Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Final Exam
Загружено:
Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Final Exam
Загружено:
Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
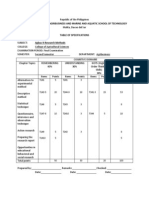
Southern Philippines Agribusiness and Marine and Aquatic School of Technology College of Agricultural Sciences Matti, Digos City
FINAL EXAM on RESEARCH METHODS Name: I. Year & Course:
Identification. Write your answer on the space provided. 5 pts. each
1. It is the general procedure employed in studies that have for their chief purpose of description of phenomena in contrast to ascertaining what caused them and what their value and significance are. 2. It is the process of choosing a representative part of the population under study. 3. It is a population list from which the sample is to be chosen. 4. It is one in which every element of the population has a chance of entering the sample. 5. It is a type of sampling that each interviewer is given a number of persons of a specific type to interview 6. It is the arithmetical average obtained when all the scores are added and divided by the number of cases. 7. It is a written or printed form used in gathering information on some subject/s consisting of a set of questions distributed to and filled out by the respondent 8. It is an intentional or explicit method of examining, describing, and interpreting the reactions or behavior of an individual or group of individuals in laboratory, classrooms or out-of-school setting for the purpose of gathering facts. 9. It refers to careful, systematic, patient study and investigation in some field of knowledge which conforms to formal or accepted standards or rules 10. This chapter contains the design, description of the sample, the measures used, and finally the steps taken in carrying out the project. II. Matching type. Match Column A with Column B. Write your answer beside the number. 3 pts. each 1. Column A It includes all studies that purport to present facts concerning the nature and status of anything-a group of persons, a number of objects, a set of conditions, a class of events, a system of thought or any kind of phenomena which one may wish to study Is the process by which practitioners attempt to study their problems scientifically in order to guide, correct, and evaluate their decisions and actions Refers to relationships between variables that can be quantified. The respondents are chosen on the basis of their knowledge of the information desired or needed. It involves the deliberate selection of individuals by the researcher based on certain pre-defined criteria. Is any quantity or characteristic which may posses different numerical values or categories. Involves asking subjects to provide names of others who may meet study criteria. It is often used when researchers do not have access to a population. Is a limited but representative subset of a population. The type of sampling that has no system of selection Column B a. Variable
2.
b. Sample
3. 4.
c. Descriptive research d. Accidental sampling
5. 6.
e. Stratified random sampling f. Simple random sampling g. Correlation h. Action research 1
7. 8.
9. The researcher or analyst divides the population into two or more strata on the basis of one or more characteristics. 10.Is another tool in research which is very common used in field surveys.
i. j.
Convenience sampling Quota sampling
k. Snowball sampling l. Purposive sampling m. Personal interview n. Observation o. Cluster sampling p. Population III. Discussion. Briefly explain your answer. 5 pts. each. 1. 2. 3. 4. When When When When should should should should simple random sampling be used? cluster sampling be used? accidental sampling be used? quota sampling be used?
I. 1. Descriptive survey 2. Sampling 3. Sampling frame. 4. Probability sampling 5. Quota sampling. 6. Mean 7. Questionnaire. 8. Observation 9. Conventional research 10. Methodology II. 1. Descriptive research 2. Action research. 3. Correlation 4. Purposive sampling 5. Variable 6. Snowball sampling 7. Sample 8. Accidental sampling 9. Stratified random sampling 10. Personal interview III. 1. When one wants to generalize as to the whole population from which the sample is drawn or if the population is not scattered. 2. When the population to be sample is very large. 3. When it is known in advance that a special segment of the population would not have enough persons in the sample if simple random was used. 4. When no alternative is available 5. When the analyst knows exactly what type of persons he/she wants to interview and that this type is fairly and easily recognized.
