUОценок пока нет
- Earthquake: Naturally Occurring EarthquakesДокумент5 страницEarthquake: Naturally Occurring EarthquakesShree VidhyaОценок пока нет
- Earthquake: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент11 страницEarthquake: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSoulcoldОценок пока нет
- Earthquake: Navigation SearchДокумент14 страницEarthquake: Navigation SearchSyuk-run Mohd NoorОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING PDFДокумент9 страницLecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING PDFowaisОценок пока нет
- Earth Quake Resistant Design and Disaster Management: Class 1Документ20 страницEarth Quake Resistant Design and Disaster Management: Class 1Linas FathimaОценок пока нет
- Naturally Occurring Earthquakes: Earthquake Fault TypesДокумент6 страницNaturally Occurring Earthquakes: Earthquake Fault TypesJoel JollyОценок пока нет
- Classification of Earthquakes: A. Based On LocationДокумент6 страницClassification of Earthquakes: A. Based On LocationYusuf TurgutОценок пока нет
- Earthquakes and FaultsДокумент19 страницEarthquakes and FaultsMasTer CrafT (MasTerCrafT89)Оценок пока нет
- EarthquakesДокумент36 страницEarthquakesrojalingeo24Оценок пока нет
- PM 211 Module 3Документ16 страницPM 211 Module 3Louray JeanОценок пока нет
- Description EarthquakeДокумент2 страницыDescription EarthquakearsarcanumОценок пока нет
- EarthquakeДокумент6 страницEarthquakeJohnrey DapitoОценок пока нет
- A Tragedy To Life and Property: Department:-YearДокумент47 страницA Tragedy To Life and Property: Department:-Year김나연0% (1)
- GMT102 L5 SGДокумент30 страницGMT102 L5 SGTasnim Alam NafijОценок пока нет
- Why? and How?: EarthquakesДокумент38 страницWhy? and How?: EarthquakesDiana Rose Gozon100% (1)
- Earthquake IntroductionДокумент4 страницыEarthquake IntroductionHimanshuОценок пока нет
- Science Fest (Earthquakes)Документ7 страницScience Fest (Earthquakes)Jash ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Earthquake: Causes of EarthquakesДокумент9 страницEarthquake: Causes of EarthquakesChetan KaushikОценок пока нет
- Earthquake: Basics: Compiled by Mrs MakurumidzeДокумент25 страницEarthquake: Basics: Compiled by Mrs MakurumidzeRegis WachenukaОценок пока нет
- 12: Earthquake and Earthquake Hazards: March 3, 2018Документ43 страницы12: Earthquake and Earthquake Hazards: March 3, 2018Matthew DavidОценок пока нет
- The Ground Is Shaking! What Happens During An Earthquake? Geology for Beginners| Children's Geology BooksОт EverandThe Ground Is Shaking! What Happens During An Earthquake? Geology for Beginners| Children's Geology BooksОценок пока нет
- Pile Foundations: Equations For Estimating Pile CapacityДокумент1 страницаPile Foundations: Equations For Estimating Pile CapacitymttaibОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Static Pile DriverДокумент9 страницHydraulic Static Pile DrivermttaibОценок пока нет
- Settlement 1Документ1 страницаSettlement 1mttaibОценок пока нет
- Kndlillll1: ": - ' Rr.4 - "-:: Ii"""""' - "'"Документ1 страницаKndlillll1: ": - ' Rr.4 - "-:: Ii"""""' - "'"mttaibОценок пока нет
- Smertman 1 PDFДокумент1 страницаSmertman 1 PDFmttaibОценок пока нет
- Table 2007 CBCДокумент21 страницаTable 2007 CBCmttaibОценок пока нет
- Q RataДокумент1 страницаQ RatamttaibОценок пока нет
- Building Seismic Design v1.0Документ1 страницаBuilding Seismic Design v1.0mttaibОценок пока нет
- Unit ConversionДокумент1 страницаUnit ConversionmttaibОценок пока нет
- Shear Wall Analysis For Shear Wall With Opening Using Finite Element MethodДокумент3 страницыShear Wall Analysis For Shear Wall With Opening Using Finite Element MethodmttaibОценок пока нет
- Is 1904 1986Документ24 страницыIs 1904 1986mttaibОценок пока нет
- As Ce 2013 e Book CollectionДокумент10 страницAs Ce 2013 e Book CollectionmttaibОценок пока нет
- Sanspro PenjelasanДокумент42 страницыSanspro Penjelasanmttaib100% (1)
- 01 - Wall Slab Joint DetailsДокумент1 страница01 - Wall Slab Joint DetailsmttaibОценок пока нет
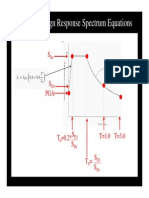
- Step 7: Design Response Spectrum EquationsДокумент1 страницаStep 7: Design Response Spectrum EquationsmttaibОценок пока нет
- Shear Strength of Soils and Site InvestigationДокумент2 страницыShear Strength of Soils and Site InvestigationSUNDARAVELОценок пока нет
- Grade 11 & 12 2nd Prelim ExamДокумент2 страницыGrade 11 & 12 2nd Prelim ExamHealth NutritionОценок пока нет
- NASA Black Hole ShortДокумент5 страницNASA Black Hole ShortAndrej Vuk BlesićОценок пока нет
- YEARLYPLANSCIENCEYEAR4Документ120 страницYEARLYPLANSCIENCEYEAR4Aziz AljaffariОценок пока нет
- EGU Abstract BenaichoucheДокумент1 страницаEGU Abstract BenaichouchesimplyinvincibleОценок пока нет
- List of Brightest StarsДокумент6 страницList of Brightest StarsmanuelОценок пока нет
- Manual ClustalX PDFДокумент23 страницыManual ClustalX PDFpicapenasОценок пока нет
- Hyperbolic Constitutive Model For Tropical Residual SoilsДокумент13 страницHyperbolic Constitutive Model For Tropical Residual SoilsIAEME PublicationОценок пока нет
- Light and TelescopesДокумент51 страницаLight and TelescopesKentОценок пока нет
- LABiTec Control 1 Insert 1956 35 Revision 2.0Документ1 страницаLABiTec Control 1 Insert 1956 35 Revision 2.0Carla YcoОценок пока нет
- Archaeozoology: Camelopardalis Brisson, From The Prehistoric Site of Susunia, District BankuraДокумент7 страницArchaeozoology: Camelopardalis Brisson, From The Prehistoric Site of Susunia, District BankuraDibyendu DasОценок пока нет
- Book ListДокумент241 страницаBook ListA. Mariana Gómez0% (1)
- Sediment and Sedimentary RocksДокумент10 страницSediment and Sedimentary RocksNanah NocaОценок пока нет
- QAed-SSLM EALS Q1 WK2 SANTOS-EDITEDДокумент5 страницQAed-SSLM EALS Q1 WK2 SANTOS-EDITEDTrash BinОценок пока нет
- LonarДокумент7 страницLonarKishor DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- 5.section-Xi Interim Report On Geotechnical InvestigationДокумент27 страниц5.section-Xi Interim Report On Geotechnical InvestigationRaghavОценок пока нет
- Topographic Map of RochesterДокумент1 страницаTopographic Map of RochesterHistoricalMapsОценок пока нет
- Eco Comport AmДокумент10 страницEco Comport AmIHОценок пока нет