Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cumulative Trauma Disorders
Загружено:
ravinaj21Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cumulative Trauma Disorders
Загружено:
ravinaj21Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
3/27/2009
CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS ME 502
PRESENTATION FLOW
General Introduction Background Definition Stages of disorders Disorders seen in workers Symptoms of CTD How CTDs are treated Ergonomic measures to avoid CTD
HIGGODA W.R.S.M.U.A E/04/344
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
Cumulative Trauma Disorders, CTD, are the summary results of many micro trauma. Though known since the early 1800s, they have become a matter of urgent ergonomics concern in the 1980s. Usually caused by repeated and/or forceful exertions, often in the hand-arm-shoulder region.
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
Predominantly occur to soft tissues, such as tendons and ligaments, and to nerves and blood vessels. Associated with certain occupational and leisure activities. CTD can be avoided by a set of fairly simple and straightforward ergonomics procedures.
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
Single-event injuries, called acute or traumatic injuries Injuries that are sustained through often repeated actions whose cumulative effects finally result in an injury-CTDs Cumulative injuries occur often in connective soft tissues, particularly to tendons and their sheaths. They are frequent in the hand-wrist ,forearm area shoulder and neck.
BACKGROUND
Bernardino Ramazzini reported in 1813 that this condition occurred among clerks and scribes In 1960, 1960 the International Labour Office recognised repetition strain injury as an occupational disease.
3/27/2009
DEFINITION
DEFINITION
This is also known as,
over-use
CTD-collective term for syndromes characterised by,
discomfort impairment disability persistent pain in joints, joints muscles, muscles tendons and other soft tissues
with or without physical manifestations. It is caused or aggravated by repetitive motions,
Vibrations Sustained or constrained postures Forceful movements at work or leisure
injury cervicobrachial disorder cumulative trauma injury repetition strain injury repetitive motion injury rheumatic disease
DEFINITION
DEFINITION
NonOccupational Age Gender Acutetrauma ChronicDisease Useofbirthcontrol Circumstancesin pregnancy Menopause Occupational Repetitiveactivities ForcefulActivities Staticmuscleload Bodyposture Stress Vibration Cold
Repetitive strains clearly occur from many occupational activities, assembly, manufacturing, sewing, packing cashiers in supermarkets and among keyboard operators. Also associated with leisure and sports activities; the tennis elbow
STAGES OF DISORDERS
Stage 1
STAGES OF DISORDERS
Stage 2
Shows aches and tiredness during the working hours, but which usually settle overnight and over days off work. There is usually no reduction in work performance. This condition may persist for weeks or months, and is reversible.
Has symptoms that start early in the work shift, and which do not settle overnight. Sleep may be disturbed and the capacity to perform the repetitive work reduced. This condition usually persists over months.
3/27/2009
STAGES OF DISORDERS
Stage 3
DISORDERS SEEN IN WORKERS
Hand and wrist problems Arm and elbow problems Shoulder and neck disorders Leg and foot problems
Is characterised by symptoms that persist at rest, pain that occurs with non-repetitive movements, and p disturbed sleep. The person is unable to perform even light duties, and experiences difficulties in other tasks. This condition may last for months or years.
DISORDERS SEEN IN WORKERS
DISORDERS SEEN IN WORKERS
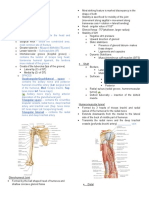
DeQuervain's Disease - a type of synovitis that involves the base of the thumb
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome - a compression of the median nerve in the wrist that may be caused by swelling and irritation of tendons and tendon sheaths.
Palmar aponeurosis
Median nerve
DISORDERS SEEN IN WORKERS
DISORDERS SEEN IN WORKERS
Epicondylitis - elbow pain associated with extreme rotation of the forearm and bending of the wrist. The condition is also called tennis elbow or golfer's elbow
Associated with repetitive use
Occupational Sports Musicians
Pain on resisted wrist extension
3/27/2009
DISORDERS SEEN IN WORKERS
DISORDERS SEEN IN WORKERS
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - a compression of nerves and blood vessels between the first rib, clavicle (collar bone), and accompanying muscles as they leave the thorax (chest) and enter the shoulder. Cervical Radiculopathy - a compression of the nerve roots in the neck. Ulnar Nerve Entrapment - a compression of the ulnar nerve in the wrist.
