Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Aspartate Transaminase
Загружено:
Tel SisonАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aspartate Transaminase
Загружено:
Tel SisonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aspartate transaminase (AST), also called aspartate aminotransferase is commonly known as sgot (AspAT/ASAT/AAT) or serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase
(SGOT), is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme (EC 2.6.1.1). AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an -amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in theliver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, and red blood cells, and it is commonly measured clinically as a marker for liver health.
Function[edit source | editbeta]
Aspartate transaminase catalyzes the interconversion of aspartate and ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and glutamate. Aspartate (Asp) + -ketoglutarate oxaloacetate + glutamate (Glu)
Reaction catalyzed by aspartate aminotransferase
As a prototypical transaminase, AST relies on PLP as a cofactor to transfer the amino group from aspartate or glutamate to the correspondingketoacid. In the process, the cofactor shuttles between PLP [2] and the pyridoxamine phosphate (PMP) form. The amino group transfer catalyzed by this enzyme is crucial in both amino acid degradation and biosynthesis. In amino acid degradation, following the conversion of -ketoglutarate to glutamate, glutamate subsequently undergoes oxidative deamination to form ammonium ions, which are excreted as urea. In the reverse reaction, aspartate may be synthesized from oxaloacetate, which is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle
Creatine kinase (CK), also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) or phospho-creatine kinase (and sometimes incorrectly as creatininekinase), is an enzyme (EC 2.7.3.2) expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and consumes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to create phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). This CK enzyme [2] reaction is reversible and thus ATP can be generated from PCr and ADP. In tissues and cells that consume ATP rapidly, especially skeletal muscle, but also brain, photoreceptor cells of the retina, hair cells of the inner ear,spermatozoa and smooth muscle, PCr serves as an energy reservoir for the rapid buffering and regeneration of ATP in situ, as well as for intracellular energy [3] [4] transport by the PCr shuttle or circuit. Thus creatine kinase is an important enzyme in such tissues. Clinically, creatine kinase is assayed in blood tests as a marker of myocardial infarction (heart attack), rhabdomyolysis (severe muscle breakdown),muscular dystrophy, the autoimmune myositides and in acute renal failure.
Functions[edit source]
The mitochondrial creatine kinase (CKm) is present in the mitochondrial intermembrane space, where it produces phosphocreatine (PCr) from mitochondrially generated ATP and creatine (Cr) imported from the cytosol. Apart from the two mitochondrial CK isoenzyme forms, that is, ubiquitous mtCK (present in non-
muscle tissues) and sarcomeric mtCK (present in sarcomeric muscle), there are three cytosolic CK isoforms present in the cytosol, depending on the tissue. Whereas MM-CK is expressed in sarcomeric muscle, that is, skeletal and cardiac muscle, MB-CK is expressed in cardiac muscle, and BB-CK is expressed in smooth muscle and in most non-muscle tissues. Mitochondrial mtCK and cytosolic CK are connected in a so-called PCr/Cr-shuttle or circuit. PCr generated by mtCK in mitochondria is shuttled to cytosolic CK that is coupled to ATP-dependent processes, e.g. ATPases, like acto-myosin ATPase for muscle contraction, or ion pumps, like the calcium pump for muscle relaxation. There, the bound cytosolic CK accepts the PCr shuttled through the cell and uses it to regenerate ATP, which can then be used as energy source by the ATPases. (CK is associated intimately with the ATPases, forming a functionally coupled microcompartment.) Thus, PCr is not only an energy buffer but also a cellular transport form of energy between subcellular sites of energy (ATP) production (mitochondria and glycolysis) and those of energy utilization (ATPases) A prothrombin time test measures how quickly your blood clots. Sometimes called a pro time test or PT test, a prothrombin time test uses a sample of your blood. Prothrombin is a protein produced by your liver that helps your blood to clot. When you bleed, a series of chemicals (clotting factors) activate in a stepwise fashion. The end result is a clot which stops the bleeding. One step in the process is prothrombin turning into another protein called thrombin. The prothrombin time test measures how well the clotting process works and how long it takes to occur.
