Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Control
Загружено:
adauАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Control
Загружено:
adauАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PRINT VERSION: Control Theory
Page 1 of 2
Control Theory
Posted @ 3/29/2012 7:18 AM by Steven | Files in Control & Automation
Control theory looks at how systems work and are controlled from a mathematical view. This note gives a brief introduction to some of the concepts more of a notepad of concepts really, which can be added to over time.
Introduction
The diagram illustrates a control system at its simplest. The required output of the system is the reference. A sensor measures the system output and a controller compares this to the reference to determine the necessary actions to ensure the output moves towards the value given by the reference. The taking of the system output back to the input of the controller and using this (in conjunction with the reference) is called feedback. There are two types of feedback:
Negative where the system responds in the opposite direction to the error (difference Positive where the system responds in the same direction as the error.
between the measured output and reference). For example a thermostat at a set temperature will turn off when the room temperature exceeds this, thus cooling the room. An example of positive feedback would be placing a microphone near a speaker, where the sound will grow louder and louder.
Electrical Analogies
Building blocks for electrical, mechanical, fluid and thermal systems are often similar and analogous to each other. The use of analogies is often helpful in explaining how things work and is particularly useful in control systems. Voltage (V) Current (i) Resistor (R) Capacitor Inductor
Electrical Mechanical
Force (F) Velocity (v) Dashpot (c) Spring Mass
Pressure (p) Flow (q) Hydraulic Resistance (R) Hydraulic Capacitance (C) Hydraulic Inertance (I)
Fluid
Temperature (T, T1-T2) Heat Flow (q) Thermal Resistance (R) Thermal Capacitance(C) No Equivalent
Thermal
Energy Dissipation
Electrical Mechanical - Linear
Describing Equation
Energy / Power
Analogous Constant
PRINT VERSION: Control Theory
Page 2 of 2
Mechanical - Rotational Fluid - Hydraulic Fluid - Pneumatic Thermal
Energy Storage (Inductive)
Electrical Mechanical - Linear Mechanical - Rotational Fluid - Hydraulic Fluid - Pneumatic Thermal
Energy Storage (Capacitive)
Electrical Mechanical - Linear Mechanical - Rotational Fluid - Hydraulic Fluid - Pneumatic Thermal -
More This is an introductory post, I together as things were being moved across from the old Wiki. If there is anything you would like adding to the post, please let me know below and Ill look at adding it.
Вам также может понравиться
- ContДокумент95 страницContMilion dugumaОценок пока нет
- Out2t1 PDFДокумент27 страницOut2t1 PDFAjay Nath S AОценок пока нет
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorОт EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorОценок пока нет
- Mechatronic System ElementДокумент73 страницыMechatronic System ElementAbhijit AtoliyaОценок пока нет
- Engineering SystemsДокумент5 страницEngineering Systemsbedilu77Оценок пока нет
- Lab 3Документ17 страницLab 3hassan ullah khanОценок пока нет
- Introduction and Chapter Objectives: Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 4: Systems and Network TheoremsДокумент42 страницыIntroduction and Chapter Objectives: Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 4: Systems and Network TheoremskrajasekarantutiОценок пока нет
- 4th Class, Production Engineering Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy, University of Technology, BaghdadДокумент94 страницы4th Class, Production Engineering Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy, University of Technology, BaghdadMegaroboMegaroboОценок пока нет
- CS Two MarksДокумент7 страницCS Two MarkssivaeinfoОценок пока нет
- Ambo University: Regulation and ControlДокумент20 страницAmbo University: Regulation and ControlFikadu EshetuОценок пока нет
- Quick Review Outline - Masschusetts Testing for Educator Licensure (MTEL) Tech and Eng ExamОт EverandQuick Review Outline - Masschusetts Testing for Educator Licensure (MTEL) Tech and Eng ExamОценок пока нет
