Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ulasan Artikel Journal
Загружено:
my_sweetheart820 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
655 просмотров7 страницJournal 1 summarizes a classroom observation of a student teacher employing more student-centered and engaging teaching methods in a 6th grade classroom. The students responded positively and were more focused and motivated to learn. Journal 2 describes a program where English language trainee teachers conduct action research on their own teaching in pairs. They analyze data, plan research, and present findings. Journal 3 outlines a graduate education course where the professor co-constructs the syllabus and assessments with students over three class sessions. Students provided input into topics and requirements and expressed feeling their needs were met in the flexible course design.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документJournal 1 summarizes a classroom observation of a student teacher employing more student-centered and engaging teaching methods in a 6th grade classroom. The students responded positively and were more focused and motivated to learn. Journal 2 describes a program where English language trainee teachers conduct action research on their own teaching in pairs. They analyze data, plan research, and present findings. Journal 3 outlines a graduate education course where the professor co-constructs the syllabus and assessments with students over three class sessions. Students provided input into topics and requirements and expressed feeling their needs were met in the flexible course design.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
655 просмотров7 страницUlasan Artikel Journal
Загружено:
my_sweetheart82Journal 1 summarizes a classroom observation of a student teacher employing more student-centered and engaging teaching methods in a 6th grade classroom. The students responded positively and were more focused and motivated to learn. Journal 2 describes a program where English language trainee teachers conduct action research on their own teaching in pairs. They analyze data, plan research, and present findings. Journal 3 outlines a graduate education course where the professor co-constructs the syllabus and assessments with students over three class sessions. Students provided input into topics and requirements and expressed feeling their needs were met in the flexible course design.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 7
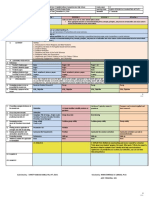
JOURNAL ANALYSIS
Item Journal 1 Journal 2 Journal 3
Sample -Students of a sixth grade -Trainee English Language -Graduate students of
classroom Teacher education program
Setting -A professional development -Sino-British MA in English -Foundation of education
school associated with the programme at Beijing Normal class at university
Benedum Five Year Teacher University
Education Program.
Procedures -Students were forced to think for -Research project was runs -The researcher asked the
themselves, encouraged to ask parallel to both teaching practice students to join her in co-
questions and participate fully in and ELT Methodology constructing the full course.
class discussions. The student components (2 semesters). -Day one:
teacher wanted to hear how they -The trainee teacher work in Discussed about the
related what they were studying pairs. students’ preferences. Did
to themselves or prior -Teaching English (five contact they want a teacher-directed
experiences. Students quickly hours each week) to science and course or a more student-
learned that once they got humanities undergraduates at centred one? Virtually all the
through background information the university (one class of class of twenty-five sided
on a new topic, they would get students for entire year) with the more student-
into truly engaging activities, -Involved two stages; 1) directed philosophies, and
which led to their being more Familiarize the participants both the researcher proceed with
focused and motivated to learn theoretically and practically with co-construction. The
throughout. the action research approach on researcher asked the
-Copying vocabulary terms into 1st Semester. students to come up with
notebook, a classroom read of -An understanding of what action questions, topics, and
background information, and a research is and what it is for. themes they wanted to
follow-up Arts integrative activity -By organize workshops, tackle. Before proceeding to
corresponding to the new seminars, and discussions their input, the researcher
information. designed to allow them to offered the caveat that they
- The student teacher felt that the discover the meaning of action needed to coexist with the
activities and classroom research for themselves, and to more teacher-directed
discussion were more meaningful reflect about its nature and philosophy of the university
to the students than were origins. as a whole and stick to
completing workbook pages. But -1st step: Initiate a discussion by topics generally related to
the student teacher was giving a number of statements the mandated foundations
obligated to finish workbook (comments & criticisms about content (history, philosophy,
pages assigned by the host teacher training programmes sociology of schooling). Then
teacher, these were often collected from classroom they went through a
assigned as homework. Once teachers & educators) and some PowerPoint presentation on
students recognized the trade-off practical questions about them; topics typically covered in a
and found that they enjoyed the ask them to consider the foundations course (hidden
new teaching style, they stopped statements & the questions in curriculum, nature and aims
complaining about homework the light of their own experiences of education, history of
assignments. and beliefs. education, funding and
-2nd step: Divide students into organization of schools,
groups. Each group is assigned a socialization of social class,
reading task with specific gender, and race and
questions on different aspects of ethnicity, curriculum and
the theories of action research. knowledge, achievement
The group then research their and ability).
