Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
What I Need To Know About Hirschsprung Disease 1
Загружено:
David Sek Wai YeИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
What I Need To Know About Hirschsprung Disease 1
Загружено:
David Sek Wai YeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
What I need to know about Hirschsprung Disease
What is Hirschsprung disease (HD)?
Hirschsprung* disease (HD) is a disease of the large intestine that causes severe constipation or intestinal obstruction. Constipation means stool moves through the intestines slower than usual. Bowel movements occur less often than normal and stools are difficult to pass. Some children with HD cant pass stool at all, which can result in the complete blockage of the intestines, a condition called intestinal obstruction. People with HD are born with it and are usually diagnosed when they are infants. Less severe cases are sometimes diagnosed when a child is older. An HD diagnosis in an adult is rare. *See Pronounciation Guide for tips on how to say the words in bold type.
HD is a disease of the large intestine that causes severe constipation or intestinal obstruction.
[Top] What are the large intestine, colon, rectum, and anus?
The large intestine, which includes the colon and rectum, is the last part of the digestive tract. The large intestines main job is to absorb water and hold stool. The rectum connects the colon to the anus. Stool passes out of the body through the anus. At birth, the large intestine is about 2 feet long. An adults large intestine is about 5 feet long.
[Top] Why does HD cause constipation?
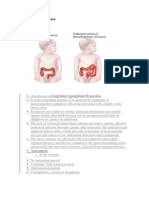
People with HD have constipation because they lack nerve cells in a part or all of the large intestine. The nerve cells signal muscles in the large intestine to push stool toward the anus. Without a signal to push stool along, stool will remain in the large intestine.
Healthy large intestine. Nerve Short-segment HD. Nerve cells Long-segment HD. Nerve cells cells are found throughout the are missing from the last are missing from most or all of large intestine. segment of the large intestine. the large intestine and sometimes the last part of the small intestine.
How severe HD is depends on how much of the large intestine is affected. Short-segment HD means only the last part of the large intestine lacks nerve cells. Long-segment HD means most or all of the large intestine, and sometimes the last part of the small intestine, lacks nerve cells. In a person with HD, stool moves through the large intestine until it reaches the part lacking nerve cells. At that point, the stool moves slowly or stops, causing an intestinal obstruction.
[Top] What causes HD?
Before birth, a childs nerve cells normally grow along the intestines in the direction of the anus. With HD, the nerve cells stop growing too soon. Why the nerve cells stop growing is unclear. Some HD is inherited, meaning it is passed from parent to child through genes. HD is not caused by anything a mother did while pregnant.
[Top]
What are the symptoms of HD?
The main symptoms of HD are constipation or intestinal obstruction, usually appearing shortly after birth. Constipation in infants and children is common and usually comes and goes, but if your child has had ongoing constipation since birth, HD may be the problem.
Symptoms in Newborns
Newborns with HD almost always fail to have their first bowel movement within 48 hours after birth. Other symptoms include
green or brown vomit explosive stools after a doctor inserts a finger into the rectum swelling of the belly, also known as the abdomen lots of gas bloody diarrhea
Symptoms in Symptoms in Toddlers and Older Children
Symptoms of HD in toddlers and older children include
not being able to pass stools without laxatives or enemas. A laxative is medicine that loosens stool and increases bowel movements. An enema is performed by flushing water, or sometimes a mild soap solution, into the anus using a special wash bottle. swelling of the abdomen. lots of gas. bloody diarrhea. slow growth or development. lack of energy because of a shortage of red blood cells, called anemia.
People with anemia tire easily because of a shortage of red blood cells.
