Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lill's Method
Загружено:
Tony FosterАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lill's Method
Загружено:
Tony FosterАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lills Geometric Method for Approximating Polynomial Roots
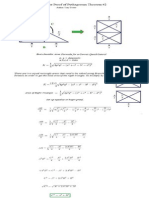
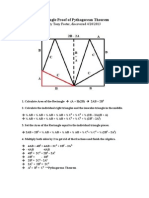
Author Tony Foster 1. Divide quadratic by leading coefficient (3) 2. Coefficients 1, 10, 11 are used in order for the quadratic pathway (green) 3. Starting point is (0,-1), move up +1 on the y-axis, and then follow the direction scheme below for the rest of the coefficients to construct the quadratic pathway. 4. Direction paths: horizontal path: + coefficients = left, - coefficients = right vertical path: + coefficients = down, - coefficients = up 5. Once quadratic path is finished, draw a line from the starting point to the terminus (blue dash line). Take a compass and draw a solution circle based on that diameter (blue dash line). 6. The roots of the quadratic equation will be where the circle intersects with the B-line (yellow points). The roots also can be found using the tangent of the angles shown below. (Notice that Lill made use of right angle pathways to approximate the roots)
1. Divide quadratic by leading coefficient if needed. 2. Coefficients 1,-10, -15 are used in order for the quadratic pathway (green) 3. Starting point is (0,-1), move up +1 on the y-axis, and then follow the direction scheme below for the rest of the coefficients to construct the quadratic pathway. 4. Direction paths: horizontal path: + coefficients = left, - coefficients = right vertical path: + coefficients = down, - coefficients = up 5. Once quadratic path is finished, draw a line from the starting point to the terminus (blue dash line). Take a compass and draw a solution circle based on that diameter (blue dash line). 6. The roots of the quadratic equation exist where the circle intersects with the X-axis (yellow points). The roots also can be found using the tangent of the angles shown below.
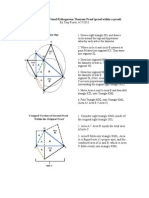
1. Coefficients of the quartic equation (10, 17, 15, 11, 3) are used for the quartic pathway starting at (0, 0). 2. Using the coefficients in sequence build the pathway by going right 10, up 17, left 15, down 11, rig. 3. Once the quartic pathway is made, construct a right angle pathway inside that reflects off the walls from the starting point to the terminus. The right angle pathway must reflect off the walls in such a way that when it arrives at the terminus, the pathway intersects the terminus point perfectly (see diagram below). If done by hand, this will take several attempts. 4. The root of the quartic can be ascertained by taking the tangent of the angle below (yellow).
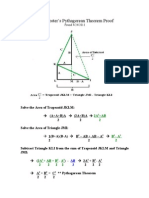
1. Coefficients 1, 14, 28, 14 are used for the cubic path (green) 2. Starting point is (0,-1). move up +1 on the y-axis 3. Using the coefficients in sequence, go left 14, down 28, and right 14. 4. Construct a right angle pathway that reflects off the walls from the starting point to the terminus (note: right angle pathway must intersect perfectly with terminus point (red point)) 5. Line B reveals a root (yellow point). Another method for find the root would be using the tangent of the angles shown in the diagram (blue)
Вам также может понравиться
- Horner's MethodДокумент12 страницHorner's Methodhmltdt9221Оценок пока нет
- BJT Basics 1Документ69 страницBJT Basics 1Sarvesh RajbharОценок пока нет
- Example A Small Signal Analysis of A BJT AmpДокумент10 страницExample A Small Signal Analysis of A BJT AmpFilipe da SilveiraОценок пока нет
- 1 FlowchartДокумент15 страниц1 FlowchartCharlene Leuterio Delas AlasОценок пока нет
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Report5 - BJT AmplifiersДокумент11 страницEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Report5 - BJT Amplifiersdonatello84100% (1)
- CAD Coordinate System ExerciseДокумент7 страницCAD Coordinate System ExerciseKate BarilОценок пока нет
- PermutationДокумент41 страницаPermutationAnurag Srivastav100% (1)