questions and familiarize with the -Day two:
available literature on action Launched immediately into
research. So that they can co-constructing the course
present a seminar paper on their requirements. The
topic. researcher asked the class
-3rd step: Looking at data. An to create an agenda of
examination of various data discussion items, such as
collection techniques, including participation, attendance,
case studies, audio and video short-term (more frequent,
techniques, teacher and learner minor) assessment, long-
diaries, questionnaires, term (less frequent, major)
interviewing, and classroom assessment, and content.
observation sheets. Each student was assigned
-There are 2 aims of study to a task force that dealt
authentic examples of each type with one topic. Each task
of data: force was charged with
1) To show trainees what sort of collecting classmates’ input
material it sis possible to collect on its topic (by interviewing
from their own classrooms, and or by posting questions on
what that material can reveal chart paper to collect
about teaching & learning answers) and then
processes discussing what suggestions
2) To equip them with the skills to make to the whole class
necessary to construct their own on that topic. The task forces
data-collecting instruments. collected input and met for
-Task for trainees: thirty to forty minutes, and
a) Video and audio data then came together as a
-Trainees observed and whole class to discuss the
discussed about the data from myriad ideas.
databank of video and audio -Day three:
tapes of former trainees. The third night of class
-Through discussion of their began by asking the
observation results the trainee students to journal on these
teachers become sensitized to questions: What do you
problem they may never have think of the new syllabus
thought about before, and begin and grade menu? Do you
to establish a critical attitude believe your needs were
towards their own teaching. met? Will you feel
b)Questionnaires comfortable exercising your
-Trainee teacher analysed “protest rights” if some
questionnaires containing data aspect of the syllabus ends
on English teaching or learning up being problematic?
problem (data collected from the Again, responses were
class taught by trainee teacher in positive.
the previous year). Nearly all students
-They have to analysis a pack of expressed appreciation of
questionnaires from one class of the level of choice and
students (work in teaching pair), flexibility and indicated that
and asked to prepare an oral their opinions, concerns, and
presentation and a written report questions had been taken
on the design of the into account. The process
questionnaires and on its also seemed to reduce, to a
findings, and the possible degree, conventional
implications of the findings for teacher-student antagonism:
their own teaching. many students expressed
4th step: Planning the research. comfort with protesting or
Each trainee teacher pairs raising future questions. It
planning their research. There seemed that the students
are 4 steps in planning research: had “bought into” the course
1) Problem identification session and that they were
2) Preliminary investigation beginning to trust the
3) Formulation of possible researcher as well as their
solutions fellow students. Overall the
4) Data collection and evaluation class displayed a positive
ambience; the students
2) Students teaching pairs seemed to realize that the
undertake their own cycle of researcher was not trying to
research with their TP class on 2nd “force” them to do
Semester. something.
-The focus is on the full-scale -The researcher start the
implementation of the research first discussion topic by
plan. asking the class why all
-Tutor input at this stage mainly courses are not c-
takes the form of weekly tutorial constructed. Responses
meetings with trainee teachers to included all the challenges
discuss specific problems and to democratic education
solutions, stages of outlined in “Democratic
implementation, data collecting Classrooms: Promises and
instruments, and data analysis. Challenges of Student Voice
-Lesson observed regularly, face and Choice (Morrison 2008),
to face and written feedback to and the students really
help trainees with the practical seemed to understand the
skills of teaching. difference between a
-By the end of the second personally meaningful
semester, a research report is education and “schooling”
required of each pair, which through the hidden
should include problems curriculum: doing what
identified for the next cycle of others ask without thought
research, as well as possible of one’s own needs and
solutions. interests.
-At the end of the semester,
to obtain empirical
confirmation of this
perception of student
engagement, the researcher
distributed a questionnaire
culled from the National
Survey of Student
Engagement. Then the
researcher analysis the
responses.
