Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Alkalinity of Water
Загружено:
roshan034Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Alkalinity of Water
Загружено:
roshan034Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
AIM: DETERMINE ALKALINITY (BY VISUAL TITRATION)
Introduction
The alkalinity of water may be defined as its capacity to neutralize acid, that is, the ability to maintain a relatively constant pH. Alkalinity of water may be due to the presence of one or more of a number
of ions. These include hydroxides, carbonates and bicarbonates. Alkalinity is important because it buffers against rapid pH changes. However, large amount of alkalinity imparts bitter taste in water.
Principle Alkalinity is determined by titration of the sample with a standard solution of a mineral acid. Sulphuric acid of known concentration is used. When titrated with acid, the OH-, CO32- and HCO3- ions will be neutralized.
Reagents to be used: a) Sodium carbonate solution, 0.05 mol L-1 b) Sulphuric acid, 0.05 mol L-1 c) Phenolphthalein indicator d) Methyl orange indicator
Apparatus a) Conical flask b) Burette c) Measuring Cylinder d) Volumetric pipette and pipette pump e) Beakers
Procedure
Part 1: Titration using Phenolphthalein Indicator
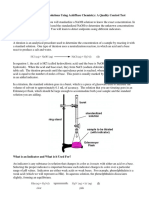
Standardization of Sulphuric Acid (to chek molarity of acid) a) The burette is tightly clamped and using a burette funnel, the burette is filled with sulphuric acid till about the 0 mark. The funnel is removed and the burette tap is opened so as to adjust the sulphuric acid at the 0 mark and to remove air bubbles in the burette. b) 25 ml of sodium carbonate solution is transferred to a conical flask with a 25 ml volumetric pipette and 20 ml of distilled water is added to it. c) 2 or 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator is added to the conical flask and swirled. The solution turns pink. d) A piece of white paper is placed under the conical flask before starting the titration so that colour change is easily seen. e) The initial burette reading is recorded. f) The Sodium Carbonate is then titrated with sulphuric acid until the pink colour disappears. g) The final burette reading is then recorded. h) The titration is again repeated so as to obtain a more accurate titration value.
Titration No. Final burette reading/ cm3 Initial burette reading/ cm3 Volume required/ cm3
1 28.60 0.00 28.60
2 28.60 0.00 28.60
The above procedure is then repeated using the sample of water. However, on addition of 2 or 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator, no colour change was observed. Hence we can conclude that phenolphthalein alkalinity is 0.
Part 2: Titration using Methyl Orange indicator a) The burette is tightly clamped and using a burette funnel, the burette is filled with sulphuric acid till about the 0 mark. The funnel is removed and the burette tap is opened so as to adjust the sulphuric acid at the 0 mark and to remove air bubbles in the burette. b) 100 ml of sample is placed in a conical flask and is mixed with a few drops of methyl orange indicator. The sample turns yellow. c) The initial burette reading is recorded. d) The sample is then titrated with the acid until the first perceptible colour change towards orange take place.
e) The final burette reading is then recorded. f) The titration is again repeated so as to obtain a more accurate value.
Titration No. Final burette reading/ cm3 Initial burette reading/ cm3 Volume required/ cm3
1 1.30 0.00 1.30
2 1.30 0.00 1.30
Calculations Phenolphthalein alkalinity (as CaCO3) = (A M 105) / V mg/L Where A = volume of standard acid solution (mL) to reach the phenolphthalein end point M = concentration of acid (mol/L) V = volume of sample (mL) The Phenolphthalein alkalinity is 0 since there is no colour produced.
Phenolphthalein alkalinity (as CaCO3) = 0
Total alkalinity (as CaCO3 ) = B x M x 105) / V mg/L Where B = Volume of standard acid solution (ml) to reach methyl orange end point M = concentration of acid (mol/L) V = volume of sample (mL) Therefore, total alkalinity (as CaCO3) = (1.30 x 0.05 x 105) / 100 = 65 mg/L Conclusion According to the WHO guidelines the alkalinity should be <200 mg/L, thus 65 mg/L lies within the said range.
Precautions The following precautions should be observed while performing the experiment: a) Do not keep the indicator solution open since it contains the alcohol which tends to evaporate. b) Care should be taken while handling acids. If in contact with skin, it should be immediately washed under running water.
