Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
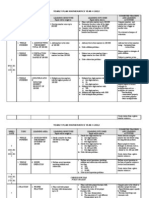
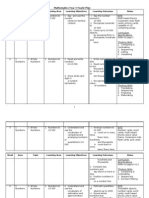
Mathematics Year 4 Yearly Plan 2012: Week Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Notes
Загружено:
Mazlan IshakИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mathematics Year 4 Yearly Plan 2012: Week Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Notes
Загружено:
Mazlan IshakАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
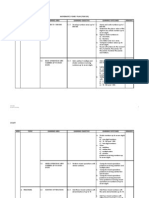
MATHEMATICS YEAR 4 YEARLY PLAN 2012
Week 1. Topic Learning Area 1. Numbers to 100 000 Learning Objectives 1. Develop number sense involving numbers of up to 100 000. Learning Outcomes i. Name and write numbers up to 100 000. ii. Determine the place value of the digits in any whole number up to 100 000. Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, flash cards, picture cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 1 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Sequencing 3. Listing 4. Visualizing 1. Whole Numbers 1. Numbers to 100 000 1. Develop number sense involving numbers of up to 100 000. iii. Compare value of numbers to 100 000. iv. Round off numbers to the nearest tens, hundreds and thousands. KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, flash cards, picture cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 1 Thinking Skills 1. Translating 2. Sequencing 3. Analysing 4. Elaborating 1. Whole Numbers 2. Addition with the highest total of 100 000. 1. Add numbers to the total of 100 000. i. Add any two to four numbers to 100 000: ii. Solve addition problems. KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, flash cards, picture cards, word cards.
1
4-6 Jan
Whole Numbers
2012
2
9-13 Jan
2012
Week
Topic
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
Learning Outcomes
Notes Curriculum Specifications Refer to pages 2 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Decision Making 3. Problem Solving
9-13 Jan
2012
21 29 JANUARI 2012 ( CUTI TAHUN BARU CINA )
1. Whole
4
30 Jan 3 Feb
Numbers
3. Subtraction within the range of 100 000.
1. Subtract numbers from a number less than 100 000.
i. Subtract one or two numbers from a bigger number less than 100 000. ii. Solve subtraction problems.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, flash cards, picture cards, word cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 3 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Decision Making 3. Problem Solving
2012
4 7 FEBRUARY 2012 ( MAULIDUR RASUL & THAIPUSAM )
1. Whole
5
8 10 Feb
Numbers
4. Multiplication with the highest product of 100 000.
1. Multiply any two numbers with the highest product of 100 000.
i. Multiply three-digit numbers with a) 100, b) two-digit numbers ii. Multiply four-digit numbers with a) one-digit numbers, b) 10, c) two-digit numbers
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, flash cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 4 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
2012
Week
Topic 1. Whole
Learning Area 4. Multiplication with the highest product of 100 000.
Learning Objectives 1. Multiply any two numbers with the highest product of 100 000.
Learning Outcomes iii. Multiply two-digit numbers with 1 000. iv. Solve multiplication problems.
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 4 & 5 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
6
13 17 Feb
Numbers
2012
1. Whole 5. Division with the highest dividend of 100 000. 1. Divide a number less than 100 000 by a twodigit numbers. i. Divide four-digit numbers by a) one-digit numbers, b) 10, 100 and 1 000, c) two-digit numbers. ii. Divide five-digit numbers by a) one-digit numbers, b) 10, 100 and 1 000, c) two-digit numbers. iii. Solve division problems.
7
20 24 Feb
Numbers
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 6 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 7 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
2012
8
27 Feb 3 Mac
1. Whole Numbers
6. Mixed Operations
1. Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction.
2012
i. Perform mixed operations involving addition and subtraction with numbers less than a) 100, b) 1 000, c) 10 000. ii. Solve mixed operation problems.
