Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
BOSCH D JETRONIC Fuel Injection of Renault 17 TS
Загружено:
Raul Quispe RamirezИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
BOSCH D JETRONIC Fuel Injection of Renault 17 TS
Загружено:
Raul Quispe RamirezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The BOSCH D JETRONIC fuel injection of Renault 17 TS
The fuelinjection of Renault 17 TS was designed by Bosch and it was used by some other car makes as well. So it might be easier to find sare parts to the fuel injection from a Bosch dealer, I have made this translation list so it is possible to get the Bosch part numbers. But if you are having problems with your fuel injection such as lack of power in high revs always start with replacing the fuelfilter, another thing to start with might be to add some kind of fuel injection cleaner. Another fuel injection tip is to add some twostroke oil to the petrol everytime you fill the tank, this oil makes the life easier for the electric fuelpump.
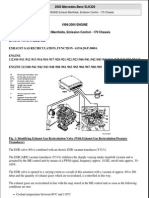
This scematic drawing shows the indexes from the table below.
BOSCH D JETRONIC PART NUMBERS (R1313 R1323)
Index on drawing Name 1 2 3 4 5 Electric fuelpump Fuel filter Pressure regulator Fuel injector Cold start injector Bosch part number Renault part number 0 580 960 007 ?? 0 280 160 001 0 280 150 016 0 280 170 013 77 00 557 763 77 00 545 787 77 00 545 780 77 00 545784 77 00 545 782
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Distributor JFUX 4 Pessure sensor Auxiliary air conrol Throttle switch Air temperature sensor Coolant temperature sensor Temperature time switch Ignition / starter switch Control box Main relay Pump relay Auxiliary air vaccum valve (just on some models)
0 231 163 064 0 280 100 031 0 280 140 019 0 280 120 011 0 280 130 016 0 280 130 014 0 280 130 201 -0 280 000 025 --0 280 160 106
77 00 577 336 77 00 545 776 77 00 545 783 77 00 569 162 77 00 545 778 77 00 545 779 77 00 556 448 77 00 534 018 77 00 545 851 77 00 545 853 77 00 545 853 77 00 556 449
The Renault 17 TS Bosch fuel injection system.
D Jetronic Fuel Injection - Mercedes Benz Tech Tips
D Jetronic Fuel Injection Tech Tips 1971 to 1976 The D Jetronic system was introduced in 1967 and started appearing widespread in Volkswagens. Sensors constantly sense the operating conditions of the engine and transmit signals to an electrical control unit. When and how much fuel injected into the engine, is calculated on intake manifold pressure and engine speed. The most critical measure is intake manifold pressure. For the trivia nuts, D, the first letter of D Jetronic is also the first letter of the German word Druck that means pressure The D Jetronic system relies on constant fuel pressure if the electronic control unit is to deliver the precise amount of fuel during different operating conditions. To achieve this constant pressure the fuel pump needs to be able to deliver more fuel than the engine will ever require thus the pressure can be regulated by re-circulating the excess fuel back to the fuel tank. First we will list a brief description of each part, followed by their operation with a few little tips we have picked up along the way. Electric Fuel Pump The fuel pump is a roller type electric fuel pump, which delivers fuel under pressure in a closed system. The closed system consists of a pipeline to a fuel rail, which contains solenoid-operated injectors a fuel pressure regulator and a fuel return line to the fuel tank. The fuel pump also contains a one-way check valve, or non-return valve, in it's outlet to prevent fuel flowing backward and maintain pressure in the system after shutoff.
Fuel Pressure Regulator Since the fuel pump delivers more pressure than the maximum requirement of the engine the fuel pressure must be regulated. It is this constant fuel pressure, which enables the electronic control unit to deliver the precise amount of fuel. The fuel pressure regulator, located at the back of the fuel rail, consists of spring-loaded diaphragm in a steel housing. When fuel pressure overcomes spring pressure the valve opens and fuel is diverted back to the tank thus maintaining a constant pressure. The spring pressure is adjustable by turning an adjustment screw which increases or decreases spring pressure and consequently increases or decreases fuel pressure. Fuel pressure is normally 28 to 30 lbs. in the fuel rail. Check the service manual for your pressure setting. Fuel Filter
Filters out the impurities of the fuel to protect the fuel system components. Electronic Control Unit (ECU) The electronic control unit back then was an analog control unit. Transistors still weren't cheap then as those of you who owned and listened to their transistor radio can attest to. Remember them? The electrical control unit receives inputs from various sensors and determines the amount of fuel the engine requires to operating conditions. It controls the fuel flow by controlling how long the electronic injector valves remain open.
Mercedes Benz Tech Tips - D Jetronic Fuel Injection
Electronic Fuel Injector The fuel injector is an electric solenoid operated valve. The electronic control unit sends electrical pulses to the fuel injector, which energizes the solenoid and results in fuel, which is under pressure, being injected in front of the intake valve.
Cold Start Valve
A cold engine causes fuel to condense on the cylinder walls and in the intake manifold. The end result is
that fuel that is condensed does not mix well with the incoming air and is extremely hard to ignite. The solution was the cold start valve. The cold start valve is designed to inject atomized fuel near the air inlet thus creating an ignitable mixture. The cold start valve only operates when the starter is engaged
Thermo Time Switch The thermo time switch opens and closes the current that flows to the cold start valve depending on the temperature of the engine. The design and operation is simple.
Inside the thermal time switch is a strip of bimetallic metal connected to one terminal of the sensor. Heating windings surround this bimetallic strip. When the engine is cold the bimetallic strip contacts the strip that the other terminal is connected to. Picture a set of ignition points. When it is cold the points are closed and when the engine is warm the points are open. This construction enables the thermo time switch to control how long current is supplied to the cold start valve. When the starter is engaged current flows through the heating windings heating the bimetallic strip of the thermo time switch. As the bimetallic strip heats up it spreads the contacts and the connection is lost with the other terminal which cuts off the current to the cold start valve. Therefore the colder the bimetallic strip is, the longer time it takes to spread the terminals and the longer time the cold start valve receives current and remains activated. This time interval can be as short as 1 second or up to 20 seconds when the temperature is -20 degrees Celsius. Remember the cold start valve only works when the starter is engaged.
