Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cost Engineering - Analyse Your Projects Through Estimating Life Cycle
Загружено:
Mauricio FurtadoИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cost Engineering - Analyse Your Projects Through Estimating Life Cycle
Загружено:
Mauricio FurtadoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Analysing your Projects through your Estimating Life Cycle
Raymond Hagedoorn (CCE)
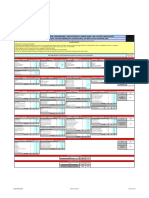
Project Life Cycle
Identification phase Definition phase Execution phase Operational phase Abandon phase
Project initiation note
40% Screening estimate Economics Step 1
Feasibility study
25% Study estimate
Development plan
25% Budget estimate Economics Step 3 Initial commit. plan
Basis for design
Project specification
10% Control estimate
commit. plan Economics Step 4 Project execution plan
Detailed design
Materials procurement
Construction
Commission. start-up handover
Economics
Step 2
Commit. & cost control
Change control 5% Counter estimate Step 5
Step 6 Operations reference plan Identical to Execution phase
Step 7 Identical to Execution phase
Close out
Abandon project
Approval
Approval
initial execution plan
Operations reference plan
Review Review Approval Approval
Contract control Purchase order control Reporting
Project debrief
How much time is spent?
AACE Cost Estimate Classification System - Process Industries
Primary Characteristic ESTIMATE CLASS 5 LEVEL OF PROJECT DEFINITION 0% to 2% END USAGE concept screening Secondary Characteristic
METHODOLOGY
EXPECTED ACCURACY RANGE L: -20% to -50% H: +30% to + 100%
PREPARATION EFFORT 1
capacity factored, parametric models, judgment, or analogy equipment factored or parametric models semi-detailed unit cost with assembly level line items detailed unit cost with forced detailed take-off detailed unit cost with detailed takeoff
1% to 15%
study or feasibility budget, authorization or control control or bid / tender check estimate or bid / tender
L: -15% to -30% H: +20% to + 50% L: -10% to -20% H: +10% to + 30%
2 to 4
10% to 40%
3 to 10
30% to 70%
L: -5% to -15% H: +5% to + 20% L: -3% to -10% H: +3% to + 15%
4 to 20
50% to 100%
5 to 100
Estimating cycle: the ideal scenario
INITIATION UP TO CLOSE-OUT PHASE
Analyse your Projects through the Life Cycle
> Learn from your estimates in previous phase
> Compare class 4 -> class 3 -> class 2 > Learn from your past projects
> Compare similar projects and historical data > Classification required!
> Analyze scope development
> Perform health checks to be more confident
> Time analysis and cash flow trending > Determine key metrics to benchmark your organization > Business intelligence through regression analysis, pivot tables, or other methods of data mining
www.costengineering.eu
Estimating with Cleopatra
> > > > Estimate your whole project life cycle (design, build, maintain) in one system; Class 4 (40%), Class 3 (20%), Class 2 (10%) in one package Gradual increase of accuracy (Class 3, Class 2) Closing the loop: analyze benchmarks in class 2 estimates as input for class 4 estimates. > Enhance your business intelligence through transparency: > Knowing your exact cost
(direct, allowances, indirect, escalation, contingency)
> Knowing the effects on cost of scope changes > Keep an overview in complex projects
www.costengineering.eu
Breakdown structures How to compare various levels of granularity?
www.costengineering.eu
Breakdown structures: multi-dimensional view
www.costengineering.eu
Show case:
Example project Estimating through the project life cycle Analyse the various phases
www.costengineering.eu
Show case: Example Plant
> Scope
> Distillate process: raw product to middle distillate > By products: top and bottom > 28 pieces of equipment (columns, heat exchangers, tanks, pumps, vessels) > Executed in Western-Europe > Price level date 2011 > Finish date: November 2012 > Project life cycle: from feed to execution
> Plant design
> 3D model > Process flow diagram > Equipment list
www.costengineering.eu
Show case: Example Plant
> Class 4 estimate (40% accuracy):
> > > >
>
Based on Factors Parametric Equipment Models Applying Hand methodology Distribution of disciplines
Object re-use (Engineering Standards) Tuning for more accuracy Include allowance, indirect, escalation and contingency Disciplines: piping, mechanical, E&I, civil, etc. Parts to be estimated
Class 3 estimate (20% accuracy):
> > > > >
>
Class 2 estimate (10% accuracy)
> Detailed Unit-Cost > Bill of Quantity / Material take off input > Equipment Parameters
www.costengineering.eu
Show case: Example Plant
> Learn from estimates in previous phases
> Compare Class 4 with Class 3 Estimate > Compare Class 3 with Class 2 Estimate > Compare Class 2 (industry norm) with Class 1 (vendor norm)
> Metrics & Benchmarking
> Analyze metrics using pivot tables > View Key Quantities > Closing the loop: class 1 ratios for factor estimating
> Business intelligence
> Regression analysis > Create What-if scenario
> Cash Flow Analysis
> Show cash flow and schedule
www.costengineering.eu
Questions ?