Week
Topic
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
Learning Outcomes
Notes
9
59 Mac
UJIAN FORMATIF 1
2012
10 18 MAC 2012 ( CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 1 )
2. Fractions 1. Proper Fractions 1. Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10. i. Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10. ii. Compare the value of two proper fractions with a) the same denominators, b) the numerator of 1 and different denominators up to 10. 2. Fractions 2. Equivalent Fractions 1. Express equivalent fractions i. Express and write equivalent fractions for proper fractions. ii. Express equivalent fractions to its simplest form. KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards, Cuisenaire rods Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 8 & 9 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
10
19 23 Mac
2012
11
27 30 Mac
2012
4
Week
Topic 2. Fractions
Learning Area 3. Addition of Fractions
Learning Objectives 1. Add two proper fractions with denominators up to 10.
Learning Outcomes i. Add two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form a) with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, b) with different numerators. ii. Add two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form a) with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, b) with different numerators. iii. Solve problems involving addition of proper fractions i. Subtract two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form a) with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, b) with different numerators. ii. Subtract two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form a) with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, b) with different numerators. iii. Solve problems involving subtraction of proper fractions
5
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards, Cuisenaire rods Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 10 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
12
2 6 April
2012
2. Fractions
4. Subtraction of Fractions
13
9 - 14 April
1. Subtract proper fractions with denominators up to 10.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards, Cuisenaire rods Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 11 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
2012
Week
Topic 3. Decimals
Learning Area 1. Decimal Numbers
Learning Objectives 1. Understand decimal numbers.
Learning Outcomes i. Name and write decimals with a) one decimal place, b) two decimal places. ii. Recognize the place value of a) tenths, b) hundredths, c) tenths and hundredths. iii. Convert fractions to decimals of a) tenths, b) hundredths, c) tenths and hundredths. and vice versa.
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards, Cuisenaire rods Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 12 & 13 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
14
16 - 20 April
2012
15
23 23 April
3. Decimals
2. Addition of decimal numbers
1. Add decimals up to two decimal places.
2012
i. Add any two to four decimals of one decimal place involving a) decimals only, b) whole numbers and decimals, c) mixed decimals. ii. Add any two to four decimals of two decimal places involving a) decimals only, b) whole numbers and decimals, c) mixed decimals. iii. Solve problems involving addition of decimal numbers.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards, Cuisenaire rods Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 14 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
Week
Topic 3. Decimals
Learning Area 3. Subtraction of decimal numbers
Learning Objectives 1. Subtract decimals up to two decimal places.
Learning Outcomes i. Subtract one to two decimals from a decimal of one decimal place involving a) decimals only, b) mixed decimals, c) whole numbers and decimals (mixed decimals). ii. Subtract one to two decimals of one or two decimal places. iii. Solve problems involving subtraction of decimals.
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards, Cuisenaire rods Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 15 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
16
30 April 4 Mei
2012
17
7 11 Mei
3. Decimals
4. Multiplication of decimal numbers
1. Multiply decimals up to two decimal places with a whole number.
i. Multiply any decimal of one decimal place with a) one-digit number, b) 10, 100 and 1 000. ii. Multiply any decimals of two decimal places with a) one-digit number, b) 10, 100 and 1 000. iii. Solve problems involving multiplication of decimals.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 16 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
2012
Week
Topic 3. Decimals
Learning Area 5. Division of decimal numbers
Learning Objectives 1. Divide decimals up to two decimal places by a whole number.
Learning Outcomes i. Divide decimals of one decimal place by a) one-digit number, b) 10. ii. Divide decimals of two decimal places by onedigit number. iii. Divide decimals by a whole number with the dividend value of up to two decimal places. iv. Solve problems involving division of decimals.
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, place value frame, number cards, word cards. Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 17 Thinking Skills 1. Elaborating 2. Drawing Conclusion 3. Problem Solving
18
14 18 Mei
2012
19
21 25 Mei
PEPERIKSAAN KENDALIAN SEKOLAH RENDAH ( PKSR 1 )
2012
26 MAY 10 JUNE 2012 ( CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN )
20
11- 15 Jun
4. Money
1. Money to RM10 000
1. Understand and use the vocabulary related to money. 2. Use and apply knowledge of money in real life.
i. Read and write the value of money up to RM10 000. i. Add money up to RM10 000. ii. Subtract money from up to RM10 000.