Вам также может понравиться
- Distillation Lab Separates Acetone and Water MixtureДокумент3 страницыDistillation Lab Separates Acetone and Water MixtureVince100% (1)
- CHM170L - Final Report 3Документ5 страницCHM170L - Final Report 3Katrina BucudОценок пока нет
- Experiment Iii AlkalinityДокумент13 страницExperiment Iii Alkalinitycutetamtam101Оценок пока нет
- Total Alkalinity Determination - and Its Rule in An Aerobic Wastewater TreatmentДокумент8 страницTotal Alkalinity Determination - and Its Rule in An Aerobic Wastewater Treatmenthayder alaliОценок пока нет
- FerroceneДокумент20 страницFerroceneKalfakОценок пока нет
- Flame Tests Reveal Ion ColorsДокумент2 страницыFlame Tests Reveal Ion ColorsMark SakaguchiОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Resident EngineerДокумент5 страницResident Engineerroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Expt 1-Alkalinity of Water SampleДокумент4 страницыExpt 1-Alkalinity of Water SampleAbdul RehmanОценок пока нет
- Lab 3: AlkalinityДокумент7 страницLab 3: Alkalinityabulyalee0% (1)
- Lab Manual-Total AlkalinityДокумент4 страницыLab Manual-Total AlkalinitySuvanka DuttaОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4: Measuring AlkalinityДокумент7 страницExperiment 4: Measuring AlkalinityUbeiden CifuentesОценок пока нет
- Viscosity ExperimentДокумент17 страницViscosity Experimentmohammad. 21Оценок пока нет
- Lab Experiment AdsorptionДокумент7 страницLab Experiment AdsorptionchiragdbeckОценок пока нет
- Chem 156.1 Experiment 5 - Determination of Partial Molar VolumesДокумент4 страницыChem 156.1 Experiment 5 - Determination of Partial Molar Volumesティン ヨロベОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 7 (Chem 26.1)Документ12 страницLab Report 7 (Chem 26.1)Richelle Mae PadillaОценок пока нет
- Pseudo First Order ReactionsДокумент5 страницPseudo First Order ReactionsgiridharrajuОценок пока нет
- Electroplating Experiment Determines Faraday's ConstantДокумент3 страницыElectroplating Experiment Determines Faraday's ConstantMaiSakurajima100% (1)
- Experiment 2 Standardization of Sodium Hydroxide With HCLДокумент2 страницыExperiment 2 Standardization of Sodium Hydroxide With HCLvafaashkОценок пока нет
- Heat of Solution ReportДокумент29 страницHeat of Solution ReportFavour100% (1)
- Specific Heat of Metals ExperimentДокумент8 страницSpecific Heat of Metals ExperimentRobert MarcoliniОценок пока нет
- Conductometric TitrationsДокумент19 страницConductometric Titrationsusman_uet08100% (5)
- Total Alkalinity of Pond Water ExperimentДокумент5 страницTotal Alkalinity of Pond Water ExperimentKeziah Casco CortadoОценок пока нет
- Determination of Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) in Waste Water - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesДокумент3 страницыDetermination of Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) in Waste Water - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesIrfan SalimОценок пока нет
- The Heat of Solution LabДокумент4 страницыThe Heat of Solution Labapi-310957734Оценок пока нет
- Experiment No. (2) : Determination of Liquid Viscosity by Stock'S MethodДокумент5 страницExperiment No. (2) : Determination of Liquid Viscosity by Stock'S MethodKawar Abid100% (1)
- Experiment # 6 Heat of Solution Uy, Angelica A., Uson, Ma. Agatha Beatrice, Vargas, Louise ErikaДокумент7 страницExperiment # 6 Heat of Solution Uy, Angelica A., Uson, Ma. Agatha Beatrice, Vargas, Louise ErikaAngelica UyОценок пока нет
- Questions (Cod Lab Report)Документ1 страницаQuestions (Cod Lab Report)putriyusairah_91Оценок пока нет
- CHE 435 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Lab ManualДокумент24 страницыCHE 435 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Lab ManualStolen RememberОценок пока нет
