Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CSW Pharmacology - Pharm Chapt
Загружено:
Kishore Chandra KoradaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CSW Pharmacology - Pharm Chapt
Загружено:
Kishore Chandra KoradaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CSW Pharmacology - Pharm Chapter, Step 1
Study online at quizlet.com/_axmap
1.
2 drugs that cause dilated cardiomyopathy (both start with D) 4 drugs that cause cutaneous flushing A drug infused at a constant rate reaches about 94% of steady state after A lower Km means A partial agonist has a lower Acute alcohol use, P450 interaction Acute cholestatic hepatitis Acute systems of iron poisoning Adrenocortical insufficiency Alpha 1 receptor uses which G protein signal system? Alpha 2 receptor uses which G protein signal system? Anticholinergic used to treat asthma, COPD Anticholinergic used to treat peptic ulcer disease (3) antidepressant that causes atropine like sideeffects Antidote for acetaminophen Antidote for amphetamines Antidote for anticholinesterases Antidote for Antimuscarinic agents; anticholinergics Antidote for arsenic, gold, mercury
doxorubicin (chemotherapy agent that intercalates into DNA) , daunorubicin (intercalating agent) VANC: vancomycin, adenosine, niacin, Ca2+ channel blockers 4t(1/2) -- four half lives
20.
Antidote for benzodiazepines Antidote for Betablocker Antidote for CO Antidote for copper, arsenic, gold Antidote for cyanide Antidote for Digitalis Antidote for Heparin Antidote for iron Antidote for lead Antidote for Methanol, ethylene glycol (antifreeze) Antidote for methemoglobin Antidote for opioids Antidote for organophosphates Antidote for salicylates Antidote for TCA Antidote for theophylline Antidote for tPA, streptokinase Antidote for warfarn Atropine action at Eye, airway, stomach, gut, bladder Barbiturates, P450 interaction Beta 1 receptor uses which G protein signal system?
flumazenil glucagon 100% O2, hyperbaric O2 penicillamine
21.
2.
22. 23.
3.
24.
nitrites, hydroxocobalamin, thiosulfate stop dig, normalize K, lidocaine, antidig Fab fragments, Mg2+ Protamine deferozamine CaEDTA, dimercaprol, succimer, penicillamine ethanolo, dialysis, fomepizole
4. 5.
Increased affinity maximal efficacy (result produced); may be more potent, less potent or equally potent inhibitor
27. 25.
26.
6.
7.
macrolides gastric bleeding glucocorticoid withdrawal
28.
8.
29.
9.
30.
methylene blue, vitamin C nalozone/naltrexone atropine, pralidoxime (regenerates Ach Esterase NaHCO3 or dialysis NaHCO3 B-blocker aminocaproic acid vit. K, fresh frozen plas Anticholinergic: pupil dilation, cycloplegia; decreased secretion, decreased acid secretion, decrease motility, decreased urgency inducer S --> adenylyl cyclase --> ATP -> cAMP --> increased protein kinase A
10.
q --> Phospholipase C --> increased Ca I --> adenylyl cyclase --> decreased cAMP --> less protein A ipratropium; M3 antagonist
31.
11.
32.
33.
12.
34.
13.
methscopolamine, pirenzepine, propantheline (decrease exocrine secretions by binding to M3) TCAs
35.
36.
14.
37.
15.
n-acetylcystein NH4Cl (acidify the urine) atropine, pralidoxime (regenerates Ach Esterase physostigmine salicylate
38.
16.
39.
17.
40.
18.
19.
dimercaprol (BAL), succimer
41.
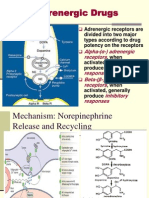
Beta 2 receptor uses which G protein signal system?
S --> adenylyl cyclase --> ATP -> cAMP --> increased protein kinase A M2
60. 61.