8
2012
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, simulation notes and coins, cut out notes and coins, flash cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 18 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Elaborating
Week
Topic 4. Money
Learning Area 1. Money to RM10 000
Learning Objectives 2. Use and apply knowledge of money in real life.
Learning Outcomes iii. Multiply money to the highest product of RM10 000. iv. Divide money with dividend not more than RM10 000. v. Perform mixed operation involving adddition and subtraction involving money up to RM10 000. vi. Round off money to the nearest ringgit. vii. Solve problems involving money of up to RM10 000.
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, simulation notes and coins, cut out notes and coins, flash cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 18 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Elaborating
21
18- 22 June
2012
5. Time
22
25 - 29 June
1. Reading and writing time.
1. Understand, read and write time in hours and minutes.
i. Read the time in hours and minutes according to the 12-hours system. ii. Write time in hours and minutes according to the 12-hours system.
KITS Analogue clock face, flash cards, number cards, word cards, phrase cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 19 Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing
2012
Week
Topic 5. Time
Learning Area 2. Time Schedule
Learning Objectives 1. Construct a simple schedule. 2. Read a calendar.
Learning Outcomes i. Construct, read and extract information from a simple schedule. i. Extract information from a calendar. ii. Solve simple real life problems involving reading the calendar.
Notes KITS Timetables of programmers, bus or flight schedule, calendars, cards, word cards, phrase cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to pages 20 Thinking Skills 1. Translating 2. Drawing Conclusion KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, number cards, word cards, phrase cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to pages 21 Thinking Skills 1. Drawing Conclusion 2. Relaying Information 3. Planning 4. Elaborating
23
26 July
2012
5. Time 3. Relationship between units of time. 1. Understand the relationship between units of time.
24
9 13 July
i. State the relationship between units of time:a) 1 day = 24 hours b) 1 year = 365 / 366 days c) 1 decade = 10 years ii. Convert a) years to days, and vice versa, b) decades to years, and vice versa, c) years to months, and vice versa, d) hours to days, and vice versa. iii. Convert time from a) hours to minutes, and vice versa, b) hours and minutes to minutes, and vice versa. c) minutes to hours and minutes, and vice versa.
2012
10
Week
Topic 5. Time
Learning Area 4. Basic operations involving time.
Learning Objectives 1. Add, subtract, multiply and divide units of time.
Learning Outcomes i. Add time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of: a) hours and minutes, b) years and months, c) decades and years. ii. Subtract time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of a) hours and minutes b) years and months, c) decades and years.
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, number cards, place value frame , word cards, phrase cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 22 Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing
25
17 20 July
2012
5. Time
26
23 27 July
4. Basic operations involving time.
1. Add, subtract, multiply and divide units of time.
2012
iii. Multiply time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of a) hours and minutes b) years and months, c) decades and years. iv. Divide time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units for time duration of a) hours and minutes b) years and months, c) decades and years. v. Solve problems involving basic operation of time: a) hours and minutes b) years and months, c) decades and years.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, number cards, place value frame, word cards, phrase cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 22 & 23 Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing
11
Week
Topic 5. Time
Learning Area 5. Time Duration
Learning Objectives 1. Use and apply knowledge of time to find the duration.
Learning Outcomes i. Read and state the start and and end of an event from a schedule. ii. Calculate the duration of an event from a schedule in a) minutes, b) hours, c) hours and minutes within a day and two consecutive live days. iii. Calculate the start or the end of an event from a given duration of time and read the start or end of an event.
Notes KITS Analogue clock face, flash cards, number cards, word cards, phrase cards, sentence cards, Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 24 Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing
27
30 July 3 Ogos
2012
6. Length
28
6 10 August
1. Measuring lengths
1. Measure lengths using standard units.
2012
i. Read measurement of length using units of milimetre. ii. Write measurement of length to the nearest scales of tenth division for a) centimetre, b) metre. iii. Measure and record lengths of objects using units of a) milimetre, b) centimeter and milimetre, c) metre and centimetre iv. Estimate the lengths of objects in a) milimetre, b) centimeter and milimetre, c) metre and centimetre
12
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, measuring tapes, rulers, objects of different length such as pencils, rope, ribbons place value frame, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 25 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Sequencing
Week
Topic
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
Learning Outcomes
Notes
29
13 - 17 August
UJIAN FORMATIF 2
2012
18 26 AUGUST 2012 (CUTI HARI RAYA AIDILFITRI & CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 2)
6. Length 2. Relationship between units of length. 1. Understand the relationship between units of length. i. State the relationship between centimetre and milimeter. ii. Convert units of length from: a) milimetres to centimetres and vice versa. b) compound units to a single unit. KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, measuring tapes, rulers, objects of different length such as pencils, rope, ribbons word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 26 Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing 4. Problem Solving
30
27-30 August
2012
13
Week
Topic 6. Length
Learning Area 3. Basic operations involving length.
Learning Objectives 1. Add and subtract length.
Learning Outcomes i. Add units of length, involving conversion of units in; a) milimetre, b) meter and centimetre, c) centimetre and milimetre. ii. Subtract units of length, involving conversion of units in; a) milimetre, b) meter and centimetre, c) centimetre and milimetre.
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, measuring tapes, rulers, place value frame, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 27 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Sequencing
31
37 September
2012
6. Length
32
10 14 September
3. Basic operations involving length.
2. Multiply and divide length.
i. Multiply units of length, involving conversion of units, by; a) a one-digit number, b) 10, 100, 1 000. ii. Divide units of length, involving conversion of units, by; a) a one-digit number, b) 10, 100, 1 000. iii. Solve problems involving basic operations of length.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, measuring tapes, rulers, place value frame, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 27 & 28 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Sequencing 3. Listing
2012
14
Week
Topic 7. Mass
Learning Area 1. Measuring mass 2. Relationship between units of mass
Learning Objectives 1. Measure mass using standard units. 2. Understand the relationship between units of mass.
Learning Outcomes i. Measure of masses using in units of kilogram and gram. ii. Read measurement of masses to the nearest scales division of kilograms and grams. iii. Estimate the masses of objects using kilograms and grams. i. Convert units of mass from a) kilograms to grams, b) kilograms and grams to grams, c) kilograms and grams to kilograms
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, weighing scales, flash cards, number cards, word cards, phrase cards, sentence cards, Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 29 & 30 Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing
33
18 21 September
2012
34
24 28 September
7. Mass
3. Basic operations involving mass.
1. Add and subtract involving unit of mass. 2. Multiply and divide units of mass.
i. Add mass involving units of mass in; a) kilograms, b) grams, c) kilograms and grams. ii. Divide mass involving conversion of units, by; a) a one-digit number, b) 10, 100, 1 000. iii. Solve problems involving basic operations with mass.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, weighing scales, flash cards, number cards, word cards, phrase cards, sentence cards, Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 31 & 32 Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing 4. Problem Solving 5. Relaying Information
2012
15
Week
Topic 8. Volume Of Liquid
Learning Area 1. Measuring volume of liquid
Learning Objectives 1. Measure and compare volume of liquid using standard units.
Learning Outcomes i. Read measurement of volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. ii. Write measurement of volume of liquid to the nearest scales of tenth division for a) litre b) mililitre. iii. Measure and record volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. iv. Estimate the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres i. Convert units of volume, from a) litres to mililitres, b) mililitres to litres, c) litres and mililitres to litres, d) litres and mililitres to mililitres.
Notes KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, measuring cylinders, variety of containers such as bottles, jugs, cans, cups, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 33 & 34 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Sequencing 3. Listing 4. Problem Solving 5. Relaying Information
35
1-5 Oktober
2012
2. Relationship between units of volume of liquid.
2. Understand the relationship between units of volume of liquid.
16
Week
Topic
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
Learning Outcomes
Notes
36
8 12 Oktober
8. Volume Of Liquid
3. Basic operations involving volume of liquid.
1. Add and subtract units of volume.
i. Add volume of liquid involving conversion of units in; a) litre, b) mililitre, c) litre and mililitre. ii. Subtract volume of liquid involving conversion of units in; a) litre, b) mililitre, c) litre and mililitre. i. Multiply volume of liquid involving conversion of units, by; a) a one-digit number, b) 10, 100, 1 000. ii. Divide volume of liquid involving conversion of units, by; a) a one-digit number, b) 10, 100, 1 000. iii. Solve problems involving volume of liquids. i. Identify the sides of a: a) square, b) rectangle, c) triangle. ii. Measure and record the perimeter of a: a) square, b) rectangle, c) triangle.