- Reviewer ControlДокумент10 страницReviewer ControlDioyo, ArvieОценок пока нет
- 1 - Introduction To Control SystemsДокумент11 страниц1 - Introduction To Control SystemsKenzie WalipiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Transfer FunctionДокумент52 страницыChapter 1 - Transfer FunctionNahome NigussieОценок пока нет
- Assistant Professor Dr. Khalaf S Gaeid: Electrical Engineering Department/Tikrit UniversityДокумент39 страницAssistant Professor Dr. Khalaf S Gaeid: Electrical Engineering Department/Tikrit Universityaditee saxenaaОценок пока нет
- System SimulationДокумент2 страницыSystem SimulationCarlo James LopezОценок пока нет
- Techteach - No Simview Time Constant IndexДокумент3 страницыTechteach - No Simview Time Constant IndexDiabloОценок пока нет
- SP Lab Exp1Документ4 страницыSP Lab Exp1himanshuОценок пока нет
- Control Theories Commonly Used Today Are Classical Control TheoryДокумент12 страницControl Theories Commonly Used Today Are Classical Control TheoryJuliánОценок пока нет
- Instrumentation (Chapter 2)Документ7 страницInstrumentation (Chapter 2)Yab TadОценок пока нет
- Modelling of Electrical SystemsДокумент3 страницыModelling of Electrical SystemsPandu KОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ38 страницLecture 2Haisham AliОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts in ThermodynamicsДокумент79 страницBasic Concepts in ThermodynamicsZul HakimОценок пока нет
- ES197 LectureДокумент45 страницES197 LectureAbisan ArulananthamОценок пока нет
- OCW - Control Systems - I (EE 503) - AY 2016-17 - 2017-18 PDFДокумент100 страницOCW - Control Systems - I (EE 503) - AY 2016-17 - 2017-18 PDFCiczmockingbird TsvkAdm100% (1)
- SMC (SE) - Capstone Project - PresentationДокумент28 страницSMC (SE) - Capstone Project - PresentationShun Myat ChalОценок пока нет
- Control System LabДокумент15 страницControl System Labhassan ullah khanОценок пока нет
- MPPT AlgorithmsДокумент9 страницMPPT AlgorithmssimmulationОценок пока нет
- Week 5 - 6Документ68 страницWeek 5 - 6KarimSAl-tamimiОценок пока нет
- Tuning A PID Controller: Guillermo J. CostaДокумент6 страницTuning A PID Controller: Guillermo J. CostaDeepak RainaОценок пока нет
- Control System 2MARKSДокумент16 страницControl System 2MARKSSeekay Alais Karuppaiah CОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Models: Module - 2Документ13 страницMathematical Models: Module - 2Rajath UpadhyaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Control SystemsДокумент45 страницIntroduction To Control SystemsLeta EmiruОценок пока нет
- Review of Techniques To Detect Harmonic Injection Into The Distribution SystemДокумент19 страницReview of Techniques To Detect Harmonic Injection Into The Distribution SystemSaurav BhattaraiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 01Документ10 страницChapter 01Gustavo CedenoОценок пока нет
- Modelling and Analysis of The Simple Water Heater SystemДокумент4 страницыModelling and Analysis of The Simple Water Heater SystemJohandi PatriaОценок пока нет
- Control System Engineering Lab: Avanish Niranjan 17104088 EEN 210Документ17 страницControl System Engineering Lab: Avanish Niranjan 17104088 EEN 210Umang SoinОценок пока нет
- Ystem Nalogies: Across Variables (V, T, and P)Документ7 страницYstem Nalogies: Across Variables (V, T, and P)Bryle CoОценок пока нет
- Examples of Control Systems:: Lecture OneДокумент4 страницыExamples of Control Systems:: Lecture OnemornyОценок пока нет
- Water CadДокумент29 страницWater CadPaijo TejoОценок пока нет
- Sensor Dynamic Static CharacteristicsДокумент6 страницSensor Dynamic Static CharacteristicsMantuomОценок пока нет
- What Is A "System"?Документ6 страницWhat Is A "System"?Ryan HiraniОценок пока нет
- Control m1-3Документ86 страницControl m1-3naughty dela cruzОценок пока нет
- Application of Laplace Transform in ControlsДокумент31 страницаApplication of Laplace Transform in ControlshportezОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlОт EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Glossary of Mechanical Engineering - WikipediaДокумент140 страницGlossary of Mechanical Engineering - WikipediaUchechukwu MarizuОценок пока нет
- Mechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersДокумент6 страницMechatronics Unit III and IV Question and AnswersSaravanan MathiОценок пока нет