Tendinitis - an inflammation (swelling) or irritation of a tendon. It develops when the tendon is repeatedly tensed from overuse or unaccustomed use of the hand, wrist, arm, or shoulder. Tenosynovitis - an inflammation (swelling) or irritation of a tendon sheath associated with extreme flexion and extension of the wrist. Low Back Disorders - these include pulled or strained muscles, ligaments, tendons, or ruptured disks. They may be caused by cumulative effects of faulty body mechanics, poor posture, and/or improper lifting techniques.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS?
HOW ARE CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS TREATED? Wrist splint to keep the wrist from bending Anti-inflammatory medications Steroid injections Physical and/or occupational therapy Cold and hot baths Surgery in advanced cases
Numbness Decreased Joint Motion Swelling Burning Pain Aching Redness Weakness Tingling Clumsiness Cracking or popping of joints
HOW ARE CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS TREATED?
Deep Breathing for Overall Relaxation Relief of Hand and Finger Tension Relief of Hand and Wrist Tension Relief of Shoulder Tightness Relief of a Stiff Neck Relief of Arm Tension Relief of Shoulder and Back Tension Relief of Low Back Tension Relief of Cramping and Tightness in Legs Relief of Eye Fatigue
The overall principle is to fit the job to the person, and d not tt to attempt tt t to t fit person to t the th job
3/27/2009
ERGONOMICS MEASURES TO AVOID CTD
There are seven conditions that specifically need to be avoided:
1. Job activities with many repetitions.(work in which each cycle lasts less than 30 s, or as work in which one basic activity element is present during more than 50% of the total cycle time) 2. Work that requires prolonged or repetitive exertion of more than 30% of the operators muscle strength available for that activity.
ERGONOMICS MEASURES TO AVOID CTD
3. Putting body segments in an extreme position, such as severely bending at the wrist. 4. Work that makes a person maintain the same body posture for long periods of time. 5. Work in which a tool vibrates the body or part of the body. 6. Exposure of working body segments to cold, including air flow from pneumatic tools. 7. Combinations of the conditions mentioned above
Вам также может понравиться
- Sensual Massage For Couples (PDFDrive)Документ196 страницSensual Massage For Couples (PDFDrive)Lauren Xavier100% (3)
- Daily Practice For Clarinet: By, John TheineДокумент68 страницDaily Practice For Clarinet: By, John TheineOluwatobiloba FaithОценок пока нет
- TACFIT26 Mobility ManualДокумент33 страницыTACFIT26 Mobility ManualEndika Sa Go100% (10)
- Joints and Ligaments Anatomy TablesДокумент32 страницыJoints and Ligaments Anatomy TablessmoggindakrakОценок пока нет
- Hung Gar Lam Sai Wing Tiet Sien Kwuen The Iron ThreadДокумент80 страницHung Gar Lam Sai Wing Tiet Sien Kwuen The Iron ThreadBrian Nguyen94% (17)
- Hosford Muscle Tables PDFДокумент0 страницHosford Muscle Tables PDFryanbroad82Оценок пока нет
- Peripheral Nerve DisordersДокумент75 страницPeripheral Nerve DisordersAllahbesertkitaОценок пока нет
- ACL and PCL ReconstructionДокумент25 страницACL and PCL ReconstructionAli Aufar HutasuhutОценок пока нет
- Piano Technique - Anatomy of The Hand and Its Relevance To A Fluent Finger TechniqueДокумент31 страницаPiano Technique - Anatomy of The Hand and Its Relevance To A Fluent Finger TechniqueMartha Argerich100% (6)