- 50 Simple Interest Problems With SolutionsДокумент46 страниц50 Simple Interest Problems With SolutionsArnel MedinaОценок пока нет
- Diode CircuitsДокумент23 страницыDiode CircuitsSurendra BachinaОценок пока нет
- Phi Coefficient Example Power Point 97-03Документ14 страницPhi Coefficient Example Power Point 97-03Rineeta BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Confidence IntervalДокумент14 страницChapter 8 Confidence IntervalFadli Bakhtiar AjiОценок пока нет
- BSEM 25 Lecture Chapter 1Документ3 страницыBSEM 25 Lecture Chapter 1Mari YanОценок пока нет
- Module 10 - Paralleling of DC GeneratorsДокумент24 страницыModule 10 - Paralleling of DC GeneratorsNoel Bacton100% (1)
- 3 - 3 An Useful Overview Of: Definitions Operations SAS/IML Matrix CommandsДокумент37 страниц3 - 3 An Useful Overview Of: Definitions Operations SAS/IML Matrix Commandsgebreslassie gereziherОценок пока нет
- SURVEYING Lec2 19 20Документ13 страницSURVEYING Lec2 19 20brandonОценок пока нет
- Experiment 2: Vector AdditionДокумент45 страницExperiment 2: Vector Additionamcb_003Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 04Документ17 страницChapter 04Ena BorlatОценок пока нет
- Determinants, Inverse, Adjoint, S.equationДокумент21 страницаDeterminants, Inverse, Adjoint, S.equationHARB Learning CentreОценок пока нет
- Lab Report - OscilloscopeДокумент3 страницыLab Report - Oscilloscopehyeon님Оценок пока нет
- 3-Geometrical Applications of IntegrationДокумент63 страницы3-Geometrical Applications of IntegrationKingshuk MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Part II - Codes PDFДокумент68 страницModule 2 Part II - Codes PDFChinee AmanteОценок пока нет
- Topic 3 - TrigonometryДокумент51 страницаTopic 3 - Trigonometryskyrunner31Оценок пока нет
- Iterative Methods System of EquationsДокумент8 страницIterative Methods System of EquationsAsim Aziz100% (1)
- Parallel Lines Cut by A Transversal ActivityДокумент5 страницParallel Lines Cut by A Transversal Activityapi-534095936Оценок пока нет
- Ch09-Areas and VolumesДокумент36 страницCh09-Areas and VolumesRizwan ullahОценок пока нет
- Problem SetsДокумент4 страницыProblem SetsMichael PantonillaОценок пока нет
- Applications of First Order Differential EquationsДокумент9 страницApplications of First Order Differential EquationsArt CaubaОценок пока нет
- SOLIDS FOR WHICH V (Mean Base) X (Height) Frustum of A Regular PyramidДокумент4 страницыSOLIDS FOR WHICH V (Mean Base) X (Height) Frustum of A Regular PyramidGil John Awisen0% (1)
- Trigonometric Limits PDFДокумент5 страницTrigonometric Limits PDFPhil Saraspe0% (1)
- Fieldwork No. 2 - Measuring Distances On Level Surfaces With A TapeДокумент5 страницFieldwork No. 2 - Measuring Distances On Level Surfaces With A Tapefotes fortesОценок пока нет
- Age ProblemsДокумент5 страницAge ProblemsSittieAyeeshaMacapundagDicaliОценок пока нет
- Learning CurvesДокумент6 страницLearning CurvesTimothy Liwag Quiros0% (1)
- University of Guyana, Department of Economics ECN 1203 Introductory Statistics Worksheet 2Документ3 страницыUniversity of Guyana, Department of Economics ECN 1203 Introductory Statistics Worksheet 2Shantie Pitt100% (1)
- The Definite Integral and Its ApplicationsДокумент13 страницThe Definite Integral and Its Applicationsapi-312673653100% (1)
- 6.1.1 The Multiplication RuleДокумент10 страниц6.1.1 The Multiplication RulehakimОценок пока нет
- 6 Unit 6 Practice TestДокумент10 страниц6 Unit 6 Practice Testapi-286079895Оценок пока нет
- Dot ProductДокумент11 страницDot ProductmadОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 PowerpointДокумент29 страницChapter 2 Powerpointalii2223Оценок пока нет
- Practice Problem 2 (s2 - 3)Документ1 страницаPractice Problem 2 (s2 - 3)de_stanszaОценок пока нет
- One Way AnnovaДокумент23 страницыOne Way Annovaanmolgarg129Оценок пока нет
- F Distribution PDFДокумент2 страницыF Distribution PDFTracyОценок пока нет
- Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Metals1.Документ34 страницыFerrous and Non-Ferrous Metals1.Daryl Gomez TimatimОценок пока нет
