Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Federal Government
Загружено:
ملک محمد صابرشہزادИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Federal Government
Загружено:
ملک محمد صابرشہزادАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
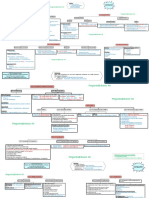
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _
Federal Government
The Government of Pakistan, is a federal government established by the Constitution of Pakistan as a centralized governing authority of the four provinces of a proclaimed and established parliamentary democratic republic,
constitutionally called the State of Pakistan.[1] The order of operations constitutes a Westminster system, and it comprises three branches of government: the executive, the legislature, and the judiciary. The executive branch is headed by the Prime Minister of Pakistan, who is a chief executive (Head of Government) and exercises his or her power on officers subordinate to him or her. The President of Pakistan is merely a figurehead and Head of State who is a civilian commander-in-chief of the Pakistan Armed Forces and holds ceremonial powers to fulfill the constitutional requirements; the President's appointment and tenure is dependent, constitutionally, on the Prime Ministers term. The Parliament (Legislature) consists of a lower house (National Assembly) and an upper house (Senate), as well as the President. The judicial branch consists of a Supreme Court (its apex), five provisional high courts, numerous other district courts a specially designated anti-terrorism court, a Sharia court, and the Green Court. The Electoral College, composed of the Senate, the National Assembly, and the four Provincial Assemblies, chooses a President, through indirect elections, for a five-year term. The Prime Minister is a supreme leader of the majority party (or director of the coalition government) in the National Assembly and is assisted by a cabinet of ministers drawn from both chambers of the Parliamen.
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _
Government Structure
Pakistan's independence was won through a democratic and constitutional struggle. Although the country's record with parliamentary democracy has been mixed, Pakistan, after lapses, has returned to this form of government. The constitution of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, 1973 provides for a federal parliamentary system with a president as head of state and a popularly elected prime minister as head of government. Pakistan has a federal and a parliamentary y form of government with a president as head of state and Prime Minister as the head of government. It has a bicameral system of legislature. There are two houses. The upper house is called Senate and the lower house the National Assembly. The provincial
assemblies elect the Senate on the basis of equal repress entation from all provinces. Members of the National Assembly are elected directly by the people . Provincial represent ation in the national assembly is made on the bas is of population. Every Pakistani over the age of 18 years is entitled to elect representative from each constituency. The electoral college of the national and provincial assemblies together elects the president of Pakistan for a period of five years. Elections are to be held every five years according to the constitution
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _
President
The president, in keeping with the constitutional provision that the state religion is Islam, must be a Muslim. Elected for a five-year term by an electoral college consisting of members of the Senate and National Assembly and members of the provincial assemblies, the president is eligible for reelection. But no individual may hold the office for more than two consecutive terms. The president may resign or be impeached and may be removed from office for incapacity or gross misconduct by a two-thirds vote of the members of the parliament. The president generally acts on the advice of the prime minister but has important residual powers. One of the most important--a legacy of Zia--is contained in the Eighth Amendment, which gives the president the power to dissolve the National Assembly "in his discretion where, in his opinion . . . a situation has arisen in which the Government of the Federation cannot be carried on in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution and an appeal to the electorate is necessary." Term of office of President. (1) Subject to the Constitution, the President shall hold office for a term of five
years from the day he enters upon his office: Provided that the President shall, notwithstanding the expiration of his term, continue to hold office until his successor enters upon his office.
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ (2) Subject to the Constitution, a person holding office as President shall be eligible for re-election to that office, but no person shall hold that office for more than two consecutive terms. (3) The President may, by writing under his hand addressed to the Speaker of
the National Assembly, resign his office. President's power to grant pardon, etc. The President shall have power to grant pardon, reprieve and respite, and to remit, suspend or commute any sentence passed by any court, tribunal or other authority. President to be kept informed: The Prime Minister shall keep the President informed on all matters of internal and foreign policy and on all legislative proposals the Federal Government intends to bring before Majlis-e-Shoora (Parliament).
