Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transistor Current Configurations
Загружено:
lvsaruОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Transistor Current Configurations
Загружено:
lvsaruАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
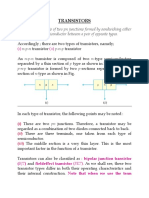
TRANSISTOR CURRENT CONFIGURATIONS
5.1 5.2 There are three basic configuration for transistor circuits. The three configurations are called the common emitter, the common base, and the common collector circuit. The input signal to a transistor is applied between two elements. The output signal is taken between two elements. ~ Since there are only three elements in a transistor, one of the elements has to be part of both the input and output circuits. The type of configuration derives its name from the element that is common to both input and output. The most widely used transistor circuit is the common emitter. It is called thus because the emitter is common to both the input and output circuits. This is shown in figure. Figure A shows the input circuit and figure B shows the output circuit. An important point should be mentioned concerning the illustration is figure 5.3. The emitter is shown as grounded. Ground is the reference point in the circuit from which voltages are measured.
5.3
5.4 It will be noticed in Figure that both the input and output signals are measured with reference to ground. This reference point is called ground because quite often it is connected to the actual earth or ground. -Because the common element, the emitter in this case, is grounded this circuit is sometimes referred to as a grounded emitter circuit. Common emitter or grounded emitter refer to the same type of circuit. The drawing shows a common emitter stage. Figure does not show all the components usually needed for a working circuit, but is intended to show that emitter is common to both the input and output.
5.5 The example shown above is for the NPN type transistor. Every thing would still be valid for the PNP type, except that the power supply polarity would be reversed. 5.6 Figure shows the common base configuration. The input signal is applied to the emitter base circuit. Thus the base of the transistor is the common element. As was the case for the
common emitter, figure is only intended to show' why this circuit is called the common base and does not represent a complete working circuit. In PNP transistor except that the polarity of the power supply would be reversed and naturally, the arrow on the emitter lead would point in the opposite direction.
5.7 The third and final type of configuration is called is common collector and is illustrated in figure A and B. The input signal is applied between the base and collector, and the output signal is taken between the emitter and collector. Figure A shows the circuit as is normally drawn, but it does not clearly illustrate why it is called a common collector. The identical circuit is redrawn in figure B. The transistor has been turned around and this shows clearly that the collector is common to both the input and output signals.
5.8 As in the case of the other two configurations, another name for the common collector is the grounded collector. The most popular name for this circuit is the emitter follower.
Вам также может понравиться
- Transistors PDFДокумент11 страницTransistors PDFVannak Vislow100% (1)
- Bipolar Junction Transistors: Figure 1. BJT Symbols and RepresentationsДокумент26 страницBipolar Junction Transistors: Figure 1. BJT Symbols and RepresentationsVikram Raj SinghОценок пока нет
- 2Документ100 страниц2arvind pandeyОценок пока нет
- Constructional Details of A Transistor: Why Do We Need Transistors?Документ18 страницConstructional Details of A Transistor: Why Do We Need Transistors?sreenadh reddyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2-BJT Applics and Feedback AmpliДокумент37 страницChapter 2-BJT Applics and Feedback Ampliramya hegdeОценок пока нет
