Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
An Ergonomic Mobile Phone Design by M Ghosh
Загружено:
mourighoshИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
An Ergonomic Mobile Phone Design by M Ghosh
Загружено:
mourighoshАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
An Ergonomic Mobile Phone Design by M Ghosh.
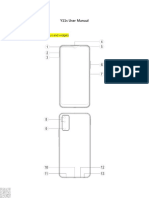
Diagram of an ergonomic mobile phone handset (for a right handed user), all pictures designed and painted by self using Microsoft PowerPoint 2007, WINDOWS 7 Ultimate.
Front View, Lid Closed Front View, Lid Open Fig 1 Fig 2
Back View, Lid Closed
Left side view, First lid open (detached to understand better), then closed. Fig 4
Right side view, lid open (detached to understand better) Fig 5
Fig 3
Legends: A - receiver holes, B port for charger, C soft key, D - Blind bump (standard), E curved body for better grip, F key pad (situated above the display screen), I Display screen, J concave body part for better fit of the thenar part , K curve to fit hypothenar, L speaker holes, M flipopen lid, G, H pressure clasp for the lid, N slight depressions for finger grips on the back, O camera, P USB port for data transfer, Q Port for headphone, R side switch for most used function (in this case volume, ringtone, vibration etc)
Page 1 of 4
A few Ergonomic benefits of the newly designed mobile phone.
Fig 6
Fig 7
Fig 8 The plane rectangular body shape of the old designs are upgraded to a palm fitting shape, making for a better grip in this design, yet thumb pain during texting cant be avoided in this.
Fig 9 This new ergonomic phone I designed for the assignment will solve both problems as it gives better grip while texting is no more painful. Plus the smaller size makes the grip easier.
Fig 10 The old designs called for gripping the mobile in such a way that it was cradled between the palm and neck for better hearing, resulting in neck pain.
Fig 11 The new design with receiver holes on the top of the phone and speaker holes on the lid allows the user to hold it straighter, and relieves neck pain.
With old designs such as these with keypad below display, we had to hold the phone like Fig 6with only the lower part of the phone lying on the palm making for a unstable grip as well as making it hard on the little and ring fingers, or we had to hold it like Fig 7, bending the thumb at an acute angle to type and thus making it hard on the thumb and the wrist and the flexor tendon and palmer fascia for the index and thumb.
Logic behind the improved design enlisted below Sr No Special Characterist ics Design of a mobile phone with the keypad positioned above the display screen. Fig. 1, 2, 4, 5, 9 Curved shape Logic behind the Special Characteristics to implement the ergonomic design The new design repositions the keypad above the screen and ensures that most of the handset rests in the palm of the hand for improved support and control. This design is more ergonomic for texting, The thumb rests in a comfortable position directly above the buttons of the keypad. The improved angle for the thumb makes it unnecessary to shift the mobile phone around in the hand while typing text. Not moving the thumb in an acute angle constantly while texting gives pain relief to the thenar muscles as well as the palmer fascia and flexor tendons attached to the index finger and thumb. The concave curvature of the lower part of the phone is to accommodate
Page 2 of 4
of the body of the phone giving it a top heavy dumbbell shaped look. Fig. 1 -3, 8, 9
the pillow of the thumb (thenar) better, as well as the hypothenar. This allows for improved grip as the phone rests comfortably in the hollow of the palm. While the convex upper part sits better on the spread fingers. The phone's gentle curve ensures a smooth and ergonomic user experience. The popular peanut shape of TV remotes etc has been tweaked for this ergonomically competent line of phone. The peanut shape is a time tested form factor that settles comfortably in both the left and right hand. More weight at the bottom provides good balance. This phone I have designed specifically for right handed persons such as myself by giving the thenar side more curve than the hypothenar. Two concave indentions on the underside of the phone will provide resting places for the fingers. Sliding the pointer and middle finger into one of these two grooves registers the thumb in one of three positions for engaging the three button groupings.