- 3.6 Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Three VariablesДокумент12 страниц3.6 Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Three VariablesBorhan Nordin DaudОценок пока нет
- D. EquationsДокумент39 страницD. Equationsmumtaz aliОценок пока нет
- Revcards SSMДокумент12 страницRevcards SSMapi-200177496Оценок пока нет
- Geo B 1 4 NotesДокумент1 страницаGeo B 1 4 Notesapi-276774539Оценок пока нет
- If You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanДокумент16 страницIf You Know The Coordinates of A Group of Points You CanSanaka LogesОценок пока нет
- Map Work O'levelДокумент18 страницMap Work O'levelDealОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1Документ10 страницLecture 1Paulpablo ZaireОценок пока нет
- Tarea IДокумент10 страницTarea IErison's SmithОценок пока нет
- Synergetics in The PlaneДокумент27 страницSynergetics in The PlaneIan BeardsleyОценок пока нет
- Contour LinesДокумент64 страницыContour LinesAkshay D NicatorОценок пока нет
- Analytic GeometryДокумент60 страницAnalytic GeometryLouise Umali100% (1)
- 3.2.1. Basics of GeometryДокумент10 страниц3.2.1. Basics of GeometryIsagaki RikuОценок пока нет
- Coordinate and GeometryДокумент98 страницCoordinate and GeometryTanveerAli01Оценок пока нет
- CONTOURINGДокумент68 страницCONTOURINGSwati ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- How To Solve The 3x3 CubeДокумент3 страницыHow To Solve The 3x3 CubeNikhil Devdhar100% (1)
- Math8 Q1 Week5Документ2 страницыMath8 Q1 Week5Marilou Iamztol RecamaraОценок пока нет
- Analytic GeometryДокумент72 страницыAnalytic GeometryindaiОценок пока нет
- Analytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)Документ9 страницAnalytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)James Lindo100% (1)
- Bretschneider Method of Proving Pythagorean TheoremДокумент1 страницаBretschneider Method of Proving Pythagorean TheoremTony FosterОценок пока нет
- The Precious Metals in Pascal's Triangle - Tony FosterДокумент12 страницThe Precious Metals in Pascal's Triangle - Tony FosterTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Bretschneider Number 2 Pythagorean Theorem ProofДокумент1 страницаBretschneider Number 2 Pythagorean Theorem ProofTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Continued Fraction For The Golden Ratio Using Fibonacci Squares - Author Tony Foster (7/5/2017)Документ4 страницыContinued Fraction For The Golden Ratio Using Fibonacci Squares - Author Tony Foster (7/5/2017)Tony FosterОценок пока нет
- Pretty Unique Parallelogram Pythagorean Theorem Proof - Author Tony FosterДокумент1 страницаPretty Unique Parallelogram Pythagorean Theorem Proof - Author Tony FosterTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Inverse Matrix QuestionДокумент1 страницаInverse Matrix QuestionTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Polynomial InterpolationДокумент4 страницыPolynomial InterpolationTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Creative Visual Solution of Solving The Area of A TriangleДокумент4 страницыCreative Visual Solution of Solving The Area of A TriangleTony Foster100% (2)
- Bird Proof, Pythagorean TheoremДокумент1 страницаBird Proof, Pythagorean TheoremTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Geometric Visual of Solving The Roots of A Cubic Equation - Tony FosterДокумент1 страницаGeometric Visual of Solving The Roots of A Cubic Equation - Tony FosterTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Quadratic Treasures From 10th Century Persia - Author Tony FosterДокумент2 страницыQuadratic Treasures From 10th Century Persia - Author Tony FosterTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Pythagorean Theorem ProofДокумент1 страницаPythagorean Theorem ProofTony Foster100% (1)
- Euclid Variant Pythagorean Theorem (Visual Proof)Документ2 страницыEuclid Variant Pythagorean Theorem (Visual Proof)Tony FosterОценок пока нет
- Solving A Triangle With Linear Algebra (No Reliance On Trigonometry or Heron's Formula) - Author Tony FosterДокумент3 страницыSolving A Triangle With Linear Algebra (No Reliance On Trigonometry or Heron's Formula) - Author Tony FosterTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Rectangle Pythagorean ProofДокумент2 страницыRectangle Pythagorean ProofTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Proof #6Документ1 страницаProof #6Tony FosterОценок пока нет