Вам также может понравиться
- Poultry Diseases and Their TreatmentДокумент159 страницPoultry Diseases and Their TreatmentAbubakar Tahir Ramay67% (12)
- Usmle SuperДокумент239 страницUsmle SupermaksventileОценок пока нет
- Hiatal Hernia Syndrome: A Beginner's 3-Step Plan to Managing Hiatal Hernia Syndrome Through Diet, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanОт EverandHiatal Hernia Syndrome: A Beginner's 3-Step Plan to Managing Hiatal Hernia Syndrome Through Diet, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanОценок пока нет
- (Encyclopedia of Pathology) Pieter J. Slootweg (Eds.) - Dental and Oral Pathology-Springer International Publishing (2016)Документ372 страницы(Encyclopedia of Pathology) Pieter J. Slootweg (Eds.) - Dental and Oral Pathology-Springer International Publishing (2016)Maria Mery Garcia VelascoОценок пока нет
- Rab Flow CHT 3 PeopleДокумент2 страницыRab Flow CHT 3 PeopleWDIV/ClickOnDetroitОценок пока нет
- Camp NotesДокумент17 страницCamp NotesTeOmbre GarciaОценок пока нет
- The Clinical Laboratory and Its LawsДокумент1 страницаThe Clinical Laboratory and Its LawsAldren BeliberОценок пока нет
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALДокумент16 страницPractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses CentralОценок пока нет
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Fecal ImpactionДокумент5 страницFecal Impactioncharie2Оценок пока нет
- Patient Information: Acid Reflux (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) in Adults (Beyond The Basics)Документ10 страницPatient Information: Acid Reflux (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) in Adults (Beyond The Basics)wandaОценок пока нет
- GerdДокумент9 страницGerdPriyaОценок пока нет
- Dyspepsia BrochureДокумент5 страницDyspepsia BrochureJns RamОценок пока нет
- Bowel TrainingДокумент2 страницыBowel Trainingdickie.gdrОценок пока нет
- Bipolar 1 DisorderДокумент11 страницBipolar 1 DisorderGirlly AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- IMCIДокумент3 страницыIMCIwordlife360Оценок пока нет
- Tugas Bu IllonaДокумент16 страницTugas Bu IllonaIntania PoetrieОценок пока нет
- What Is Hirschsprung DiseaseДокумент19 страницWhat Is Hirschsprung DiseaseSintong SianturiОценок пока нет
- What Is Hirschsprung Disease?Документ8 страницWhat Is Hirschsprung Disease?kristel_ticarОценок пока нет
- HirschДокумент24 страницыHirschKimBummies KakaBieber YukersImhotepОценок пока нет
- Case Report Hirschsprung's DseДокумент10 страницCase Report Hirschsprung's DseJane Pineda CuraОценок пока нет
- Hirschsprungs Disease: What Is Hirschsprung's Disease?Документ9 страницHirschsprungs Disease: What Is Hirschsprung's Disease?Karina Jane Farnacio PuruggananОценок пока нет
- HirschzxcxzcДокумент2 страницыHirschzxcxzcZNEROLОценок пока нет
- Aquinas University of Legazpi College of Nursing and Health SciencesДокумент7 страницAquinas University of Legazpi College of Nursing and Health SciencesMaRVОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal Problems in Children With Down's Syndrome: by DR Liz MarderДокумент5 страницGastrointestinal Problems in Children With Down's Syndrome: by DR Liz MarderNur Haziq HasОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент8 страницDigestive SystemJonas Tristan Del MundoОценок пока нет
- Anaphy ActivityДокумент13 страницAnaphy ActivityJonas Tristan Del MundoОценок пока нет
- What Is HirschsprungДокумент4 страницыWhat Is HirschsprungMicah SaberОценок пока нет
- Heartburn, Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER), and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)Документ8 страницHeartburn, Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER), and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)Aya SorayaОценок пока нет
- HirschsprungДокумент4 страницыHirschsprungMrmonstrosityОценок пока нет
- Idiopathic Constipation Parent EduДокумент7 страницIdiopathic Constipation Parent EduEl Mono Cardona VeraОценок пока нет
- GerdДокумент8 страницGerdarinrinОценок пока нет
- Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsДокумент20 страницGastroesophageal Reflux in Children and AdolescentsruthmindosiahaanОценок пока нет
- What Causes Reflux in Babies and ChildrenДокумент3 страницыWhat Causes Reflux in Babies and ChildrenWahyunita IlhamОценок пока нет