- Measurement Systems Block DiagramДокумент3 страницыMeasurement Systems Block Diagramchiranjib_kОценок пока нет
- Dynamic SystemДокумент28 страницDynamic SystemA - STARОценок пока нет
- Temperature Control Using LabviewДокумент5 страницTemperature Control Using LabviewReyyan KhalidОценок пока нет
- Vibration: Fundamentals and PracticeДокумент19 страницVibration: Fundamentals and PracticeMuket AgmasОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Models of SystemsДокумент45 страницMathematical Models of SystemsSaid Ahmed AliОценок пока нет
- Summary of Topic Covered in ECE408Документ89 страницSummary of Topic Covered in ECE408Nishikata ManipolОценок пока нет
- Ee-474 Feedback Control System - 2012Документ69 страницEe-474 Feedback Control System - 2012Ali RazaОценок пока нет
- Energy Audit of Industrial Processes - Chap 1-2Документ52 страницыEnergy Audit of Industrial Processes - Chap 1-2simomedmed2000Оценок пока нет
- ISA Transactions: Rames C. Panda, V. Vijayan, V. Sujatha, P. Deepa, D. Manamali, A.B. MandalДокумент9 страницISA Transactions: Rames C. Panda, V. Vijayan, V. Sujatha, P. Deepa, D. Manamali, A.B. MandalAnonymous WkbmWCa8MОценок пока нет
- Mathematical ModelingДокумент8 страницMathematical ModelingMourougapragash SubramanianОценок пока нет
- PID Control Without Math: The Darker Side by Robert LacosteДокумент7 страницPID Control Without Math: The Darker Side by Robert LacosteNae GoguОценок пока нет
- EEE 402 Exp1Документ5 страницEEE 402 Exp1Sunil KumarОценок пока нет
- PLC and SCADA PowerpointДокумент172 страницыPLC and SCADA PowerpointRay WongОценок пока нет
- Fig. 13.43 Reduction of Mho Relay Angular Range: Tripping Can Occur Only For Impedance Between O and O, and Within MДокумент4 страницыFig. 13.43 Reduction of Mho Relay Angular Range: Tripping Can Occur Only For Impedance Between O and O, and Within MadauОценок пока нет
- Fig. 13.52 Diagram of System in The Vicinity of A 7000 MW Nuclear Power PlantДокумент4 страницыFig. 13.52 Diagram of System in The Vicinity of A 7000 MW Nuclear Power PlantadauОценок пока нет
- Discontinuous Excitation ControlДокумент6 страницDiscontinuous Excitation Controladau100% (1)
- However, The Level of Damping of Oscillations Is LowДокумент6 страницHowever, The Level of Damping of Oscillations Is LowadauОценок пока нет
- Performance of Protective RelayingДокумент6 страницPerformance of Protective RelayingadauОценок пока нет
- Relaying Quantities During SwingsДокумент6 страницRelaying Quantities During SwingsadauОценок пока нет
- (C) Pilot Relaying Schemes: Communication Medium May Be Pilot Wire (Metallic Wires), Power-LineДокумент6 страниц(C) Pilot Relaying Schemes: Communication Medium May Be Pilot Wire (Metallic Wires), Power-LineadauОценок пока нет
- Power-Angle RelationshipДокумент6 страницPower-Angle RelationshipadauОценок пока нет
- Models Used Must Be Appropriate For Transient Stability AnalysisДокумент6 страницModels Used Must Be Appropriate For Transient Stability AnalysisadauОценок пока нет
- Unstable Case: - Area A Above P Is Less Than AДокумент6 страницUnstable Case: - Area A Above P Is Less Than AadauОценок пока нет
- Wise: /wīz/ Adjective Having or Showing Experience, Knowledge, and Good Judgment: "A Wise Precaution"Документ5 страницWise: /wīz/ Adjective Having or Showing Experience, Knowledge, and Good Judgment: "A Wise Precaution"adauОценок пока нет
- Numerical Stability of Explicit Integration MethodsДокумент6 страницNumerical Stability of Explicit Integration MethodsadauОценок пока нет
- Things I Need To Know 5W, 1HДокумент1 страницаThings I Need To Know 5W, 1HadauОценок пока нет
- Future Perfect ContinuousДокумент4 страницыFuture Perfect ContinuousadauОценок пока нет
- Matching (Part 2)Документ9 страницMatching (Part 2)adauОценок пока нет
- On The Insulation Co-Ordination Studies Using (Emtp)Документ5 страницOn The Insulation Co-Ordination Studies Using (Emtp)adauОценок пока нет
- What's All This Critical Thinking Stuff AnyhowДокумент3 страницыWhat's All This Critical Thinking Stuff AnyhowadauОценок пока нет
- Past Continuous: Types of Verbs Active/Passive Simple Present Present Continuous Simple Past Past ContinuousДокумент4 страницыPast Continuous: Types of Verbs Active/Passive Simple Present Present Continuous Simple Past Past ContinuousadauОценок пока нет
