Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Vomiting Agent Adamsite
Загружено:
Lance McClureАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Vomiting Agent Adamsite
Загружено:
Lance McClureАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
U.S.
Army Center for Health Promotion and Preventive Medicine
AC HD CN GA
BZ PS CG
Detailed Facts About Vomiting Agent Adamsite (DM)
218-17-1096
Physical Properties of Adamsite
Cl Chemical Structure As N H Chemical Formula Description C12 Hg As ClN Light green to yellow crystals at room temperature; irritates nasal passages similar to pepper; no odor, but irritating. 277.54 410 C Forms no appreciable vapor. 195 C Solid = 1.65 @ 20 C Vapor = negligible Soluble in furfural and acetone; slightly soluble in common organic solvents; insoluble in water. Not readily soluble in any of the liquid chemical warfare agents. Does not flash.
Molecular Weight Boiling Point Vapor Pressure (mm Hg) Freezing Point Density
Solubility
Flash Point
Agent DM - The chemical diphenylaminochloroarsine, Chemical Abstract Service registry No. 578-94-9.
Volatility
19,300 mg/m3 @ 0 C 26,000 to 120,000 mg/m3 @ 20 C 72,500 to 143,000 mg/m3 @ 25 C Ict50 Lct50 = 22 to 150 mg-min/m3 = variable, average 11,000 mg-min/m3 NOAEL (inhalation) = 4 mg-min/m3
Toxicity Values
Airborne Exposure Limit (AEL) Workplace Time-Weighted Average General Population Limits No standard identified No standard identified
Toxic Properties of Adamsite
DM was first produced during World War I. Adamsite was not toxic enough for the battlefield, but it proved to be too drastic for use against civilian mobs; it was banned for use against civilian populations in the 1930s in the Western nations. DM was produced worldwide until superseded by the CN series of tear agents. Overexposure Effects DM is a vomiting compound. It is normally a solid, but upon heating, DM first vaporizes and then condenses to form aerosols. It is toxic through inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact. Adamsite is dispersed as an aerosol, irritating to the eyes and respiratory tract but not necessarily to the skin. Under field conditions, vomiting agents can cause great discomfort to the victims; when released indoors, they can cause serious illness or death. Symptoms include irritation of eyes and mucous membranes, coughing, sneezing, severe headache, acute pain and tightness in the chest, nausea, and vomiting. DM has been noted to cause necrosis of corneal epithelium in humans. The human body will detoxify the effects of mild exposures within 30 minutes of evacuation. Severe exposures may take several hours to detoxify and minor sensory disturbances may persist for up to one day. Emergency and First Aid Procedures Inhalation: remove victim to fresh air; wear a mask/respirator in spite of coughing, sneezing, salivation, and nausea; lift the mask from the face briefly, if necessary, to permit vomiting or to drain saliva from the facepiece; seek medical attention immediately. Eye Contact: don a respiratory protective mask; seek medical attention immediately. Skin Contact: rinse the nose and throat with saline water or bicarbonate of soda solution; wash exposed skin and scalp with soap and water and allow to dry on the skin; dust the skin with borated talcum.
Ingestion: seek medical attention immediately; carry on duties as vigorously as possible; this will help to lessen and shorten the symptoms; combat duties usually can be performed in spite of the effects of sternutators. Protective Equipment Protective Gloves: Eye Protection: Wear Chemical Protective Glove Set. Wear chemical goggles; wear a mask/respirator in open areas. Wear additional protective clothing, such as gloves and lab coat with an M9, M17, or M40 mask readily available in closed or confined spaces.
Other:
Reactivity Data Stability: Stable in pure form; after 3 months, caused extensive corrosion of aluminum, anodized aluminum, and stainless steel; will corrode iron, bronze, and brass when moist. Acidic (pH) - 0.5 percent; prevents hydrolysis at room temperature; 9.8 percent HCl; prevents hydrolysis @ 70 C. Basic (pH) - slowly hydrolyzes in water. [NH(C6H4)2AS]2O & HCl. Titanium - 71 C, 6 months, appeared good. Stainless Steel - 43 C, 30 days, slight discoloration. Common Steel - 43 C, 30 days, covered with rust. Aluminum Anodized - 43 C, 30 days, minor corrosion and pitting. Aluminum - 43 C, 30 days, severe corrosion. Short, because compounds are disseminated as an aerosol. Soil - persistent Surface (wood, metal, masonry, rubber, paint) - persistent. Water - persistent; when material is covered with water, an insoluble film forms which prevents further hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis Rate:
Hydrolysis Products: Corrosive Properties:
Persistency
References 1. Department of the Army Field Manual (DA FM) 3-9, Potential Military Chemical/Biological Agents and Compounds, 1990. 2. Department of the Army Technical Manual (DA TM) 3-250, Storage, Shipment, Handling, and Disposal of Chemical Agents and Hazardous Chemicals, 1969.