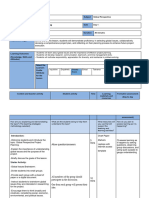
Collecting & Analysing -Reflective teaching journal to -Observation -Journal
Data record daily conversation -Research report prepared by -Observation
regarding how they felt about the trainee teacher pairing -Survey
lessons and what changes were -Questionnaire
going on in the classroom, daily
notes on how each activity went
and if any modifications should
be made for future lessons,
student participation levels for
each lesson and activity.
-An informal online Multiple
Intelligence evaluation was given
to students at the start of the
study in order to understand
students’ interest and current
areas of strength. Result from the
Multiple Intelligence evaluations
were used as a guide to create
diverse and engaging lesson
plans. Students completed
attitude surveys at the beginning
and end of the Action Research
project. This survey gave insight
into how students felt about
social studies before and after
Arts integration was
implemented.
-At the end of each lesson,
students would complete a “Rate
this Lesson” card using 1-10 scale
and including written feedback
regarding their least and most
favourite aspects of the lesson or
activity. The students’ ratings and
feedback were incorporated into
subsequent lesson.
-Three big projects (students had
choice as to how to represent
their learning) were graded using
rubrics specific to the type of
project turned in. Tests, quizzes,
workbook pages, and graphic
organizer allowed students to
earn points, as did participation in
classroom activities and
discussion.
-Data analysis was an ongoing
process throughout the study. The
student teacher reflected daily on
lessons taught and data
collected, using those reflections
to plan subsequent lessons.
Based on “Rate this Lesson”
scores and students’ written
comments, lesson with highest
ratings were grouped to find
common threads. If most
students did not like a particular
activity or assignment and
participation was low on that say,
that activity removed from
subsequent lesson plans.
Finding, Result and -The student teacher gained a -Increased awareness of teaching --This approach is especially
Discussion variety of skills and knowledge and learning process necessary and
that she could not have learned -Improvement in classroom transformative for
in a classroom lecture setting. research skills individuals who will be or
-By offering students choice and -Increased awareness and who are teacher. These
mobility in classroom activities sensitivity about the classroom individuals need such
was a great way to get students situation experiences to widen their
involved in the learning process. -More variety of classroom vision of what education can
-Students were much more activities be and to begin to imagine
involved in activities that were themselves
different from what they saw as as the agents of change.
“regular classroom activities” and
hands-on activity.
-The most important aspect of
this study was the relationship
and communication between
teacher and students. Students
must know exactly what the
teacher will be doing and what
she expected from them. (two-
ways communication)
Вам также может понравиться
- Lesson Plan Components: (Modified List Courtesy of TEP 3-4-3 Lesson Plan Template)Документ10 страницLesson Plan Components: (Modified List Courtesy of TEP 3-4-3 Lesson Plan Template)mary jane100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Week 5-1,5-2 "Finding Literature"Документ4 страницыLesson Plan Week 5-1,5-2 "Finding Literature"Sran LouthОценок пока нет
- Victorian Curriculum Overview and Lesson Plan Format - One LessonДокумент6 страницVictorian Curriculum Overview and Lesson Plan Format - One Lessonapi-611920958Оценок пока нет
- Udl Lesson Plan For WebsiteДокумент19 страницUdl Lesson Plan For Websiteapi-578964781Оценок пока нет