17
KITS Specific courseware, powerpoint presentation, place value frame, flash cards, number cards, word cards, sentence cards, Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 35 & 36 Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing
2012
2. Multiply and divide units of volume.
37
15 - 19 Oktober
9. Shape and Space
1. TwoDimensional Shapes
1. Understand the perimeter of a twodimensional shape.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, cut out cards of various polygons, pictures cards, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to page 37 & 38
2012
Week
Topic
Learning Area
Learning Objectives 2. Understand the area of a two-dimensional shape.
Learning Outcomes i. Identify the dimensions of a: a) square, b) rectangle, ii. Compare with unit squares the size of a: a) rectangle, b) square. iii. Measure and record the dimensions of squares and rectangles. Thinking Skills 1. Planning 2. Elaborating 3. Listing
Notes
37
15 - 19 Oktober
9. Shape and Space
1. TwoDimensional Shapes
3. Find the area and perimeter twodimensional shapes.
i. Calculate the area of square and rectangles. ii. Solve problems involving perimeter and area of twodmensional shapes.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, cut out cards of various polygons, pictures cards, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to pages 38 & 39 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Elaborating 3. Planning
2012
37
15 - 19 Oktober
9. Shape and Space
2. ThreeDimensional Shapes
1. Understand the volume for cubes and cuboids.
i. Identify the dimensions of cubes and cuboids. ii. Compare with a unit cube: a) cuboid b) cube iii. Measure and record the dimensions of cubes and cuboids.
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, cut out cards of various polygons, cards with tables, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to pages 40 & 41
2012
18
Week
Topic
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
2. Find the volume for cubes and cuboids.
Learning Outcomes
i. Calculate the volume of cubes and cuboids. ii. Solve problems involving volume of cubes and cuboids.
Notes
Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Elaborating 3. Listing 4. Planning KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, newspaper cutting, pictures cards, calendars, cards with tables, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to pages 42 & 43 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Elaborating 3. Listing 4. Planning
10. Data
1. Pictograph
38
22 23 October
1. Use a pictograph to read and display data.
Handling
2012
i. Describe a pictograph featuring a) the picture used to represent data, b) the title of the graph, c) what the axes represent, d) what one unit of picture represent. ii. Extract and interpret information from pictographs. iii. Construct pictographs to illustrate given in formations. iv. Solve a given problem by organizing and interpreting numerical data in pictographs.
24 28 OCTOBER 2012 ( CUTI HARI RAYA AIDILADHA )
19
Week
Topic
10. Data Handling
Learning Area
2. Bar Graph
Learning Objectives
2. Use bar graphs to read and display data.
Learning Outcomes
i. Describe a bar graph featuring a) the title of the graph, b) what the axes represent, ii. Extract and interpret information from bar graphs. iii. Construct bar graphs to illustrate given information. iv. Solve a given problem by organizing and interpreting numerical data in bar graphs.