Sr No
Special Characteristics Finger grips on the back. Fig 3 Side switch for volume adjustment, on the thumb side. Fig. 3 Side ports for USB. Fig 4 Side ports for headphone and head phone. Fig 4 Flip open front lid with mouth piece and voice receiver holes on the key pad as well as the top of the phone Fig 1, 2
Logic behind the Special Characteristics to implement the ergonomic design For better grip, so that one can hold the phone casually without fear of it falling of. Keeping a death grip on the handset while talking or texting is often hard on the hand. Pressing the upper part will increase volume from mute, to vibrate to low volume high volume through gradations speaker on. Pressing the lower part will make it walk the opposite way. To transfer songs, video, picture etc. For headphone attachment. As the radiation is harmful, using headphone is always a safe bet. Ideal Headphone ear plug should be soft and comfortably fitting. A comfortable ear piece needs to have a good shape, be made of supple material and fit correctly. This is so that the user doesnt have to bend his or her neck while making a phone call, to cradle the phone for better reception of sound even without using a headset holding the phone in straight position gives relief from neck pain. The hearing is not obstructed due to the holes on the top of the phone for receiver. The flip open lid may be fitted with pressure clasp so that pressing the lid will flip it open, while it can be closed by the hand holding it pressing against the chin of the user. Standard for visually handicapped persons to navigate the keys
Blind bump on middle key Fig 1, 2, 4, 5
Page 3 of 4
Camera on back and charger insert point on top. Fig 3 Large flat display Fig 1 screen
Standard feature, placement implements best utility and serves functional purpose. Placement is such that it is not obstructed by fingers while holding the phone. Non reflective LED screen. Better suited to visual ergonomics. Color coded and oriented as standard, only placed on the top of the display screen for better access with the thumb; thus eliminating unnecessary motions that arent just repetitive theyre also wasteful and results in less fatigue at the end of the day. Two different button zones (color coded) to provide a hierarchy of button groupings for efficient locating and activation with the thumb. The First is the 12 alphanumeric keys on the upper portion, and the other is the rest of the keys mainly dealing with control function, makes for better hand eye co-ordination.S Feels better on the thumb pad and fingers. The metallic shine on many phones may look good but renders the phone slippery in sweating hand. The padded soft- rough texture of certain materials can make the grip easy and firm. Small size fitting the palm, makes it more comfortable to carry and less likely to lose. This is not a headset character but an ergonomic phone should have an ear piece that is loud and clear. The microphone will digitally enhance the sound and cancel noise, to transmit the talkers voice only.
10
11
Keypad. Fig 1, 2
12
Soft key. Fig 1, 2, 4, 5 Padded body cover of the mobile.
13
14
compact headset
15
Voice quality reception
and
Acknowledgement: Core 77 Design Magazine and Resource and PatentDesign.com
Page 4 of 4
Вам также может понравиться
- Project 2 Final Report - Egr 100Документ13 страницProject 2 Final Report - Egr 100api-542535294Оценок пока нет
- Phone Holder Design ReportДокумент9 страницPhone Holder Design Reportapi-512393144Оценок пока нет
- Phone Holder Project SpecificationДокумент18 страницPhone Holder Project SpecificationEricОценок пока нет
- Amc AgreementДокумент5 страницAmc AgreementSujit Dey75% (4)