- November 28, 2018Документ3 страницыNovember 28, 2018Ma Alona Tan DimaculanganОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 01Документ13 страницLesson Plan 01yuliОценок пока нет
- SyllabusДокумент10 страницSyllabusapi-548592060Оценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines West Prime Horizon Institute, Inc. Course Syllabus in Language and Education ResearchДокумент11 страницRepublic of The Philippines West Prime Horizon Institute, Inc. Course Syllabus in Language and Education ResearchJessaMae AlbaracinОценок пока нет
- Science Week 6 Snap Tear or Stretch PDFДокумент5 страницScience Week 6 Snap Tear or Stretch PDFapi-450540021Оценок пока нет
- Y2U6Документ10 страницY2U6Tamizh PonniОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan For Week 8-1, 8-2 "Formulating Research Questions"Документ4 страницыLesson Plan For Week 8-1, 8-2 "Formulating Research Questions"Sran Louth100% (1)
- LOQ-model-of-science-teaching PendukungДокумент8 страницLOQ-model-of-science-teaching Pendukungkamilah kurniaОценок пока нет
- Week 2-1, 2-2Документ5 страницWeek 2-1, 2-2Sran LouthОценок пока нет
- Grade-9-DLL-Practical Research 1-Q3-Week-1Документ3 страницыGrade-9-DLL-Practical Research 1-Q3-Week-1Love Apalla100% (1)
- DLL With Differentiated InstructionДокумент4 страницыDLL With Differentiated InstructionHeilene Ethel Angcaya50% (2)
- Lesson Plan: For Everyone Undertaking A Research ProjectДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan: For Everyone Undertaking A Research ProjectSran LouthОценок пока нет
- Onstructing OUR OurseДокумент44 страницыOnstructing OUR OurseMrsriyansyahОценок пока нет
- Hamdi Ria FirstiawanДокумент4 страницыHamdi Ria FirstiawanHamdi Ria FirstiavvanОценок пока нет
- Daily Lesson LOGДокумент3 страницыDaily Lesson LOGLeah CrisostomoОценок пока нет
- Action Research: A Way To Explore and Understand Your Classroom Anne Burns, University of NSW, SydneyДокумент4 страницыAction Research: A Way To Explore and Understand Your Classroom Anne Burns, University of NSW, SydneyArt VilОценок пока нет
- 2nd Modified DLL For 3rd COTДокумент4 страницы2nd Modified DLL For 3rd COTRedОценок пока нет
- Meaning and Nature of Approach, Strategies and Techniques (Agnes Doco) 1Документ13 страницMeaning and Nature of Approach, Strategies and Techniques (Agnes Doco) 1Izzabella MustacisaОценок пока нет
- Consolidated DLP - EndangeredДокумент22 страницыConsolidated DLP - EndangeredTJ SabadoОценок пока нет
- S7 Q1 - Week 1-2 Scientific InvestigationДокумент4 страницыS7 Q1 - Week 1-2 Scientific InvestigationMa. Bernadette EballeОценок пока нет
- Group Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыGroup Lesson Planapi-524797749Оценок пока нет
- Center of Excellence For Teacher EducationДокумент5 страницCenter of Excellence For Teacher EducationKhim Bryan RebutaОценок пока нет
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Practical Research 1Документ3 страницыA Detailed Lesson Plan in Practical Research 1Blue CarnationОценок пока нет
- Jordan ConnorsДокумент5 страницJordan ConnorsohioseaprincipleОценок пока нет
- Outcome 1 - Lesson 5 - Reproduction PubertyДокумент11 страницOutcome 1 - Lesson 5 - Reproduction Pubertyapi-310123009Оценок пока нет
- HUMSS Research 1st DLL DepedДокумент2 страницыHUMSS Research 1st DLL DepedAlexis V. LarosaОценок пока нет
- RESEARCH WORKSHOP QualitativeДокумент55 страницRESEARCH WORKSHOP QualitativeAlyssa JaneОценок пока нет
- 4169 10170 1 SMДокумент10 страниц4169 10170 1 SMisaayu fatimahОценок пока нет
- RPS IRM - Iroh 9 Feb 2021Документ8 страницRPS IRM - Iroh 9 Feb 2021Muhammad PanjiОценок пока нет
- Pop Fall2023 KosareffДокумент10 страницPop Fall2023 Kosareffapi-700901076Оценок пока нет
- Forces Causing Movement CompletelessonДокумент28 страницForces Causing Movement Completelessonapi-616056306Оценок пока нет
- PR 1 Week 1 Q2Документ3 страницыPR 1 Week 1 Q2Romeo M. Laguardia Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Class 11th English Snapshot Chapter-The Address Lesson PlanДокумент11 страницClass 11th English Snapshot Chapter-The Address Lesson PlanSurya Krishna MohanОценок пока нет