Temperature Sensors There are a few temperature sensors located throughout the engine compartment. The hollow threaded sensors contain a semiconductor material whose resistance decreases as the temperature increases. One sensor measures the temperature of the coolant while the other sensor or sensors measure the temperature of the air. A cold engine requires more fuel than a engine at operating temperature since it must overcome additional friction and the effects of fuel condensation. The electronic control unit constantly monitors the resistance values of these sensors. The electronic control unit uses these resistance values to calculate the proper amount of fuel to be injected based on coolant and air temperature.
Auxiliary Air Valve As we have stated above, a cold engine requires more fuel than a warm one to overcome additional friction and combustion deficiency. A cold engine also needs to produce more torque. The extra torque is achieved by the introduction of more air into the engine. Not only does this increase the idle speed slightly, the electronic control unit will react to this additional air by injecting an additional amount of fuel. Thus the requirement of extra torque and extra air and fuel is met. They're a few different styles of auxiliary air valve but they essentially perform the same function, which is the introduction of additional air behind the throttle plate. The size of the opening in the auxiliary air valve is determined by temperature. The colder it is, the larger the opening that will be uncovered inside the auxiliary valve. The larger the opening uncovered inside the auxiliary air valve the more bypassed air flows behind the throttle plate. The opening in the auxiliary air valve will be slowly reduced and the temperature rises and will close at operating temperature, at which time bypassed air will not flow behind the throttle plate through the auxiliary valve.
The two most common types you will see are the electrically heated bimetallic type and the wax pellet type, which is immersed in engine coolant.
Trigger Contacts Trigger contacts, also referred to as trigger points, are housed in the lower section of the ignition distributor underneath the mechanical centrifugal advance plates. The opening and closing of the trigger contacts indicate the speed of the engine since the ECU monitors the interval of time between trigger pulses. Tech Tipthe trigger contacts signal the "start" of injection while the "duration" of injection, which is how long the injectors remain open, is determined by the inputs of the pressure sensor, engine speed, and the various other engine sensors to the electronic time switch of the ECU. The trigger points, on a V8 engine contain four sets of points. The trigger points are not that dissimilar from ignition points in looks except they do not carry voltage. As each set of points is opened and closed the ECU knows when to fire each set of corresponding injectors based on crankshaft position. Since the distributor is installed at top dead center, the trigger points corresponding lobes inside the distributor correlate to the position of the crankshaft. Consequently the injectors are pulsed at the precise time.
Throttle Switch The throttle switch, in a pressure type system, is used to bridge the gap or time delay between the time intake pressure signals the ECU for an increase in fuel versus the immediate call for fuel when the throttle plate is opened. The throttle switch performs the same function as the accelerator pump does on a vehicle equipped with a conventional carburetor. The throttle switch is connected directly to the throttle plate. It consists of two contact arms, which slide or sweep across a graduated zigzag contact path. This zigzag pattern allows the ECU to receive signals as the contact arm sweeps up that the throttle is being depressed and therefore enrich the fuel. One contact path is used for acceleration while the other contact path is contains a full load and an idle contact.
Pressure Sensor The pressure sensor is the most critical sensor in the D Jetronic system. The pressure sensor is housed in a metal housing and contains two diaphragm cells, which displace an armature that is inside a coil. When the armature is moved inside the coil, the inductance of the coil changes Therefore, the pressure sensor converts a pneumatic signal into an electrical signal which the ECU can measure and determine the correct duration of the injector pulses.
One chamber of the pressure sensor is at atmospheric pressure while the other is at intake manifold pressure since a vacuum line is connected from the intake manifold to the pressure sensor. The difference between these two pressures will cause the armature to move within the coil changing the induction of the coil. The resulting electrical value that the ECU receives will determine the load of the engine and consequently the amount of fuel to be injected. Pretty trick for the late sixties.
Series Resistors Some D Jetronic systems use a set of resistors to drop the voltage to the injectors. We have rarely seen these fail. Refer To Your Service Manual For Your Car.
You must use extreme caution when working with gasoline because of the extreme risk of fire and injury. Follow the procedures in the genuine Mercedes Benz service manual for your car. The text below is general knowledge and is not meant to take the place of the service procedures that your manufacturer recommends. Many different vehicles have different versions of the D Jetronic system and different procedures may apply. the starter is engaged.
Working With D Jetronic We cannot empathize more the importance of doing all the basics first before beginning to diagnose a fuel injection problem. Rule number 1do not assume it is a fuel injection problem. Rule number 2read rule 1 again Before you start you must have fresh fuel. If the vehicle has been sitting for a prolonged period of time the fuel must be drained, the fuel filter changed, and possibly the fuel tank cleaned.
You must make sure your ignition points are in good condition and that you have checked your dwell and timing and that the rubbing block of the points is lubricated. So many people drop the ball here. I normally just pop a new set of points in just to eliminate any doubt. Make sure your centrifugal advance is free and lubricate if possible. Some of the distributors have a wick under the rotor where you can apply a couple of drops of oil. While you are right there check your vacuum advance too. Make sure all of your maintenance has been done such as distributor cap, rotor, air filter, fuel filter and oil change. If your car is running super rich, black smoke, you may need to change your oil again even though it may have been just done recently. You must also make sure your spark plugs are new and your ignition wires are good. Visually take out each spark plug and check to make sure each plug is firing and free of deposits. The plugs should be tan in color and be free of carbon deposits. Check the spark plug gap. If the gap is higher than spec you will probably see the electrodes are rounded and the plugs are need of replacement. Before you put the spark plugs back in test the compression. See your service manual for procedures and specifications. The compression must meet specifications or the fuel injection system will not work correctly.