- Goniometry and Manual Muscle Testing A Handbook For Students and Clinicians PDFДокумент376 страницGoniometry and Manual Muscle Testing A Handbook For Students and Clinicians PDFEma Danciu67% (3)
- Knee Biomechanics: Mark Arthur Martinez Trauma 1 April 5, 2018Документ7 страницKnee Biomechanics: Mark Arthur Martinez Trauma 1 April 5, 2018Juan Alvaro EstradaОценок пока нет
- Ergonomics: Zero - Gee Ergonomic Computer and Gaming WorkstationДокумент38 страницErgonomics: Zero - Gee Ergonomic Computer and Gaming WorkstationsoumikhalderОценок пока нет
- EssayДокумент2 страницыEssayFelipe AndinoОценок пока нет
- Physical Examination of The Shoulder FinalДокумент28 страницPhysical Examination of The Shoulder FinalAndinОценок пока нет
- Definations of The Key Concepts Curriculum StudiesДокумент13 страницDefinations of The Key Concepts Curriculum StudiesJohnsonОценок пока нет
- Head, Neck, Limbs OINAДокумент17 страницHead, Neck, Limbs OINAFrancis HenaresОценок пока нет
- Chapter 04 - Rehabilitation Systems in Ambient Assisted Living EnvironmentsДокумент19 страницChapter 04 - Rehabilitation Systems in Ambient Assisted Living EnvironmentsFernanda CamposОценок пока нет
- Introductio To OrthoticsДокумент8 страницIntroductio To OrthoticsGopi Krishnan100% (1)
- Curriculum Note 713Документ34 страницыCurriculum Note 713drajani.adeolaОценок пока нет
- Ergonomics - Group 2Документ101 страницаErgonomics - Group 2AnkurSingh100% (1)
- postural control (서성우)Документ4 страницыpostural control (서성우)Faisal QureshiОценок пока нет
- Best Exercises For Rotator Cuff TendonitisДокумент2 страницыBest Exercises For Rotator Cuff TendonitisKhandkar Sahil RidwanОценок пока нет
- Rough DraftДокумент12 страницRough Draftapi-248853282Оценок пока нет
- Scale For The Assessment and Rating of Ataxia (SARA) : 1) Gait 2) StanceДокумент2 страницыScale For The Assessment and Rating of Ataxia (SARA) : 1) Gait 2) StancetrcoskiОценок пока нет
- Orthopedic SummaryДокумент14 страницOrthopedic SummaryNavine NavОценок пока нет
- Lecture - 7 - Work - Capacity, - Stress - and - Fatigue (Autosaved)Документ51 страницаLecture - 7 - Work - Capacity, - Stress - and - Fatigue (Autosaved)Aizat RomainoОценок пока нет
- Palpation FinalДокумент11 страницPalpation FinalIvan SeaОценок пока нет
- Driving ErgonomicsДокумент58 страницDriving ErgonomicsPriyo Djatmiko100% (1)
- HumanBody - 3d Model and AnalysisДокумент407 страницHumanBody - 3d Model and Analysissssq1Оценок пока нет
- Ergonomics Sewing Machine Paper at Longowal ConferenceДокумент4 страницыErgonomics Sewing Machine Paper at Longowal ConferenceRogatianus Caesar BimantoroОценок пока нет
- Ergonomic Assessment: Vimal Singh Assistant Professor Department of Fashion Technology, NIFT, GandhinagarДокумент51 страницаErgonomic Assessment: Vimal Singh Assistant Professor Department of Fashion Technology, NIFT, GandhinagarSimoni KhetaniОценок пока нет
- Motor Relearning ProgrammeДокумент22 страницыMotor Relearning ProgrammeUzra ShujaatОценок пока нет
- Summary of Work Capacity Stress and FatigueДокумент6 страницSummary of Work Capacity Stress and Fatiguekishor11Оценок пока нет
- Research Report: Lecture # 1: Research: A Way of ThinkingДокумент35 страницResearch Report: Lecture # 1: Research: A Way of ThinkingUniVersEОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Exedrcises & TechniquesДокумент4 страницыTherapeutic Exedrcises & Techniquesrabia khalidОценок пока нет