- BIR 60204 Qualitative Research Methods and Approaches Classroom Observation Task: Teaching ActivitiesДокумент19 страницBIR 60204 Qualitative Research Methods and Approaches Classroom Observation Task: Teaching ActivitiesShalini A/P SurianarayananОценок пока нет
- Ethangreen 18498515 1a Sequenced LessonsДокумент31 страницаEthangreen 18498515 1a Sequenced Lessonsapi-552869059Оценок пока нет
- TCH 76220 wk5 Learning Theory Social Cognitive Theory LPДокумент7 страницTCH 76220 wk5 Learning Theory Social Cognitive Theory LPapi-307146309Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - ProceduresДокумент22 страницыChapter 3 - ProceduresVicente Lacsa IIIОценок пока нет
- Per Group: Through The Group Work. Per StudentДокумент3 страницыPer Group: Through The Group Work. Per StudentAmina NazirОценок пока нет
- Research Methodologies in Science Education: Qualitative DataДокумент6 страницResearch Methodologies in Science Education: Qualitative DataBisera KrstevskaОценок пока нет
- Science Forward Planning Document Year 4 Chemical Science MaterialsДокумент7 страницScience Forward Planning Document Year 4 Chemical Science Materialsapi-427933815Оценок пока нет
- 5b: Think-Pair-Share: Components of Curriculum Answer/sДокумент2 страницы5b: Think-Pair-Share: Components of Curriculum Answer/sFilmar Urmanita JoseОценок пока нет
- ITWRBДокумент4 страницыITWRBjaeson marianoОценок пока нет
- Global Perspective Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницGlobal Perspective Lesson Planhira yaqoobОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan. English ChemistryДокумент5 страницLesson Plan. English ChemistryMahendra Saputra 1805110485Оценок пока нет
- Group 2Документ4 страницыGroup 2ewolramnasomitelimusОценок пока нет
- Toaz - Info Practical Research 1 DLL Week 1 PRДокумент10 страницToaz - Info Practical Research 1 DLL Week 1 PR김티카Оценок пока нет
- Module Discourse AnalysisДокумент21 страницаModule Discourse AnalysisNaftal NyakundiОценок пока нет
- PROF ED 15 Demo 1Документ4 страницыPROF ED 15 Demo 1blossommae171Оценок пока нет
- Globalization Debate Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыGlobalization Debate Lesson Planapi-375601641Оценок пока нет
- 8vo - InglésДокумент3 страницы8vo - InglésAlison TacoОценок пока нет
- .Action Research Focusing On English Language Teaching Practices For Professional DevelopmentДокумент4 страницы.Action Research Focusing On English Language Teaching Practices For Professional DevelopmentLuu TranОценок пока нет
- VL Script PR1 M1-L4Документ7 страницVL Script PR1 M1-L4Artemist FowlОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines West Prime Horizon Institute, Inc. Course Syllabus in Language and Education ResearchДокумент7 страницRepublic of The Philippines West Prime Horizon Institute, Inc. Course Syllabus in Language and Education ResearchJessaMae AlbaracinОценок пока нет
- Grade 2 Social Studies Grade 2 Social Studies 80min (9:50am-11:55am) Arctic Animals Research Project: Pre-Research Trinh PhamДокумент6 страницGrade 2 Social Studies Grade 2 Social Studies 80min (9:50am-11:55am) Arctic Animals Research Project: Pre-Research Trinh Phamapi-445796471Оценок пока нет
- Interactional Research Into Problem-Based LearningОт EverandInteractional Research Into Problem-Based LearningSusan M. BridgesОценок пока нет
- Uncovering Student Ideas in Physical Science, Volume 1: 45 New Force and Motion Assessment ProbesОт EverandUncovering Student Ideas in Physical Science, Volume 1: 45 New Force and Motion Assessment ProbesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- NetApp2016 PDFДокумент8 страницNetApp2016 PDFAung Zaw LinОценок пока нет