- 1 Utkarsh: Technical Description On I-PhoneДокумент7 страниц1 Utkarsh: Technical Description On I-PhoneUtkarsh Hathi75% (4)
- The Best iPhone SE 2020 User Guide Ever: The Super Easy Ways to handle your iPhone SE 2020 UncoveredОт EverandThe Best iPhone SE 2020 User Guide Ever: The Super Easy Ways to handle your iPhone SE 2020 UncoveredОценок пока нет
- Sony dcrtrv103 ManualДокумент213 страницSony dcrtrv103 ManualAnonymous KWO434Оценок пока нет
- Smart Phones ErgonomicsДокумент12 страницSmart Phones ErgonomicsAnonymous F1eDbwN0t100% (1)
- ASUS Zenfone 2 ZE550ML ReviewДокумент30 страницASUS Zenfone 2 ZE550ML ReviewZenas EffervescenceОценок пока нет
- Individual Assignment 1Документ5 страницIndividual Assignment 1Aliff FaizОценок пока нет
- Mobile Phones Tablets TipsДокумент5 страницMobile Phones Tablets TipsAjay KumarОценок пока нет
- Mobile Phones & Tablets Tips: Accounting For TouchДокумент5 страницMobile Phones & Tablets Tips: Accounting For TouchAjay KumarОценок пока нет
- Manual Vivo Y11sДокумент17 страницManual Vivo Y11sa6Оценок пока нет
- Faq - Epure Cordless Analogue Telephone (Dect)Документ3 страницыFaq - Epure Cordless Analogue Telephone (Dect)Daiana VillegasОценок пока нет
- Heuristc Evaluation Blackberrycurve SoreganДокумент9 страницHeuristc Evaluation Blackberrycurve Soreganapi-23274026Оценок пока нет
- Example Product Design Spec - Phone HolderДокумент2 страницыExample Product Design Spec - Phone HolderConor PearsonОценок пока нет
- HCI AssignmentДокумент9 страницHCI AssignmentMuhammad Nauman AliОценок пока нет
- Instruction Manual: Model: K-EQ40Документ12 страницInstruction Manual: Model: K-EQ40Payphone.comОценок пока нет
- Tips & Tricks of 7610Документ5 страницTips & Tricks of 7610ali khan100% (7)
- Xiaomi Mi Bluetooth EarphoneДокумент8 страницXiaomi Mi Bluetooth EarphonehashashashasОценок пока нет
- Summary 2Документ7 страницSummary 2Christina TambunanОценок пока нет
- Btootos A90 Pro Wireless Bluetooth Earbuds 1Документ18 страницBtootos A90 Pro Wireless Bluetooth Earbuds 1Roberto Orbea SuarezОценок пока нет
- G5 User ManualOKcvcvcДокумент16 страницG5 User ManualOKcvcvcRohanPuthalathОценок пока нет
- Review of Samsung Xcover 271Документ59 страницReview of Samsung Xcover 271darkprince3Оценок пока нет
- Accessibility AssignmentДокумент6 страницAccessibility Assignmentapi-644833394Оценок пока нет
- Your HTC Radar: User GuideДокумент100 страницYour HTC Radar: User GuideMark RayneyОценок пока нет
- Bluetooth Wireless Sports In-Ear Headphones: How To Wear Fit VideoДокумент17 страницBluetooth Wireless Sports In-Ear Headphones: How To Wear Fit VideoBracho Mondragón CarlosОценок пока нет
- Tips & Tricks For SymbiansДокумент7 страницTips & Tricks For SymbiansAsif HussainОценок пока нет
- Doro HM13WДокумент23 страницыDoro HM13Wgd3000Оценок пока нет
- Omega InstructionsДокумент6 страницOmega InstructionsAlan MitchellОценок пока нет
- Document KoДокумент1 страницаDocument KoHarrah SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Evolution of TelephoneДокумент1 страницаEvolution of TelephoneHarrah SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Evolution of TelephoneДокумент1 страницаEvolution of TelephoneHarrah SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Computer Workstations Etool: Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationДокумент3 страницыComputer Workstations Etool: Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationDiego GpsОценок пока нет
- Samsung s7 ReviewsДокумент14 страницSamsung s7 ReviewsChaman KumarОценок пока нет
- Office Wireless HeadsetsДокумент18 страницOffice Wireless Headsets308501Оценок пока нет
- Guiaapoyo OPOДокумент54 страницыGuiaapoyo OPOEstherОценок пока нет