DI Diarrhea, Urination, Miosis, Bronchospasm, Bradycardia (M2), Excitation of skeletal muscle, Lacrimation, Sweating and Salivation - think overdose of what? Direct cooms-positive hemolytic anemia Disulfiram-like reaction
lithium, demeclocycline Cholinergic agents like organophosphates
42.
binding at this receptor decreases the heart rate and contracility of the atria Binding here increase gastric acid secretion Binding here increases nasal and bronchial mucus production, contraction of bronchioles, pruritis, and pain Binding relaxes renal vascular smooth muscle Can cause acute angle-closer glaucoma in elderly (relaxes ciliary muscle and pupillary sphincter); can cause urinary retention in men with BPH (relaxes the bladder muscles), and hyperthermia in infants Carbamazepine, P450 interaction celecoxib, furosemide, probenecid, thiazide, bactrim, sulfasalazine, sulfonylureas, sumatriptan Challenge test for diagnosis of asthma
43.
H2 H1
62.
methyldopa metonidazole, some cephalosporins, procarbazine, 1st generation sulfonyluras S --> adenylyl cyclase --> ATP -> cAMP --> increased protein kinase A I --> adenylyl cyclase --> decreased cAMP --> less protein kinase A inhibitor alcohol dehydrogenase -> acetaldehyde (causes nausea, vomiting, headache, hypotension) -> acetadehyde dehydrogenase --> acetic acid Rash
44.
63.
45.
D1 atropine
64.
46.
Dopamine 1 receptor uses which G protein signal system? Dopamine 2 receptor uses which G protein signal system? Erythromycin, P450 interaction Ethanol metabolism
65.
66.
47. 48.
inducer ...
67.
49.
methacholine -triggers M3 mediated bronchoconstriction aplastic anemia
68.
50.
Chloramphenicol, benzene, NSAIDs, PTU, methimazole can cause Chronic alcohol use, P450 interaction Chronic symptoms of iron poisoning Cimetidine, P450 interaction Cinchonism Clearance equation
51.
inducer
69.
ethosuximide, lamotrigine, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, sulfa-drugs, penicillin, allopurinol Fanconi's syndrome focal to massive hepatic necrosis (4) Formula for Half-life Formula for the loading dose
Expired tetracycline halothane, valproic acid, acetaminophen, amanita phalloides .7 x Vd / (Clearance) Cp (target plasma concentration) x Vd/bioavailability Cp x CL/F Phase I phenytoin furosemide, thiazides inhibitor
52.
metabolic acidosis, scarring --> GI obstruction inhibitor quinidine, quinine Vd x Ke (elimination constant) agranulocytosis
70.
53. 54. 55.
71. 72.
73.
56.
Clozapine, carbamazepine, colchicine, PTU, methimazole, dapsone Major side effect: Competitive inhibitors lower Cough decreased sympathetic outflow, insulin release
Formula for the maintenance dose Geriatric patients lose which phase of metabolism first? Gingival hyperplasia gout (2) Grapefruit juice, P450 interaction
74.
57. 58. 59.
Potency ACE inhibitors alpha 2
75. 76. 77.
78. 79.
Gray baby syndrome Griseofulvin, P450 interaction Gynecomastia
Chloramphenicol inducer spironolactone, digitalis, cimetidine, alcohol, estrogens, ketoconazole (some drugs create awesome knockers) Gq (have 1 M&M in the GQ lounge) hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis cyclophosphamide, ifofamide INH distribute in tissues q --> Phospholipase C --> increased Ca S --> adenylyl cyclase --> ATP -> cAMP --> increased protein kinase A muscarinic antagonist like atropine
98.
Increase H2O permeability and reabsoprtion in the collecting tubules of the kidney increased heart rate, increased contractility, increased renin rlease increased lipolysis increases exocrine gland secretions (sweat, gastric acid), increase gut peristalsis, increase bladder contractions, bronchoconstriction, increase pupillary sphincter muscle contraction (miosis), ciliary muscle contraction (accommodation) increases vascular smooth muscle contraction Increases vascular smooth muscle contraction, pupillary dilator muscle, intestinal and bladder sphicter muscle contraction Inhibit yourself from drinking beer from a keg because it makes you acutely sick
V2 (ADH)
99.