- Tony's ProofДокумент1 страницаTony's ProofTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Quick Way To Find A Leg On A Right TriangleДокумент1 страницаQuick Way To Find A Leg On A Right TriangleTony FosterОценок пока нет
- Find A Hypotenuse With Pascal's TriangleДокумент1 страницаFind A Hypotenuse With Pascal's TriangleTony FosterОценок пока нет
- SGCSE 6880 Syllabus - Mathematics PDFДокумент20 страницSGCSE 6880 Syllabus - Mathematics PDFLindela M Buz-BèéОценок пока нет
- CIRCLESДокумент3 страницыCIRCLESAswinОценок пока нет
- Maths April 2020 Paper 2 QPДокумент15 страницMaths April 2020 Paper 2 QPCW ShamОценок пока нет
- District Achievement TestДокумент2 страницыDistrict Achievement TestClark jhonОценок пока нет
- Mathematics: Daily Practice ProblemsДокумент12 страницMathematics: Daily Practice ProblemsvkОценок пока нет
- Vesica Piscis 153Документ16 страницVesica Piscis 153Marko TasicОценок пока нет
- Geometric Transformations IIIДокумент196 страницGeometric Transformations IIITirtha Darmayasa100% (6)
- Circles Part II PDFДокумент16 страницCircles Part II PDFTEJORAM PASUMARTHI100% (1)
- CirclesCTQP With Answer KeyДокумент4 страницыCirclesCTQP With Answer KeyAyush KumarОценок пока нет
- Descriptive Title: Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент50 страницDescriptive Title: Department of Mechanical EngineeringNikol NekolОценок пока нет
- Mathematics of Air and Marine Navigation PDFДокумент170 страницMathematics of Air and Marine Navigation PDFAbu Syeed Md. Aurangzeb Al MasumОценок пока нет
- Circle Geometry Part1Документ26 страницCircle Geometry Part1DolphingОценок пока нет
- Board Question Paper: March 2020 Mathematics Part - IIДокумент4 страницыBoard Question Paper: March 2020 Mathematics Part - IIAditya BorleОценок пока нет
- Megareview Group Study 4 SurveyingДокумент73 страницыMegareview Group Study 4 SurveyingSt Peter Life Plan ChapelОценок пока нет
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Manila NAME: - DATE: - Directions: Provide The Step-By-Step Solution To Select The Correct AnswerДокумент1 страницаTechnological Institute of The Philippines Manila NAME: - DATE: - Directions: Provide The Step-By-Step Solution To Select The Correct AnswerVince SantosОценок пока нет
- Geometry Scaffolding FrameworkДокумент10 страницGeometry Scaffolding FrameworkMelanieОценок пока нет
- AEEE 2024 Sample PaperДокумент98 страницAEEE 2024 Sample Paperaiswaryasakthivel007Оценок пока нет
- Philippine Mathematical OlympiadДокумент11 страницPhilippine Mathematical OlympiadRosen Dominic Escoto100% (1)
- Key Answer MathsДокумент14 страницKey Answer MathsMr ZekeОценок пока нет
- Revision Guide Aiming For 9Документ75 страницRevision Guide Aiming For 9Nayem Hossain HemuОценок пока нет
- Robert J. T. BellДокумент79 страницRobert J. T. BellAngshika DeyОценок пока нет
- Lesson Outline Grade 9 and 10 SY 2022-23Документ12 страницLesson Outline Grade 9 and 10 SY 2022-23Hassan AliОценок пока нет
- 30-12-19 - SR - Icon All - GTM-7 - CODE-B - Question Paper Key and SolutionsДокумент41 страница30-12-19 - SR - Icon All - GTM-7 - CODE-B - Question Paper Key and SolutionsGowri ShankarОценок пока нет
- Complete Maths For Cambridge IGCSE Extended 5eДокумент6 страницComplete Maths For Cambridge IGCSE Extended 5eMonydit santino100% (1)
- CGChapter 3Документ27 страницCGChapter 3Chandra DeepОценок пока нет
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 5: Secants, Tangents, Segments and Sectors of A CircleДокумент18 страницMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 5: Secants, Tangents, Segments and Sectors of A CircleJay Vincent MacadangdangОценок пока нет
- Study Centre April 24, 2018Документ40 страницStudy Centre April 24, 2018Joshua BlackОценок пока нет
- Top-100 Most Expected CAT Questions and Answers PDFДокумент59 страницTop-100 Most Expected CAT Questions and Answers PDFIqbal MohammadОценок пока нет
- In Euclidean GeometryДокумент32 страницыIn Euclidean GeometryGilar JatisundaОценок пока нет