- CHM170L Exp6 Heat of CombustionДокумент5 страницCHM170L Exp6 Heat of CombustionKaiser SaltoОценок пока нет
- Air Flow Velocity and Pressure Coefficient Around The 90o Rectangular Duct (Fluid Exp 5)Документ9 страницAir Flow Velocity and Pressure Coefficient Around The 90o Rectangular Duct (Fluid Exp 5)hayder alaliОценок пока нет
- Measure Water ConductivityДокумент7 страницMeasure Water ConductivitySilvy SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Inorg and Analytical Chemistry 1Документ39 страницInorg and Analytical Chemistry 1MhelveneОценок пока нет
- 1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityДокумент13 страниц1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityShaniCoolestОценок пока нет
- Heat of ReactionДокумент8 страницHeat of ReactionNece Jean Tagam83% (6)
- Fluid Flow Thru A Bed of Particles: Che 317E Particle TechnologyДокумент19 страницFluid Flow Thru A Bed of Particles: Che 317E Particle TechnologyJulie Anne Cristales100% (1)
- Optimized Solids Suspension: Achieving Uniform Dispersion is Critical to Product QualityДокумент7 страницOptimized Solids Suspension: Achieving Uniform Dispersion is Critical to Product QualitymichsantosОценок пока нет
- Detection of Ions in Solutions Using Acid/Base Chemistry: A Quality Control TestДокумент4 страницыDetection of Ions in Solutions Using Acid/Base Chemistry: A Quality Control TestRuchika Sood100% (1)
- Lab LleДокумент20 страницLab LleMuhamad Baihakhi Shamsudin100% (1)
- Adsorption From SolutionsДокумент4 страницыAdsorption From SolutionsJennifer Yano MangilaОценок пока нет
- Electrochemical Conductivity PDFДокумент18 страницElectrochemical Conductivity PDFwatum ambrose100% (1)
- BOD5 For Testing Polluted Water FIVE-DAY BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMANDДокумент9 страницBOD5 For Testing Polluted Water FIVE-DAY BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMANDhayder alaliОценок пока нет
- Electrolytic ConductanceДокумент8 страницElectrolytic Conductancevijaye36100% (1)
- Adsorption IsothermДокумент4 страницыAdsorption Isothermahkiujtsw0% (1)
- Nitrogen Phosphorus Detector TheoryДокумент3 страницыNitrogen Phosphorus Detector TheoryVarun Kumar100% (1)
- Momentum Problem Set PDFДокумент3 страницыMomentum Problem Set PDFNirmaan ShankerОценок пока нет
- HTL-04 Thermal Conductivity of LiquidДокумент2 страницыHTL-04 Thermal Conductivity of Liquidvindiesel9222Оценок пока нет
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsДокумент31 страницаColligative Properties of SolutionsKasandra AprestoОценок пока нет
- Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesДокумент3 страницыTitration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesMatthew Runyon50% (2)
- Instrumental AnalysisДокумент15 страницInstrumental AnalysisAbhiram ChandranОценок пока нет
- Experiment 8Документ4 страницыExperiment 8api-252952453100% (3)
- PRODUCTION OF HYDROGEN GAS USING ELECTROLYSISДокумент15 страницPRODUCTION OF HYDROGEN GAS USING ELECTROLYSISInda RobayaniОценок пока нет
- AbstractДокумент10 страницAbstractmarkОценок пока нет
- Measurement of The Gas Constant and Molar Volume of Oxygen GasДокумент12 страницMeasurement of The Gas Constant and Molar Volume of Oxygen GasJennifer Im0% (1)
- Transition Temperature of Salt HydratesДокумент2 страницыTransition Temperature of Salt HydratesDelin Shaji JohnОценок пока нет
- Determination of The Molecular Weight of Polystyrene Using Ubbelhode ViscometerДокумент5 страницDetermination of The Molecular Weight of Polystyrene Using Ubbelhode ViscometerMatthew OngОценок пока нет
- Hexane and Toluene Simple and Fractional DistillationДокумент12 страницHexane and Toluene Simple and Fractional Distillationrodneyperu0% (1)