80.
B1
100.
M3
81.
H1, alpha1, V1, M1, M3 all use which second messanger system? Hemapoetic effects of sulfa reaction hemorrhagic cystitis Hepatitis High Vd (> body weight) Histamine 1 receptor uses which G protein signal system? Histamine 2 receptor uses which G protein signal system? hot as a hare, dry as a bone, red as a beet, blind as a bat, mad as a hatter -- overdose of what? hot flashes How is the signal transduced at muscarinic Ach receptors How is the signal transduced at Nicotinic Ach receptors How is the therapeutic index calculated Hypothydoidism If a patient has renal or hepatic dysfunction, the maintenance dose should be if patient has renal or hepatic dysfunction, the loading dose should be... In first order kinetics, the plasma concentration of a drug concentration decreases In zero-order, the drug concentration decreases
82.
101.
V1 alpha 1
83. 84. 85. 86.
102.
103.
87.
88.
Inhibitors: Ketoconazole, Erythromycin, Grapefruit juice, Sulfonamide, isoniazid, cimetidine Methicillin, NSAIDs, furosemide inhibitor all cause hemolysis in patients with G6PD deficiency inhibitor volume of distribution for plasma protein-bound drugs pyridostigmine; does not penetrate the CNS, stronger than neostigmine Blood CNS and enteric nervous system
104.
Interstitial nephritis
89. 90.
tamoxifen, clomphene G-protein coupled with second messenger systems ligand gated N+/K+ channel
105. 106.
Isoniazid, P450 interaction Isoniazid, sulfonamides, primaquine, aspirin, ibuprofen, nitrofurantoin
91.
92.
LD50/ED50 (median toxic dose / median effective dose) lithium, amiodarone Decreased
107. 108.
Ketoconazole, P450 interaction Liver and Kidney disease lower what in pharmacokinetics
93. 94.
109. 95.
unchanged
Long acting treatment for MG
96.
exponentially, the fraction of the drug excreted is the same
110. 111.
Low Vd drugs are distributed where? M1 is found where?
97.
linearly
112.
M2, Alpha 2, and Dopamine 2 all use which second messanger system? Mechanism of iron poisoning Mechanism of lead poisoning
Gi (I'm MAD at 2s)
128.
Parkinson-like syndrome Phase I metabolism usually involves ... and the chemical reactions are Phase II metabolism chemical reactions usually are Phenytoin, P450 interaction Photosensitivity (3) Potent stimulator of sweat, tears and saliva Pseudomembraneous colitis pulmonary fibrosis Queen Barb Steals Phen-phen and Refuses Greasy Carbs Chronically Quinidine, P450 interaction Rifampin, P450 interaction Safer drugs have a ____ TI Seizures side effects of hexamethonium SLE-like syndrome St. John's wart, P450 interaction Sulfonamide, P450 interaction Tardive dyskinesia Tendointis, tendon rupture in kids The ___ receptor modulates dopamine release in the brain
haloperidol, chlorpromazine, reserpine, metoclopramide cytochrome P450 system, reduction, oxidation, hydrolysis --> metabolites are water-soluble and slightly polar, usually still active acetylation, glucuronidation, sulfation --> yields very polar, inactive metabolites inducer sulfonamides, amiodarone, tetracyclines (SAT for a photo) Pilocarpine (directly increases exocrine gland secretions, resistance to AChE) clindamycin, ampicillin bleomycine, amiodarone, busulfan (hard to BLAB) induces of P450: quinidine, Barbiturates, st. johns wart, phenytoin, rifampin, griseofulvin, carbamazepine, chronic alcohol inducer inducer higher Bupropion, impenem/cilastatin, isoniazid severe orthostatic hypotension, blurred vision, constipation, sexual dysfunction hydralazine, INH, procainamide, phenytoin inducer inhibitor antipychotics fluoroquinolones D2
129.