Notes
KITS Specific courseware, power point presentation, newspaper cutting, pictures cards, calendars, cards with tables, word cards, sentence cards Curriculum Specifications Refer to pages 44 & 45 Thinking Skills 1. Comparing & Contrasting 2. Elaborating 3. Listing 4. Planning
39
29 Oct - 2 November
2012
40
59 November
PEPERIKSAAN KENDALIAN SEKOLAH RENDAH (PKSR 2)
2012
10 NOVEMBER 31 DISEMBER 2012 ( CUTI AKHIR TAHUN)
20
Вам также может понравиться
- Mathematics Year 5 Yearly Plan 2012: Week Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesДокумент22 страницыMathematics Year 5 Yearly Plan 2012: Week Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesMuhammadAl-fatehОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Year 4 Yearly Plan: Week Area Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesДокумент18 страницMathematics Year 4 Yearly Plan: Week Area Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesAsniza Mohd SaniОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Year 4 PlanДокумент21 страницаMathematics Year 4 PlanNas NasnMasОценок пока нет
- MATHEMATICS YEAR 5 YEARLY PLANДокумент19 страницMATHEMATICS YEAR 5 YEARLY PLANMasyitah AzizОценок пока нет
- Week Area Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesДокумент19 страницWeek Area Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesuchumanangОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2013Документ19 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2013Norwahidah RashidОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Year 5 Yearly PlanДокумент16 страницMathematics Year 5 Yearly PlanIsmayati OmarОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Year6 Bestari2015Документ14 страницYearly Plan Year6 Bestari2015Sangara NandaОценок пока нет
- Week Area Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesДокумент25 страницWeek Area Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesnanijikalОценок пока нет
- Yearly Mathematics Plan Year 4Документ17 страницYearly Mathematics Plan Year 4Yakin DayyanОценок пока нет
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2012Документ26 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2012sapuanazianОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Year 3 Yearly Plan: Week Area Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesДокумент15 страницMathematics Year 3 Yearly Plan: Week Area Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes NotesSk Kubang Telaga BachokОценок пока нет
- RPT Matematik Tahun 4Документ11 страницRPT Matematik Tahun 4mees-samaОценок пока нет
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 4 2013Документ15 страницYearly Scheme of Work Year 4 2013muhdmudzakkirОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Year 3 Yearly PlanДокумент20 страницMathematics Year 3 Yearly PlanAnonymous qXklPgGnMVОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4Sk Saujana Impian DuaОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4startecerОценок пока нет
- SK Seri Cempaka, Bandar Seberang Perak, 36800 Kampong Gajah, Perak Mathematics Yearly Plan Year 5Документ21 страницаSK Seri Cempaka, Bandar Seberang Perak, 36800 Kampong Gajah, Perak Mathematics Yearly Plan Year 5Zuhaidi YunusОценок пока нет
- Rpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Документ27 страницRpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Kee SekKhaiОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Mathematic Year 6Документ8 страницYearly Plan Mathematic Year 6Rosni OthmanОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 6 2013 Topic/ Learning Area Objectives/ Learning Out Comes RemarksДокумент2 страницыYearly Plan Mathematics Year 6 2013 Topic/ Learning Area Objectives/ Learning Out Comes RemarksNor AishahОценок пока нет
- RPT: Mathematics Year 5Документ20 страницRPT: Mathematics Year 5man_zero1984Оценок пока нет
- RPT MT Tahun 4 DLPДокумент26 страницRPT MT Tahun 4 DLPRaja Poobalan0% (2)
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2010Документ20 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2010Zoe KooОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan MathДокумент12 страницLesson Plan MathAlex BerlinОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan MathsДокумент8 страницYearly Plan MathsTasaratha Rajan AnamalaiОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyДокумент13 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyTravis MonroeОценок пока нет
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 4: Norahazleenda Hairuman SK Trolak SelatanДокумент16 страницYearly Scheme of Work Year 4: Norahazleenda Hairuman SK Trolak SelatanSalwa HanimОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 - 2012Документ8 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 - 2012mrdan100% (1)