Cost Engineering
E-mail: info@costengineering.eu www.costengineering.eu
Вам также может понравиться
- Man-Hour EstimateДокумент1 страницаMan-Hour EstimateImtinan Mohsin85% (20)
- Estimation Man HourДокумент241 страницаEstimation Man HourAnonymous ynJByUs52% (42)
- Standard Deliverable List For Feasibility Conceptual FEED Detailed DesignДокумент22 страницыStandard Deliverable List For Feasibility Conceptual FEED Detailed DesignRamamurthy Narshya92% (53)
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionОт EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Modern Cost EngineeringДокумент38 страницModern Cost Engineeringamcandia100% (5)
- Preview Power of Burp SuiteДокумент33 страницыPreview Power of Burp Suitebinux egaHYFGKIRTJОценок пока нет
- Cost Estimating HandbookДокумент158 страницCost Estimating Handbookcocko01100% (4)
- Project Execution ModelДокумент99 страницProject Execution ModelEdha Ali100% (3)
- Cost EstimatingДокумент27 страницCost EstimatingArief Budiman Hermani100% (1)
- Project Cost Estimating Guide - PracticeДокумент58 страницProject Cost Estimating Guide - PracticeMurat Syzdykov100% (5)
- Cost Engineer Reference BookДокумент13 страницCost Engineer Reference Bookmosinqs100% (1)
- 2009 Front End Conceptual Estimating YearbookДокумент470 страниц2009 Front End Conceptual Estimating YearbookGerardo Delgado100% (4)
- Best Practices in Cost EngineeringДокумент9 страницBest Practices in Cost EngineeringAl-Kawthari As-SunniОценок пока нет
- Joshua Bell Violin Manual v110Документ15 страницJoshua Bell Violin Manual v110emanuelОценок пока нет
- CCC CCESampleExamДокумент24 страницыCCC CCESampleExamapi-3842704100% (1)
- Estimating 100 Introduction To EstimatingДокумент23 страницыEstimating 100 Introduction To EstimatingCarina Anselmo de Lima88% (8)
- PMBOK - v5 - Quality MGMT by Skanchi - 20150802Документ26 страницPMBOK - v5 - Quality MGMT by Skanchi - 20150802ksreddy58Оценок пока нет
- The Use of Professional Credentialing in Helping To Establish A Cost Estimating CapabilityДокумент23 страницыThe Use of Professional Credentialing in Helping To Establish A Cost Estimating Capabilitybernardo_chavez100% (1)
- Cost Estimating Manual for Pipelines and Marine Structures: New Printing 1999От EverandCost Estimating Manual for Pipelines and Marine Structures: New Printing 1999Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Britannia Non Functional Test Plan Ver 1.2Документ26 страницBritannia Non Functional Test Plan Ver 1.2Kelli ReillyОценок пока нет
- 22r-01 Direct Labor Productivity MeasurementДокумент19 страниц22r-01 Direct Labor Productivity Measurementmax73100% (4)
- Global SCANДокумент187 страницGlobal SCANLuis GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Cost EstimationДокумент46 страницCost EstimationvinaykdrОценок пока нет
- Hackney Model For Contingengy and Accuracy Range Analysis: Rating WorksheetДокумент3 страницыHackney Model For Contingengy and Accuracy Range Analysis: Rating Worksheetyamanta_rajОценок пока нет
- Bapi Idoc PresentationДокумент13 страницBapi Idoc Presentationapi-26420083100% (4)
- Hvac5 0506Документ43 страницыHvac5 0506Nadia Fahmi SilabiОценок пока нет
- Engineering Cost Escalations Project Report PDFДокумент106 страницEngineering Cost Escalations Project Report PDFRahul RaghukumarОценок пока нет
- DC30-049 TechVision Service Manual - Rev QДокумент103 страницыDC30-049 TechVision Service Manual - Rev Qmario feuilladeОценок пока нет