113.
causes cell dreath due to peroxidation of membrane lipids Prevents iron from being incorporating into the heme molecule; actions of delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase and ferrochetase are decreased extracellular space or body water Phenytoin, methotrexate, sulfa drugs (have a blast with PMS) alcohol dehydrogenase --> oxalic acid --> acidosis, nephrotoxicity alcohol dehydrogenase --> formaldehyde and formic acid --> severe acidosis and retinal damage q --> Phospholipase C --> increased Ca I --> adenylyl cyclase --> decreased cAMP --> less protein kinase A q --> Phospholipase C --> increased Ca polymyxins aminoglycosides, vancomycin, loop diuretics, cisplatin hexamethonium
130.
114.
131.
115.
Medium Vd durgs are distributed where? Megaloblastic anemia
132.
133.
116.
117.
Metabolism of ethylene glycol: Metabolism of methanol:
134.
135.
118.
136.
119.
Muscarinic 1 receptor receptor uses which G protein signal system? Muscarinic 2 receptor uses which G protein signal system? Muscarinic 3 receptor uses which G protein signal system? Nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity nephrotoxicity/ototoxicity
137.
120.
138.
139.
121.
140.
122.
141.
123.
142.
124.
Nicotonic antagonist used in experimental models to prevent vagal reflex responses to change in blood pressure (preventing reflex bradycardia) Noncompetitive inhibitors lower osteoporosis (2) Overdose should be treated with ammonium chloride since this drug is trapped in an acidic environment
143.
144.
145.
125.
efficacy corticosteroids, heparin amphetamine
146.
126. 127.
147.
148.
These four drugs are trapped in a basic environement and so overdose should be treated with bicarb three examples of zero-order drugs thrombosis Torsades de pointes Treatment for organosphosphate or cholinergic overdose Treatment for postoperative and neurogenic ileus and urinary retention Treatment of glaucoma, to induce pupillary contraction, and used to decrease intraocular pressure two CNS drugs that cause coronary vasospasm Use to treat glaucoma Used for the treatment of motion sickness Used for the treatment of parkinsons Used to diagnose MG (very short acting) Used to produce mydriasis and cycloplegia (3) Used to reduce urgency in mild cystitis and reduce bladder spasms Used to treat atropine overdose
phenobarb, methotrexate, TCA, aspirin (T MAP)
163.
Used to treat mysthenia gravis, reverse NM junction blockade postoperatively vasodilation, bronchodilation, increased heart rate, increased contractility, increase lipolysis, increased insulin release, decrease uterine tone Vasopressin 1 receptor uses which G protein signal system? Vasopressin 2 receptor uses which G protein signal system?
neostigmine (inhibits AChE) B2
164.
149.
phenytoin, ethanol and aspirin
165.
150. 151.
OCPs Class III agents (sotalol), class IA antiarrhythmics (quinidine), cisprida Atropine (muscarinic antangonist) and pralidoxime (used to regenerate active cholinesterase) Bethanechol (directly activates M3 Ach receptor, increases bladder contraction and peristalsis); neostigmine (increase endogenous Ach by inhibiting anticholinesterase; does not penetrate the CNS) Carbachol (directly actives M3 Ach receptor)
167.
q --> Phospholipase C -> increased Ca S --> adenylyl cyclase --> ATP -> cAMP --> increased protein kinase A Volume of distribution = (amount of drug in the body)/(plasma drug concentration) on acetaldehyde dehydrogenase On alcohol dehydrogenase
166.
152.
153.
Vd = (equations)
168.
154.
Where does disulfiram work? Where does fomepizole work
169.
155.
cocaine, sumatriptan
156.
Physostigmine (PHYS for EYES); crosses the blood brain barrier scopolamine (Muscarinic antagonist)
157.
158.
Benzotropine (antagonist to M1 receptor in the brain) edrophonium
159.