- HirschsprungdiseaseДокумент2 страницыHirschsprungdiseaseZarme De GuiaОценок пока нет
- What Is Dysphagia - Tactus TherapyДокумент3 страницыWhat Is Dysphagia - Tactus TherapyTaylor MayОценок пока нет
- Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) in InfantsДокумент8 страницGastroesophageal Reflux (GER) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) in Infantstj_sweetgirlОценок пока нет
- Hirschsprung's Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)Документ3 страницыHirschsprung's Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)JOANMA_NEWОценок пока нет
- Hemorrhoids and IBS OSCE NotesДокумент4 страницыHemorrhoids and IBS OSCE Notes️Abdullah jaafarОценок пока нет
- Diarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013Документ9 страницDiarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013emmi_valentinaОценок пока нет
- CHWguidelines DiarrheaДокумент25 страницCHWguidelines DiarrheaYurika SastyarinaОценок пока нет
- Pyloric StenosisДокумент8 страницPyloric StenosisRej PanganibanОценок пока нет
- DIARRHEAДокумент39 страницDIARRHEAJessa RedondoОценок пока нет
- ConstipationДокумент7 страницConstipationaldriansilverОценок пока нет
- Kidney Works: Can Kidney Disease Cured?Документ4 страницыKidney Works: Can Kidney Disease Cured?Jacinto Adolph Agustin CagorolОценок пока нет
- Dysphagia: NIDCD Fact Sheet - Voice, Speech, and LanguageДокумент4 страницыDysphagia: NIDCD Fact Sheet - Voice, Speech, and LanguageLouguward MiraiОценок пока нет
- Nursing SurgicalДокумент27 страницNursing SurgicalShubhra PaulОценок пока нет
- Hiatal HerniaДокумент9 страницHiatal HerniaAnnJenn AsideraОценок пока нет
- Understanding Constipation in People With Learning Difficulties For ReviewДокумент7 страницUnderstanding Constipation in People With Learning Difficulties For Reviewzulu alphaОценок пока нет
- Hirschsprung DiseaseДокумент14 страницHirschsprung DiseaseFlordelyn Anuales100% (2)
- The First Step in Treating Your Child Is Forming An Accurate and Complete DiagnosisДокумент3 страницыThe First Step in Treating Your Child Is Forming An Accurate and Complete DiagnosisDimpuulina Erna Mariati SihombingОценок пока нет
- 3 Clinical Types of Diarrhea: (Define) Pakidagdagan HeheДокумент4 страницы3 Clinical Types of Diarrhea: (Define) Pakidagdagan Hehekristelaaa guevarraОценок пока нет
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseДокумент8 страницGastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseRicoSopoОценок пока нет
- Gerd PDFДокумент51 страницаGerd PDFmonir61Оценок пока нет
- Hiatal Hernia FactsheetДокумент6 страницHiatal Hernia FactsheetHoney Bee S. PlatolonОценок пока нет
- Acid Reflux Disease Symptoms, Causes, Tests, and TreatmentsДокумент1 страницаAcid Reflux Disease Symptoms, Causes, Tests, and TreatmentsJuliana AhmadОценок пока нет
- Caregiver Guide - Constipation ProblemsДокумент11 страницCaregiver Guide - Constipation ProblemsHayuta WatamotoОценок пока нет
- Hirsch SprungДокумент4 страницыHirsch SprungRy AnneОценок пока нет
- Constipation CouncellingДокумент2 страницыConstipation CouncellingsakariyeОценок пока нет
- English Gastroenteritis PDFДокумент2 страницыEnglish Gastroenteritis PDFkatyweymОценок пока нет
- Gastroenteritis (Gastro) : Signs and Symptoms of GastroДокумент2 страницыGastroenteritis (Gastro) : Signs and Symptoms of GastrokatyweymОценок пока нет
- NUrsing Care PreschoolerДокумент15 страницNUrsing Care PreschoolerShamie ColozaОценок пока нет
- Patient Information Leaflet - Constipation in AdultsДокумент36 страницPatient Information Leaflet - Constipation in AdultsJohnny JunksterОценок пока нет
- A B C D E: Answer: D (Small Intestine)Документ14 страницA B C D E: Answer: D (Small Intestine)misschenОценок пока нет
- Illness Symptoms Reasons Solutions Homemade Solutions Ways To Avoid Such Health IssuesДокумент9 страницIllness Symptoms Reasons Solutions Homemade Solutions Ways To Avoid Such Health IssuessunilviniОценок пока нет
- Dygestive DyspepsiaДокумент7 страницDygestive DyspepsiaChatrina TandiloloОценок пока нет
- Gastroesophageal Reflux What Is Gastroesophageal Reflux?Документ18 страницGastroesophageal Reflux What Is Gastroesophageal Reflux?Zed P. EstalillaОценок пока нет
- Food Is Figureoutable: AN ESSENTIAL GUIDE TO BODY SYSTEMSОт EverandFood Is Figureoutable: AN ESSENTIAL GUIDE TO BODY SYSTEMSОценок пока нет
