Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Exercise 111
Загружено:
rsac_1997Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Exercise 111
Загружено:
rsac_1997Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Exercise 111
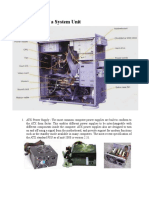
CPU: hardware within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing
the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system
RAM: form of computer data storage. A random-access device allows stored data to be accessed directly in any random order. In contrast, other data storage media such as hard disks, CDs, DVDs and magnetic tape, as well as early primary memory types such as drum memory, read and write data only in a predetermined order, consecutively, because of mechanical design limitations.
Expansion Cards: is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.
Power supply: A power supply is a device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The term is most commonly applied to electric power converters that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy.
ATX Power connector: ATX is a motherboard form factor specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT form factor. It was the first major change in desktop computer enclosure, motherboard, and power supply design in many years, improving
standardization and interchangeability of parts.
Hard disk: is a data storage device used for storing and retrieving digital information using rapidly rotating discs coated with magnetic material. An HDD retains its data even when powered off. Data is read in a random-access manner, meaning individual blocks of data can be stored or retrieved in any order rather than sequentially.
Sata Connector:
is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives. Serial ATA replaces the older AT Attachment standard
IDE connector: An IDE connector is the contact point between the long flat ribbon cable and a hardware device. Normally they are used to connect a CD/DVD-ROM drive to the motherboard inside the computer using a ribbon cable.
CPU fan connector:
is a port that allows a fan to connect to it to cool a CPU/ Northbridge heat sink in bios PC health menu it registers the speed of fan to make sure the CPU ain't to hot and fan spinning maximum speed
CPU socket:
A CPU socket or CPU slot is a mechanical component(s) that provides mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows the CPU to
be replaced without soldering.
CMOS backup battery: Modern personal computer motherboards have a backup battery to run the clock circuit and retain configuration memory while the system is turned off. This is often called the CMOS battery. The original IBM AT, for example, used a small primary lithium battery to retain the clock and [1] configuration memory. Modern systems use either primary or rechargeable batteries. Primary batteries required periodic replacement; rechargeable types often lasted as long as the system they supported. Backup batteries are used in uninterruptible power supplies, and provide power to the computers they supply for a variable period after a power failure, usually long enough to at least allow the computer to be shut down gracefully.
Connectors for integrated peripherals:
PS/2: The PS/2 connector is a 6-pin Mini-DIN connector used for connecting
some keyboards and mice to a PC compatible computer system.
Serial Port: is a serial communication physical interface through which information transfers
in or out one bit at a time (in contrast to a parallel port).
[1]
Throughout most of the history
of personal computers, data was transferred through serial ports connected the computer to devices such as terminals and various peripherals.
Parallel Port: A parallel port is a type of interface found on computers for connecting peripherals. In computing, a parallel port is a parallel communication physical interface.
VGA: the VGA analog interface is used for high definition video including 1080p and higher. While the VGA transmission bandwidth is high enough to support even higher resolution playback, there can be picture quality degradation depending on cable quality and length.
USB: USB was designed to standardize the connection of computer peripherals become commonplace on other devices, such as smartphones, PDAs and video game consoles. USB has effectively replaced a variety of earlier interfaces, such as serial and parallel ports, as well as separate power chargers for portable devices.
Ethernet: Systems communicating over Ethernet divide a stream of data into shorter pieces called frames. Each frame contains source and destination addresses and error-checking data so that damaged data can be detected and re-transmitted. As per the OSI model Ethernet provides services up to and including the data link layer.
Audio: Audio connectors are electrical connectors for carrying audio signal of either analog or digital format. Analog A/V connectors often use shielded cables to
inhibit radio frequency interference (RFI) and noise.
Вам также может понравиться
- Hardware and SoftwareДокумент13 страницHardware and SoftwareAvash JoshiОценок пока нет
- Central Processing UnitДокумент5 страницCentral Processing UnitssssmailnatОценок пока нет
- Computer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersДокумент12 страницComputer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersRohan DhawaОценок пока нет
- 21BCS11360 (Workshop Tech. 1.1)Документ6 страниц21BCS11360 (Workshop Tech. 1.1)Shreyank PushkarОценок пока нет
- Give All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipДокумент7 страницGive All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipjanОценок пока нет
- Motherboard Components and FunctionДокумент5 страницMotherboard Components and FunctionnominnanaaespasolОценок пока нет
- Unit - I Structure of Modern ComputerДокумент10 страницUnit - I Structure of Modern ComputerxsaaОценок пока нет
- ICCS 2 Converted Word To PDFДокумент5 страницICCS 2 Converted Word To PDFElleera RemorerasОценок пока нет
- Components of System UnitДокумент8 страницComponents of System UnitIvan Louie Cruto100% (1)
- Motherboards and Power SupplyДокумент6 страницMotherboards and Power SupplyThairu KamauОценок пока нет