- Esquematico YEZZ 5EДокумент32 страницыEsquematico YEZZ 5EJose LunarОценок пока нет
- User Manual - Motorola MOTOZINE ZN5Документ104 страницыUser Manual - Motorola MOTOZINE ZN5oswal787Оценок пока нет
- Techtrends: Governmentpolytechnicfor Girls, SuratДокумент13 страницTechtrends: Governmentpolytechnicfor Girls, SuratpavanОценок пока нет
- Part 1 - Task 1 - Assignment 3Документ7 страницPart 1 - Task 1 - Assignment 3api-276086887Оценок пока нет
- Original Lenovo lp3 Pro Earbuds Wireless 5 0 Bluetooth For Ios and Android Phones User GuideДокумент4 страницыOriginal Lenovo lp3 Pro Earbuds Wireless 5 0 Bluetooth For Ios and Android Phones User Guideal221410219Оценок пока нет
- Iphone XR Accessibility Features-Taylor TurnerДокумент8 страницIphone XR Accessibility Features-Taylor Turnerapi-549554746Оценок пока нет
- Experiment 10 HMIДокумент7 страницExperiment 10 HMIEdu FreeОценок пока нет
- Doogee Dg850 HitmanДокумент8 страницDoogee Dg850 HitmanAstrit StratiОценок пока нет
- iPhone 11 Quick User Starter Guide: Get a Fast Understanding on Your iPhone Features and Essential AppsОт EverandiPhone 11 Quick User Starter Guide: Get a Fast Understanding on Your iPhone Features and Essential AppsОценок пока нет
- Developing Keyboard SkillДокумент7 страницDeveloping Keyboard Skillmelkamu endaleОценок пока нет
- Xenxo S-RingДокумент6 страницXenxo S-RingShaden ComasОценок пока нет
- Samsung Att I907Документ23 страницыSamsung Att I907jonnyguga261Оценок пока нет
- HCI (3) ComputerДокумент51 страницаHCI (3) ComputerDaniel Bintang PrikitewОценок пока нет
- Quick Start Guide Cisco 7940/7960 IP TelephoneДокумент12 страницQuick Start Guide Cisco 7940/7960 IP TelephonezghanemОценок пока нет
- iPhone 13 Pro and Pro Max User Manual: Get The Most Out of Your iPhone 13 Pro/Pro Max with This Comprehensive Guide That Covers Both Beginners and Advanced UsersОт EverandiPhone 13 Pro and Pro Max User Manual: Get The Most Out of Your iPhone 13 Pro/Pro Max with This Comprehensive Guide That Covers Both Beginners and Advanced UsersОценок пока нет
- Contoh Paragraf Bahasa InggrisДокумент4 страницыContoh Paragraf Bahasa InggrisAwal RaisОценок пока нет
- Gebruikershandleiding Com 1Документ57 страницGebruikershandleiding Com 1NacewiОценок пока нет
- BlueParrott M300-XT User Manual - EN - English - RevBДокумент19 страницBlueParrott M300-XT User Manual - EN - English - RevBandi andiОценок пока нет
- Enterprise Edge M7310 Quick Reference Guide: © 2000 Nortel Networks P0908513 Issue 03Документ8 страницEnterprise Edge M7310 Quick Reference Guide: © 2000 Nortel Networks P0908513 Issue 03Terry BuddОценок пока нет
- D10000431ENAДокумент4 страницыD10000431ENAfaten bouchibaОценок пока нет
- Samsung SCH-i920 Omnia II Owner's ManualДокумент122 страницыSamsung SCH-i920 Omnia II Owner's ManualFirefly666Оценок пока нет
- MobileДокумент26 страницMobilevijaysingh100% (30)
- Simplified iPhone 11 Pro Max Manual: Understanding and Maximizing the Full Features of Your iPhone 11 Pro MaxОт EverandSimplified iPhone 11 Pro Max Manual: Understanding and Maximizing the Full Features of Your iPhone 11 Pro MaxОценок пока нет
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XОт EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Back 1 2 3 4 Arms 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4Документ4 страницыBack 1 2 3 4 Arms 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4mourighoshОценок пока нет
- 2011 Complete Journals Catalog (Incl Open Access Journals)Документ292 страницы2011 Complete Journals Catalog (Incl Open Access Journals)mourighoshОценок пока нет