Remember the pressure sensor monitors intake manifold pressure. The engine must be in good mechanical condition if it is to work correctly. Do not assume any of the parts are good. Don't guesstest! Check and repair as necessary before proceeding. If you skip the above steps you are very likely not to diagnose the problem correctly and buy a part that you did not need. Examples of this are changing your fuel pump because of a clogged fuel filter, changing the control unit over a set of points, etc., etc., etc. The next step is to perform a visual check of all vacuum lines and replace all that are cracked, spongy, or rock hard. If they have never been changed before now is the time since a couple of decades have taken its toll. If you need to change any of the vacuum lines, we recommend using the German line with the cloth braid. Any vacuum leaks will surely cause drivability problems since the pressure sensor will report inaccurate readings to the ECU. Make sure you check all of your fuel lines for cracks and any other signs of deterioration, which can cause a fuel leak. The rubber fuel lines should not be hard. Check all the clamps and make sure they are tight. You should not see any evidence of the hose clamp cutting into the hose or a swelling or mushrooming next to the clamp.
If you are going to change any fuel line you must use fuel line that is designed for fuel injection and can withstand the high pressure. You must use a clamp that is designed for fuel injection. These are smooth on the underside and will not cut into the hose. The cheap screw type clamps, not designed for fuel injection, will actually cut through the fuel hose over time. Failure to use the wrong type of fuel hose or hose clamp will result in a rupture and a fuel leak, which may result in a severe engine fire. Believe it or not, the majority of you have probably found and repaired your problem after following the steps above. If you are still experiencing problems now we can start to look for a possible fuel injection problem
Check All The Connectors And Connections
The first step is to remove the air cleaner assembly and check all of the connectors and connections of all sensors and injectors. Over time the rubber boots may have deteriorated and may have led to a corrosion problem. Remember the connectors back then were not very weather resistant so you should remove each connector and check for corrosion and pull back the boot and check for broken wires and corrosion. The wires sometimes get so brittle from being baked for two decades that they may have broken. Also be sure to check the wiring for any broken insulation Another cause for injection problems and driveability problems are bad grounds caused by corrosion. These grounds are usually comprised of multiple wires bolted to the intake manifold or engine.
Test Fuel Pressure The next step is to check your fuel pressure in the fuel rail. This can be checked using a fuel gauge designed for testing fuel injection. The fuel pump is capable of delivering more fuel and pressure than is required to run the vehicle at all operating conditions. As was mentioned earlier, the fuel pressure regulator bypasses this excess fuel and pressure and returns it to the tank.
We are interested in checking the pressure in the fuel rail. This pressure must be constant since the electronic control unit's calculation of the duration of injector opening is based on constant fuel pressure. If the pressure were allowed to vary in this system there would be no way to control the amount of fuel being injected. For example, if you had one fuel injector connected to a source of fuel at 20 pounds per square inch and opened the injector for 10 milliseconds less fuel would flow from that injector than if you had a similar injector connected to a source of fuel at 30 pounds per square inch. More pressure more fuel. To check the pressure in the fuel rail disconnect the fuel hose from the cold start valve and connect your fuel pressure gauge to the hose to the hose. Cycle the ignition key a few times and check for any fuel leaks. While you are cycling the key check the pressure. The pressure varies between vehicle applications but a rule of thumb is 28 to 30 pounds per square inch. If your vehicle runs then start the
engine and check the fuel pressure. If the pressure does not meet specification it may be adjusted by loosening the lock nut on the fuel pressure regulator and rotate the adjusting screw in or out until you reach the proper pressure. Turning the screw in raises pressure and out lowers pressure. Be sure to re-torque the lock nut after setting the pressure. If you do not have fuel pressure, read on and this topic will be discussed under the topic no start. If you cannot obtain high enough fuel pressure to meet the specification, then your fuel pump or fuel pressure regulator is defective. We already know your fuel filter is good since you did the maintenance above before checking for an injection problem. Shut the engine off and note the pressure. The pressure should not fall to 0 instantly. Pressure should be maintained in the rail after shut off. This is called rest pressure. If the correct pressure is maintained for the specified time you can now ignore any further text dealing with rest pressure since you just tested it. For those of you who failed, we will discuss some of the drivability problems associated with loss of rest pressure. Tech TipIf you are going to buy a gauge set; buy the gauge set that also adapts to check K and KE CIS systems and L Jetronic systems. This way you can check the fuel systems of most European vehicles.
The Basics Are Done We have now done all the work that was necessary before we can start to look for problems with our D Jetronic system. We have done all the maintenance, checked compression, checked all the vacuum and fuel lines, checked all of our connections, and we know we have the correct fuel pressure. We now have the platform where the ECU can effectively run the vehicle.
Problem By Symptom This section is only concerned with D Jetronic fuel injection and from this point on we have to assume you have found and repaired any malfunctions in the primary and secondary ignition system. No Start In order for an engine to start we must have compression, the correct ratio of fuel and air, and spark delivered at the correct time. Compression and ignition systems will not be covered here but spark must be present. In some systems if you do not have spark you will not have fuel. When you first cycle, sometimes called tapping, the ignition key you should hear the fuel pump start, a slight buzz from the rear, and then shut off after two seconds. We now determine that the buzz is not present and we have no fuel pressure reading on our fuel pressure gauge. What do you do?
First is to check for voltage at the fuel pump. Using a voltmeter or an automotive test light check for 12 volts at the fuel pump when the key is cycled. We normally use a test light with the alligator clip
connected to the negative feed to the fuel pump and the tip of the probe touching the positive feed to the pump. This way you know you have a good ground and hot feed if the light lights up. If the light lights up and the pump does not run the fuel pump is defective If the light does not light up you need to check the ground and the hot separately. Connecting the test light to a known good ground try again. If the light lights up repair the ground wire circuit. If it does not light up the problem is probably the fuel pump relay or fuse.