- The Physical Components of A Computer System, Such As The Circuit Boards, Enclosures, Peripherals, Cables, EtcДокумент30 страницThe Physical Components of A Computer System, Such As The Circuit Boards, Enclosures, Peripherals, Cables, EtcRanz Monterde100% (1)
- APT2020Документ7 страницAPT2020Thairu KamauОценок пока нет
- Parts of MotherboardДокумент63 страницыParts of MotherboardMarivic Omosura ItongОценок пока нет
- Summary Report in TRДокумент9 страницSummary Report in TREllie KimОценок пока нет
- Nursing InformaticsДокумент13 страницNursing InformaticsNursidar Pascual MukattilОценок пока нет
- Ports and CablesДокумент6 страницPorts and CablesAlfredo DimaanoОценок пока нет
- Is The Enclosure For All The Other Main Interior Components of A Computer. It Is Also Called The Computer Case, Computer Chassis, or Computer TowerДокумент5 страницIs The Enclosure For All The Other Main Interior Components of A Computer. It Is Also Called The Computer Case, Computer Chassis, or Computer TowerAlfredo DimaanoОценок пока нет
- Parts of ComputerДокумент18 страницParts of ComputerJazzt D MerencillaОценок пока нет
- Computer Unit 1Документ6 страницComputer Unit 1hindrixcatayas8Оценок пока нет
- Experiment No.4Документ12 страницExperiment No.4Kshitij DudheОценок пока нет
- Parts of System Unit & MotherboardДокумент6 страницParts of System Unit & MotherboardNonoy Enopena100% (2)
- Parts of MotherboardДокумент18 страницParts of MotherboardEviok Anfone ZosaОценок пока нет
- Processor, But More Commonly Called Processor, The CPU Is The Brains of The ComputerwhereДокумент7 страницProcessor, But More Commonly Called Processor, The CPU Is The Brains of The ComputerwheremateocalderonОценок пока нет
- Tle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Документ5 страницTle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Rose FloresОценок пока нет
- Module 4Документ16 страницModule 4CABADONGA, Justin M.Оценок пока нет
- Computer MotherboardДокумент15 страницComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeОценок пока нет
- Computer Components ListДокумент7 страницComputer Components Listapi-357587326Оценок пока нет
- Parts of MotherboardДокумент5 страницParts of MotherboardAnika Kane Barrios80% (5)
- 1internal Parts of ComputerДокумент53 страницы1internal Parts of Computersheeshableangeline208Оценок пока нет
- Components of System UnitДокумент8 страницComponents of System Unitroger_embalsado331988% (16)
- Experiment:-3: Processor Sockets and SlotsДокумент4 страницыExperiment:-3: Processor Sockets and SlotsVishv PatelОценок пока нет
- Compilations of Computer Installation and TroubleshootingДокумент44 страницыCompilations of Computer Installation and TroubleshootingLlordie MontecarloОценок пока нет
- Lab 02 - EEDДокумент18 страницLab 02 - EEDAhmad MusabОценок пока нет
- Parts of MotherboardДокумент86 страницParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniОценок пока нет
- Assignment CS by ABRARДокумент9 страницAssignment CS by ABRARThe King studioОценок пока нет
- Parts of MotherboardДокумент14 страницParts of MotherboardNoelyn GarciaОценок пока нет
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsДокумент4 страницыMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsRige Mae MuescoОценок пока нет
- Basic Hardware Computer SystemДокумент82 страницыBasic Hardware Computer SystemTVET OfficeОценок пока нет
- Motherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardДокумент7 страницMotherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardMustafa MuhammedОценок пока нет
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemДокумент13 страницBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemSaymon Casilang SarmientoОценок пока нет
- MotherboardДокумент4 страницыMotherboardTalha MughalОценок пока нет
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsДокумент3 страницыWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functionsjoel lacayОценок пока нет
- Basic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitДокумент35 страницBasic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitShenny CariscalОценок пока нет
- Component of A System Unit - Desktop PCДокумент8 страницComponent of A System Unit - Desktop PCRoger EmbalsadoОценок пока нет
- Power PointДокумент33 страницыPower PointJames LopezОценок пока нет
- Motherboard PartsДокумент4 страницыMotherboard PartsabelОценок пока нет
- Computer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardДокумент5 страницComputer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardErickson JavonitallaОценок пока нет
- LESSON 2 Basic Hardware Components of Computer SystemsДокумент26 страницLESSON 2 Basic Hardware Components of Computer Systemskate cacayОценок пока нет
- Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetДокумент13 страницHomework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetJohn Kerby CorralОценок пока нет
- Module 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardДокумент8 страницModule 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardChristopher AdvinculaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ6 страницChapter 4Lloyd RevesОценок пока нет
- Basic Computer Hardware and TroubleshootingДокумент39 страницBasic Computer Hardware and TroubleshootingR. BorresОценок пока нет
- Information Technology Assignment:: Motherboard Write-UpДокумент16 страницInformation Technology Assignment:: Motherboard Write-UpJuline AsmeryОценок пока нет
- Motherboard Components of A Desktop Computer: CPU RAM CD DVD Hard DiskДокумент5 страницMotherboard Components of A Desktop Computer: CPU RAM CD DVD Hard DiskRoger EmbalsadoОценок пока нет
- Computer Assignment... To Mr. OdnanДокумент4 страницыComputer Assignment... To Mr. OdnanehlLaine24Оценок пока нет
- Computer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsДокумент70 страницComputer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsMary MillareОценок пока нет
- ITGSdevicesДокумент3 страницыITGSdevicesrsac_1997Оценок пока нет
- Computer Instructions Computer Program: Exercise 111Документ6 страницComputer Instructions Computer Program: Exercise 111rsac_1997Оценок пока нет
- Exercise 111Документ3 страницыExercise 111rsac_1997Оценок пока нет
- It Gs Social and Ethnical IssuesДокумент10 страницIt Gs Social and Ethnical Issuesrsac_1997Оценок пока нет