Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Foreign Studies NRES Chapter 2
Загружено:
Lyka Milo AvilaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Foreign Studies NRES Chapter 2
Загружено:
Lyka Milo AvilaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Foreign Studies [13]
A study by Richard W. Redman, PhD, RN /Carrie B. Lenburg, EdD, RN, FAAN /Patricia Hinton Walker, PhD, FAAN, Deals with competency assessment in nursing education.
Competency Assessment: Methods for Development and Implementation in Nursing Education Competent performance by health care professionals is expected throughout society. However, defining what it is and teaching students how to perform competently faces many challenges. This article provides a brief overview of the contemporary focus on competency assessment in nursing education. The redesigned nursing curriculum at the University of Colorado is presented as an exemplar of a practice-oriented model that requires competent performance among students. Methods for implementing a competency-based curriculum and lessons learned during the process are discussed.
Those in nursing education face many challenges. Students approach the learning institution with the assumption that they will be taught the requisite knowledge and skills to become competent nurses. Employers of nursing graduates assume that the nursing degree and the state licensure certify competent performance. Many definitional and methodological issues evolve from these assumptions. The social mandate for accountability, however, does not tolerate ambiguous assumptions or debate. While the assessment of competent practice in the service sector has received considerable attention the past 25 years, the implementation of competency assessment models in nursing education has moved at a much slower pace.
Multiple requirements for competent nursing practice in the health care system have been established by national associations and agencies. These include the American Nurses Association, the American Association of Critical Care Nurses Standards for Nursing Care of the Critically Ill and their Education Standards for Critical Care Nursing (Alspach, 1992). The Joint Commission for Accreditation of health care Organizations requires that clinical competence be assessed for all nursing staff and holds institutional leaders accountable for ensuring that competency of all staff is assessed, maintained, demonstrated, and continually improved (JCAHO, 1999).
Competency assessment is always outcome oriented; the goal is to evaluate performance for the effective application of knowledge and skill in the practice setting.
Competency assessment techniques address psychomotor, cognitive, and affective domains. Competencies can be generic to clinical practice in any setting, specific to a clinical specialty, basic or advanced (Benner, 1982; Gurvis & Grey, 1995).
Competency-based education has been found to be equally effective in both didactic and self-learning approaches (Lenburg, 1990; Schlomer, Anderson, & Shaw, 1997). Alspach(1984) presents hallmarks of competency-based education that make them applicable both in practice and in educational settings. These include competencies based on validation of what performance by competent practitioners actually comprises. In addition, competency assessment is based on criterion-referenced evaluation methods where the learners performance is evaluated against a set of criteria provided to the learner so that both the learner and the assessor are clear on what performance is required. Finally, competencybased education is learner-centered in that outcomes are specified and describe what the learner must do to demonstrate competency.
Masson & Fain (1997) discuss the value of a competency-based system in crosstraining, which is commonly used in todays cost-containment environment. They illustrate the effectiveness of a comprehensive system of competency validation for long-term staff, orientees, and nursing students.
Del Bueno reports it took approximately eight months of clinical experience before new BSN graduates felt confident and competent in their clinical judgments. Given the array of individual differences in nursing performance, she recommends that employers and educators assess competencies before assigning nurses to practice settings or advancing them in educational programs (Del Bueno, 1990).
The redesigned curriculum resulted in a unique approach to nursing education. The experience in converting to a competency-based curriculum has been both successful and challenging. Faculty and student experiences to date have been positive. The redesigned curriculum is viewed as responsive to the competency-oriented environment and employers believe the transition of graduates into practice settings will be more effective, efficient, and successful. This competency-based approach to education can serve as a model which offers a wide variety of applications to education and service environments.
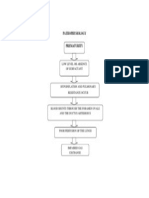
The researchers adopted the criterion-referenced evaluation methods. Competency is evaluated against a set of criteria. In this study, the criteria to be used is the Eleven Core Competency Standards.
Synthesis
CMO No. 14 mandates the implementation of the new nursing curriculum. It contains the standard curriculum and syllabi of the nursing subjects. This memorandum was developed to improve the competency of Filipino nurses and produce higly qualified nurses.
From the literatures collected, the researchers are able to extract the information that graduating nursing students are expected to be knowledgeable and confident in the 11 Core Competency areas. With this, the researchers will utilize the Core Competencies to test the graduating students knowledge and skills in terms of their duty in Related learning experience.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Roosevelt College System Institute of Nursing and Health Education Sumulong Cainta, RizalДокумент1 страницаRoosevelt College System Institute of Nursing and Health Education Sumulong Cainta, RizalLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology: Low Level or Absence of SurfactantДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology: Low Level or Absence of SurfactantLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- Head Nursing FrontpageДокумент1 страницаHead Nursing FrontpageLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- Record of VisitДокумент5 страницRecord of VisitLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Nursing Aptitude Test and Philippine Nursing Licensure ExaminationДокумент50 страницNursing Aptitude Test and Philippine Nursing Licensure Examinationchaos_knight100% (2)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Drug Study CeftriaxoneДокумент3 страницыDrug Study CeftriaxoneLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Calcibloc ODДокумент2 страницыCalcibloc ODianecunarОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Ma. Lizbeth A. EspirituДокумент1 страницаMa. Lizbeth A. EspirituLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Nursing Thesis ExampleДокумент10 страницNursing Thesis ExampleLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Nurse-Patient Interaction: Type/S of Therapeutic Communication Answer AnalysisДокумент5 страницNurse-Patient Interaction: Type/S of Therapeutic Communication Answer AnalysisLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Conceptusl Framework RevisedДокумент1 страницаConceptusl Framework RevisedLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Drug StudyДокумент40 страницDrug StudyLyka Milo AvilaОценок пока нет
- Ob Maternity NotesДокумент46 страницOb Maternity Notesr79cb5480100% (4)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)