Parliament and Federal Government
The bicameral federal legislature is the Majlis-i-Shoora (Council of Advisers), consisting of the Senate (upper house) and National Assembly (lower house). Members of the National Assembly are elected by universal adult suffrage (over eighteen years of age in Pakistan). Seats are allocated to each of the four provinces, the Federally Administered Tribal Areas, and Islamabad Capital
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ Territory on the basis of population. National Assembly members serve for the parliamentary term, which is five years, unless they die or resign sooner, or unless the National Assembly is dissolved. Although the vast majority of the members are Muslim, about 5 percent of the seats are reserved for minorities, including Christians, Hindus, and Sikhs. Elections for minority seats are held on the basis of joint electorates at the same time as the polls for Muslim seats during the general elections. The prime minister is appointed by the president from among the members of the National Assembly. The prime minister is assisted by the Federal Cabinet, a council of ministers whose members are appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister. The Federal Cabinet comprises the ministers, ministers of state, and advisers. The Senate is a permanent legislative body with equal representation from each of the four provinces, elected by the members of their respective provincial assemblies. There are representatives from the Federally Administered Tribal Areas and from Islamabad Capital Territory. The chairman of the Senate, under the constitution, is next in line to act as president should the office become vacant and until such time as a new president can be formally elected. Both the Senate and the National Assembly can initiate and pass legislation except for finance bills. Only the National Assembly can approve the federal budget and all finance bills. In the case of other bills, the president may prevent passage unless
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ the legislature in joint sitting overrules the president by a majority of members of both houses present and voting. Other offices and bodies having important roles in the federal structure include the attorney general, the auditor general, the Federal Land Commission, the Federal Public Service Commission, Election Commission of Pakistan, and the Wafaqi Mohtasib (Ombudsman). The Federal Government: (1) Subject to the Constitution, the executive authority of the Federation shall
be exercised in the name of the President by the Federal Government, consisting of the Prime Minister and the Federal Ministers, which shall act through the Prime Minister, who shall be the chief executive of the Federation. (2) In the performance of his functions under the Constitution, the Prime
Minister may act either directly or through the Federal Ministers." The Cabinet: (1) There shall be a Cabinet of Ministers, with the Prime Minister at its head,
to aid and advise the President in the exercise of his functions. (2) The National Assembly shall meet on the twenty-first day following the day
on which a general election to the Assembly is held, unless sooner summoned by the President.
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ (3) After the election of the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker, the National Assembly shall, to the exclusion of any other business, proceed to elect without debate one of its Muslim members to be the Prime Minister. (4) The Prime Minister shall be elected by the votes of the majority of the total
membership of the National Assembly: Provided that, if no member secures such majority in the first poll, a second poll shall be held between the members who secure the two highest numbers of votes in the first poll and the member who secures a majority of votes of the members present and voting shall be declared to have been elected as Prime Minister: Provided further that, if the number of votes secured by two or more members securing the highest number of votes is equal, further poll shall be held between them until one of them secures a majority of votes of the members present and voting. (5) The member elected under clause (4) shall be called upon by the
President to assume the office of Prime Minister and he shall, before entering upon the office, make before the President oath in the form set out in the Third Schedule: Provided that there shall be no restriction on the number of terms for the office of the Prime Minister.
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ (6) The Cabinet, together with the Ministers of State, shall be collectively responsible to the Senate and the National Assembly. (7) The Prime Minister shall hold office during the pleasure of the President,
but the President shall not exercise his powers under this clause unless he is satisfied that the Prime Minister does not command the confidence of the majority of the members of the National Assembly, in which case he shall summon the National Assembly and require the Prime Minister to obtain a vote of confidence from the Assembly. (8) The Prime Minister may, by writing under his hand addressed to the
President, resign his office. (9) A Minister who for any period of six consecutive months is not a member
of the National Assembly shall, at the expiration of that period, cease to be a Minister and shall not before the dissolution of that Assembly be again appointed a Minister unless he is elected a member of that Assembly: Provided that nothing in this clause shall apply to a Minister who is a member of the Senate. (10) Nothing in this Article shall be construed as disqualifying the Prime
Minister or any other Minister or a Minister of State for continuing in office during any period during which the National Assembly stands dissolved, or as
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ preventing the appointment of any person as Prime Minister or other Minister or a Minister of State during any such period.
Conferring of functions on subordinate authorities.
On the recommendation of the Federal Government, 211[Majlis-e-Shoora
(Parliament)] 211 may by law confer functions upon officers or authorities subordinate to the Federal Government. Conduct of business of Federal Government. (1) All executive actions of the Federal Government shall be expressed to be
taken in the name of the President. (2) The 213[Federal Government] 213 shall by rules specify the manner in
which orders and other instruments made and executed 214[in the name of the President] 214 shall be authenticated, and the validity of any order or instrument so authenticated shall not be questioned in any court on the ground that it was not made or executed by the President. (3) The Federal Government shall also make rules for the allocation and
transaction of its business. Attorney-General for Pakistan. (1) The President shall appoint a person, being a person qualified to be
appointed a Judge of the Supreme Court, to be the Attorney-General for Pakistan.