Вам также может понравиться
- Monthly Performance Output ReportДокумент2 страницыMonthly Performance Output ReportCherry Ann Pascua Roxas100% (1)
- Monthly Performance Output ReportДокумент2 страницыMonthly Performance Output ReportCherry Ann Pascua Roxas100% (1)
- Faculty WorkloadДокумент2 страницыFaculty WorkloadCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Southern Philippines Agribusiness and Marine and Aquatic School of TechnologyДокумент1 страницаSouthern Philippines Agribusiness and Marine and Aquatic School of TechnologyCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- (03-04-13) Bsab-Cas Action Plan SY 2013-2014Документ4 страницы(03-04-13) Bsab-Cas Action Plan SY 2013-2014Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- List of Officers: Noted by AdviserДокумент3 страницыList of Officers: Noted by AdviserCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Southern Philippines agri-business and marine workload scheduleДокумент2 страницыSouthern Philippines agri-business and marine workload scheduleCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- 2013 Annual Work Plan and Budget (EDUCATION-CAS)Документ3 страницы2013 Annual Work Plan and Budget (EDUCATION-CAS)Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Summary of Workload (Faculty) New Form For B Fill-UpДокумент2 страницыSummary of Workload (Faculty) New Form For B Fill-UpCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Southern Philippines Agri-Business and Marine and Aquatic School of TechnologyДокумент2 страницыSouthern Philippines Agri-Business and Marine and Aquatic School of TechnologyCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Faculty Workload Form - 1st Sem 2013-2014Документ12 страницFaculty Workload Form - 1st Sem 2013-2014Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Faculty Workload Form - DistributedДокумент6 страницFaculty Workload Form - DistributedCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Multi - Step Income StatementДокумент2 страницыMulti - Step Income StatementCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- General Education Courses: Course No. Descriptive Title UnitsДокумент3 страницыGeneral Education Courses: Course No. Descriptive Title UnitsCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Bible verses about strength and courage in GodДокумент2 страницыBible verses about strength and courage in GodCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Personal Data SheetДокумент2 страницыPersonal Data SheetCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Personal Data SheetДокумент2 страницыPersonal Data SheetCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines Southern Philippines Agribusiness and Marine and Aquatic School of Technology (Spamast)Документ4 страницыRepublic of The Philippines Southern Philippines Agribusiness and Marine and Aquatic School of Technology (Spamast)Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- April 29-IT BoracayДокумент1 страницаApril 29-IT BoracayCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Letter For InceptionДокумент13 страницLetter For InceptionCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Accomplishment Report Business Mentor - Cocopal Project: Date Activity RemarksДокумент2 страницыAccomplishment Report Business Mentor - Cocopal Project: Date Activity RemarksCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Product Development and Market MissionДокумент1 страницаProduct Development and Market MissionCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Entrepreneurship Characteristics and Leadership StylesДокумент38 страницEntrepreneurship Characteristics and Leadership StylesCherry Ann Pascua Roxas100% (2)
- List of Farmers For Business Planning SupportДокумент6 страницList of Farmers For Business Planning SupportCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Classrecord 2nd Sem 2012-2013Документ12 страницClassrecord 2nd Sem 2012-2013Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Copy of CII 2012-13 Spring Course Schedule - JSE 12 Jan 2013-1Документ6 страницCopy of CII 2012-13 Spring Course Schedule - JSE 12 Jan 2013-1Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- Day 1Документ1 страницаDay 1Cherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- TosДокумент4 страницыTosCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- TOSДокумент5 страницTOSCherry Ann Pascua RoxasОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Chapter 1 ProjectДокумент5 страницChapter 1 ProjectFabeenaОценок пока нет