3. The Merck Index, An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, Eleventh Edition, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, New Jersey, 1989. 4. Somani, Satu M., Chemical Warfare Agents, Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, California, 1992. 5. U.S. Army Chemical Command Materiel Destruction Agency, Site Monitoring Concept Study, 15 September 1993.
For more information, contact: Kenneth E. Williams USACHPPM Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD 21010-5422 Commercial (410) 671-2208, DSN: 584-2208 email: kwilliam@aeha1.apgea.army.mil
Вам также может понравиться
- Blister Agent Phosgene OximeДокумент3 страницыBlister Agent Phosgene OximeLance McClureОценок пока нет
- Blood Agent CyanogenДокумент5 страницBlood Agent CyanogenLance McClureОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data SheetДокумент7 страницMaterial Safety Data SheetCatalin SevastianОценок пока нет
- MSDS Sodium Hypochlorite CoatzaДокумент3 страницыMSDS Sodium Hypochlorite CoatzaDefenceDogОценок пока нет
- 19 2B4 - Safety Data Sheet For Coshh AssessmentДокумент6 страниц19 2B4 - Safety Data Sheet For Coshh AssessmentRauf HaciyevОценок пока нет
- The Science Company® Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company IdentificationДокумент4 страницыThe Science Company® Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company IdentificationjeriОценок пока нет
- Mercury: 1. Product IdentificationДокумент4 страницыMercury: 1. Product IdentificationchapulincoloradoОценок пока нет
- Sodium Hydroxide MSDSДокумент7 страницSodium Hydroxide MSDSMuhammad Rizki Ash-ShidiqОценок пока нет
- LD50 Cr3+Документ7 страницLD50 Cr3+mukhsalОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Restore Alkaline Cleaner - Heavy DutyДокумент8 страницMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Restore Alkaline Cleaner - Heavy DutyCastro RicardoОценок пока нет
- Weld-On 3 MsdsДокумент2 страницыWeld-On 3 MsdsSergio SanchezОценок пока нет
- MSDS, Chromium Trioxide CrystalsДокумент9 страницMSDS, Chromium Trioxide CrystalsNikesh ShahОценок пока нет
- P B Msds HydroxideДокумент5 страницP B Msds HydroxideJulioОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationДокумент8 страницSafety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationRafi UdeenОценок пока нет
- Carbon RemoverДокумент6 страницCarbon RemoverdimasfebriantoОценок пока нет
- MSDS DimethylglyoximeДокумент6 страницMSDS DimethylglyoximeMia BarzagaОценок пока нет
- Sethard S100 - 0Документ5 страницSethard S100 - 0bsmaan3Оценок пока нет
- Methylene Chloride: Safety Data SheetДокумент5 страницMethylene Chloride: Safety Data SheetAnuj Kumar Mishra100% (1)
- Nax Eco 2K Metal Filler - MSDSДокумент6 страницNax Eco 2K Metal Filler - MSDSjanakaОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationДокумент6 страницMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationOnnFuiSiongОценок пока нет
- SludgeДокумент6 страницSludgefahmiОценок пока нет
- 210 PDFДокумент6 страниц210 PDFAlejandro VescovoОценок пока нет
- HealthAndSafetySheet 1Документ5 страницHealthAndSafetySheet 1Bello-Ososo JeremiahОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet ALUMON 5825 (QA) : 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyДокумент7 страницSafety Data Sheet ALUMON 5825 (QA) : 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyUtilities2Оценок пока нет
- 0076 Fi41c5kubДокумент5 страниц0076 Fi41c5kubNandar Min HtetОценок пока нет
- SulfuricacidДокумент9 страницSulfuricacidqavictoriacareОценок пока нет
- H2so4 MSDSДокумент6 страницH2so4 MSDSMuhammad Aasim HassanОценок пока нет
- MSDS - Hydrochloric Acid 32-35%Документ5 страницMSDS - Hydrochloric Acid 32-35%sandip pundeОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet Ultrasil 75: Page 1 of 5 S001: HNO3Документ5 страницSafety Data Sheet Ultrasil 75: Page 1 of 5 S001: HNO3nasser kamakenОценок пока нет
- Caustic Soda Data SheetДокумент5 страницCaustic Soda Data SheetKudakwashe Walter MakoniОценок пока нет