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ (2) The Attorney-General shall hold office during the pleasure of the President 216[and shall not engage in private practice so long as he holds the office of the Attorney-General] 216. (3) It shall be the duty of the Attorney-General to give advice to the Federal
Government upon such legal matters, and to perform such other duties of a legal character as may be referred or assigned to him by the Federal Government, and in the performance of his duties he shall have the right of audience in all courts and tribunals in Pakistan. (4) The Attorney-General may, by writing under his hand addressed to the
President, resign his office.
PRIME MINISTER
The Prime Minister of Pakistan is the head of government of the Islamic
Republic of Pakistan who is designated to exercise as the country's Chief Executive (CE). By the Constitution of Pakistan, Pakistan has the parliamentary democratic system of government, consisting Prime minister as Chief Executive and head of government.
Duties of Prime Minister in relation to President.
It shall be the duty of the Prime Minister: (a) to communicate to the President all decisions of the Cabinet relating to the
administration of the affairs of the Federation and proposals for legislation; (b) to furnish such information relating to the administration of the affairs of
the Federation and proposals for legislation as the President may call for; and
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ (c) if the President so requires, to submit for the consideration of the Cabinet any matter on which a decision has been taken by the Prime Minister or a Minister but which has not been considered by the Cabinet. The Prime Minister shall keep the President informed on matters of internal and foreign policy and on all legislative proposals the Federal Government intends to bring before Parliament.
Powers and functions of the prime ministers (powers of federal Government):
The powers and functions of the prime minister are as under. (i) Chief Advisor of the president: The prime minister is the Chief advisor of the president. the president performs his duties with the consultation of the prime minister. (ii) Formation of the cabinet: The prime minister, after taking oath, select his cabinet. every minister, individually and cabinet as whole are responsible for their acts to the parliament. (iii) National leader: The prime minister is a national leader. he leads the nation and organizes the public opinion in favour of his party. (iv) Leader of the cabinet: The prime minister is the leader of the cabinet. all the minister work under the supervision of the prime minister. (v) Leader of the house:
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ The prime minister is the leader of the national assembly. his proposals are honoured in the house. he expresses his views in the assembly. (vi) Power to confer titles and awards: The prime minister has power to confer titles and awards to those who show excellent performance in different field of life.
(vii) Power of appointment: The prime minister has power to appoint the high ranking officials with the approval of the president of Islamic republic of Pakistan. he appoints diplomats, ministerial staff and Judges of the supreme courts and the high court. he also appoints the members of national finance commission etc. (viii) Financial powers: The prime minister also performs finance matters. the budget is prepared under his supervision. (ix) Public welfare: The prime minister works for the public welfare. he takes every possible step to improve the life style of the people of his country. (xi) Power of Legislation: The prime minister takes part in legislation. all proceedings are conducted with the consent of the prime minister. he plays a vital role in law making. (xii) Administrative duties:
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ The prime minister performs the administrative function. he is responsible for the smooth running of the affairs of the country. he maintains law and order in the country. (xiii) Defence of the country: The prime minister is responsible for the defence of the country. he can take step to improve the defence system of the country. (xiv) Power to dissolve the national assembly: The prime minister can ask the president to dissolve the national assembly. (xv) Party head: The prime minister is the party head. he belongs to party who has majority in the house. he has political his political significance. (xvi) Power to terminate ministers: The prime minister it is not satisfied with the function of his minister he can terminate them. (xvii) Bridge between president and cabinet: The prime minister is link between president and cabinet. the prime minister is duty bound to inform the president about work f cabinet. (xviii) Representative of the nation: The prime minister is representative of the nation in international level. Resign of prime minister: The prime minister may tender his resignation to the president as and when he desires so. after prime minister as resignation all the minister shall cease to hold offices.
Structure of Federal Government In Pakistan By Malik Muhammad Sabir Shahzad , Internet Researcher Faisalabad, Pakistan _______________________________________________________________________ _ Termination/vote of no-confidence against prime minister: Under the present procedure, a resolution for a vote of no-confidence can be moved by not less than twenty percent of the total membership of the national assembly. the resolution shall not be voted upon before the expiration of three days, from the day on which such resolution is moved in the national assembly. in the resolution for vote of no-confidence is passed by majority of the total membership of the national assembly, the prime minister shall cease to hold office immediately. Acting prime minister: On the death, sickness leave, resignation or foreign tour of the prime minister the senior minister look after the work.