Engine Does Not Start ColdSpark Present 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Incorrect or no fuel pressure Defective cold start valve Defective thermal time switch Defective electronic control unitor wiring Defective temperature sensor Defective pressure sensor
Engine Will Not Start HotOtherwise No Problems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. No rest pressure caused by defective fuel pump check valve Leaking fuel injectors after shut off Defective fuel pressure accumulator Defective cold start valveleaking Defective thermal time switch Engine overheated
Engine Runs Rich 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Defective Defective Defective Defective Defective Defective fuel pressure regulatorcheck fuel pressure and adjust. cold start injectorcold start valve is leaking injectorinjector stuck open or leaking pressure sensor temperature sensor electronic control unit
Engine Runs Lean 1. 2. 3. 4. Clogged or dirty fuel injectors Low fuel pressurecheck and adjust Defective electronic control unit Defective pressure sensor
Engine Misfires 1. Defective trigger contacts 2. Defective injector or injectors 3. Defective series resistor
4. Defective pressure sensor 5. Defective electronic control unit
Idle Too High 1. 2. 3. 4. Vacuum leak Auxiliary valve not closing Incorrect base throttle plate setting Air by pass screw not adjusted properly
Idle Too Low 1. 2. 3. 4. Coldauxiliary air valve defective Hot Incorrect base throttle plate setting Air by pass screw not adjusted properly Improper fuel mixture caused by a rich or lean condition.
Idle Hunts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Vacuum leak Defective throttle switch Improper fuel mixture caused by a rich or lean condition. Defective trigger contacts Defective or clogged injectors Defective pressure sensor
Full Throttle Output Poor 1. Defective throttle switchfull load enrichment switch is bad 2. Defective pressure sensor 3. Improper fuel pressure and or fuel pump volume
Engine Hesitates 1. Defective throttle switch 2. Defective pressure sensor 3. Improper fuel mixture caused by a rich or lean condition. 4. Defective electronic control unit 5. Defective fuel pressure regulatorsome regulators have a vacuum line, which increases fuel pressure as intake manifold drops.
Some Quick Tips To Check The System
Electronic Control Unit
The electronic control unit is normally very reliable. Before you change the control unit make sure you have gone to a wiring diagram and checked all the 12-volt inputs and the necessary grounds at the control unit wiring connector. Although it may seem like the control unit works on magic it does not. Wiring is the most common cause of the control unit not working. The electronic control unit should only be changed after you have checked every sensor and all the wiring. Most control units have an adjusting screw on the top of the unit, which is a fine tune for the fuel mixture. You can smooth out your idle by turning the screw in or out until the engine idles smoothly.
Cold Start Valve And Thermal Time Switch The cold start valve is another part that does not fail often. Usually the reason it does not fire is due to a defective thermal time switch or the wire fell off the starter. You can unbolt the cold start valve from the intake and place it in a glass beacon. Ground the coil wire and tap the ignition key. The cold start valve should fire a very fine atomized spray if the temperature is low enough and should not leak when you turn the key off. Check your manual for the correct procedure for your car. The temperature at which it will activate is usually marked on the casing of the thermal time switch.
If the cold start valve does not fire check the starter solenoid wiring. If the wires are in place, check to see if you have current flow in and out of the thermal time switch. If you have current flow in but none out and the temperature of the coolant is below the specified rating of the thermal time switch that thermal time switch is defective. Tech Tipif the engine starts then stalls after a few seconds the cold start valve is probably good. That is why the engine started. The engine started and ran on the amount of fuel the cold start valve injected and then stalled because something else is askew. The cold start valve has no effect on the performance of the engine during warm up. Check the other conditions above and below.
Trigger Contacts
The trigger contacts are housed in the lower section of the ignition distributor underneath the mechanical centrifugal advance plates. On a V-8 engine the trigger contacts have a set of four points. The trigger contacts signal the "start" of injection while the "duration" of injection, which is how long the injectors remain open, is determined by the inputs of the pressure sensor, engine speed, and the various other engine sensors to the electronic time switch of the ECU.
If your engine is misfiring badly, barring an ignition problem, the most common culprit is the trigger contacts. Since the points do not have current flowing through them, unlike ignition points, the point contact surfaces last for quite a long time and are not subject to the pitting that occurs on ignition points. However, the rubbing blocks wear out, just as ignition points, because of lack of lubrication and from normal wear. This will result in the failure of the ECU to receive the signal to fire a pair of injectors, thus the bad miss. Another problem is the point contact surface corrodes causing the same scenario.
We have mentioned that you must check the connectors before replacing the parts; this is one area that we have seen frequent connection problems. There are two different types of trigger contacts. The pigtail type has a short wiring harness that is connected to the trigger contacts and the other type has no wiring attached just the male ends. Make sure you check the pigtail connector for any reason that could cause a poor connection. It does not take much to cause a really bad misfire making it seem that the engine is running on four cylinders. The truth is, it probably is. You can tell that injectors are not receiving the signal to fire it by testing with a 12-volt test light. Connect the alligator clip to ground, pull back the connector boot and so you can touch each wire connector of the injector with the probe. When the engine is running one wire will have a solid light and the other wire will flash or pulse. When this is occurring the injectors have the proper electrical signal to fire. If both wires have a steady light the injector is not receiving the ground from the control unit. You need a hot and a ground to pulse the injector. Two positives don't make a negative in this case. The most common cause of the above scenario is the failure of the ECU to receive a signal from the trigger points either due to a wiring problem or a mechanical failure. Other causes may be a series resistor, extremely rare, or a control unit failure. Removing the two screws and sliding the trigger contact set out of the distributor will easily remove the trigger contacts. Make sure you grease the rubbing blocks of the points when you reinstall them . One final note on trigger contacts; although you can test the trigger points with an analog meter to see if each set of points is working, we have found that there is a big difference with the results by bench testing versus driving conditions. We have seen many contact sets check out good on the bench, when they are only subject to very slow RPM, but fail miserably under driving conditions. My personal rule of thumb is that if the car is an everyday driver and the contact points are decades old, I am changing them for reliability sake.
