Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Roculax
Загружено:
vannyanoyИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Roculax
Загружено:
vannyanoyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ROCULAX
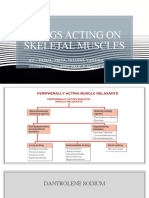
Description Roculax is a nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent, supplied as a sterile, nonpyrogenic, isotonic solution for intravenous injection only. Composition Each ampoule of Roculax contains Rocuronium bromide 10 mg/mL. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics : Rocuronium bromide acts by competing for cholinergic receptors at the motor end-plate. This action is antagonized by acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, such as neostigmine and edrophonium. The recovery of neuromuscular function is satisfactory. The neuromuscular blocking action of rocuronium bromide may be enhanced in the presence of potent inhalation anaesthetics. Pharmacokinetics : Rocuronium is a nondepolarizing neuromuscular agent with rapid to intermediate onset depending on dose, and intermediate duration. The rapid distribution half-life is 1-2 minutes and the slower distribution half-life is 14-18 minutes. Rocuronium is approximately 30% bound to human plasma proteins. Rocuronium is eliminated primarily by the liver. The metabolite of rocuronium,17desacetyl-rocuronium, has been rarely observed in the plasma or urine of humans administered single doses of 0.5-1 mg/kgBW with or without a subsequent infusion of rocuronium. Indications Roculax is indicated as an adjunct to general anesthesia to facilitate endotracheal intubation, and to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery. Contraindications Roculax is contraindicated in : - Patients known to have hypersensitivity to rocuronium bromide or to bromide ion. - Pregnancy. Warnings and Precautions
Roculax should be administered in carefully adjusted dosages under the supervision of experienced clinicians who are familiar with the drugs actions and the possible complications of its use. Roculax should not be administrated unless facilities for intubation, artificial respiration, oxygen therapy, and an antagonist are immediately available. It is recommended that administration of Roculax employ a peripheral nerve stimulator to monitor drug response, need for additional relaxant, and adequacy of spontaneous recovery or antagonism. Roculax administration must be accompanied by adequate anaesthesia or sedation. In patients with myasthenia gravis, small doses of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents may have profound effects.
Roculax, which has an acid pH, should not be mixed with alkaline solutions (e.g. barbiturate solutions) in the same syringe or administered simultaneously during intravenous infusion through the same needle. In the use of Roculax, increases or decreases in MAP (Mean Arterial Pressure) and tachycardia may occurred. Most of the pediatric patients developed tachycardia were anaesthetized with halothane and who did not receive atropine for induction. Laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation following Roculax administration were accompanied by transient tachycardia ( 30 % increment) in adult patients under opioid/ N2O/O2 anaesthesia. The tachycardia observed in some patients may result from this vagal blocking activity. Prolonged paralysis and/or skeletal muscle weakness may be noted during initial attempts to wean from the ventilator patients who have chronically received neuromuscular blocking drugs in the ICU. So Roculax should only be used if the specific advantages of the drug outweigh the risk. Roculax is not recommended for rapid induction in cesarean section patients. Roculax should be used with caution in patients with clinically significant hepatic disease because clinial duration and the recovery was moderately prolonged in these patients. Both respiratory and metabolic acidosis prolonged the recovery time. The potency of Roculax was significantly enhanced in metabolic acidosis and alkalosis, but was reduced in respiratory alkalosis. Severe acid-base and/or electrolyte abnormalities may potentiate or cause resistance to the neuromuscular blocking action of Roculax. Extravasation of Roculax may result signs or symptoms of local irritation; the injection or infusion should be terminated immediately and restarted in another vein. Burns, disuse atrophy, denervation, direct muscle trauma, and cerebral palsy may result the development of resistance to nondepolarizing muscle relaxants.