- 09 Determining Mass and Mole RelationshipsДокумент9 страниц09 Determining Mass and Mole RelationshipsOmar Khan100% (1)
- Analytically ChemistryДокумент24 страницыAnalytically ChemistryWaleed El-azab100% (1)
- AlkalinityДокумент2 страницыAlkalinityMicrotesting labОценок пока нет
- Alkalinity of WaterДокумент3 страницыAlkalinity of WaterZeel PatelОценок пока нет
- Bes - Acid - Base TitrationДокумент7 страницBes - Acid - Base TitrationGhalib HusainОценок пока нет
- Potable WaterДокумент19 страницPotable Waterroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Spectroscopic Measurements and The BeerДокумент3 страницыSpectroscopic Measurements and The Beerroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Beer-Lambert Law: Spectrophotometer CuvetteДокумент1 страницаBeer-Lambert Law: Spectrophotometer Cuvetteroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Spreadsheets To BS 8110 & EC2 Advisory Group 32nd Floor - Corner Panel RMW 24-Aug-2020 130 CHG R68Документ1 страницаSpreadsheets To BS 8110 & EC2 Advisory Group 32nd Floor - Corner Panel RMW 24-Aug-2020 130 CHG R68roshan034Оценок пока нет
- Manufacture of SteelДокумент5 страницManufacture of Steelroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Standard Deviation and Variance (Example)Документ4 страницыStandard Deviation and Variance (Example)roshan034Оценок пока нет
- Guidelines on Electrical Installation DesignДокумент40 страницGuidelines on Electrical Installation DesignbalabhaviniОценок пока нет
- ASCE 7.10 - Wind Loads PDFДокумент60 страницASCE 7.10 - Wind Loads PDFOsama TamariОценок пока нет
- ASCE 7.10 - Wind Loads PDFДокумент60 страницASCE 7.10 - Wind Loads PDFOsama TamariОценок пока нет
- Cement Hydration Explained: The Chemical Reactions That Give Concrete Its StrengthДокумент4 страницыCement Hydration Explained: The Chemical Reactions That Give Concrete Its Strengthroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Spreadsheets To BS 8110 & EC2 Advisory Group 32nd Floor - Corner Panel RMW 24-Aug-2020 130 CHG R68Документ1 страницаSpreadsheets To BS 8110 & EC2 Advisory Group 32nd Floor - Corner Panel RMW 24-Aug-2020 130 CHG R68roshan034Оценок пока нет
- Verifying Bernoulli's Principle Lab ReportДокумент6 страницVerifying Bernoulli's Principle Lab Reportroshan034Оценок пока нет
- EcoДокумент1 страницаEcoroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Spreadsheets To BS 8110 & EC2 Advisory Group 32nd Floor - Corner Panel RMW 24-Aug-2020 130 CHG R68Документ1 страницаSpreadsheets To BS 8110 & EC2 Advisory Group 32nd Floor - Corner Panel RMW 24-Aug-2020 130 CHG R68roshan034Оценок пока нет
- Pavement Desig1Документ1 страницаPavement Desig1roshan034Оценок пока нет
- Traffic Analysis MethodДокумент8 страницTraffic Analysis Methodroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Pneumatic Tired RollerДокумент1 страницаPneumatic Tired Rollerroshan034Оценок пока нет
- House LayoutДокумент1 страницаHouse Layoutroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Flat SlabДокумент4 страницыFlat Slabroshan034Оценок пока нет
- FIDICДокумент5 страницFIDICroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Traffic ModelsДокумент2 страницыTraffic Modelsroshan034Оценок пока нет
- SwiimiДокумент1 страницаSwiimiroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Traffic SoftwareДокумент1 страницаTraffic Softwareroshan034Оценок пока нет
- HAChapter 03Документ15 страницHAChapter 03gskodikara2000Оценок пока нет
- Traffic QuestДокумент2 страницыTraffic Questroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Applications in Transportation Engineering: Systems PlanningДокумент1 страницаApplications in Transportation Engineering: Systems Planningroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Traffic ModelsДокумент1 страницаTraffic Modelsroshan034Оценок пока нет