- Wellness Massage 9-Q2-Module 3Документ30 страницWellness Massage 9-Q2-Module 3Kim Caguioa75% (4)
- Ergonomics Handbook PDFДокумент69 страницErgonomics Handbook PDFshaharyarОценок пока нет
- Discuss Common Indicators of Ergonomic ProblemДокумент10 страницDiscuss Common Indicators of Ergonomic ProblemLekshman KumarОценок пока нет
- Principal of BudgetingДокумент6 страницPrincipal of BudgetingZulkarnain DahalanОценок пока нет
- Common Spinal Disorders Explained PDFДокумент2 страницыCommon Spinal Disorders Explained PDFTamekaОценок пока нет
- ErgonomicsДокумент18 страницErgonomicsVeeramani Mari Muthu100% (1)
- The Ergonomic Design of Classroom Furniture:computer Work Station For First Graders in The Elementary School PDFДокумент11 страницThe Ergonomic Design of Classroom Furniture:computer Work Station For First Graders in The Elementary School PDFDebrina Puspitarini100% (2)
- Tools of Research (Interview and Observation)Документ38 страницTools of Research (Interview and Observation)Scorpian MouniehОценок пока нет
- 2 Lect 2 Ergonomics 91302 HSHF w2018 16jan18 Act x6Документ15 страниц2 Lect 2 Ergonomics 91302 HSHF w2018 16jan18 Act x6Mo ChoukeirОценок пока нет
- Ergonomics Awareness TrainingДокумент2 страницыErgonomics Awareness TrainingCassandra ChanОценок пока нет
- Presentation Ergonomics Oct2010Документ32 страницыPresentation Ergonomics Oct2010harshvardhan0% (1)
- Design of Repetitive WorkДокумент18 страницDesign of Repetitive WorkSandeep HarshvardhanОценок пока нет
- Work Physiology: "Underloading", in Which Human Capacities AreДокумент35 страницWork Physiology: "Underloading", in Which Human Capacities AreLance SantiagoОценок пока нет
- Walking Aids KinesiologyДокумент26 страницWalking Aids Kinesiologyfarwafurqan1Оценок пока нет
- Material Handling 20 PrinciplesДокумент2 страницыMaterial Handling 20 Principlesmicroman_123Оценок пока нет
- ErgonomicsДокумент21 страницаErgonomicsfayee123100% (1)
- Awareness of Good Posture and Computer Ergonomics Aming Medical Students PDFДокумент5 страницAwareness of Good Posture and Computer Ergonomics Aming Medical Students PDFWagiono SuparanОценок пока нет
- American Posture Institute GuideДокумент17 страницAmerican Posture Institute GuidesololuiОценок пока нет
- Joint of Lower LimbДокумент16 страницJoint of Lower LimbZA ID100% (1)
- Delhi Council For Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy Act, 1997Документ17 страницDelhi Council For Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy Act, 1997Latest Laws TeamОценок пока нет
- Ergonomics NotesДокумент15 страницErgonomics NotesSarah Abdalla100% (1)
- (Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders WMSDS) - Risk FactorsДокумент9 страниц(Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders WMSDS) - Risk FactorsDipeshBardoliaОценок пока нет
- Aims of ICFДокумент3 страницыAims of ICFthayu85Оценок пока нет
- Research Problem, Questions and HypothesesДокумент16 страницResearch Problem, Questions and HypothesesDarwin Ferrer100% (1)
- Surface Anatomy Lower Limb PDFДокумент10 страницSurface Anatomy Lower Limb PDFArunprasath SivaramanОценок пока нет
- Common Injuries of The Musculoskeletal SystemДокумент4 страницыCommon Injuries of The Musculoskeletal SystemJoniele Angelo AninОценок пока нет