Other nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents exhibit profound neuromuscular blocking effects in cachectic or debilitated patients, patients with neuromuscular diseases, and patients with carcinomatosis. In these patients a decrease from the recommended initial dose should be considered. Roculax may be associated with increased pulmonary vascular resistance so caution in patients with pulmonary hypertension or valvular heart disease. Anaphylactic reactions to neuromuscular blocking agents in general have been reported Because Roculax is always used with other agents and because the occurrence of malignant hyperthermia during anaesthesia is possible, even in the absence of known triggering agents, clinicians should be familiar with early signs, confirmatory diagnosis and treatment of malignant hyperthermia prior to the start of any anaesthesia. Roculax should be used with caution in patients with clinically significant hepatic and/ or billiary tract diseases and/ or renal failure. Conditions associated with prolonged circulation time such as cardiovascular disease, old age, and oedematous state resulting in an increased volume of distribution, may contribute to a slower onset of action. Like other neuromuscular blocking agents, Roculax should be used with extreme caution in patients with a neuromuscular disease or after poliomyelitis since the response to neuromuscular blocking agents may be considerably altered in these cases. In surgery under hypothermic condition, the neuromuscular blocking effect of Roculax is increased and the duration prolonged. Roculax may exhibit a prolonged duration and a prolonged spontaneous recovery in obese patients. Roculax should be given to lactating women only when the physician decides that the benefits outweigh the risk. It is not recommended to use potentially dangerous machinery or drive a car within 24 hours after the full recovery from the neuromuscular blocking action of Roculax.
Adverse Effects Prolonged neuromuscular block is associated with neuromuscular blockers. Adverse experiences with probable or unknown relationship: Cardiovascular : arrhythmia, abnormal electrocardiogram, tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension. Digestive : nausea, vomiting. Respiratory : asthma (bronchospasm, wheezing, or rhonchi), hiccup. Skin and Appendages : allergic reactions (rash, pruritus, anaphylactic and anaphylactoid), injection site edema. Dosage and Administration - Endotracheal Intubation : The dose is 0.6-1.2 mg/kgBW. - Maintenance Dose: The maintenance dose is 0.1- 0.2 mg/kgBW. - Use by Continuous Infusion:
It is recommended to give loading dose of 0.6 mg Roculax/kgBW, when neuromuscular block starts to recover, to start administration by infusion. In adults under i.v anaesthesia, the infusion rate required to maintain neuromuscular block at this level ranges from 5-10 g/kgBW/min (0,3-0,6 mg/kg/h). Continuous monitoring of neuromuscular block is essential since infusion rate requirements vary from patient to patient and with the anaesthetic method used. Pediatrics : The initial dose is 0.6 mg/kgBW. The maintenance dose is 0.075-0.125 mg/kgBW. A continuous infusion of Roculax initiated at a rate of 0.012 mg/kgBW/min may also be used to maintain neuromuscular blockade in pediatric patients. There are no data to support the recommendation for the use of rocuronium bromide in neonates (0-3 months). Geriatrics ( 65 years) and patients with hepatic and/or biliary tract disease and/or renal failure : The dose is 0.6 - 1.2 mg/kgBW. The maintenance dose is 0.075-0.1 mg/kgBW. The recommended infusion rate is 5-6 g/kgBW/min. Obese Patients : When used in overweight or obese patients (defined as patients with a body weight of 30% or more above ideal body weight) doses should be reduced taking into account a lean body mass.
Administration: Roculax administered intravenously either as a bolus injection or as a continuous infusion. Presentation Ampoules 5 mL in box @ 10 ampoules. Roculax should be stored under refrigeration (2 - 8)C. Do not freeze. Upon removal from refrigeration to room temperature storage conditions (25C), use Roculax within 60 days. Do not use solution if particulate matter is present.