- Traffic Analysis MethodДокумент8 страницTraffic Analysis Methodroshan034Оценок пока нет
- CH1502LДокумент87 страницCH1502LDivyakumar PatelОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Poster ExperimentДокумент8 страницChemistry Poster ExperimentPutri SalsabilaОценок пока нет
- Unit I Water TechnologyДокумент23 страницыUnit I Water TechnologyRajeevSangamОценок пока нет
- Unit I Water AnalysisДокумент8 страницUnit I Water AnalysisAyush Kr. SharmaОценок пока нет
- Exp No. 3: Standardization of HCL With Standard Na Co SolutionДокумент16 страницExp No. 3: Standardization of HCL With Standard Na Co SolutionAsif Ur Rahman AdibОценок пока нет
- Pharmaceutical Analysis ManualДокумент58 страницPharmaceutical Analysis Manualsrisabarigiri net centerОценок пока нет
- MODUL PINTAS 2020 TINGKATAN 5: KIMIA Kertas 3 September/OktoberДокумент13 страницMODUL PINTAS 2020 TINGKATAN 5: KIMIA Kertas 3 September/OktoberHafizoh HarunОценок пока нет
- SKL Lab Report 2Документ10 страницSKL Lab Report 2Nisha Lauren VishvanathОценок пока нет
- Results and Discussionexp1Документ4 страницыResults and Discussionexp1Vince PaelmoОценок пока нет
- What Are Different Chemical Tests On Concrete StructuresДокумент3 страницыWhat Are Different Chemical Tests On Concrete StructuresAnish PandeyОценок пока нет
- 111l Experiment 8 - NaohДокумент10 страниц111l Experiment 8 - NaohKrishna RajОценок пока нет
- Dextran 1 For InjectionsДокумент2 страницыDextran 1 For InjectionsMulayam Singh YadavОценок пока нет
- Forensic Analysis PDFДокумент20 страницForensic Analysis PDFhenriquehmОценок пока нет
- Acid-Base TitrationДокумент16 страницAcid-Base TitrationChloe KittyОценок пока нет
- NDT Concrete TestsДокумент36 страницNDT Concrete TestsYogesh KumarОценок пока нет
- WBM Important Testing ProceduresДокумент84 страницыWBM Important Testing ProceduresLazharОценок пока нет
- 20 CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL SAMPLES MSCEДокумент24 страницы20 CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL SAMPLES MSCEMalack ChagwaОценок пока нет
- CFP 00105 CHEMISTRY 1 - Laboratory Manual UNIKLДокумент21 страницаCFP 00105 CHEMISTRY 1 - Laboratory Manual UNIKLIrham SyahmiОценок пока нет
- Phenolphthalein Alkalinity TestДокумент3 страницыPhenolphthalein Alkalinity TestRosa JasmeneОценок пока нет
- Theory of Indicators Ostwalds TheoryДокумент3 страницыTheory of Indicators Ostwalds TheoryKala SuvarnaОценок пока нет
- Acid, Bases and SaltДокумент8 страницAcid, Bases and SaltAbdul Raheem UlОценок пока нет
- Acids, Bases and Salts: Factual QuestionsДокумент17 страницAcids, Bases and Salts: Factual QuestionsRahul RajОценок пока нет
- Experiment 6 Acid and Bases CHM 420Документ9 страницExperiment 6 Acid and Bases CHM 420najwa nabila100% (1)
- Chemistry Lab Journal Write UpДокумент44 страницыChemistry Lab Journal Write UprohitОценок пока нет
- Alkalinity of Water: Dr. Tejendra Kumar GuptaДокумент11 страницAlkalinity of Water: Dr. Tejendra Kumar Guptagaurav toppoОценок пока нет
- Bs8161 - Chemistry Laboratory Syllabus: Course ObjectivesДокумент47 страницBs8161 - Chemistry Laboratory Syllabus: Course ObjectiveslevisОценок пока нет
- Field Drilling Fluid TestsДокумент8 страницField Drilling Fluid TestsNakkolopОценок пока нет
- Lab. Manual On Environmental Engineering (Water and Waste Water EngineeringДокумент11 страницLab. Manual On Environmental Engineering (Water and Waste Water EngineeringSantosh Kumar100% (5)
- PS 13-2018Документ17 страницPS 13-2018Muhammad Sami100% (1)
- Inorg Chem Lab Manual PDFДокумент47 страницInorg Chem Lab Manual PDFPrateek bhardwaj100% (1)