- 2017 Unit 3 4 Physical Education Course OutlineДокумент10 страниц2017 Unit 3 4 Physical Education Course Outlineapi-334968025Оценок пока нет
- Ergonomics: Work Smarter Not HarderДокумент29 страницErgonomics: Work Smarter Not HarderMd. Nazmul Nazmul Ahshan SawonОценок пока нет
- EE3BA3 2013 OutlineДокумент4 страницыEE3BA3 2013 OutlineadiazОценок пока нет
- Ergonomics Evaluation Methods: This Chapter ProvidesДокумент22 страницыErgonomics Evaluation Methods: This Chapter ProvidesSherina Capola100% (1)
- Cumulative Trauma DisorderДокумент39 страницCumulative Trauma DisorderChanda NathaniОценок пока нет
- Gait AssessmentДокумент12 страницGait Assessmentahmed K.Abd el SaterОценок пока нет
- 1 Introduction To Safety EngineeringДокумент5 страниц1 Introduction To Safety EngineeringMANNОценок пока нет
- 2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsДокумент3 страницы2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDi CanОценок пока нет
- Ergonomics in Office Work - OSHwikiДокумент16 страницErgonomics in Office Work - OSHwikiZPPT74Оценок пока нет
- Acute Care For TBIДокумент32 страницыAcute Care For TBISudhakar SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Organizational Behaviour: Bba & BHMДокумент249 страницOrganizational Behaviour: Bba & BHMKhushi NaharОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics of Work: Yansen Theopilus, S.T., M.TДокумент68 страницBiomechanics of Work: Yansen Theopilus, S.T., M.TuytyuytryuОценок пока нет
- Birth Brachial Plexus Palsy UpdateДокумент8 страницBirth Brachial Plexus Palsy UpdateDyah SafitriОценок пока нет
- Muscular Trauma in Dogs and Cats - Musculoskeletal System - MSD Veterinary ManualДокумент1 страницаMuscular Trauma in Dogs and Cats - Musculoskeletal System - MSD Veterinary ManualZullyОценок пока нет
- Dempster BodySegmentParametersДокумент2 страницыDempster BodySegmentParametersAlex RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Physiotheraphy Role in Pain ManagementДокумент63 страницыPhysiotheraphy Role in Pain Management姐姐雯Оценок пока нет
- CAPR 50 Written Component Practice QuestionsДокумент25 страницCAPR 50 Written Component Practice QuestionsBhaskar Kumar JhaОценок пока нет
- Shoulder Orthosis - DevadriДокумент18 страницShoulder Orthosis - DevadriDevadri DeyОценок пока нет
- Acland Human AnatomyДокумент51 страницаAcland Human Anatomyjust for download matterОценок пока нет
- Homoeopathy For Sports Exercise and Dance Emlyn Thomas.02996 1contentsДокумент13 страницHomoeopathy For Sports Exercise and Dance Emlyn Thomas.02996 1contentsdipgang7174Оценок пока нет
- Nerves and Innervated MusclesДокумент108 страницNerves and Innervated Musclesphantasma669Оценок пока нет
- Gujarat High Court Ordered Probe in Custodial Death Case - Shwetang Patel Murder Case - Patidar Agitation - Police Atrocity - (Read The Order)Документ9 страницGujarat High Court Ordered Probe in Custodial Death Case - Shwetang Patel Murder Case - Patidar Agitation - Police Atrocity - (Read The Order)Manan BhattОценок пока нет
- 1 Antropometri CSДокумент17 страниц1 Antropometri CSTop Eleven2Оценок пока нет
- ch9 PDFДокумент53 страницыch9 PDFHONGJYОценок пока нет
- Shoulder Rotator Cuff Workshop Exercise Handout PDFДокумент7 страницShoulder Rotator Cuff Workshop Exercise Handout PDFsaputradhanu1Оценок пока нет
- English AnatomiiiiДокумент19 страницEnglish Anatomiiiikiki ssОценок пока нет
- Team Sports - Quiz 6Документ16 страницTeam Sports - Quiz 6Sophia PaparroОценок пока нет