Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Normal Range of Eye in Optom - Wall Hanger
Загружено:
JLoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Normal Range of Eye in Optom - Wall Hanger
Загружено:
JLoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
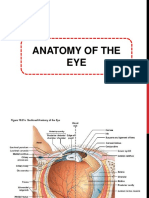
NORMAL VALUES IN OPHTHALMOLOGY
PARAMETER Diameter of eye ball Antero posterior Lateral (horizontal) Vertical Axial length of eye ball At birth At 3 yrs age At 14 yrs age Circumference of eye ball Volume of eye ball Weight of eye ball Diameter of ant horizontal surface of cornea vertical Diameter of posterior surface of cornea Thickness of cornea In the centre In periphery Radius of curvature of anterior central cornea posterior Refractive index of cornea Refractive power of As a whole cornea Anterior surface Posterior surface Corneal endothelial At birth cell density Young adults decompensation Thickness of sclera Posteriorly -thickest EO muscle insertion At equator Near limbus Width of ciliary body Ant part- pars plicata Post part- pars plana Central depth of ant. Chamber Volume of aqueous humour in anterior chamber Volume of aqueous humour in posterior chamber Rate of formation of aq. humour Refractive index of aqueous humour pH of aq. humour in ant chamber Normal range of IOP Equatorial diameter At birth of lens In 2nd decade for life VALUES 24 mm 23.5 mm 23 mm 18 mm 23 mm 24 mm 75 mm 6.5 ml 7 gm 11.75 mm 11 mm 11.5 mm 0.52 mm 0.67 mm 7.8 mm 6.5 mm 1.376 + 43 D + 48 D -5D 6000 /mm2 2400-3000 /mm2(parson 2800 /mm2) <500 /mm2 ( 75% loss) 1 mm 0.3 mm 0.4 0.6 mm 0.8 mm 2 mm 5 mm temporally and 3 mm nasally 3 mm (Parson 2.5 mm) 0.25 ml 0.06 ml 2.3 l/min (1% of ant ch. vol.) 1.336 7.2 (acidic) 10.5- 20.5 mm Hg (15.5+/- 2.57) 6.5 mm 9-10 mm
www.eophtha.com
Thickness of lens Weight of lens Radius of curvature of ant surface of lens
At birth At extreme of age
Without accommodation With accommodation Radius of curvature of post surface of lens Refractive index of lens Refractive power of lens Accommodative At birth power of lens At 25 yrs of age At 50 yrs of age Near point At 10 yrs At 30 yrs age At 40, 45 yrs age Weight and volume, refractive index of vitreus Thickness of retina at post pole, equator, ora serrata Diameter of Optic disc Macula lutea Fovea centralis Foveola Foveal avascular zone Thickness of ora serrata nasally and temporally Distance of ora serrata from limbus Total number of rods and cones Density of cones, length of cone cells in fovea Length of optic nerve Total Intraocular Intra orbital Intracanalicular Intracranial Total number and thickness of fibres of optic nerve Size of optic chiasma Visible portion of EM radiation spectrum Dark adaptation time- cone and rod adaptation Light adaptation time EO muscle insertion Medial rectus distance from limbus Inferior rectus by Fuchs, 1884, length Lateral rectus of contact arc at Superior rectus
3.5 mm 5 mm 135- 255 mg 10 mm 6 mm 6 mm 1.39 (nucleus 1.42, cortex 1.38) 16-17 D 14-16 D 7-8 D 1-2 D 7 cm 14 cm 25, 33 cm 4g, 4cc, 1.3349 0.56 mm, 0.18- 0.2 mm, 0.1 mm 1.5 mm 5.5 mm / 15o of visual field 1.85 mm / 5o of visual field 0.35 mm (2 DD from disc edge) 0.8 mm (P) 0.7- 0.8 mm and 2.1 mm 6mm nasally, 7 mm temporally 120 million and 6.5 million 1,99,000 /mm2, 80 m 47- 50 mm 1 mm 30 mm 6-9 mm 10 mm 1.2 million, 2-10 m 12 mm horizontal, 8 mm AP 400 (violet)- 750 (red) 5 min (cone) 30 min (rod) 5- 10 min 5.5 mm, 6 mm, 40 mm, 3.7 mm 6.5 mm, 9 mm, 40 mm, 5.5 mm 6.9 mm, 15 mm, 48 mm, 8.8 mm 7.7 mm, 8.4 mm, 42 mm, 5.8
www.eophtha.com
primary gaze, length Superior oblique of muscle and tendon Inferior oblique length Centre of rotation of eye ball in primary position Angle between muscle Sup and inf recti plane and visual line Sup and inf oblique Angle between axis of eye ball and orbit Number of cell layer Marginal of different parts of Tarsal conjunctival Fornix and bulbar epithelium Limbal Number of glands of Krause in the fornices Number of glands of Wolfring in the tarsal border Distance of puncta from inner canthus Lacrimal canaliculus- diameter Length of canaliculus Vertical part Horizontal part Lacrimal sac- length Total Fundus Body Lacrimal sac breath and capacity Length of NLD Total Intraosseous Intra meatal Diameter of NLD Rate of secretion of tear Refractive index and pH of tear Normal BUT, height of marginal tear strip Length of palpebral Horizontal fissure Vertical in the centre Length of LPS muscle and tendon Size of tarsus- length, thickness Height of tarsus Upper lid Lower lid Number of meibomian glands Number of glands of Zeis Number of glands of Moll (modified sweat) Normal rate of blinking Depth of orbit- along medial and lateral wall 1 mm change in axial length gives ametropia of 1 mm change in radius of curvature of cornea gives ametropia of