- msdsa-cpd-SikaSil 728 RCS-usДокумент5 страницmsdsa-cpd-SikaSil 728 RCS-usCARMEN LINARESОценок пока нет
- Refrigerant R 22Документ6 страницRefrigerant R 22Anca ParaschivОценок пока нет
- MSDS RO1 enДокумент5 страницMSDS RO1 enTito Prastyo RОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet: Masterflow 648 Part B Also Masterflow 648Cp Plus GRT PTBДокумент7 страницSafety Data Sheet: Masterflow 648 Part B Also Masterflow 648Cp Plus GRT PTBAlves EdattukaranОценок пока нет
- MSDS MC Methylene ChlorideДокумент6 страницMSDS MC Methylene ChloridecoanacagmОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet According To (EC) No 1907/2006 - ISO 11014-1Документ6 страницSafety Data Sheet According To (EC) No 1907/2006 - ISO 11014-1Ahmed Emad AhmedОценок пока нет
- MSDS MercuriДокумент4 страницыMSDS MercuriSiti RojanahОценок пока нет
- Evfuel Mccabe Gasoline Level Indicator Paste MsdsДокумент9 страницEvfuel Mccabe Gasoline Level Indicator Paste Msdsapi-525617690Оценок пока нет
- MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET 16-101 3M General Purpose Contact CleanerДокумент9 страницMATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET 16-101 3M General Purpose Contact CleanerCarlos Gabriel Quintero RodríguezОценок пока нет
- Australian Builders Ground SlagДокумент5 страницAustralian Builders Ground SlagDirga Delonix RegiaОценок пока нет
- 4907 Avkbc5kubДокумент5 страниц4907 Avkbc5kubNandar Min HtetОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Carbon Remover SPДокумент6 страницMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Carbon Remover SPJezrell JaravataОценок пока нет
- MSDS HCLДокумент8 страницMSDS HCLdaniОценок пока нет
- 6 Unitor Metal Brite HDДокумент4 страницы6 Unitor Metal Brite HDreujiОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet Colron Refined Danish Oil: 1 Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingДокумент5 страницSafety Data Sheet Colron Refined Danish Oil: 1 Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingteehoweОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Chloride 0163: April 2000Документ2 страницыHydrogen Chloride 0163: April 2000vivekpattniОценок пока нет
- RP 6302Документ5 страницRP 6302AmenОценок пока нет
- 0089 Ei6uc5kubДокумент5 страниц0089 Ei6uc5kubNandar Min HtetОценок пока нет
- Aluminum StearateДокумент6 страницAluminum Stearatesajad gohariОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet Chromic Acid Section 1 - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationДокумент6 страницMaterial Safety Data Sheet Chromic Acid Section 1 - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationSurya Theja ReddyОценок пока нет
- Urethane 852851-17925-glДокумент7 страницUrethane 852851-17925-glElías VillegasОценок пока нет
- Ammonium Kloride (NH4Cl)Документ4 страницыAmmonium Kloride (NH4Cl)Fauzi Apriadi0% (1)
- Calcium Hydrooxide MistureДокумент5 страницCalcium Hydrooxide MistureDarius DsouzaОценок пока нет
- Dicumyl Peroxide 1346: October 1999Документ2 страницыDicumyl Peroxide 1346: October 1999Asima AtharОценок пока нет
- Sulph Acid (MSDS) PDFДокумент4 страницыSulph Acid (MSDS) PDFKhursheed AhmadОценок пока нет
- NAX Premila 2K Polyester Putty-MSDSДокумент6 страницNAX Premila 2K Polyester Putty-MSDSjanakaОценок пока нет
- Schlumberger MSDS M091Документ7 страницSchlumberger MSDS M091sajad gohariОценок пока нет
- Msds - Limpia Contacto 3m 16-101Документ8 страницMsds - Limpia Contacto 3m 16-101Ruth E. Pisco VillavicencioОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen peroxide uses for the body: 31 5 Minute Remedies! Discover Uses for Hydrogen Peroxide including Mouthwash & Bad Breath, Teeth Whitening, Acne, Ear Wax, Hair, Allergy & Nasal Spray and MOREОт EverandHydrogen peroxide uses for the body: 31 5 Minute Remedies! Discover Uses for Hydrogen Peroxide including Mouthwash & Bad Breath, Teeth Whitening, Acne, Ear Wax, Hair, Allergy & Nasal Spray and MOREРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Sulfur Mustard Agents H and HDДокумент4 страницыSulfur Mustard Agents H and HDLance McClureОценок пока нет