- Chapter Two 2Документ36 страницChapter Two 2denm1073Оценок пока нет
- 9 Transister PDFДокумент17 страниц9 Transister PDFpankaj jagadaleОценок пока нет
- 3D Analysis of A Bipolar Transistor: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3Документ32 страницы3D Analysis of A Bipolar Transistor: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3hijerОценок пока нет
- Uni Junction Transistor: Working Principle of UJTДокумент6 страницUni Junction Transistor: Working Principle of UJTSanyam jainОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Class PPT (BJT)Документ30 страницChapter 3 Class PPT (BJT)Yeabsira WorkagegnehuОценок пока нет
- The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) : Emitter (E), Base (B), and Collector (C)Документ146 страницThe Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) : Emitter (E), Base (B), and Collector (C)bhbmvvspkhОценок пока нет
- TransisterДокумент26 страницTransistersenpaixd0110Оценок пока нет
- Bipolar TransistorДокумент8 страницBipolar TransistorfcmandiОценок пока нет
- BE 3 UnitДокумент19 страницBE 3 Unit08sunnyjaganОценок пока нет
- Bipolar TransistorДокумент9 страницBipolar TransistorMariusОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 1 21E001 AbishekДокумент10 страницCHAPTER 1 21E001 Abishek21E001 - ABISHEK VОценок пока нет
- Bipolar TransisДокумент21 страницаBipolar TransisYashobhit SharmaОценок пока нет
- 3.transistors FinalДокумент43 страницы3.transistors FinalSanjana HaqueОценок пока нет
- Bec (BJT Transistor)Документ23 страницыBec (BJT Transistor)aditi pawarОценок пока нет
- 02A Lesson Proper For Week 8Документ12 страниц02A Lesson Proper For Week 8Maxela CastroОценок пока нет
- 2.1 TransistorДокумент19 страниц2.1 TransistorKshitij ParshettiОценок пока нет
- Experiment No 2: BJT Characteristics: Operation of Transistor in Active ModeДокумент3 страницыExperiment No 2: BJT Characteristics: Operation of Transistor in Active ModeGREATJUSTGREATОценок пока нет
- Lecture5 (Analogue Electronics I)Документ15 страницLecture5 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyОценок пока нет
- Common Collector - Wikip..., The Free EncyclopediaДокумент5 страницCommon Collector - Wikip..., The Free EncyclopediaSuneelkrishna RallabhandiОценок пока нет
- Homework 1 COE0047Документ16 страницHomework 1 COE0047ADRIAN MINAОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics BJT TutorialspointДокумент24 страницыBasic Electronics BJT TutorialspointDavid TalamОценок пока нет
- Edc Unit 3 TransistorДокумент17 страницEdc Unit 3 TransistorsrinivasОценок пока нет
- BJT 1Документ33 страницыBJT 1Deepthi S RОценок пока нет
- Transistor Operating Conditions:: AnswerДокумент7 страницTransistor Operating Conditions:: Answersara khanОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three Bipolar Junction TransistorsДокумент16 страницChapter Three Bipolar Junction TransistorsGizachew BalchaОценок пока нет
- Study Materials - EDC 01Документ104 страницыStudy Materials - EDC 01pandaros000Оценок пока нет
- Chapter ThreeДокумент38 страницChapter ThreeTolesa ShoreОценок пока нет
- Transistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiДокумент15 страницTransistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiPRANGHI80% (10)
- Transistors 1-Introduction To TransistorsДокумент27 страницTransistors 1-Introduction To Transistorsdiya shajiОценок пока нет
- Conclusion Elec Exp2Документ1 страницаConclusion Elec Exp2Gena Lapuz100% (2)
- Unit 5 Transistor NotesДокумент12 страницUnit 5 Transistor NotesShreyash SargarОценок пока нет
- Unit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Документ9 страницUnit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Gunjan GuptaОценок пока нет
- Electronics Fund - Ch3 - BJTДокумент36 страницElectronics Fund - Ch3 - BJTshivampatelОценок пока нет
- Day 4Документ34 страницыDay 4PoonthalirОценок пока нет
- Task 2 DhiviyanshДокумент15 страницTask 2 DhiviyanshDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433Оценок пока нет
- Lecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorДокумент21 страницаLecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorGEORGEОценок пока нет
- Electronics-I (EEE 231) : Syed Bilal JavedДокумент68 страницElectronics-I (EEE 231) : Syed Bilal JavedNihala KhalidОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 BJTДокумент5 страницChapter 4 BJTBRIGHT TZZZY CHINGWENAОценок пока нет
- BJT TouhidДокумент38 страницBJT TouhidA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANОценок пока нет
- Unit 4Документ35 страницUnit 4Venkat ChadalavadaОценок пока нет
- Configuration of Bipolar Junction TransistorДокумент6 страницConfiguration of Bipolar Junction TransistorhilloОценок пока нет
- 231Документ14 страниц231Hussin LampoyangОценок пока нет
- Unit-Ii Bipolar Junction TransistorДокумент39 страницUnit-Ii Bipolar Junction Transistorpooja shutradharОценок пока нет
- Edc Unit-3Документ19 страницEdc Unit-3jeganece84Оценок пока нет
- Electronic-Devices Mod2Документ21 страницаElectronic-Devices Mod2ShanОценок пока нет
- Transistor Operation: Chapter - 4Документ3 страницыTransistor Operation: Chapter - 4lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Unit 2Документ46 страницUnit 2Manan JainОценок пока нет
- Chap 3Документ48 страницChap 3belacheweshetu222Оценок пока нет
- Lecureson BJTДокумент46 страницLecureson BJTJai KumarОценок пока нет
- BJT TransistorДокумент10 страницBJT TransistorShreepad Shivkar100% (1)
- BJT CharacteristicsДокумент9 страницBJT CharacteristicsCeferinoTanОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsОт EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsОценок пока нет
- ModemДокумент2 страницыModemlvsaruОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 SDH Basics: ObjectiveДокумент10 страницChapter 2 SDH Basics: ObjectivelvsaruОценок пока нет
- SPST-S&T-Telecom On Indian RailwaysДокумент66 страницSPST-S&T-Telecom On Indian RailwayslvsaruОценок пока нет
- Presentation On SDH Vs SS7Документ59 страницPresentation On SDH Vs SS7lvsaruОценок пока нет
- SPST-S&T-5 6 7Документ113 страницSPST-S&T-5 6 7lvsaruОценок пока нет
- SDH Transport SystemsДокумент185 страницSDH Transport SystemsMofasser Ahmed (Tamal)94% (16)
- IPISДокумент27 страницIPISlvsaruОценок пока нет
- Introduction To WindowsДокумент21 страницаIntroduction To WindowslvsaruОценок пока нет
- Itrailnetv 1Документ53 страницыItrailnetv 1lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Advt 25feb2015 01Документ1 страницаAdvt 25feb2015 01Sree BloggersОценок пока нет
- Introduction To ComputersДокумент68 страницIntroduction To ComputerslvsaruОценок пока нет
- T17 Interfaces: Chapter - 6Документ7 страницT17 Interfaces: Chapter - 6lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Introduction To NetworkingДокумент36 страницIntroduction To Networkinglvsaru100% (2)
- ModemДокумент2 страницыModemlvsaruОценок пока нет
- Chap 3Документ24 страницыChap 3lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Chap 4Документ19 страницChap 4lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Chap 2Документ4 страницыChap 2lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Chap 1Документ7 страницChap 1lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Trouble Shooting: 1) System Power ProblemsДокумент3 страницыTrouble Shooting: 1) System Power ProblemslvsaruОценок пока нет
- Attendant Console: Chapter - 6Документ7 страницAttendant Console: Chapter - 6lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Station Service Features: Chapter - 2Документ7 страницStation Service Features: Chapter - 2lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Chap 7Документ5 страницChap 7lvsaruОценок пока нет
- NOISEДокумент22 страницыNOISElvsaruОценок пока нет
- IndexДокумент1 страницаIndexlvsaruОценок пока нет
- Station Service Features: Chapter - 2Документ7 страницStation Service Features: Chapter - 2lvsaruОценок пока нет
- T17 Computerized Passenger Reservation System (PRS) : Chapter - 10Документ10 страницT17 Computerized Passenger Reservation System (PRS) : Chapter - 10lvsaruОценок пока нет