- Posture Type of Posture Owas Code Remarks Action To Be Taken Maximum Area of DiscomfortДокумент2 страницыPosture Type of Posture Owas Code Remarks Action To Be Taken Maximum Area of DiscomfortmourighoshОценок пока нет
- New LowryДокумент6 страницNew LowrymourighoshОценок пока нет
- List of Physiological SCI JournalsДокумент10 страницList of Physiological SCI JournalsmourighoshОценок пока нет
- Banana and Health: Positives and Negatives: Blood PressureДокумент5 страницBanana and Health: Positives and Negatives: Blood PressuremourighoshОценок пока нет
- Protocol For: Gram StainingДокумент19 страницProtocol For: Gram StainingmourighoshОценок пока нет
- Thomann SP5600 ManualДокумент76 страницThomann SP5600 ManualFabrizioОценок пока нет
- Parts of ComputersДокумент4 страницыParts of ComputersFe Marie JisonОценок пока нет
- Interrupts in Microprocessor: Types and FunctionДокумент12 страницInterrupts in Microprocessor: Types and FunctionGowri ShankarОценок пока нет
- Rapier Weaving Today Exists in Diversified FormsДокумент10 страницRapier Weaving Today Exists in Diversified Formsamar9247Оценок пока нет
- Interfacing High-Voltage Applications To Low-Power ControllersДокумент8 страницInterfacing High-Voltage Applications To Low-Power ControllersIr Mathan RajОценок пока нет
- Introduction To SuperMap IDesktopДокумент36 страницIntroduction To SuperMap IDesktopArif W. SunarsoОценок пока нет
- Homogeneous System Copy Using Online/Offline Database BackupДокумент9 страницHomogeneous System Copy Using Online/Offline Database BackupJatinWadhwaОценок пока нет
- Ansys Pipe StressДокумент26 страницAnsys Pipe StressjsmnjasminesОценок пока нет
- Principles & Applications: Digital ElectronicsДокумент14 страницPrinciples & Applications: Digital ElectronicsAnmar AhmedОценок пока нет
- Doors & Gates BT PresentationДокумент76 страницDoors & Gates BT Presentationcrimsonbunnie100% (1)
- Familiarization With Logical InstructionsДокумент2 страницыFamiliarization With Logical InstructionsSagar TimalsinaОценок пока нет
- IBM Think Pad A, T, and X Series TransNoteДокумент32 страницыIBM Think Pad A, T, and X Series TransNoteberr1ckОценок пока нет
- IOS XR Routing Policy LanguageДокумент17 страницIOS XR Routing Policy LanguageSurath KumarОценок пока нет
- PCC 2100 Commissioning Guide Lines - Rev2.6Документ14 страницPCC 2100 Commissioning Guide Lines - Rev2.6Khaled Kamel83% (6)
- Intro Health InformaticsДокумент18 страницIntro Health Informaticsdemonray@gmail.comОценок пока нет
- 8086 - Arithmetic Logic UnitДокумент11 страниц8086 - Arithmetic Logic UnitAhaduzzaman DipuОценок пока нет
- Memory Basics: - Ram - Rom - VolatilityДокумент5 страницMemory Basics: - Ram - Rom - VolatilityYogesh Kumar DewanganОценок пока нет
- Lab 3.6.4: Floppy Drive, Hard Drive, and CD-ROM InstallationДокумент3 страницыLab 3.6.4: Floppy Drive, Hard Drive, and CD-ROM InstallationHamzaSpahijaОценок пока нет
- DS - 20200601 - PVM1000 DatasheetV152 - ENДокумент1 страницаDS - 20200601 - PVM1000 DatasheetV152 - ENAzree CollinОценок пока нет
- DatasheetДокумент106 страницDatasheetjose mojikОценок пока нет
- Efront ArchitectureДокумент5 страницEfront ArchitectureAhmed Al-AntaryОценок пока нет
- Jcl-Mat at TecsaconДокумент64 страницыJcl-Mat at TecsaconSiva Sankar100% (1)
- Centos Server Configuration A-Z PDFДокумент70 страницCentos Server Configuration A-Z PDFMarina Derrude100% (1)
- Informe Inspc JLG MastilДокумент1 страницаInforme Inspc JLG Mastilanmec20Оценок пока нет
- 2TR-FE Engine Control SystemДокумент4 страницы2TR-FE Engine Control SystemFernando Condori Calle80% (5)
- High Bay 200w LedДокумент3 страницыHigh Bay 200w LedEdizon Ramos OrtizОценок пока нет
- CoaXPress - Cables DefinitionДокумент2 страницыCoaXPress - Cables DefinitionXto PeregrinОценок пока нет