- t1 I Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Instructional Materials in Teaching EslДокумент2 страницыt1 I Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Instructional Materials in Teaching EslchiewjungОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Practice - Listening 2Документ1 страницаUnit 1 - Practice - Listening 2PT PhạmОценок пока нет
- After Marist Girls Expelled Over Racist Texts, Dads Sue School: ReportДокумент22 страницыAfter Marist Girls Expelled Over Racist Texts, Dads Sue School: ReportDNAinfo ChicagoОценок пока нет
- Differentiated Lesson Plan 1: CCSS - Math.Content - HSG.SRT.C.6Документ9 страницDifferentiated Lesson Plan 1: CCSS - Math.Content - HSG.SRT.C.6api-373598912Оценок пока нет
- Pygmalion Study Questions Acts 2-5 and Sequel: Chris Busco Period 2 5/18/15Документ20 страницPygmalion Study Questions Acts 2-5 and Sequel: Chris Busco Period 2 5/18/15api-287354343Оценок пока нет
- Top Down Bottom UpДокумент6 страницTop Down Bottom UpRohayu ZahariОценок пока нет
- Fce Use of English Part 3Документ4 страницыFce Use of English Part 3Andre FredericoОценок пока нет
- Types of AssessmentДокумент4 страницыTypes of AssessmentAegi InfanteОценок пока нет
- Purpose of Curriculum - BojosДокумент3 страницыPurpose of Curriculum - BojosIan Mark Loreto RemanesОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Subject Title: Subject ObjectivesДокумент3 страницыSyllabus Subject Title: Subject ObjectivesLeonard Andrew ManuevoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Failure Analysis and PreventionДокумент8 страницChapter 1 - Introduction To Failure Analysis and PreventionSayedMahdyОценок пока нет
- Teaching Strategies in The New Normal - GudesДокумент2 страницыTeaching Strategies in The New Normal - GudesMaria Conxedes GudesОценок пока нет
- This Study Resource Was: FS 2: Episode 6: Deductive & Inductive Methods of TeachingДокумент6 страницThis Study Resource Was: FS 2: Episode 6: Deductive & Inductive Methods of TeachingHenry Kahal Orio Jr.100% (3)
- Reference Form: Information About This Programme Can Be Found OnДокумент2 страницыReference Form: Information About This Programme Can Be Found OnChem VathoОценок пока нет
- PortfolioДокумент6 страницPortfolioapi-360888326Оценок пока нет
- Legal Basis FinalДокумент57 страницLegal Basis FinalAnna ParelОценок пока нет
- English 3143: Marketing The English MajorДокумент7 страницEnglish 3143: Marketing The English MajorWill KurlinkusОценок пока нет
- Greenhill School SP 2010Документ24 страницыGreenhill School SP 2010Kevin J RuthОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Cultural Politics and EducationДокумент97 страницHandbook of Cultural Politics and EducationbettscОценок пока нет
- A4 Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыA4 Lesson Planapi-349699549Оценок пока нет
- Action Plan in Edukasyon Sa PagpapakataoДокумент4 страницыAction Plan in Edukasyon Sa PagpapakataoRenalyn C. Pagasi-anОценок пока нет
- B.tech - Syllabus Oct 2016Документ144 страницыB.tech - Syllabus Oct 2016Ravi RanjanОценок пока нет
- Operational Plan Template. Assess 2 Part 2Документ4 страницыOperational Plan Template. Assess 2 Part 2Milena Maria Sarmiento Perez100% (3)
- Narrative Inquiry - Clandinin ConnellyДокумент10 страницNarrative Inquiry - Clandinin ConnellyDrKhuramAzam100% (1)
- Melvin L.Landiongan & Roxanne Janine PeñaflorДокумент4 страницыMelvin L.Landiongan & Roxanne Janine PeñaflorVin91% (11)
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciences Humss 11AДокумент4 страницыDisciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciences Humss 11Aangie vibarОценок пока нет
- Soneida Rodriguez ResumeДокумент1 страницаSoneida Rodriguez Resumeapi-280995362Оценок пока нет
- English 3-Q4-L8 ModuleДокумент15 страницEnglish 3-Q4-L8 ModuleZosima AbalosОценок пока нет
- The Teaching Profession: Title of The Report: The Teacher As A Person inДокумент49 страницThe Teaching Profession: Title of The Report: The Teacher As A Person inArianne Rose FangonОценок пока нет