16.3 mm, 5 mm, 60 mm, 20 mm 18.4 mm, 17 mm, 37 mm, 1-2 13.5 mm behind apex of cornea 23o in primary position of gaze 51o 23o 5 2 3 8-10 40-42 upper and 6-8 lower 2-5 upper, 2-3 lower Upper- 6 mm, lower- 6.5 mm 0.5 mm 2 mm 8 mm 15 mm 3-5 mm 10-12 mm 5-6 mm, 20 c. mm 18 mm (12-24 mm) 12.5 mm 5.5 mm 3 mm (upper end is narrowest) 1.2 l/ min or 10 cu ml/24 hrs 1.357, 7.4 (7.3-7.7) in sleep > 10 sec, 0.5 mm 18-21 mm at birth, 28-30 mm adult 8 mm at birth, 9-11 mm adult 40 mm, 15 mm 29 mm,1 mm 10-11 mm 4-5 mm 20-30 in each lid, single row 2 glands associated with each cilia Between the cilia, LL>UL 12- 20 times/min 42 mm and 50 mm 3D 6D
www.eophtha.com
Hypermetropia at birth Listings reduced eye Total dioptric power Principal point Nodal point Anterior focal point Posterior focal point Ant & post focal length
2.5 D + 60 D 1.5 mm behind ant. surface of cornea 7.2 mm behind ant surface of cornea 15.7 mm in front of ant surf of cornea 24.4 mm behind ant surf of cornea 17.2 (15.7+1.5) & 22.9 (24.4-1.5)
Compiled by: Dr Sarbani Roy, MS
www.eophtha.com
Вам также может понравиться
- PAL Identifier 2015-16Документ72 страницыPAL Identifier 2015-16vinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Ophthalmology: Anatomy, Examination, Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент83 страницыIntroduction to Ophthalmology: Anatomy, Examination, Diagnosis and TreatmentHassan Raza100% (1)
- Eyes and Vision PresentationДокумент142 страницыEyes and Vision Presentationrhimineecat71100% (1)
- Full Anatomy CoassДокумент74 страницыFull Anatomy CoassAuliaRusdiAllmuttaqienОценок пока нет
- Anatomy&Physiology.eye สอน นศพ. 2Документ77 страницAnatomy&Physiology.eye สอน นศพ. 2ณัช เกษมОценок пока нет
- Suturing Skills Ebook Marshall SuturingДокумент23 страницыSuturing Skills Ebook Marshall SuturingErbert De Langer100% (2)
- A Scan BiometryДокумент37 страницA Scan BiometryAnonymous Wb2LoZv9c100% (1)
- Max Illo Facial SurgeryДокумент92 страницыMax Illo Facial Surgerychueychuan100% (1)
- Notes Dr. Wahid Wanis Biology ASFrom His BookДокумент10 страницNotes Dr. Wahid Wanis Biology ASFrom His BookBooksОценок пока нет
- Visual System For Medical StudentsДокумент238 страницVisual System For Medical Studentskhorrami4Оценок пока нет
- Visual Field Loss in the Real World: A Book of Static Perimetry Test Targets for Eye Health ProfessionalsОт EverandVisual Field Loss in the Real World: A Book of Static Perimetry Test Targets for Eye Health ProfessionalsОценок пока нет
- The role of nurses in cataract diagnosis, surgery and aftercareДокумент5 страницThe role of nurses in cataract diagnosis, surgery and aftercareFara Sakina RahmaОценок пока нет
- A-Scan Biometry: Understanding Ultrasound Principles and InstrumentationДокумент16 страницA-Scan Biometry: Understanding Ultrasound Principles and InstrumentationSadegh ShebaniОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Cornea: Dr. Joseph JohnДокумент46 страницAnatomy and Physiology of Cornea: Dr. Joseph JohnBIBI MOHANAN100% (1)
- A Scan BiometryДокумент28 страницA Scan Biometrysolex_Оценок пока нет
- Fast Track Series - Microsoft Office Excel Advanced (Manual) - CompleteДокумент66 страницFast Track Series - Microsoft Office Excel Advanced (Manual) - Completevinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- B SCAN PPPДокумент92 страницыB SCAN PPPSiva Wurity100% (1)
- Understand Glaucoma: Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент57 страницUnderstand Glaucoma: Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentDarshan SinghОценок пока нет
- Normal Values in OphthalmologyДокумент4 страницыNormal Values in OphthalmologyRameshОценок пока нет