160.
atropine, homatropine, tropicamide
161.
oxybutynin and glycopyrrolate (M3 antagonist)
162.
physostigmine
Вам также может понравиться
- RECALLs 19 July 2022Документ3 страницыRECALLs 19 July 2022Aamir MunawarОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicДокумент13 страницPharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicSherlock HolmesОценок пока нет
- Pharma ChartsДокумент33 страницыPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Secret Pharmacology Step 1 Study Guide: Pharm"Документ29 страницSecret Pharmacology Step 1 Study Guide: Pharm"Fahd Abdullah Al-refaiОценок пока нет
- ADR PharmacologyДокумент30 страницADR PharmacologySumanth Kumar ReddyОценок пока нет
- 100 Most Important DrugsДокумент13 страниц100 Most Important Drugsngopya djiki67% (3)
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.DДокумент28 страницReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.Dmus zaharaОценок пока нет
- 3 Analgesic Anitpyretic InfamДокумент10 страниц3 Analgesic Anitpyretic InfamAnonymous dRAu54Оценок пока нет
- Name Types Disease Mechanism AE Other C. Cycle Resistance (CP Pg. 326) Alkylating AgentsДокумент12 страницName Types Disease Mechanism AE Other C. Cycle Resistance (CP Pg. 326) Alkylating AgentsM PatelОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology KatzДокумент13 страницPharmacology KatzFahd Abdullah Al-refaiОценок пока нет
- Bronchial Asthma 2.0Документ15 страницBronchial Asthma 2.0Bisweswar OjhaОценок пока нет
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiДокумент146 страницMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraОценок пока нет
- Step 1 DrugsДокумент46 страницStep 1 DrugsZebram ZeeОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology Table For Cardiovascular LectureДокумент10 страницPharmacology Table For Cardiovascular LecturemuhammadridhwanОценок пока нет
- Chemical Mediators in Health & Disease: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DДокумент34 страницыChemical Mediators in Health & Disease: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiОценок пока нет
- Drug in MuskuloskeletalДокумент17 страницDrug in MuskuloskeletalDwi Kurnia SariОценок пока нет
- Dept - Farmakologi & Terapeutik Fak - Kedokteran U S U Medan: Prof - Dr.H.Aznan Lelo PHD - SPFK DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKДокумент62 страницыDept - Farmakologi & Terapeutik Fak - Kedokteran U S U Medan: Prof - Dr.H.Aznan Lelo PHD - SPFK DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKAnonymous zZrGTONhОценок пока нет
- Anti-cancer drugs: mechanisms, uses, and side effectsДокумент6 страницAnti-cancer drugs: mechanisms, uses, and side effectskitsilcОценок пока нет
- MedSurg Medications & TablesДокумент71 страницаMedSurg Medications & TablesSarah PlunkettОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Tract PharmacologyДокумент68 страницRespiratory Tract PharmacologyRohaan SharmaОценок пока нет
- Gout DrugsДокумент1 страницаGout DrugsMichael BrownОценок пока нет
- Drug Cheat SheetДокумент6 страницDrug Cheat SheetSheldon LordОценок пока нет
- NSAIDs, DMARDs & Antigout1Документ69 страницNSAIDs, DMARDs & Antigout1Melissa SalayogОценок пока нет
- Anti-Hypertensive DrugsДокумент56 страницAnti-Hypertensive Drugsapi-3815243Оценок пока нет
- MedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Документ12 страницMedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Sarah PlunkettОценок пока нет
- Pharma Drug Tables - 1st ShiftingДокумент29 страницPharma Drug Tables - 1st ShiftingHei LeeОценок пока нет