- T 17A Local Area Network: Chapter - 9Документ4 страницыT 17A Local Area Network: Chapter - 9lvsaruОценок пока нет
- T9 Paging and Talkback: Chapter - 6Документ5 страницT9 Paging and Talkback: Chapter - 6lvsaruОценок пока нет
- T 17A Half Duplex and Full Duplex Protocols: Chapter - 7Документ4 страницыT 17A Half Duplex and Full Duplex Protocols: Chapter - 7lvsaruОценок пока нет
- Chap 5Документ14 страницChap 5lvsaruОценок пока нет
- DDR TI GuidelinesДокумент41 страницаDDR TI Guidelinesnusha aОценок пока нет
- Dold TimerДокумент19 страницDold TimerHemraj Singh RautelaОценок пока нет
- Resume Kummari Paramesh: (Power Electronics and Drives)Документ3 страницыResume Kummari Paramesh: (Power Electronics and Drives)Paramesh KumarОценок пока нет
- CapacitorДокумент5 страницCapacitorAina shivhareОценок пока нет
- DS - SG10KTL-MT Datasheet - V10 - EN PDFДокумент1 страницаDS - SG10KTL-MT Datasheet - V10 - EN PDFalbertusngОценок пока нет
- Implementation of AES Algorithm in UART Module For Secured Data TransferДокумент1 страницаImplementation of AES Algorithm in UART Module For Secured Data Transferblesson123Оценок пока нет
- Danfoss VLT Aqua Drive Fc202Документ98 страницDanfoss VLT Aqua Drive Fc202api-3696336Оценок пока нет
- European Catalog Direct Operated Solenoid Valves Series 126 Asco en 7029040Документ6 страницEuropean Catalog Direct Operated Solenoid Valves Series 126 Asco en 7029040Yasser Al NasrОценок пока нет
- Valvula de Leve MasterДокумент20 страницValvula de Leve Masterguillermo trejosОценок пока нет
- Ficha 7GSC - 8GSAC v2 PDFДокумент4 страницыFicha 7GSC - 8GSAC v2 PDFLorenzo Balaguer HuguetОценок пока нет
- P 3 U 30Документ120 страницP 3 U 30ArcoolОценок пока нет
- IEC 61850-7-410 Edition 2.0 2012Документ126 страницIEC 61850-7-410 Edition 2.0 2012Sergio Blanco CorreaОценок пока нет
- BEDIA Level MonitoringДокумент29 страницBEDIA Level Monitoringm_najmanОценок пока нет
- Troubleshooting The Syringe PumpДокумент2 страницыTroubleshooting The Syringe PumpbleaurosenОценок пока нет
- Nec B310-10Документ3 страницыNec B310-10ICerebro ElengkumaranОценок пока нет
- LNC R6000 Series Hardware Application Manual V01.00 ENGДокумент36 страницLNC R6000 Series Hardware Application Manual V01.00 ENGs_barriosОценок пока нет
- 4.4 LineRunner Products CatalougeДокумент12 страниц4.4 LineRunner Products CatalougeCristiano PortoОценок пока нет
- Installation Instructions and Wiring Diagrams For All Models and RangesДокумент8 страницInstallation Instructions and Wiring Diagrams For All Models and RangesMaria MusyОценок пока нет
- Manual Partes Millermatic 350Документ43 страницыManual Partes Millermatic 350Miguel Angel Pavon CarbonellОценок пока нет
- Assignment EEE437Документ2 страницыAssignment EEE437Abu RaihanОценок пока нет
- ReleaseNotes IndraDrive MPB20VRS ENДокумент224 страницыReleaseNotes IndraDrive MPB20VRS ENLinh Pham0% (1)
- Digital Circuits: EE/CE 3320 / Spring 2020 / Lecture 12Документ82 страницыDigital Circuits: EE/CE 3320 / Spring 2020 / Lecture 12Muhammad MontahaОценок пока нет
- Kataloq CKD AD11-10A-02C-200VДокумент4 страницыKataloq CKD AD11-10A-02C-200Vgeneral affairsОценок пока нет
- Ecom En2 Parts ListДокумент6 страницEcom En2 Parts ListGhoza AbiwaraОценок пока нет
- Daewoo DLX32D1SMSB Manual de Servicio LCDДокумент40 страницDaewoo DLX32D1SMSB Manual de Servicio LCDAlexis ColmenaresОценок пока нет
- Camara Vivotek PZ7111Документ12 страницCamara Vivotek PZ7111TecnoSmartОценок пока нет
- Simple Agelesss Methods For Field Testing Power TransformersДокумент13 страницSimple Agelesss Methods For Field Testing Power Transformersraza239Оценок пока нет
- Bonga Main Gate Revised El - 010321Документ5 страницBonga Main Gate Revised El - 010321RedietОценок пока нет
- PPM 2017 1.0 HV (Weekly)Документ2 страницыPPM 2017 1.0 HV (Weekly)Nazlie NasirОценок пока нет
- Typical Wiring Diagram: 7320 Installation InstructionsДокумент2 страницыTypical Wiring Diagram: 7320 Installation InstructionsMecatrónica IgnacioОценок пока нет