- How To Make Black TeaДокумент2 страницыHow To Make Black TeaDavid Sek Wai Ye100% (1)
- Rose Petal TeaДокумент1 страницаRose Petal TeaDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- How To Make Kimchi Part 2Документ2 страницыHow To Make Kimchi Part 2David Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- How To Make Teh TarikДокумент1 страницаHow To Make Teh TarikDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Muslim Indonesian Eid-ul-Fitr Eid-ul-Adha Orang Asli NegritoДокумент1 страницаMuslim Indonesian Eid-ul-Fitr Eid-ul-Adha Orang Asli NegritoDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Indonesia Minangkabau Iban Borneo Minahasans TapaiДокумент1 страницаIndonesia Minangkabau Iban Borneo Minahasans TapaiDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Lemang Is A TraditionalДокумент1 страницаLemang Is A TraditionalDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Indonesian Prawn and Vegetable CurryДокумент2 страницыIndonesian Prawn and Vegetable CurryDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Malaysian Style Vegetable CurryДокумент2 страницыMalaysian Style Vegetable CurryDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Malaysian-Style Mixed Vegetable CurryДокумент2 страницыMalaysian-Style Mixed Vegetable CurryDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Origin Distribution ModalityДокумент15 страницOrigin Distribution ModalityDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Singaporean Tender Pork Spare RibsДокумент2 страницыSingaporean Tender Pork Spare RibsDavid Sek Wai YeОценок пока нет
- Lab ManualДокумент4 страницыLab ManualSagar AryalОценок пока нет
- Nbns2203 Renal and Endocrine NursingДокумент10 страницNbns2203 Renal and Endocrine Nursingdicky chongОценок пока нет
- Conference & Workshop ScheduleДокумент5 страницConference & Workshop ScheduleglmoningkaОценок пока нет
- UPDS Telehealth Data ReportДокумент3 страницыUPDS Telehealth Data ReportCorey LarkinsОценок пока нет
- ZolfinДокумент3 страницыZolfinKhaled HasanОценок пока нет
- External Stressors: - Physical Environment - Social Interaction - Organisational - Major Life Events - Daily HasslesДокумент71 страницаExternal Stressors: - Physical Environment - Social Interaction - Organisational - Major Life Events - Daily HasslesSara NaeemОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Manajemen Apotek PDFДокумент11 страницJurnal Manajemen Apotek PDFAlexSiNagaОценок пока нет
- Case 4Документ5 страницCase 4angelica dizonОценок пока нет
- BESOKKKДокумент5 страницBESOKKKpt. maha rendra utamaОценок пока нет
- What Are The Reasons For Your Course ChoiceДокумент2 страницыWhat Are The Reasons For Your Course Choiceasaad biqaiОценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент3 страницыProjectAnshul PaunikarОценок пока нет
- Use of "Zingiber Officinale Roscoe L" Root in Various DiseasesДокумент8 страницUse of "Zingiber Officinale Roscoe L" Root in Various DiseasesCentral Asian StudiesОценок пока нет
- State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy Reaches SettlementДокумент3 страницыState of Ohio Board of Pharmacy Reaches SettlementLydia TaylorОценок пока нет
- A Slice O F: MMR EditionДокумент20 страницA Slice O F: MMR EditionTomTomОценок пока нет
- Anatomy & Physiology - Chapter 19: BLOOD Book Questions and AnswersДокумент6 страницAnatomy & Physiology - Chapter 19: BLOOD Book Questions and AnswersVanessa CarmodyОценок пока нет
- Tonetti Et Al-2018-Journal of Periodontology TДокумент14 страницTonetti Et Al-2018-Journal of Periodontology TJonathan Meza MauricioОценок пока нет
- Cover Letter Heidi BosmansДокумент1 страницаCover Letter Heidi Bosmansapi-283672381Оценок пока нет
- Case SheetДокумент23 страницыCase SheetMuhammad SdiqОценок пока нет
- SRH Case Study-GadДокумент7 страницSRH Case Study-Gadapi-721737872Оценок пока нет
- Prevention of Pin Site Infection in External FixatioДокумент11 страницPrevention of Pin Site Infection in External FixatioKim Gabrielle Exene LeeОценок пока нет
- Uporaba Metoda Palijativne Skrbi U Djece Implementation of Palliative Care Methods in ChildrenДокумент7 страницUporaba Metoda Palijativne Skrbi U Djece Implementation of Palliative Care Methods in ChildrenMoonyОценок пока нет