- Cancer Chemo TableДокумент5 страницCancer Chemo TableChristine NazarenoОценок пока нет
- Mefenamic Acid Is A Non-SteroidalДокумент4 страницыMefenamic Acid Is A Non-SteroidalAnkan PalОценок пока нет
- Obat-Obat NefrotoksikДокумент43 страницыObat-Obat Nefrotoksiknursidiq10100% (1)
- Obat SimpatomimetikДокумент42 страницыObat SimpatomimetiknatinlalaОценок пока нет
- MS2 USMLE Pharm ReviewДокумент25 страницMS2 USMLE Pharm ReviewAnna ArtyОценок пока нет
- CASE PRESENTATION ON STROKE MANAGEMENTДокумент17 страницCASE PRESENTATION ON STROKE MANAGEMENTGURUPRAKASH RОценок пока нет
- June 2019 154points Ashraf-1Документ11 страницJune 2019 154points Ashraf-1majid tariqОценок пока нет
- All DrugsДокумент482 страницыAll DrugsJessica IbañezОценок пока нет
- Musculoskeletal PharmacologyДокумент18 страницMusculoskeletal PharmacologyBLEEMAGE100% (1)
- Chemotherapy and Renal Andhepatic Insufficiency 2008Документ24 страницыChemotherapy and Renal Andhepatic Insufficiency 2008Vika RatuОценок пока нет
- Endocrine HypertensionДокумент43 страницыEndocrine HypertensionAlessia GuerraОценок пока нет
- LECOM Pharm One-Liners 2012Документ6 страницLECOM Pharm One-Liners 2012cofodike1Оценок пока нет
- Cancer ChemotherapyДокумент19 страницCancer ChemotherapySamatha Mohan100% (1)
- Clinical Application of EnzymesДокумент6 страницClinical Application of EnzymesTemesgen MucheyeОценок пока нет
- Pharma CollectionДокумент40 страницPharma CollectionMuhd Nico DariyantoОценок пока нет
- Vasopressors and Inotropes in Shock ManagementДокумент63 страницыVasopressors and Inotropes in Shock ManagementCraig DuHaney50% (2)
- Case Presentation On Op PoisoningДокумент34 страницыCase Presentation On Op PoisoningSwerika KotteОценок пока нет
- Cancer Chemo TableДокумент4 страницыCancer Chemo TableChristine NazarenoОценок пока нет
- Studi Kasus Penyakit HatiДокумент27 страницStudi Kasus Penyakit HatiEfraim MangalukОценок пока нет
- ICU DRug 2Документ7 страницICU DRug 2Loiegy PaetОценок пока нет
- C C C CДокумент7 страницC C C CMadel de GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Adverse ReactionsДокумент1 страницаAdverse ReactionsChrissieОценок пока нет
- Anticoagulation Guidelines JMДокумент32 страницыAnticoagulation Guidelines JMMichael HuntОценок пока нет
- Oncology Drug ListДокумент11 страницOncology Drug Listashrafh100% (1)
- Opiate Analgesics and Clinical UsesДокумент40 страницOpiate Analgesics and Clinical UsesAnonymous 7hJgATОценок пока нет
- Female and Male SkullДокумент2 страницыFemale and Male SkullKishore Chandra KoradaОценок пока нет
- Anticancer DrugsДокумент117 страницAnticancer DrugsKishore Chandra Korada100% (1)
- Department of Vaccines and BiologicalsДокумент4 страницыDepartment of Vaccines and BiologicalsKishore Chandra KoradaОценок пока нет
- Accounting Exam Questions PatternДокумент1 страницаAccounting Exam Questions PatternKishore Chandra KoradaОценок пока нет
- Development of EyeДокумент3 страницыDevelopment of EyeKishore Chandra KoradaОценок пока нет
- R Practice TestДокумент45 страницR Practice TestKishore Chandra KoradaОценок пока нет
- Vertebra Column - Ns Aimst 12 To1 PM, 2.12.12Документ50 страницVertebra Column - Ns Aimst 12 To1 PM, 2.12.12Kishore Chandra KoradaОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Group 2 ModuleДокумент16 страницGroup 2 Moduledatu itimОценок пока нет
- Introduction To PharmacologyДокумент11 страницIntroduction To PharmacologyMaryam ElammaryОценок пока нет
- Compilation of Key GMP Requirements in Us and Japan For Tablet ManufacturingДокумент10 страницCompilation of Key GMP Requirements in Us and Japan For Tablet ManufacturingmarwaОценок пока нет