- Schedule for Sale: Workface Planning for Construction ProjectsОт EverandSchedule for Sale: Workface Planning for Construction ProjectsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Gemini 1 ReportДокумент62 страницыGemini 1 ReportCuong NguyenОценок пока нет
- Construction Cost Management: Cost Engineering, Cost Controls & Controlled BiddingОт EverandConstruction Cost Management: Cost Engineering, Cost Controls & Controlled BiddingРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Implementing Best Practices in Capital Project ManagementДокумент32 страницыImplementing Best Practices in Capital Project ManagementBela UlicsakОценок пока нет
- Quantity Estimating: Indiana Department of Transportation-2013 Design ManualДокумент137 страницQuantity Estimating: Indiana Department of Transportation-2013 Design ManualjaveedОценок пока нет
- 2nd Superseding Indictment, USA V Michael J Miske JR., Et AlДокумент45 страниц2nd Superseding Indictment, USA V Michael J Miske JR., Et AlIan Lind100% (1)
- Labor Requirements For Construction M Aterials: Par T Il-Concrete Masonry UnitsДокумент22 страницыLabor Requirements For Construction M Aterials: Par T Il-Concrete Masonry UnitsMohammed AffrozeОценок пока нет
- 00 000000 000000 NEO PCO EMR 000002 Employer Requirements Progress Measurement Rev 1Документ9 страниц00 000000 000000 NEO PCO EMR 000002 Employer Requirements Progress Measurement Rev 1Iftikhar AhmadОценок пока нет
- Skills and Knowledge of CostДокумент33 страницыSkills and Knowledge of CostMohamed Omar SileemОценок пока нет
- AACEI Houston Jan 2008Документ84 страницыAACEI Houston Jan 2008klibiОценок пока нет
- Total Cost Management of Capital ProjectДокумент7 страницTotal Cost Management of Capital ProjectSoeghy AlieОценок пока нет
- Making Sense Your Project Cost EstimateДокумент5 страницMaking Sense Your Project Cost Estimateromulussikalit100% (1)
- Cost Engineers Notebook!!!!!Документ5 страницCost Engineers Notebook!!!!!Anonymous 19hUyem0% (2)
- Estimate Class Class 5 Class 4 Class 3 Class 2 Class 1Документ3 страницыEstimate Class Class 5 Class 4 Class 3 Class 2 Class 1arlekinoburatinoОценок пока нет
- Cost Estimate PDFДокумент44 страницыCost Estimate PDFananyo_sengupta100% (2)
- The Total Cost Management (TCM) Framework: PrefaceДокумент6 страницThe Total Cost Management (TCM) Framework: PrefaceRonald Kahora100% (1)
- 2015 Bebras Solution GuideДокумент56 страниц2015 Bebras Solution GuidedesОценок пока нет
- Construction Cost EngineeringДокумент23 страницыConstruction Cost Engineeringmatthew cometaОценок пока нет
- 46R-11 - AACE InternationalДокумент27 страниц46R-11 - AACE InternationalFirasAlnaimi50% (2)
- 000.100.8100 Baseline Centric Execution - Deliver To The Baseline WorkflowДокумент1 страница000.100.8100 Baseline Centric Execution - Deliver To The Baseline WorkflowmiltonОценок пока нет
- SWOOD - RX - User ManualДокумент5 страницSWOOD - RX - User Manualclient000Оценок пока нет
- Transactional Value Stream MappingДокумент25 страницTransactional Value Stream MappingChew JCОценок пока нет
- Generally Accepted Scheduling PrinciplesДокумент282 страницыGenerally Accepted Scheduling PrinciplesShashank BahiratОценок пока нет
- Control PlansДокумент29 страницControl PlansKristof MCОценок пока нет
- Software ProjectДокумент5 страницSoftware ProjectSumana NanjundaiahОценок пока нет
- Introduction of Project Quality Management: in Oil and Gas IndustryДокумент20 страницIntroduction of Project Quality Management: in Oil and Gas IndustrySufira WahyuniОценок пока нет