Throttle Switch The throttle switch is held on by two screws and is easy to test and adjust. Check your wiring diagram to see which wires are for the full throttle enrichment contacts and for the idle contacts. With the engine off, key off, and connector removed, you can check continuity with an ohmmeter at the idle contacts and full throttle contacts. If you do not have continuity either the switch is bad or out of
adjustment. If you do not have a wiring diagram, the black cover normally unclips from the switch and then you can see the full throttle and idle contacts. They are the ones the sweep the non-zigzag path. Follow the yellow brick road to the appropriate connectors. Tech TipHere is an easy way to check the adjustment of your throttle switch. This test is done with the engine off, key on, air cleaner off. Slowly, very slowly advance the throttle switch to full throttle. As you are moving the throttle forward you will hear audible clicks. Count the clicks as you continue to move the throttle forward. You should hear twenty clicks from start to end and no clicks when you release the throttle. If you do not hear twenty clicks, loosen the screws on the throttle switch and adjust it. Repeat the test above. If you hear clicking when you release the throttle the throttle switch is defective.
Temperature Sensors The temperature sensor in the air filter housing measures the temp of the incoming. The sensor is a very fine tune and has very little affect on the engines performance. The resistance of this sensor is about 400 - 500 ohms at 50 degrees F. and is about 150 - 200 ohms at 100 degrees F.
The coolant temperature sensor has the most affect on drivability. If the sensor is defective the ECU may "think" it is minus 40 out and inject lots of fuel and run super rich. If the sensor is out of range, outside specified ohm reading versus temperature, the engine will experience drivability problems during warm-up and normal operating conditions due to improper injector duration caused by an incorrect resistance reading. Check your service manual for the specifications but the resistance should be approximately 2,000 - 3,000 ohms when the engine is cold and less than 1,000 ohms when operating temperature is reached. Remember, the hollow threaded sensors contain a semiconductor material whose resistance decreases as the temperature increases. Some engines have an intake air temperature sensor in the intake manifold. This is actually the same exact sensor as the coolant temperature sensor and this sensor can also affect the performance of the engine but not nearly as much as the coolant temperature sensor. Tech TipOn engines equipped with both an intake air temperature sensor and coolant temperature sensor you can compare the resistance readings after the engine sits overnight. Since the air will be the same temperature as the coolant, the resistance values will be the same. If they are not one of the sensors is kaput. Check your resistance to temperature chart. If the coolant temperature sensor is bad you can swap it with the air intake sensor for the time being to improve drivability.
Pressure Sensor The pressure sensor is usually located on the left inner fender well. This sensor can affect performance more than any other sensor in the fuel injection system.
The sensor has two coils and a diaphragm inside. The coils can be tested using an ohmmeter. Check your service manual for the proper pins and readings but the general rule if thumb is, 90 ohms resistance for one coil and 350 ohms resistance for the other.
If the metal diaphragm inside develops a leak, the engine may not run or will run super rich. Any easy test is to blow into the sensor, yuck, and see if the diaphragm leaks. When the pressure sensor fails it is more common to have a rich running engine although it is possible to have a pressure sensor fail where the engine runs very lean. The pressure sensor is not supposed to be adjusted but if you are the type that has to mess with it even when you are told not to, make sure you set it using a gas analyzer and not by ear. Turning the screw, located behind the epoxy, in will lean the mixture and turning it out will richen the mixture. Our theory on this is that you should replace the pressure sensor if it is out of specification instead of trying to put a band-aid on the problem.
Fuel Injectors The three common problems are leaking fuel internally into the engine, leaking fuel externally from the hose or from the plastic itself, and poor spray pattern due to clogging. If the injectors are leaking fuel between the plastic housings they cannot be repaired. If they are leaking fuel into the engine after you shut the engine off we recommend that you replace them since we never have achieved good results by cleaning them.
If the rubber hoses are cracked and beginning to leak you can buy a repair kit to fix that problem. The kit consists of instructions, fuel injection hose and fuel injection clamps. Follow the manufacturer of the kits instructions and be sure to install new seals. Tech Tip. cleaning injectors. D Jetronic injectors are one of the few injectors where we have seen dramatic performance increases after cleaning. If you suspect your injectors may need cleaning , remove the injectors and place each injector in a graduated tube. The ignition system must be disabled to prevent sparks. Follow the instructions in your service manual. Crank the ignition with the throttle depressed for 15 seconds for most engines. Measure the quantity of fuel in each tube. There should be no more than ten percent variation but I am always looking for equal
If the injector does not spray an atomized conical spray you can try to clean them. There are many injector-cleaning systems that work well for injection systems that utilize a fuel rail. If you do not have one of these systems, I have witnessed people removing the injectors and installing each injector to a pump sprayer filled with injector cleaner. You can pulse the injector by making a wiring harness up to connect to the injector terminals. After you connect one wire to each injector terminal, connect one wire to the negative side of a AA battery and begin to pulse the injector by touching the other wire to the positive tip of the AA battery. Repeat the process until the injector fire a fine atomized spray. Be very careful when working with flammables, no sparks near the flammable. It stands to reason that if you cannot obtain a fine atomized spray the injector needs to be replaced.
Auxiliary Air Valve These are very easy to test. When the engine is cold, remove the hoses from the auxiliary air regulator. Peer inside the valve and observe that the part of the opening is uncovered. Use a mirror if you need to. The colder the temperature of the valve, the larger the uncovered opening will be. If the valve is not open it should be replaced. Install the hoses back on and start the engine. Allow the engine to reach normal operating temperature and shut off the engine. Remove the hoses and peer in the valve. There should be no uncovered opening when the engine is hot. Tech Tipif you see a small-uncovered opening in the valve try tapping on the valve very lightly and see if it shuts. Some valves also rely on engine vibration to assist in closing.
Hot Start Woes We just touched upon the hot start subject above, but since it is such a common problem, it warrants further elaboration. We all know that water under pressure will boil at a higher temperature than water that is not under pressure. Well the same goes for gasoline. If the gasoline is not under pressure when you shut off your hot engine, the fuel will boil causing the injectors to shoot blanks when you try to start it. This is commonly referred to as vapor lock and the pressure maintained in the fuel rail is called rest pressure. Remember when we tested our fuel pressure way up at the top of this article we mentioned rest pressure. In order to maintain rest pressure you must have fuel injectors, cold start injector, fuel pump check valve, and fuel pressure regulator that do not leak down.