- Optic Nerve Examination in Glaucoma (Edit)Документ27 страницOptic Nerve Examination in Glaucoma (Edit)mazidahzulfa100% (1)
- Stratus OCT™ Real Answers in Real Time.: Software Version 4.0Документ12 страницStratus OCT™ Real Answers in Real Time.: Software Version 4.0Mirella Carazas MontoyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and EmbryologyДокумент46 страницAnatomy and EmbryologyInTan RamliОценок пока нет
- Acestridium ColombiensisДокумент6 страницAcestridium ColombiensisLuis Carlos Villarreal DiazОценок пока нет
- Tear Film White Paper 020310Документ4 страницыTear Film White Paper 020310Prasi YusОценок пока нет
- Full Anatomy CoassДокумент74 страницыFull Anatomy CoassKartikaSariОценок пока нет
- Dr. Sashwat Ray IsmДокумент98 страницDr. Sashwat Ray IsmCastleKGОценок пока нет
- Human Eye: General PropertiesДокумент10 страницHuman Eye: General PropertiesVijay RajendiranОценок пока нет
- A-Scan Biometry Ultrasound PrinciplesДокумент19 страницA-Scan Biometry Ultrasound PrinciplesJeanna Salima100% (1)
- Ocular Anatomy OverviewДокумент89 страницOcular Anatomy OverviewFikri M Asgar SОценок пока нет
- 6.ANAtomy of CORNEA SrisДокумент108 страниц6.ANAtomy of CORNEA SrisSristi ThakurОценок пока нет
- PhotopicДокумент10 страницPhotopicVivian AmosОценок пока нет
- ,, PDFДокумент7 страниц,, PDFTiffany Rachma PutriОценок пока нет
- Ultrasonographic Study of Equine Eyes: E. Svaldenienė, M. Paunksnienė, V. BabrauskienėДокумент3 страницыUltrasonographic Study of Equine Eyes: E. Svaldenienė, M. Paunksnienė, V. BabrauskienėSantiago López BuitragoОценок пока нет
- A To Z of Relex Smile: All You Need To Know: Review ArticleДокумент7 страницA To Z of Relex Smile: All You Need To Know: Review ArticleStefanОценок пока нет
- Cobitis: Two New Species of The Genus Linnaeus (Teleostei: Cobitidae) From TurkeyДокумент8 страницCobitis: Two New Species of The Genus Linnaeus (Teleostei: Cobitidae) From TurkeySubhadra LaimayumОценок пока нет
- Measurements & Composition of Eye StructuresДокумент2 страницыMeasurements & Composition of Eye StructuresAnas AbuseifОценок пока нет
- RefraksiДокумент84 страницыRefraksinaroetocapkutilОценок пока нет
- Hard Lens PropertiesДокумент22 страницыHard Lens Propertiesblack00swanОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Mutations in Vsx1 Gene in Keratoconus PatientsДокумент69 страницAnalysis of Mutations in Vsx1 Gene in Keratoconus PatientssharammaОценок пока нет
- Immersion Biometry: Improving Accuracy for Better Surgical OutcomesДокумент19 страницImmersion Biometry: Improving Accuracy for Better Surgical Outcomesrcortez1986100% (1)
- Human EyeДокумент6 страницHuman EyeclubsanatateОценок пока нет
- Anterior Segment OctДокумент53 страницыAnterior Segment OctA.c. RaghuОценок пока нет
- Parameter of Human EyeballДокумент1 страницаParameter of Human EyeballkalinglangkammrcОценок пока нет
- Bi 302 Lab 3Документ7 страницBi 302 Lab 3SanahKumarОценок пока нет
- Manual of Retinal Surgery 2nd Edition 2001Документ138 страницManual of Retinal Surgery 2nd Edition 2001masinameaОценок пока нет
- Presentation 010306201611052016Документ80 страницPresentation 010306201611052016itsme.chandlermbingОценок пока нет
- The Multifunctional ChoroidДокумент38 страницThe Multifunctional ChoroidyinvilllОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The EyeДокумент15 страницAnatomy of The EyeZeljko TomicОценок пока нет
- Skull Base, Orbits, TB, Cran Nerv Anatomy On MRI, MRI Clin of A 2011Документ18 страницSkull Base, Orbits, TB, Cran Nerv Anatomy On MRI, MRI Clin of A 2011Mauricio FrancoОценок пока нет
- The Ocular Biometric and Corneal Topographic Characteristics of High-Anisometropic Adults in TaiwanДокумент6 страницThe Ocular Biometric and Corneal Topographic Characteristics of High-Anisometropic Adults in TaiwanNurul Falah KalokoОценок пока нет
- French gauge sizing system used for catheter calibration and cannulationДокумент12 страницFrench gauge sizing system used for catheter calibration and cannulationAhmed MohammedОценок пока нет
- Interpreting OCT Scans ChenДокумент3 страницыInterpreting OCT Scans ChenJomarОценок пока нет
- Comparision of Accommodative FacilityДокумент11 страницComparision of Accommodative FacilityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Microscope Cell GuideДокумент98 страницMicroscope Cell GuideJiezel EstiponaОценок пока нет