- Company and Industry BackgroundДокумент4 страницыCompany and Industry BackgroundVũ SơnОценок пока нет
- LercanidipineДокумент8 страницLercanidipineddandan_2Оценок пока нет
- Ethics in Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented byДокумент16 страницEthics in Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented bysiddheshsonawaneОценок пока нет
- Price List Kimia Farma 2017Документ9 страницPrice List Kimia Farma 2017Rusnansyah Unan100% (2)
- PharmacogeneticsДокумент8 страницPharmacogeneticskangaroocherryОценок пока нет
- (-) BpapДокумент2 страницы(-) BpapwpbeckettОценок пока нет
- PharmaceuticsДокумент2 страницыPharmaceuticsbrian3442Оценок пока нет
- Biostar Pharmaceuticals PVTДокумент36 страницBiostar Pharmaceuticals PVTBobby GolaОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics Used in AquacultureДокумент11 страницAntibiotics Used in AquacultureCharles FigueroaОценок пока нет
- PharmacyДокумент19 страницPharmacyBotemi0% (1)
- Final European Union Herbal Monograph Ginkgo Biloba L Folium enДокумент8 страницFinal European Union Herbal Monograph Ginkgo Biloba L Folium enDragnea AndreeaОценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting BioavailabilityДокумент11 страницFactors Affecting BioavailabilityMalvinder SharmaОценок пока нет
- Clasificator Medicamente 30.11.2016Документ1 038 страницClasificator Medicamente 30.11.2016Cătălina GîlcaОценок пока нет
- Yoo, - Jae 3D PrintingДокумент23 страницыYoo, - Jae 3D PrintingashokОценок пока нет
- Antimetabolite, alkylating agent & antibiotic antitumor drugs MOA & useДокумент11 страницAntimetabolite, alkylating agent & antibiotic antitumor drugs MOA & useAmina AmiarОценок пока нет
- DBE TablesДокумент16 страницDBE TablesAdarsh BablaniОценок пока нет
- AbateДокумент2 страницыAbateRamlan IrawanОценок пока нет
- C3.MOH AdministrativeGuidelinesBenzodiapines 2008Документ4 страницыC3.MOH AdministrativeGuidelinesBenzodiapines 2008Stephanie SennaОценок пока нет
- Criticalcaredrugs PDFДокумент2 страницыCriticalcaredrugs PDFtomywekaОценок пока нет
- Phytotherapy For Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due To Benign Hyperplasia of ProstateДокумент3 страницыPhytotherapy For Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due To Benign Hyperplasia of ProstateRidwanDwimokoОценок пока нет
- Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission Structure and Role in Formulation of IP and NFI PDFДокумент5 страницIndian Pharmacopoeia Commission Structure and Role in Formulation of IP and NFI PDFRajesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Orderan Obat - Klinik DR - Wilda: Nama Obat Harga Jumlah Satuan Total HargaДокумент3 страницыOrderan Obat - Klinik DR - Wilda: Nama Obat Harga Jumlah Satuan Total HargaWildaОценок пока нет
- Brief History and Methods of PharmacologyДокумент4 страницыBrief History and Methods of PharmacologyNiala AlmarioОценок пока нет
- Drug Addiction and Rehabilitation TermsДокумент4 страницыDrug Addiction and Rehabilitation TermsYolly Ces SecretariaОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology No Repeated QuestionДокумент28 страницPharmacology No Repeated QuestionVarunavi SivakanesanОценок пока нет
- Formulation and Evaluation of Pulsatile Drug Delivery SystemДокумент25 страницFormulation and Evaluation of Pulsatile Drug Delivery SystemAshish NavalОценок пока нет
- Materi IAI Palangka Raya - Rev PDFДокумент55 страницMateri IAI Palangka Raya - Rev PDFNopernas CahayaОценок пока нет