Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Infectious Disease Fever of Unknown Origin: Fever 14d, T 38.3C On Mult Occasions, Uncertain
Загружено:
kcxieИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Infectious Disease Fever of Unknown Origin: Fever 14d, T 38.3C On Mult Occasions, Uncertain
Загружено:
kcxieАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Infectious disease Fever of unknown origin: Fever >14d, T>38.
3C on mult occasions, uncertain etiology Ddx includes: infection, CT disease, malignancy, other (IBD, kawasaki, drug) s/s: conjunctivitis, LAD, joint tenderness, thrush, heart murmurs, organomegaly, etc Diagnostic eval: - CBC + diff, electrolytes, BUN and creatinine, LFTs, alk phos, UA - Blood, urine, stool, CSF cultures - ESR, CRP - CXR, skin test for TB Condition Definition Epidemiology Etiology
Acute otitis media
Inflammation of middle ear
Narrowing of eustachian tube by edema in URI --> Eustachian tube vaccuum draws secretions in children: from nasopharynx to middle - angle of entry ear (horizontal) MCC: - short length - S. pneumo - decr tone - H. influenza - Moraxella
Sinusitis
Bacteremia and sepsis: Occult bacteremia - appears in well-appearing child with no obvious source of infection - highest in children 2-24 mo, T >39.0C, leukocytosis - MCC S. pneumo, resolves spontaneously Sepsis: bacteremia + systemic response, altered organ perfusion - Neonates: GBS, enteric gram neg, listeria - Children <5: S. pneumo, N. meningitidis - Children > 5: S. aureus - Other: Salmonella, pseudomonas, viridans strep - Evaluation: Blood, urine, CSF cultures, CXR if respiratory signs present Signs/symptoms Ddx Otitis media with effusion: fluid behind TM but no inflammation (no fever/ear pain) - no abx Myringitis: inflammation of eardrum - no abx Otitis externa (swimmer's ear): ear pain, but TMs looks normal, erythematous canal - topical abx drops Treatment 1. High dose amoxicillin, topical abx if perforated 2. augmentin, PO second or 3rd gen cephalosporin, or IM ceftriaxone S. pneumo: 50% penicillin resistant. H. influenza and M. catarrhalis: beta- lactamase activity Consider tympanostomy tube if moderate hearing loss, recurrent AOM
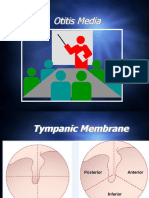
Ear pain, fever, fussiness, URI sxs TMs bulging, opaque, aberrant light reflex, decr mobility
ection
Complications Hearing loss, otitis media externa Meningitis (MC intracranial) Atopic constitution increases risk for recurrent OM Mastoiditis: severe, but uncommon - high fever, tenderness of mastoid bone
High Yield facts
Decr mobility of TM is most specific sign
Вам также может понравиться
- Board Review: PediatricsДокумент215 страницBoard Review: Pediatricsokurimkuri94% (16)
- Genetic Conditions For USMLEДокумент2 страницыGenetic Conditions For USMLEkcxieОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics NotesДокумент25 страницPediatrics Noteskcxie100% (12)
- Pediatrics NotesДокумент25 страницPediatrics Noteskcxie100% (12)
- Otorhinolaryngology Mnemonics by Medica Study CenterДокумент27 страницOtorhinolaryngology Mnemonics by Medica Study CenterPrekshi 1808Оценок пока нет
- 1-Ammar Notes (Med & Pedia)Документ23 страницы1-Ammar Notes (Med & Pedia)anmar alkhudhri100% (1)
- SketchyДокумент3 страницыSketchybellОценок пока нет
- Cns InfectionsДокумент141 страницаCns InfectionsReda AlyОценок пока нет
- Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisДокумент6 страницCavernous Sinus ThrombosisSulabh ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Signs in EntДокумент10 страницSigns in EntAbhishek BhardwajОценок пока нет
- MicrobesДокумент12 страницMicrobesDiMa MarshОценок пока нет
- Uworld Peds MicroДокумент5 страницUworld Peds MicroJoan ChoiОценок пока нет
- Pediatric SmleДокумент59 страницPediatric SmleMoayad Zeyad M100% (1)
- Tuberculosis in Infancy and ChildhoodДокумент8 страницTuberculosis in Infancy and ChildhoodsamioОценок пока нет
- Vasculitis - Student Notes Tabulated2Документ2 страницыVasculitis - Student Notes Tabulated2Kirstie de LunaОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia: Arto Yuwono Soeroto Sub Bag Pulmonologi Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK UNPAD / RSUP Dr. Hasan Sadikin BandungДокумент28 страницPneumonia: Arto Yuwono Soeroto Sub Bag Pulmonologi Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK UNPAD / RSUP Dr. Hasan Sadikin BandungMochamad HuseinОценок пока нет
- ASOMДокумент53 страницыASOMAyman YakoutОценок пока нет
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaДокумент24 страницыAcute Suppurative Otitis MediaDr Tipu SultanОценок пока нет
- Mers Nsg. DX Signs and Symtoms: Signs and Symtoms:: AtelectasisДокумент2 страницыMers Nsg. DX Signs and Symtoms: Signs and Symtoms:: AtelectasisRon ChristianОценок пока нет