- Anatomi dan Fisiologi MataДокумент91 страницаAnatomi dan Fisiologi Mataanacay87100% (1)
- EyesДокумент30 страницEyesAlfredJoshuaMirandaОценок пока нет
- Ophtha LectureДокумент634 страницыOphtha LectureIb YasОценок пока нет
- Local Flaps in Facial Reconstruction: A Defect Based ApproachОт EverandLocal Flaps in Facial Reconstruction: A Defect Based ApproachОценок пока нет
- Sukan KKM Launching QuotationДокумент1 страницаSukan KKM Launching Quotationvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- ACUVUE OASYS With Hydraclear Plus Contact Lenses: Acuvue Manufacturer: Johnson - Johnson From: U.SДокумент2 страницыACUVUE OASYS With Hydraclear Plus Contact Lenses: Acuvue Manufacturer: Johnson - Johnson From: U.Svinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Mqa Saito University CollegeДокумент1 страницаMqa Saito University Collegevinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Protocol ReviewДокумент10 страницProtocol Reviewvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- ACUVUE OASYS With Hydraclear Plus Contact LensesДокумент8 страницACUVUE OASYS With Hydraclear Plus Contact Lensesvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Lung CarcinomaДокумент29 страницLung Carcinomavinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Cellular Adaptations in Growth and DifferentiationДокумент32 страницыCellular Adaptations in Growth and Differentiationvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Layout Stor RoomДокумент1 страницаLayout Stor Roomvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Drugs in Heart Failure Zol 1Документ27 страницDrugs in Heart Failure Zol 1vinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Aetiology and Epidemiology: Prepared By: Kalppena NaiduДокумент2 страницыAetiology and Epidemiology: Prepared By: Kalppena Naiduvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- ACUVUE OASYS With Hydraclear Plus Contact LensesДокумент8 страницACUVUE OASYS With Hydraclear Plus Contact Lensesvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Cellular Adaptations in Growth and DifferentiationДокумент32 страницыCellular Adaptations in Growth and Differentiationvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Lung CarcinomaДокумент29 страницLung Carcinomavinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Revision Pe 1 (Kalppena Naidu)Документ11 страницRevision Pe 1 (Kalppena Naidu)vinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Antibody Screening: Presented by Kalppena Naidu Slide by Nur AmaniДокумент4 страницыAntibody Screening: Presented by Kalppena Naidu Slide by Nur Amanivinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Boarding Pass LangkawiДокумент3 страницыBoarding Pass Langkawivinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Introduction To MicrosДокумент11 страницIntroduction To Microsvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- The Physiology of EdemaДокумент23 страницыThe Physiology of EdemaEmira JannahОценок пока нет
- Human Health and The Environment: Key SignalsДокумент7 страницHuman Health and The Environment: Key Signalsvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- RPH FinalДокумент60 страницRPH Finalvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Human Health and The Environment: Key SignalsДокумент7 страницHuman Health and The Environment: Key Signalsvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Introduction To MicrosДокумент11 страницIntroduction To Microsvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Lab Chem 3Документ7 страницLab Chem 3sayidah nafisah83% (12)
- Blincon BB PromotionДокумент1 страницаBlincon BB Promotionvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- Exp 7 - AcidBaseF11Документ5 страницExp 7 - AcidBaseF11Elena GilbertОценок пока нет
- 3881 PDFДокумент92 страницы3881 PDFLetchumana KrishnanОценок пока нет
- Job Prospect in MalaysiaДокумент5 страницJob Prospect in Malaysiavinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет
- CPG Consensus Statement On Utilization of Cardiac CTДокумент17 страницCPG Consensus Statement On Utilization of Cardiac CTvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalОценок пока нет