- Deriving An EquationДокумент2 страницыDeriving An EquationadauОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0360544221032576 MainДокумент14 страниц1 s2.0 S0360544221032576 Mainmd yousupОценок пока нет
- DC9-12 12V 9.5ah: Sealed Lead Acid AGM BatteryДокумент2 страницыDC9-12 12V 9.5ah: Sealed Lead Acid AGM BatteryAhmed TitawiОценок пока нет
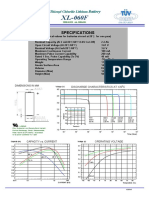
- Xeno Energy XL-060F Spec SheetДокумент1 страницаXeno Energy XL-060F Spec SheetRadiation Monitoring RadonОценок пока нет
- Automatic Battery ChargerДокумент39 страницAutomatic Battery ChargerCiprian CorneaОценок пока нет
- Katalog Produk - Panel Surya Jakarta, Panel Surya Murah, Panel Surya, Harga Panel Surya, Panel Tenaga Surya, Harga Tenaga Surya, Jual Panel SuryaДокумент16 страницKatalog Produk - Panel Surya Jakarta, Panel Surya Murah, Panel Surya, Harga Panel Surya, Panel Tenaga Surya, Harga Tenaga Surya, Jual Panel SuryabennyОценок пока нет
- Plastics TodayДокумент68 страницPlastics Todaying_marinОценок пока нет
- Nife FlyerДокумент2 страницыNife FlyerElnegro NegroОценок пока нет
- Energy Storage Technologies and ApplicationsДокумент328 страницEnergy Storage Technologies and ApplicationsAnchana Kittitanesuan100% (6)
- Catalogue Piece CouranteДокумент112 страницCatalogue Piece Courantejuliendrevet56Оценок пока нет
- DNK Power Battery Design EbookДокумент14 страницDNK Power Battery Design EbookFaisalОценок пока нет
- Circuitos para Fuentes y para Cargadores de Baterias 1-5Документ7 страницCircuitos para Fuentes y para Cargadores de Baterias 1-5EstuardoОценок пока нет
- Adl Future of Batteries-MinДокумент24 страницыAdl Future of Batteries-MinsrinathОценок пока нет
- Fuel Cell Electric VehiclesДокумент31 страницаFuel Cell Electric VehiclesKhalil RazaОценок пока нет
- Optimal Sizing of Photovoltaic Systems Based Green Hydrogen Refueling Stations Case Study OmanДокумент10 страницOptimal Sizing of Photovoltaic Systems Based Green Hydrogen Refueling Stations Case Study OmanElcy SernaОценок пока нет
- GTZ - Lead-Acid Battery RecyclingДокумент10 страницGTZ - Lead-Acid Battery RecyclingViju K G100% (1)
- ElectricityToday - Jul 27 2023Документ8 страницElectricityToday - Jul 27 2023jonazakОценок пока нет
- Owner'S Manual: Model 8$ Multi-Use Smart Battery ChargerДокумент40 страницOwner'S Manual: Model 8$ Multi-Use Smart Battery ChargerJavier VillelaОценок пока нет
- Batteries Introduction PDFДокумент30 страницBatteries Introduction PDFarthur dena-enОценок пока нет
- 4parallel Plate CapacitorДокумент1 страница4parallel Plate CapacitorDe Raghu Veer KОценок пока нет
- User'S Manual: June 2006 T.O. #33D7-22-32-1Документ194 страницыUser'S Manual: June 2006 T.O. #33D7-22-32-1Pierpaolo AparoОценок пока нет
- Types of CapacitorДокумент18 страницTypes of Capacitorsushil4056Оценок пока нет
- Litio No Recargable TL-5934Документ2 страницыLitio No Recargable TL-5934Enrique Juan CasadioОценок пока нет
- Vacuum PerliteДокумент8 страницVacuum PerlitePhilippe GhyselОценок пока нет
- Characteristics: Compact Size Ideal For Any Type of UseДокумент3 страницыCharacteristics: Compact Size Ideal For Any Type of UseVanegas YennyОценок пока нет
- Future Power Distribution Grids: Integration of Renewable Energy, Energy Storage, Electric Vehicles, Superconductor, and Magnetic BusДокумент5 страницFuture Power Distribution Grids: Integration of Renewable Energy, Energy Storage, Electric Vehicles, Superconductor, and Magnetic BusarjungangadharОценок пока нет
- Sealed Lead-Acid Battery: SpecificationДокумент2 страницыSealed Lead-Acid Battery: Specificationapi-170472102Оценок пока нет
- Low-Voltage Hydrogen Peroxide Electrolyzer For Highly Efficient - Power-To-Hydrogen ConversionДокумент8 страницLow-Voltage Hydrogen Peroxide Electrolyzer For Highly Efficient - Power-To-Hydrogen ConversionShangli HuangОценок пока нет
- Scheduling and Sizing of Campus Microgrid ConsiderДокумент24 страницыScheduling and Sizing of Campus Microgrid ConsiderKashif RehmanОценок пока нет
- Valuing-Resilience PV GridДокумент5 страницValuing-Resilience PV GridLe'Novo FernandezОценок пока нет
- Smart - Grid Assignment 1Документ9 страницSmart - Grid Assignment 1Tanzil MahmoodОценок пока нет