As fuel flows from the high-pressure side of the pump, on the way to the fuel rail on the engine, it passes through a fuel pump check valve located at the outlet of the pump and the fuel pressure accumulator. The purpose of these parts is to prevent fuel from flowing back to the tank after shut off which would result in loss of rest pressure.
The fuel pump check valve is basically a small steel ball pushed against a seat by a spring. When fuel pressure overcomes spring pressure and the fuel flows forward under pressure to the fuel rail. When the pump shuts off the ball is firmly seated against the seat so fuel cannot return to the tank. The fuel accumulator's job is to push approximately 6 ccs of fuel forward after shut off. This will momentarily show a slight increase in the fuel pressure, and then the pressure will bleed off to
approximately 24lbs., check your specification, then finally fall to final rest pressure, say 18 lbs. after a few minutes. When the pressure falls to the final rest pressure the accumulator's job is done. The systems maintains this pressure because the fuel pump check valve will not allow the fuel to return to the tank on this side of the fuel rail. Now we have incoming side of the fuel rail sealed up, we will discuss the fuel return side of the fuel system. As fuel is pumped into the fuel rail at high pressure the spring pressure of the fuel pressure regulator is overcome and excess fuel returns to the tank unrestricted and constant pressure is maintained in the fuel rail. Because of the fuel accumulator and the fuel pump check valve prevent the fuel from running backward when the engine shuts off we must now look at what seals the pressure on the return side of the fuel rail. When you turn off the engine you consequently turn off the fuel pump. The excess fuel pressure, which the fuel pump delivers, is gone and the fuel pressure regulator closes since the fuel pump fuel pressure is lower than the fuel regulator's spring pressure. The closing of the fuel pressure regulator seals the fuel from returning to the fuel tank via the fuel return hose. Now we have fuel under pressure trapped in the fuel rail. If the injectors and the cold start valve do not leak we have rest pressure. If the fuel pressure stills drops to zero after establishing the fuel pump regulator, the fuel accumulator, and the fuel pump check valve are good, the problem now points to leaking injectors or cold start valve. Tech Tip. You can easily test, and narrow down, whether you have a condition that would cause you to lose rest pressure by using a pair of needle nose vise grips with rubber hoses installed over the jaws. The hose on the jaws is to prevent damage to the fuel line. Install a fuel pressure gauge in the fuel rail. Shut off the engine and see if rest pressure is lost. If so, start the engine again and then shut the engine off. As the rest pressure is dropping pinch off before the inlet hose of the fuel rail with the vise grips. If the pressure ceases to drop you have either a bad fuel accumulator or check valve or both. If it continues to drop after pinching the hose repeat the test by pinching off the fuel return hose. If you pinch the return line off and the pressure stops dropping you know you have a bad fuel pressure regulator. If the pressure still drops you have no narrowed it down to the injectors or the cold start valve. Check each one at a time and replace as necessary. After making the above repairs you will now be able to start your engine when it is hot. No more sweating bullets when you go into the convenience store for the beverage of your choice. Fuel Dampeners One parting thought before we go. Some manufacturers installed pressure dampeners in the fuel line before and in the fuel rail. These are simply little dashpots with an inlet and outlet. If these start to leak you can simply remove them and place in the circular file. You can't buy them anymore nor do they serve much purpose other than to prevent a little noise. We hope you have a better understanding of your D Jetronic system. Good luck and be sure you read your manual for proper procedures pertaining to your car and follow every safety precaution when working with fuel.
Вам также может понравиться
- Mercedes - Benz Vito & V-Class Petrol & Diesel Models: Workshop Manual - 2000 - 2003От EverandMercedes - Benz Vito & V-Class Petrol & Diesel Models: Workshop Manual - 2000 - 2003Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Mercedes Benz & Dodge Sprinter CDI 2000-2006 Owners Workshop ManualОт EverandMercedes Benz & Dodge Sprinter CDI 2000-2006 Owners Workshop ManualОценок пока нет
- Variable Displacement Compressor - How It WorksДокумент7 страницVariable Displacement Compressor - How It WorksAbdulmajeed Al KhouriОценок пока нет
- GDIДокумент7 страницGDIlinhda561Оценок пока нет
- Cis Information DiagnosisДокумент17 страницCis Information DiagnosisrezakecilОценок пока нет
- CRP D 200 Manual EngДокумент16 страницCRP D 200 Manual EngAbbode Horani100% (2)
- Customer Experience Center 1-800-331-4331: Quick Reference GuideДокумент30 страницCustomer Experience Center 1-800-331-4331: Quick Reference GuideNaveed Gondal100% (1)
- 928 Engine ControlДокумент9 страниц928 Engine Controlbenekski100% (2)