Conclusion:
To conclude we can say, that the prime minister is the real executive of the country. he has strong constitutional position. the prime minister is the Chief advisor of president. he is the leader of the house and elected for the term of 5 years. he can be removed from his office by passing a resolution of vote of nonconfidence against him.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Pak Mcqs PK: Election Officers (Bs-17)Документ84 страницыPak Mcqs PK: Election Officers (Bs-17)MADEEHA ABIDОценок пока нет
- Constitution of PakistanДокумент8 страницConstitution of PakistanQaisar RajputОценок пока нет
- Constitutional Development of PakistanДокумент22 страницыConstitutional Development of PakistanHaseeb BozdarОценок пока нет
- Labour Officer (MCQS)Документ3 страницыLabour Officer (MCQS)alikhann7011Оценок пока нет
- MNAs Contact Numbers UpdatedДокумент68 страницMNAs Contact Numbers Updatedbytes bitsОценок пока нет
- Governance Framework of PakistanДокумент59 страницGovernance Framework of PakistanRana WaqasОценок пока нет
- Salient Features of 1956, 1962, 1973 ConstitutionДокумент10 страницSalient Features of 1956, 1962, 1973 ConstitutionSaad Khan100% (1)
- PKS Lecture-Wise Handouts - (BS)Документ32 страницыPKS Lecture-Wise Handouts - (BS)mosi100% (2)
- The Gazzat of PakistanДокумент236 страницThe Gazzat of PakistanFaheem UllahОценок пока нет
- Elections in Pakistan-1Документ6 страницElections in Pakistan-1Sania ShahОценок пока нет
- Salient Features of Constitution 1973Документ3 страницыSalient Features of Constitution 1973Qasim Sher HaiderОценок пока нет
- Esta Code Part 1Документ329 страницEsta Code Part 1nmughal200064840% (1)
- Federal Public Service CommissionДокумент25 страницFederal Public Service CommissionZawar Baqir HyderiОценок пока нет
- Constitutional Law-IiДокумент16 страницConstitutional Law-IiMujeeb Ur Rehman MarwatОценок пока нет
- Emergency Provisions 29Документ9 страницEmergency Provisions 29ravi kumarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 Constitutional Frame Work of PAДокумент28 страницLecture 3 Constitutional Frame Work of PAMuhammad Imran100% (1)
- AR2003Документ418 страницAR2003zeeshanОценок пока нет
- Distribution of Powers Between Union and StateДокумент20 страницDistribution of Powers Between Union and StateKartik SainiОценок пока нет
- Salient Features of The Constitution of 1973 of Pakistan - CSS ForumsДокумент4 страницыSalient Features of The Constitution of 1973 of Pakistan - CSS Forumssanaullah100% (1)
- LAT Solved PaperДокумент9 страницLAT Solved Paperhoneyking1278Оценок пока нет
- Parliamentarians Tax Directory: For Year Ended 30 June 2018Документ24 страницыParliamentarians Tax Directory: For Year Ended 30 June 2018Hussain ShahОценок пока нет
- Pakistan Studies Assignment # 01 Pakistan Constitution of 1973Документ18 страницPakistan Studies Assignment # 01 Pakistan Constitution of 1973Championip4p100% (2)
- Constitutional Law Part 2Документ10 страницConstitutional Law Part 2Muhammad Imran Ahmad Kamboh0% (1)
- Seminar Report Pak FP February 02 2016Документ17 страницSeminar Report Pak FP February 02 2016Wnc WestridgeОценок пока нет
- Constitution Fundamental RightsДокумент8 страницConstitution Fundamental RightsAhmed SaeedОценок пока нет
- S.M.C. 3 2018 PDFДокумент52 страницыS.M.C. 3 2018 PDFnazarОценок пока нет
- CAF-04 Mind Maps of Complete Book by Sir Asif For March 2022Документ16 страницCAF-04 Mind Maps of Complete Book by Sir Asif For March 2022muzamil azizОценок пока нет
- Constitutional Law NotesДокумент21 страницаConstitutional Law Noteslaboti2018Оценок пока нет
- Ammendments in The Constitution of PakistanДокумент15 страницAmmendments in The Constitution of PakistanYour AdvocateОценок пока нет
- Islamic Ideology Council PakistanДокумент10 страницIslamic Ideology Council PakistanArif Masood100% (3)