- Year 5 Mathematics Yearly Plan OverviewДокумент19 страницYear 5 Mathematics Yearly Plan Overviewranj19869Оценок пока нет
- RPT Mathematics Year 4Документ9 страницRPT Mathematics Year 4YoNz AliaTiОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4hafidie83Оценок пока нет
- SK Seri Cempaka, Bandar Seberang Perak, 36800 Kampong Gajah, Perak Mathematics Yearly Plan Year 6Документ12 страницSK Seri Cempaka, Bandar Seberang Perak, 36800 Kampong Gajah, Perak Mathematics Yearly Plan Year 6Zuhaidi YunusОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN2Документ9 страницRPT MT THN2Hasnawati BachoОценок пока нет
- LP in Math Vi New Second Quarter (LRMDS)Документ82 страницыLP in Math Vi New Second Quarter (LRMDS)Ella Mendoza100% (1)
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 2013Документ8 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 2013Nurulnaim OmarОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4Malcom X MalcomОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Math 5Документ72 страницыLesson Plan Math 5Ronan Sibbaluca100% (6)
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 4Документ27 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 4Syafiah EppieОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiДокумент10 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiNajwa NurОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6Документ4 страницыMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6Faridah Binti KamaludinОценок пока нет
- MT Yearly Plan Year 1 6Документ6 страницMT Yearly Plan Year 1 6abusufian80Оценок пока нет
- MATHEMATICS YEARLY PLAN FOR YEAR SIXДокумент10 страницMATHEMATICS YEARLY PLAN FOR YEAR SIXnaim8889Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) 2010: WE EK Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksДокумент10 страницMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) 2010: WE EK Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksMoorsyidee MokhtaruddinОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN 6Документ11 страницRPT MT THN 6Mohd AsrafОценок пока нет
- DLP-Q2-WK6 MathДокумент15 страницDLP-Q2-WK6 MathShella Segui100% (1)
- RPT MT THN 6Документ11 страницRPT MT THN 6Denny PetrusОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 - 2013 - BiДокумент10 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 - 2013 - BimrdanОценок пока нет
- Matematik Tahun 2Документ6 страницMatematik Tahun 2Azmin OsmanОценок пока нет
- Multiplying Numbers Lesson for Grade 3Документ3 страницыMultiplying Numbers Lesson for Grade 3Jisbert Pablo AmpoОценок пока нет
- Year 6: Topic 1: Whole NumbersДокумент29 страницYear 6: Topic 1: Whole NumbersMuhammad Azrieen SamsudinОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan 2014 Year 5 Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objectives / Learning OutcomesДокумент8 страницMathematics Yearly Plan 2014 Year 5 Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objectives / Learning OutcomesMohd ZahariОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Year 3Документ8 страницYearly Plan Year 3Shima OmarОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersДокумент3 страницыMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersRamziah BongsuОценок пока нет
- DLP - Mathematics 3 - Q1-Q4Документ224 страницыDLP - Mathematics 3 - Q1-Q4Apple DocasaoОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 6 - 2012Документ6 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 6 - 2012mrdanОценок пока нет
- Daily Lesson Plan Mathematics Year 3Документ2 страницыDaily Lesson Plan Mathematics Year 3BrianОценок пока нет
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6От EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6Оценок пока нет
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5От EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5Оценок пока нет
- Math Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeОт EverandMath Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Kbat - PPD UtaraДокумент46 страницKbat - PPD UtaraMazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- Math Final Paper 2Документ3 страницыMath Final Paper 2Mazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- Math Final Paper 2Документ3 страницыMath Final Paper 2Mazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- Bank Soalan Thn3-1Документ13 страницBank Soalan Thn3-1Mazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- Understanding Fractions for BeginnersДокумент8 страницUnderstanding Fractions for BeginnersMazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- Matematics Years 4 Jsu 2008Документ4 страницыMatematics Years 4 Jsu 2008St TeresaОценок пока нет