Вам также может понравиться
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Mechanisms and Clinical UsesДокумент5 страницNeuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Mechanisms and Clinical UsesTherese Jane TiradorОценок пока нет
- Local Anesthetics (Slide Show)Документ24 страницыLocal Anesthetics (Slide Show)Sheena Lou Regencia SalomonОценок пока нет
- RocuroniumbromideinjДокумент14 страницRocuroniumbromideinjagnes hutabaratОценок пока нет
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsДокумент34 страницыSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsLohithОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology NMB Ds and Anti Cholinesterase S FinalДокумент8 страницPharmacology NMB Ds and Anti Cholinesterase S FinalPamella Kusuma WerdanieОценок пока нет
- Succinylcholine ChlorideДокумент19 страницSuccinylcholine ChlorideAgungBudiPamungkas100% (1)
- Anesthesia and Procedural MonitoringДокумент5 страницAnesthesia and Procedural MonitoringVanesa Michelle Estrella ObregonОценок пока нет
- Journal Reading: Ko-Ass Anastesi RSISA 2014Документ32 страницыJournal Reading: Ko-Ass Anastesi RSISA 2014Sham DiyahОценок пока нет
- Suxamethonium Chloride Injection BP Product Information SummaryДокумент8 страницSuxamethonium Chloride Injection BP Product Information SummarynanaОценок пока нет
- Sugammadex - PIДокумент15 страницSugammadex - PIveliaberlianaОценок пока нет
- Antigout PDFДокумент21 страницаAntigout PDFshaifОценок пока нет
- Organophosphate Poisoning GuideДокумент28 страницOrganophosphate Poisoning GuideSumaiyyaОценок пока нет
- Product Information: Chemical StructureДокумент10 страницProduct Information: Chemical Structureddandan_2Оценок пока нет
- Uia 13 DELAYED AWAKENING OR EMERGENCE FROM ANAESTHESIAДокумент3 страницыUia 13 DELAYED AWAKENING OR EMERGENCE FROM ANAESTHESIAsunny kumarОценок пока нет
- Succinylcholine Brand and Generic NamesДокумент12 страницSuccinylcholine Brand and Generic NamesJeralyn BugayongОценок пока нет
- Delayed Awakening From AnaesthesiaДокумент3 страницыDelayed Awakening From AnaesthesiaSenthooran ArudshivsmОценок пока нет
- Montelukast SodiumДокумент10 страницMontelukast SodiumikhasilОценок пока нет
- Use of Neuromuscular Blocking Medications in Critically Ill PatientsДокумент17 страницUse of Neuromuscular Blocking Medications in Critically Ill PatientsDian HaneulОценок пока нет
- Esmeron 10 MG/ML Solution For Injection Rocuronium Bromide Prescribing InformationДокумент3 страницыEsmeron 10 MG/ML Solution For Injection Rocuronium Bromide Prescribing InformationVeeta Ruchi LieОценок пока нет
- Reversing Opioid Effects with Naloxone DosesДокумент22 страницыReversing Opioid Effects with Naloxone DosesAyman MustafaОценок пока нет
- Michael Jackson's Cause of DeathДокумент40 страницMichael Jackson's Cause of DeathYeni SuwitaОценок пока нет
- Presentation 2Документ20 страницPresentation 2Muhammad UmairОценок пока нет
- Ativan CIV Tablets: R OnlyДокумент8 страницAtivan CIV Tablets: R OnlyP KasikrishnarajaОценок пока нет
- AllopurinolДокумент31 страницаAllopurinolbeewolОценок пока нет
- Drug Study..DokcyДокумент7 страницDrug Study..DokcyPeArl Peralta0% (1)
- Evaluation and Management of Delayed Awakening or Emergence From AnaesthesiaДокумент19 страницEvaluation and Management of Delayed Awakening or Emergence From AnaesthesiaMuhammad UmairОценок пока нет
- LI Case 2 (Pharmacological Properties of Propanolol)Документ2 страницыLI Case 2 (Pharmacological Properties of Propanolol)adtyadaviaОценок пока нет
- Neuromuscular Blocking AgentsДокумент13 страницNeuromuscular Blocking AgentsSamer AlBaghdadiОценок пока нет
- Plaquenil SPCДокумент20 страницPlaquenil SPCMinas ParisisОценок пока нет
- Atropine Sulfate InjectionДокумент4 страницыAtropine Sulfate InjectionIrawanMarlyОценок пока нет
- Halcion Triazolam Tablets, USP CIV: DescriptionДокумент14 страницHalcion Triazolam Tablets, USP CIV: DescriptionAlberto JaramilloОценок пока нет
- Health Canada - HaloperidolДокумент25 страницHealth Canada - HaloperidolIndrie LestarieОценок пока нет
- Obat Ayu (Anestesi)Документ11 страницObat Ayu (Anestesi)Ayu PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Summary of Product CharacteristicДокумент5 страницSummary of Product Characteristicresearch universalОценок пока нет
- Atracurium BesylateДокумент4 страницыAtracurium BesylateStill DollОценок пока нет
- Drugs 3Документ2 страницыDrugs 3kheemeeОценок пока нет
- Clopixol Ta BinjДокумент14 страницClopixol Ta BinjLucia TarhonОценок пока нет