- Project Quality ManagementДокумент39 страницProject Quality ManagementSolich IchinОценок пока нет
- ELO 2 (Operation Management)Документ5 страницELO 2 (Operation Management)Faiq UbaidillahОценок пока нет
- CH 02Документ27 страницCH 02Norsiah ShukeriОценок пока нет
- Software Development Life Cycle: 2 WeeksДокумент8 страницSoftware Development Life Cycle: 2 WeeksmaheshpandyanОценок пока нет
- Unit V QualityДокумент51 страницаUnit V QualityMabood Ahmad AnsariОценок пока нет
- GR Types ContdДокумент27 страницGR Types ContddorcaslnuОценок пока нет
- Project Quality ManagementДокумент41 страницаProject Quality ManagementhaithamaeОценок пока нет
- Assessment and Reduction of Cost of Quality at Elgi Sauer Compressors LimitedДокумент49 страницAssessment and Reduction of Cost of Quality at Elgi Sauer Compressors LimitedVasanth KumarОценок пока нет
- 5th Sem - 2 - Civil Engg PDFДокумент25 страниц5th Sem - 2 - Civil Engg PDFBaibaswata DasОценок пока нет
- Specification-Based Regression Test Management With Risk Analysis: A New Regression Test Selection ApproachДокумент29 страницSpecification-Based Regression Test Management With Risk Analysis: A New Regression Test Selection ApproachSuresh KumarОценок пока нет
- Multiple Comparisons (Only Computing All Treatments With A Control)Документ16 страницMultiple Comparisons (Only Computing All Treatments With A Control)Rohaila RohaniОценок пока нет
- Tutorial GT3RS V1 To V2Документ41 страницаTutorial GT3RS V1 To V2JoelОценок пока нет
- A Love and Trust - PDF - Love - Staff SergeantДокумент16 страницA Love and Trust - PDF - Love - Staff SergeantSteven BarnsОценок пока нет
- 4 TuberiasДокумент8 страниц4 TuberiasVladimir VeraОценок пока нет
- ZeroXIII Controller Read MeДокумент2 страницыZeroXIII Controller Read MeJULIANОценок пока нет
- HP Elitedesk G5Документ4 страницыHP Elitedesk G5amarОценок пока нет
- HotSpotExpress MANUALДокумент142 страницыHotSpotExpress MANUALOctavio Enrique Oropeza CastellanoОценок пока нет
- New Perspectives On XML Comprehensive 3rd Edition Carey Solutions ManualДокумент36 страницNew Perspectives On XML Comprehensive 3rd Edition Carey Solutions Manualrattingbivial7ac1gr100% (20)
- Video For Linux 2 V 4 L 2: by Rahul C Alphaics CorpДокумент15 страницVideo For Linux 2 V 4 L 2: by Rahul C Alphaics CorpRahul CОценок пока нет
- ICT Tech-Drafting J-SHS Quarter-2 LAS4 FINALДокумент8 страницICT Tech-Drafting J-SHS Quarter-2 LAS4 FINALMilbert Awa-ao100% (1)
- HR990Документ17 страницHR990venkatnasikОценок пока нет
- Sample of Thesis Chapter 1-5Документ5 страницSample of Thesis Chapter 1-5f5dthdcd100% (2)
- ICT - Battery Backup Module PDFДокумент2 страницыICT - Battery Backup Module PDFmahavirochanaОценок пока нет
- PDMS 12.1 Drawing ProductionДокумент4 страницыPDMS 12.1 Drawing ProductionsadeghmsgОценок пока нет
- College FairДокумент1 страницаCollege FairLori Bernardini-RussoОценок пока нет
- Maths Book LinkДокумент1 страницаMaths Book LinkAjay PandeyОценок пока нет
- Aman Resume (PHP Developer)Документ3 страницыAman Resume (PHP Developer)Aman Jain100% (1)
- Ae3 Lem It B 2ano GabaritoДокумент8 страницAe3 Lem It B 2ano GabaritoSandra M SilvaОценок пока нет
- Article Review On Line Balancing Technique To Improve The Productivity Using Work-Sharing MethodДокумент5 страницArticle Review On Line Balancing Technique To Improve The Productivity Using Work-Sharing MethoderenaОценок пока нет
- Learning Activity Sheet Ict10Документ2 страницыLearning Activity Sheet Ict10Kenji IgnacioОценок пока нет