- Answer All The Question. Circle The Correct Answer For Each QuestionДокумент8 страницAnswer All The Question. Circle The Correct Answer For Each QuestionMazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Year 6 Yearly Plan 2012Документ21 страницаMathematics Year 6 Yearly Plan 2012Mazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- FractionДокумент17 страницFractionMazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid CarДокумент6 страницThe Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid CarMazlan IshakОценок пока нет
- Tax - CIR Vs Cebu Toyo DigestДокумент3 страницыTax - CIR Vs Cebu Toyo DigestDyannah Alexa Marie RamachoОценок пока нет
- Underpinning Methods, Procedure and ApplicationsДокумент10 страницUnderpinning Methods, Procedure and ApplicationsShivaun Seecharan0% (1)
- C15 DiagranmaДокумент2 страницыC15 Diagranmajose manuel100% (1)
- School Development Plan 2022Документ3 страницыSchool Development Plan 2022Nora Herrera100% (6)
- Danfoss DatasheetДокумент74 страницыDanfoss DatasheetzansОценок пока нет
- Moral Agent - Developing Virtue As HabitДокумент2 страницыMoral Agent - Developing Virtue As HabitCesar Jr Ornedo OrillaОценок пока нет
- Ahmed (2018)Документ9 страницAhmed (2018)zrancourttremblayОценок пока нет
- EM24DINDSДокумент14 страницEM24DINDSJavaprima Dinamika AbadiОценок пока нет
- Science 7 Module1Документ22 страницыScience 7 Module1Hector Panti0% (1)
- Chapter 4-Market EquilibriumДокумент24 страницыChapter 4-Market EquilibriumAiman Daniel100% (2)
- Linux Plus Lpi LabsДокумент94 страницыLinux Plus Lpi LabsKamib HamibebОценок пока нет
- SteroidsДокумент2 страницыSteroidsShawn FreemanОценок пока нет
- Piping and Equipment IsolationДокумент8 страницPiping and Equipment IsolationBilal Mustafa Siddiqui100% (1)
- Eslit-Vinea-LA 03 Task #1-4Документ11 страницEslit-Vinea-LA 03 Task #1-4darkОценок пока нет
- Hepatobiliary Surgery BlumgartДокумент301 страницаHepatobiliary Surgery Blumgartaejazahsan100% (7)
- SITXWHS001 Participate in Safe Work Practices - Training ManualДокумент82 страницыSITXWHS001 Participate in Safe Work Practices - Training ManualIsuru AbhimanОценок пока нет
- Beginning of Agriculture Northern Vindhyas Middle Gangetic PlainsДокумент17 страницBeginning of Agriculture Northern Vindhyas Middle Gangetic Plainsakshat aggarwal100% (1)
- Mr. Frank Remedios Certified Career Counselor Authorised Franchise-Brain CheckerДокумент24 страницыMr. Frank Remedios Certified Career Counselor Authorised Franchise-Brain Checkerrwf0606Оценок пока нет
- Family Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыFamily Nursing Care PlanSophia Ella OnanОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics of Knee Joint - 20 Questions-2Документ5 страницBiomechanics of Knee Joint - 20 Questions-2rehab aymanОценок пока нет
- Preparing For 2024: Election Technology and The Battle Against DisinformationДокумент13 страницPreparing For 2024: Election Technology and The Battle Against DisinformationVerified VotingОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7, 8, 9Документ11 страницChapter 7, 8, 9Rubilyn IbarretaОценок пока нет
- 150 C++ BitsДокумент55 страниц150 C++ BitsRavi Varma D V SОценок пока нет
- Bank 12Документ19 страницBank 12Shivangi GuptaОценок пока нет
- Appetizers Fire-Grilled Gourmet Burgers: Red Robin'S Finest Burgers Red'S Tavern MenuДокумент2 страницыAppetizers Fire-Grilled Gourmet Burgers: Red Robin'S Finest Burgers Red'S Tavern MenufruitfuckОценок пока нет
- Gen-6000-0mh0/0mhe Gen-6000-0mk0 Gen-6000-0ms0/0mse Gen-7500-0mh0/0mhe Gen-8000-0mk0/0mke Gen-8000-0ms0/0mseДокумент26 страницGen-6000-0mh0/0mhe Gen-6000-0mk0 Gen-6000-0ms0/0mse Gen-7500-0mh0/0mhe Gen-8000-0mk0/0mke Gen-8000-0ms0/0mseAhmed Khodja KarimОценок пока нет
- User Manual With FAQs - Sales Invoice For Petrol PumpsДокумент10 страницUser Manual With FAQs - Sales Invoice For Petrol PumpsRavindra MittalОценок пока нет
- Lahore School of Economics Operations Management Final Group Project Outline (Weightage 15%) Bba - Iv Instructor: Dr. Saba Fazal FirdousiДокумент3 страницыLahore School of Economics Operations Management Final Group Project Outline (Weightage 15%) Bba - Iv Instructor: Dr. Saba Fazal FirdousiAshir HassanОценок пока нет
- Boast 98Документ19 страницBoast 98jghleivaОценок пока нет
- Cambridge O Level: Agriculture 5038/12 October/November 2020Документ30 страницCambridge O Level: Agriculture 5038/12 October/November 2020Sraboni ChowdhuryОценок пока нет