- Muscle Relaxants Classification and Mechanisms of ActionДокумент22 страницыMuscle Relaxants Classification and Mechanisms of Actionvinay0717100% (1)
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: Brand Name: HaldolДокумент15 страницHaloperidol: Brand Name: Haldolteguh aminОценок пока нет
- Rocuronium: Bromide InjectionДокумент2 страницыRocuronium: Bromide InjectionNursalfarinah BasirОценок пока нет
- Inactive Ingredients: Dibasic Calcium Phosphate USP, Hypromellose USP, Magnesium Stearate NFДокумент11 страницInactive Ingredients: Dibasic Calcium Phosphate USP, Hypromellose USP, Magnesium Stearate NFJuan CaponeОценок пока нет
- Fluanxol Depot: Name of MedicineДокумент11 страницFluanxol Depot: Name of MedicineIvo_NichtОценок пока нет
- OFLOX-OZ TabletsДокумент30 страницOFLOX-OZ TabletsSilvio BarbosaОценок пока нет
- KetorolacДокумент8 страницKetorolacSan LampuyasОценок пока нет
- Sem3_Pharmacotherapy Pearls for Emergency Neurological Life SupportДокумент26 страницSem3_Pharmacotherapy Pearls for Emergency Neurological Life SupportOlga Manco GuzmánОценок пока нет
- Drugs Used in AneasthesiaДокумент73 страницыDrugs Used in AneasthesiaCabdiladif Ahmed McrfОценок пока нет
- Cholinergic SyndromeДокумент3 страницыCholinergic SyndromeEmman AguilarОценок пока нет
- Plaquenil Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Tablets, UspДокумент11 страницPlaquenil Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Tablets, UspAnmol KudalОценок пока нет
- Avelox Tablet 400mg PIДокумент26 страницAvelox Tablet 400mg PIJing Yi LeongОценок пока нет
- Netupitant 300mg + Palonosetron HCL 0.56mg (Akynzeo)Документ16 страницNetupitant 300mg + Palonosetron HCL 0.56mg (Akynzeo)ddandan_2Оценок пока нет
- Cover PortofolioДокумент6 страницCover PortofoliovannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Hellp Syndrome FINALLLLLL - Dr. VannyДокумент35 страницHellp Syndrome FINALLLLLL - Dr. VannyvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Dyspnea - Respirology AspectsДокумент30 страницDyspnea - Respirology AspectsvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- 09-08 Spondylitis TB, CP ExpДокумент20 страниц09-08 Spondylitis TB, CP ExpvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- EMG Report RSPAD April 11th, 2014Документ21 страницаEMG Report RSPAD April 11th, 2014vannyanoyОценок пока нет
- ToxoplasmosisДокумент13 страницToxoplasmosisvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Pneumothoraks (Lucinda CF)Документ28 страницPneumothoraks (Lucinda CF)vannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Rekapitulasi Stase Kepaniteraan Klinik Program Studi Profesi Dokter Upn "Veteran" JakartaДокумент1 страницаRekapitulasi Stase Kepaniteraan Klinik Program Studi Profesi Dokter Upn "Veteran" JakartavannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Pneumothoraks (Lucinda CF)Документ28 страницPneumothoraks (Lucinda CF)vannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Catatan Kuliah Penyakit Jantung BawaanIngrisДокумент29 страницCatatan Kuliah Penyakit Jantung BawaanIngrisvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Placenta PreviaДокумент11 страницPlacenta PreviavannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Psychosexual DisordersДокумент12 страницPsychosexual DisordersEJ07100% (1)
- Bang UcupДокумент34 страницыBang Ucupvannyanoy100% (1)
- Active Management of Labor Trial Reduces Duration but Not C-Section RateДокумент12 страницActive Management of Labor Trial Reduces Duration but Not C-Section RatevannyanoyОценок пока нет
- RoculaxДокумент4 страницыRoculaxvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Abortion 2Документ47 страницAbortion 2Irfandy Chairi Sulaiman LubisОценок пока нет
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaДокумент7 страницChronic Suppurative Otitis MediavannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Preeklampsia - Searching CauseДокумент2 страницыPreeklampsia - Searching CausevannyanoyОценок пока нет
- AДокумент7 страницAvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Pi Is 0886335008008481Документ2 страницыPi Is 0886335008008481vannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Katarak Kelompok 7Документ8 страницKatarak Kelompok 7vannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Nilai Normal LabДокумент1 страницаNilai Normal LabvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Acne KeloidalisДокумент11 страницAcne KeloidalisvannyanoyОценок пока нет
- Pseudo ExfoliationДокумент6 страницPseudo ExfoliationvannyanoyОценок пока нет