- Rover 14CUX Hot Wire Mass Flow EFI - Service and TroubleshootingДокумент13 страницRover 14CUX Hot Wire Mass Flow EFI - Service and TroubleshootingOlga PlohotnichenkoОценок пока нет
- Jetronic Opel MantaДокумент41 страницаJetronic Opel MantamhahtoОценок пока нет
- Electrical Test Program - Test: ABS/ASR Control Module (N30/1) Layout Connector 1 (Component Compartment)Документ2 страницыElectrical Test Program - Test: ABS/ASR Control Module (N30/1) Layout Connector 1 (Component Compartment)Paul Hanson Sr.Оценок пока нет
- Mini Cooper ATF Change PDFДокумент21 страницаMini Cooper ATF Change PDFLUKSmadrizОценок пока нет
- ENG Connecting DEC To MErcedes m102Документ3 страницыENG Connecting DEC To MErcedes m102Vincent RenaОценок пока нет
- 123 IndexДокумент18 страниц123 IndexembokoОценок пока нет
- MERCEDES MEDIC ACROYNMS GUIDEДокумент6 страницMERCEDES MEDIC ACROYNMS GUIDEDProkhorov100% (1)
- Emission Control PDFДокумент63 страницыEmission Control PDFoz23100% (1)
- Ford Fiesta Engine Cooling GuideДокумент28 страницFord Fiesta Engine Cooling GuideEko SulistyoОценок пока нет
- 18672622-2PPSRMS-2010 Porsche Panamera Service Repair Manual Software-1 PDFДокумент1 страница18672622-2PPSRMS-2010 Porsche Panamera Service Repair Manual Software-1 PDFTodor NakovОценок пока нет
- BOSCH Fuel Supply System MEV 17.4 Technical DescriptionДокумент4 страницыBOSCH Fuel Supply System MEV 17.4 Technical DescriptionRui MendesОценок пока нет
- Cylinder Head: 2011 Honda CR-V EX 2011 Honda CR-V EXДокумент149 страницCylinder Head: 2011 Honda CR-V EX 2011 Honda CR-V EXJosué PalaciosОценок пока нет
- Captiva 2.0L CDI Timing Belt R&RДокумент4 страницыCaptiva 2.0L CDI Timing Belt R&RSouth East Queensland 4x4Оценок пока нет
- Adjust Bosch KE3-Jetronic Mixture on Mercedes 560Документ5 страницAdjust Bosch KE3-Jetronic Mixture on Mercedes 560asamu10Оценок пока нет
- Diesel Fuel Injection Pump Disassemble Retainer Tools For SaleДокумент3 страницыDiesel Fuel Injection Pump Disassemble Retainer Tools For SaleChrisОценок пока нет
- Puma Race Engines - Peugeot 205 8 Valve Engine Tuning Guide: Blocks and CranksДокумент11 страницPuma Race Engines - Peugeot 205 8 Valve Engine Tuning Guide: Blocks and Cranksspidermaan67% (3)
- CIS-E Airflow Sensor Potentiometer Replacement GuideДокумент2 страницыCIS-E Airflow Sensor Potentiometer Replacement Guideazizja1100% (2)
- Boot Cable PDFДокумент2 страницыBoot Cable PDFSonny Jendhool SetyawanОценок пока нет
- GdiДокумент22 страницыGdiAnonymous ysrxggk21c100% (1)
- Bosch L-JetronicДокумент27 страницBosch L-Jetronicbarajas146100% (1)
- Harrop Lc200-1ur InstallДокумент22 страницыHarrop Lc200-1ur InstallArtur ElectroMecânicoОценок пока нет
- 1000 Manual 0407Документ60 страниц1000 Manual 0407Dharmesh patelОценок пока нет
- Rolls Bosch K Jetronic Injec 1Документ23 страницыRolls Bosch K Jetronic Injec 1mohhizbarОценок пока нет
- Diesel Pump and TimingДокумент60 страницDiesel Pump and TimingMickye Mickyedj100% (3)
- Vp44 Installation InstructionsДокумент4 страницыVp44 Installation InstructionsDony SuthanОценок пока нет
- K10B PDFДокумент93 страницыK10B PDFAkbar Zahid100% (1)
- CIRCUIT DIAGRAMДокумент40 страницCIRCUIT DIAGRAMYannick de WalqueОценок пока нет
- In This Issue: Brake System Service Toyota's Hybrid Vehicle Continuously Variable Transmission Power Steering ServiceДокумент40 страницIn This Issue: Brake System Service Toyota's Hybrid Vehicle Continuously Variable Transmission Power Steering ServiceDilan SenarathneОценок пока нет
- M800 OEM WRX78 Installation DocumentДокумент10 страницM800 OEM WRX78 Installation DocumentRaheel FaroukОценок пока нет
- THE IDIOT’S GUIDE TO TUNING SU CARBSДокумент7 страницTHE IDIOT’S GUIDE TO TUNING SU CARBSHimanshu SinghОценок пока нет
- Camshaft AdjustmentДокумент3 страницыCamshaft AdjustmentDevi Sharan PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Contrails ! Bosch VE Inection PumpДокумент17 страницContrails ! Bosch VE Inection Pumpesyjam100% (2)
- Hybrid P3130Документ6 страницHybrid P3130sajid_boyОценок пока нет
- GM ChargingДокумент20 страницGM ChargingMihai TacheОценок пока нет
- Range Rover P38 Diesel EngineДокумент5 страницRange Rover P38 Diesel EngineJoao Miguel Bernardo SaraivaОценок пока нет
- CatalogДокумент45 страницCatalogAbhinav SharmaОценок пока нет
- 206-06 Hydraulic Brake ActuationДокумент16 страниц206-06 Hydraulic Brake ActuationMiguel AngelОценок пока нет
- 206-03 Front Disc BrakeДокумент13 страниц206-03 Front Disc BrakeMiguel AngelОценок пока нет
- Mhi Turbo Applications MelettДокумент5 страницMhi Turbo Applications MelettSteven BraganОценок пока нет
- Robert Bosch Type VE Diesel Injection PumpДокумент5 страницRobert Bosch Type VE Diesel Injection PumpShahrizan abdul rahman0% (1)
- Heater & Air Conditioning Control System: SectionДокумент230 страницHeater & Air Conditioning Control System: SectionАндрей НадточийОценок пока нет
- OBD II Toyota Lexus PIDs List ModesДокумент6 страницOBD II Toyota Lexus PIDs List ModesMohamed Wahieb100% (1)
- 2006.02 Motor Toyota EVAP-Non-Intrusive SystemДокумент3 страницы2006.02 Motor Toyota EVAP-Non-Intrusive SystemMОценок пока нет
- Timing Belt Manual: From Professionals For ProfessionalsДокумент164 страницыTiming Belt Manual: From Professionals For ProfessionalsPetrus Van SchalkwykОценок пока нет