- Working in Lockdown: The Relationship Between COVID-19 Induced Work Stressors, Job Performance, Distress, and Life SatisfactionДокумент16 страницWorking in Lockdown: The Relationship Between COVID-19 Induced Work Stressors, Job Performance, Distress, and Life SatisfactionAnonymous O4qMock3YBОценок пока нет
- 2012 Multiformat Digital Products - How Design Attributes Interact With Usage Situations To Determine Choice PDFДокумент16 страниц2012 Multiformat Digital Products - How Design Attributes Interact With Usage Situations To Determine Choice PDFMaryОценок пока нет
- Planning of Research Design and ProcedureДокумент14 страницPlanning of Research Design and ProcedureDangerously CuteОценок пока нет
- Project Report On Performance Appraisal of BSNLДокумент71 страницаProject Report On Performance Appraisal of BSNLRashmi Ranjan Panigrahi100% (1)
- Study of Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Mobile Pre-Paid Products and Handset ModelsДокумент52 страницыStudy of Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Mobile Pre-Paid Products and Handset Modelsmaniche47Оценок пока нет
- Swissmetro - Data Description PDFДокумент6 страницSwissmetro - Data Description PDFjodomofoОценок пока нет
- Relationship Between Strategic Procurement and Hotel PerformanceДокумент32 страницыRelationship Between Strategic Procurement and Hotel PerformanceBrn MurgorОценок пока нет
- Cultural Influences On Consumer BehaviourДокумент17 страницCultural Influences On Consumer BehaviourBlue YurbleОценок пока нет
- Document 1Документ14 страницDocument 1Vanessa Yvonne Gurtiza100% (1)
- Buckley Training Program Plan 6Документ18 страницBuckley Training Program Plan 6api-315337943Оценок пока нет
- BRM - Water Issues in ShillongДокумент11 страницBRM - Water Issues in ShillongLijosh JoseОценок пока нет
- Staff Training and Development at JCB IndiaДокумент66 страницStaff Training and Development at JCB IndiaReena Gaonkar100% (1)
- Client Satisfaction EvaluationsДокумент38 страницClient Satisfaction EvaluationsJoee De Choudhury100% (1)
- My Summer Internship ReportДокумент84 страницыMy Summer Internship ReportEra Saluja100% (1)
- International Project Džezva To Go 1Документ24 страницыInternational Project Džezva To Go 1IbraОценок пока нет
- Egg Industry - 01 JAN 2011Документ40 страницEgg Industry - 01 JAN 2011jumanleeОценок пока нет
- Summer Training ReportДокумент80 страницSummer Training ReportAnkit DeswalОценок пока нет
- Monitoring and Evaluation Tools for Gender-Inclusive ProjectsДокумент39 страницMonitoring and Evaluation Tools for Gender-Inclusive ProjectsHening Tirta KusumawardaniОценок пока нет
- Abolish Bullying: A Phenomenology Approach On The Forts Verbal Bullying On Academic Performance Among Grade 10 StudentsДокумент28 страницAbolish Bullying: A Phenomenology Approach On The Forts Verbal Bullying On Academic Performance Among Grade 10 StudentsAlexОценок пока нет
- Research PaperДокумент18 страницResearch PaperBianca Samalea100% (2)
- Research Process Notes PDFДокумент18 страницResearch Process Notes PDFCLAUDINE MUGABEKAZIОценок пока нет
- Sample MBA Thesis - TWOДокумент72 страницыSample MBA Thesis - TWONury Aponte Aguilar100% (2)
- CHAP 123 1 RepairedДокумент23 страницыCHAP 123 1 RepairedAlyssa Mae LunodОценок пока нет
- Assignment No 2 5629-2Документ16 страницAssignment No 2 5629-2Sheikh Fareed AliОценок пока нет
- Canteen Assessment (Maysan NHS)Документ134 страницыCanteen Assessment (Maysan NHS)denizcbs90% (89)
- CRM at HondaДокумент68 страницCRM at Hondabhagathnagar69% (13)
- Assignment No.2 Course: Management Strategies in Educational Institutions (8615) Semester: Spring, 2022 Level: B.Ed. (1.5 YearsДокумент20 страницAssignment No.2 Course: Management Strategies in Educational Institutions (8615) Semester: Spring, 2022 Level: B.Ed. (1.5 Yearsmunn chОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ4 страницыChapter 3RoseAnn Jose Dela FuenteОценок пока нет
- Status and Prospects of Agri-Tourism in Selected Municipalities of The 4th District of BatangasДокумент7 страницStatus and Prospects of Agri-Tourism in Selected Municipalities of The 4th District of BatangasAsia Pacific Journal of Multidisciplinary ResearchОценок пока нет