- Sulfur Mustard Agent HTДокумент3 страницыSulfur Mustard Agent HTLance McClureОценок пока нет
- Nerve Agent VXДокумент4 страницыNerve Agent VXLance McClureОценок пока нет
- Nerve Agent GDДокумент5 страницNerve Agent GDLance McClureОценок пока нет
- Nerve Agent GBДокумент4 страницыNerve Agent GBLance McClureОценок пока нет
- Choking Agent PhosgeneДокумент4 страницыChoking Agent PhosgeneLance McClureОценок пока нет
- Nerve Agent GAДокумент5 страницNerve Agent GALance McClureОценок пока нет
- Proceeding of Rasce 2015Документ245 страницProceeding of Rasce 2015Alex ChristopherОценок пока нет
- DarcДокумент9 страницDarcJunior BermudezОценок пока нет
- HirePro Video Proctored Online-Instruction Sheet - Bain IndiaДокумент1 страницаHirePro Video Proctored Online-Instruction Sheet - Bain Indiaapoorv sharmaОценок пока нет
- CH 1 - Democracy and American PoliticsДокумент9 страницCH 1 - Democracy and American PoliticsAndrew Philip ClarkОценок пока нет
- Impact of Advertising On Consumers' Buying Behavior Through Persuasiveness, Brand Image, and Celebrity EndorsementДокумент10 страницImpact of Advertising On Consumers' Buying Behavior Through Persuasiveness, Brand Image, and Celebrity Endorsementvikram singhОценок пока нет
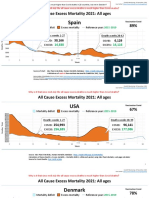
- Countries EXCESS DEATHS All Ages - 15nov2021Документ21 страницаCountries EXCESS DEATHS All Ages - 15nov2021robaksОценок пока нет
- Regions of Alaska PresentationДокумент15 страницRegions of Alaska Presentationapi-260890532Оценок пока нет
- Electives - ArchitДокумент36 страницElectives - Architkshitiz singhОценок пока нет
- Pavement Design1Документ57 страницPavement Design1Mobin AhmadОценок пока нет
- Existential ThreatsДокумент6 страницExistential Threatslolab_4Оценок пока нет
- User Manual For Speed Control of BLDC Motor Using DspicДокумент12 страницUser Manual For Speed Control of BLDC Motor Using DspicTrung TrựcОценок пока нет
- E Flight Journal Aero Special 2018 Small PDFДокумент44 страницыE Flight Journal Aero Special 2018 Small PDFMalburg100% (1)
- Carriage RequirementsДокумент63 страницыCarriage RequirementsFred GrosfilerОценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент15 страницChronic Kidney Diseaseapi-270623039Оценок пока нет
- Science7 - q1 - Mod3 - Distinguishing Mixtures From Substances - v5Документ25 страницScience7 - q1 - Mod3 - Distinguishing Mixtures From Substances - v5Bella BalendresОценок пока нет
- Azimuth Steueung - EngДокумент13 страницAzimuth Steueung - EnglacothОценок пока нет
- Revenue and Expenditure AuditДокумент38 страницRevenue and Expenditure AuditPavitra MohanОценок пока нет
- Recommendations For Students With High Functioning AutismДокумент7 страницRecommendations For Students With High Functioning AutismLucia SaizОценок пока нет
- IKEA SHANGHAI Case StudyДокумент5 страницIKEA SHANGHAI Case StudyXimo NetteОценок пока нет
- Organization and Management Module 3: Quarter 1 - Week 3Документ15 страницOrganization and Management Module 3: Quarter 1 - Week 3juvelyn luegoОценок пока нет
- Harper Independent Distributor Tri FoldДокумент2 страницыHarper Independent Distributor Tri FoldYipper ShnipperОценок пока нет
- Plaza 66 Tower 2 Structural Design ChallengesДокумент13 страницPlaza 66 Tower 2 Structural Design ChallengessrvshОценок пока нет
- The Homework Song FunnyДокумент5 страницThe Homework Song Funnyers57e8s100% (1)
- DPSD ProjectДокумент30 страницDPSD ProjectSri NidhiОценок пока нет
- PR KehumasanДокумент14 страницPR KehumasanImamОценок пока нет
- Duavent Drug Study - CunadoДокумент3 страницыDuavent Drug Study - CunadoLexa Moreene Cu�adoОценок пока нет
- Spesifikasi PM710Документ73 страницыSpesifikasi PM710Phan'iphan'Оценок пока нет
- Organizational ConflictДокумент22 страницыOrganizational ConflictTannya AlexandraОценок пока нет
- Dynamics of Machinery PDFДокумент18 страницDynamics of Machinery PDFThomas VictorОценок пока нет
- 70 Valves SolenoidДокумент105 страниц70 Valves SolenoidrizalОценок пока нет