- Cam Angle Sensor GuideДокумент9 страницCam Angle Sensor Guideedwin1520Оценок пока нет
- Galant CH 2 Engine Electrical PDFДокумент14 страницGalant CH 2 Engine Electrical PDFjustcheerfulОценок пока нет
- Mitsubishi FTOДокумент14 страницMitsubishi FTOJhonatan JalluranaОценок пока нет
- Phun Xang Dien Tu p1 8097Документ351 страницаPhun Xang Dien Tu p1 8097Đức Hòang100% (1)
- Matrices IДокумент2 страницыMatrices IRaul Quispe RamirezОценок пока нет
- BOSCH D JetronicДокумент18 страницBOSCH D JetronicRaul Quispe RamirezОценок пока нет
- BOSCH D JetronicДокумент18 страницBOSCH D JetronicRaul Quispe RamirezОценок пока нет
- BOSCH D JetronicДокумент18 страницBOSCH D JetronicRaul Quispe RamirezОценок пока нет
- BOSCH D JetronicДокумент18 страницBOSCH D JetronicRaul Quispe RamirezОценок пока нет
- Diferencial de Deslizamiento Limitado Con Engranaje HelicoidalДокумент7 страницDiferencial de Deslizamiento Limitado Con Engranaje HelicoidalRaul Quispe RamirezОценок пока нет
- BOSCH D JetronicДокумент18 страницBOSCH D JetronicRaul Quispe RamirezОценок пока нет
- Power and Wiring Cables GuideДокумент82 страницыPower and Wiring Cables GuideZzzdddОценок пока нет
- User Manual Gd30fdcДокумент17 страницUser Manual Gd30fdcdedo3Оценок пока нет
- Bahrain World Trade Center Integrated Wind TurbinesДокумент73 страницыBahrain World Trade Center Integrated Wind TurbinesMaisie SuyatОценок пока нет
- Label Odner BantexДокумент4 страницыLabel Odner Bantexdana setiawanОценок пока нет
- Hybrid Safety and Service Procedures: Automotive Technology, Fifth EditionДокумент40 страницHybrid Safety and Service Procedures: Automotive Technology, Fifth EditionSkyAnimal ChannelОценок пока нет
- HVTS-70/50: Portable High-Voltage Test SystemДокумент2 страницыHVTS-70/50: Portable High-Voltage Test SystemvhendrayawanОценок пока нет
- Protection of Synchronous Machines: Application GuideДокумент44 страницыProtection of Synchronous Machines: Application GuideDerouich2019Оценок пока нет
- Wires and Cables PDFДокумент14 страницWires and Cables PDFRomel Panis88% (8)
- CT/PT Selection Chart: Applicable Standard (A) (V) CT's Qty PT PT's Part # PT's Qty Service Size CT CT's Part # PhaseДокумент1 страницаCT/PT Selection Chart: Applicable Standard (A) (V) CT's Qty PT PT's Part # PT's Qty Service Size CT CT's Part # PhasePrabakar PОценок пока нет
- Aeroshell Ascender: Performance, Features & Benefits Main ApplicationsДокумент3 страницыAeroshell Ascender: Performance, Features & Benefits Main ApplicationsRicardo LacskoОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics of Finned Tube Banks in Forced Convection (Comparison of The Heat Transfer Characteristics Between Spiral Fin and Serrated Fin)Документ14 страницHeat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics of Finned Tube Banks in Forced Convection (Comparison of The Heat Transfer Characteristics Between Spiral Fin and Serrated Fin)nadir adel100% (1)
- Rwu90 SpecsДокумент2 страницыRwu90 SpecsEduardo LuboОценок пока нет
- LV Rating Factors in GroundДокумент3 страницыLV Rating Factors in GroundChris MostertОценок пока нет
- Clase 05 - Chapter 9 - AAS-experimentalДокумент44 страницыClase 05 - Chapter 9 - AAS-experimentalLuisa GallegoОценок пока нет
- CV Nur Atikah ShaariДокумент2 страницыCV Nur Atikah ShaariMuhammad Khairuna SyahPutraОценок пока нет
- Reading Comprehension EnviromentДокумент5 страницReading Comprehension Enviromentandreapichoni100% (1)
- Paradeep Refinery Project: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine FutureДокумент35 страницParadeep Refinery Project: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine Futuremujeebtalib80% (5)
- Hvac-Question & AnswerДокумент4 страницыHvac-Question & AnswerKkrkollam KrishnaKumarОценок пока нет
- Final Examination in Thermodynamics IДокумент3 страницыFinal Examination in Thermodynamics IChristopher AlcarazОценок пока нет
- Bài Tập Đọc Hiểu Tiếng Anh Lớp 9 HKIIДокумент4 страницыBài Tập Đọc Hiểu Tiếng Anh Lớp 9 HKIIPhương Thu Vũ ThịОценок пока нет
- Laydown Light Towers: LED/Metal Halide/LED BalloonДокумент2 страницыLaydown Light Towers: LED/Metal Halide/LED BalloonAugusto BellezaОценок пока нет
- B S T Year 5Документ9 страницB S T Year 5INCREASE & ABUNDANT SCHOOLSОценок пока нет
- Copy of Vehicle-Maintenance-Record Work BacklogsДокумент41 страницаCopy of Vehicle-Maintenance-Record Work BacklogsHughoОценок пока нет
- Giz2014 en Market Potential Study Organic Rankine Cycle Technology India PDFДокумент68 страницGiz2014 en Market Potential Study Organic Rankine Cycle Technology India PDFdolphinОценок пока нет
- An Assessment of Singapore Airlines Environmentally Sustainable Energy ManagementДокумент15 страницAn Assessment of Singapore Airlines Environmentally Sustainable Energy ManagementMamta AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Exercise 8-Life ScienceДокумент2 страницыExercise 8-Life ScienceKarinaОценок пока нет
- Techniques de Commande Des Machines Electriques - Cours Et Problèmes..Документ2 страницыTechniques de Commande Des Machines Electriques - Cours Et Problèmes..Tko ToolОценок пока нет
- Apd NG150Документ5 страницApd NG150Magaly PeraltaОценок пока нет
- Turbo CompressorДокумент6 страницTurbo Compressorrajanrane420Оценок пока нет
- About The AuthorsДокумент1 страницаAbout The AuthorsArthur CostaОценок пока нет