- He Pat Ology 2016Документ26 страницHe Pat Ology 2016Kay BristolОценок пока нет
- Casea Omsk W Fas N PalДокумент28 страницCasea Omsk W Fas N PalMegan ShanzuОценок пока нет
- IVRSДокумент61 страницаIVRSAndrew ChinchillaОценок пока нет
- DocumentДокумент4 страницыDocumentpramod singhОценок пока нет
- Tonsillitis (Autosaved)Документ54 страницыTonsillitis (Autosaved)Ojasvi Manchanda100% (1)
- Suppurative Lung DiseaseДокумент45 страницSuppurative Lung DiseasemusabОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Pneumonia: Pisespong Patamasucon, M.D Pediatric Infectious DiseasesДокумент39 страницPediatric Pneumonia: Pisespong Patamasucon, M.D Pediatric Infectious DiseasesSi PuputОценок пока нет
- Middle Ear Diseases by Prof Mahmoud AttiaДокумент84 страницыMiddle Ear Diseases by Prof Mahmoud AttiaWesam TayaОценок пока нет
- Management of Diseases of Ear, Nose and ThroatДокумент16 страницManagement of Diseases of Ear, Nose and ThroatSaurabh LamkhadeОценок пока нет
- Infectious DiseasesДокумент24 страницыInfectious DiseasesEnrique ParedesОценок пока нет
- Unit X URTIДокумент37 страницUnit X URTIdiadiaidaОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Disorders in ChildrenДокумент77 страницRespiratory Disorders in ChildrenJharaОценок пока нет
- Case OMA DR - Oscar, SPTHTДокумент29 страницCase OMA DR - Oscar, SPTHTAndy XiaoОценок пока нет
- Otitis Externa: Pieter NaudéДокумент27 страницOtitis Externa: Pieter NaudéTri Wedari BlossomОценок пока нет
- Felyanto Puspa Haryani Wirda YunitaДокумент17 страницFelyanto Puspa Haryani Wirda YunitaSilvia Hari PrastiwiОценок пока нет
- W1 L1 URTI (Outdated)Документ41 страницаW1 L1 URTI (Outdated)Anas FikriОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Pathology: Dr. Okon MRCSДокумент38 страницRespiratory Pathology: Dr. Okon MRCSEdwin OkonОценок пока нет
- Bio For Nature ?Документ81 страницаBio For Nature ?SamueltilahunОценок пока нет
- Dse Pathogenesis/ Causes Diagnosis Complications TX Prognosis NotesДокумент5 страницDse Pathogenesis/ Causes Diagnosis Complications TX Prognosis NotesLuka Desabelle- JustoОценок пока нет
- Pharyngitis: Departemen T.H.T.K.L Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas PadjadjaranДокумент64 страницыPharyngitis: Departemen T.H.T.K.L Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas PadjadjaranEtusCelloОценок пока нет
- ASOMДокумент3 страницыASOMMalvinder Singh DhillonОценок пока нет
- Infectious DiseasesДокумент140 страницInfectious DiseasesSamah IzzОценок пока нет
- Infectious DiseasesДокумент96 страницInfectious Diseasesgaffararafath21Оценок пока нет
- Acute Tonsillopharyngitis, Its Suppurative Complication - 2Документ48 страницAcute Tonsillopharyngitis, Its Suppurative Complication - 2habtshОценок пока нет
- Hydatid Disease: or Iceberg SignДокумент53 страницыHydatid Disease: or Iceberg Signj.doe.hex_87Оценок пока нет
- Diseases of The LarynxДокумент28 страницDiseases of The LarynxDon AkmalОценок пока нет
- CH 06Документ12 страницCH 06yvanne josaphatОценок пока нет
- Case DR - Oscar OMAДокумент8 страницCase DR - Oscar OMApasukan5jari100% (1)
- Infectious DiseasesДокумент43 страницыInfectious Diseasesyoussef hamdy ibrahemОценок пока нет
- Communicable Diseases: InfectiousДокумент4 страницыCommunicable Diseases: InfectiousRichmond Catchillar BonusОценок пока нет
- Chronic Rhino Sinusitis With Suspect Ion Nasal Polyps NewДокумент50 страницChronic Rhino Sinusitis With Suspect Ion Nasal Polyps NewGary PradhanaОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics L6: Dodo AgladzeДокумент32 страницыPediatrics L6: Dodo AgladzeluckyОценок пока нет
- Paeds Case 1 - Writeup-1Документ14 страницPaeds Case 1 - Writeup-1Shakshi RainaОценок пока нет
- Quiz 1 PULMONOLOGY (Basics Table)Документ2 страницыQuiz 1 PULMONOLOGY (Basics Table)Paige HardekopfОценок пока нет
- "A Day Is Not Wasted, If A Memory Is Made" - AnonymousДокумент27 страниц"A Day Is Not Wasted, If A Memory Is Made" - AnonymousAzhersyedОценок пока нет
- Some Ear DisordersДокумент71 страницаSome Ear DisordersCosbyОценок пока нет
- Otitis MediaДокумент67 страницOtitis MediaFurqan MirzaОценок пока нет
- Kabale University School of Medicine Atuhairwe Ritah I6/A/MBCHB/0739/F Ent Department DR Nyanzi DanielДокумент10 страницKabale University School of Medicine Atuhairwe Ritah I6/A/MBCHB/0739/F Ent Department DR Nyanzi DanielMasai DanielОценок пока нет
- He He He HeДокумент11 страницHe He He HeAnj LTОценок пока нет
- 2 Otitis MediaДокумент19 страниц2 Otitis MediaAparna SinghОценок пока нет
- Infectious Diseases: A Geographic GuideОт EverandInfectious Diseases: A Geographic GuideEskild PetersenОценок пока нет
- ShoulderДокумент4 страницыShoulderkcxieОценок пока нет
- Dorsal Forearm and HandДокумент2 страницыDorsal Forearm and HandkcxieОценок пока нет