Вам также может понравиться
- Cardiovascular System: Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine, UNHAS Rosdiana NatzirДокумент68 страницCardiovascular System: Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine, UNHAS Rosdiana NatzirikhyОценок пока нет
- Phosphocreatine: Phosphocreatine, Also Known As Creatine Phosphate (CP) or PCRДокумент4 страницыPhosphocreatine: Phosphocreatine, Also Known As Creatine Phosphate (CP) or PCRKlaraОценок пока нет
- Cardiac EnzymesДокумент20 страницCardiac Enzymesstrypto123aaaОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of Cardiovascular SystemДокумент27 страницBiochemistry of Cardiovascular SystemRenaldy PamungkasОценок пока нет
- Breakdown of GlucoseДокумент2 страницыBreakdown of GlucoseJAYLEN TRACEYОценок пока нет
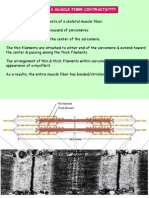
- How A Muscle Fiber Contracts????Документ30 страницHow A Muscle Fiber Contracts????Amy SyahidaОценок пока нет
- Creatine and Creatinine MetabolismДокумент143 страницыCreatine and Creatinine MetabolismFernando Fernandez HernandezОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of Cardiovascular SystemДокумент113 страницBiochemistry of Cardiovascular SystemNindy75% (4)
- Normal Myocardial Metabolism Review JournalДокумент7 страницNormal Myocardial Metabolism Review JournallilyОценок пока нет
- Creatine Supplementation May Improve Health of Dialysis PatientsДокумент14 страницCreatine Supplementation May Improve Health of Dialysis PatientsLuis VargasОценок пока нет
- Mitochondrial Creatine Kinase in Human Health and DiseaseДокумент17 страницMitochondrial Creatine Kinase in Human Health and DiseasedeviОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5 - BiochemistryДокумент34 страницыLecture 5 - Biochemistryizza ghafoorОценок пока нет
- 2. High energy cpds. shuttles. Dr Naim.Документ48 страниц2. High energy cpds. shuttles. Dr Naim.saadali919782Оценок пока нет
- C PKДокумент4 страницыC PKpreethiОценок пока нет
- CSCS Study GuideДокумент50 страницCSCS Study GuideMatt Siniscalchi100% (5)
- Adenosine TriphosphateДокумент11 страницAdenosine TriphosphateAyush LОценок пока нет
- Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine, UNHAS Rosdiana NatzirДокумент89 страницDepartment of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine, UNHAS Rosdiana NatzirBombomОценок пока нет
- Where Energy for Training Comes FromДокумент12 страницWhere Energy for Training Comes FromCanadaMikeОценок пока нет
- Biomedic Ii Cardiovascular System: Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine, UNHAS Rosdiana NatzirДокумент55 страницBiomedic Ii Cardiovascular System: Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine, UNHAS Rosdiana NatzirZurezki Yuana YafieОценок пока нет
- ATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsДокумент2 страницыATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsHayze Jones50% (2)
- FILE - 20220120 - 124136 - Cơ TimДокумент3 страницыFILE - 20220120 - 124136 - Cơ TimĐào Ngô AnhОценок пока нет
- l3 BioДокумент4 страницыl3 Biodrahmed1028Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 XДокумент8 страницChapter 1 XMatt FОценок пока нет
- RespirationДокумент100 страницRespirationColin RiddellОценок пока нет
- Mitocondra AKIДокумент13 страницMitocondra AKIMartin GomezОценок пока нет
- 08 Kongas Paper PDFДокумент10 страниц08 Kongas Paper PDFEkaSelvinaОценок пока нет
- Art 1 en Dot HeliumДокумент11 страницArt 1 en Dot HeliumMiss_PiggyОценок пока нет
- 1 Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Function in CellsДокумент5 страниц1 Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Function in CellspОценок пока нет
- Metabolic Aspect of CVSДокумент25 страницMetabolic Aspect of CVSsamar yousif mohamedОценок пока нет
- MI - 11 - Ciclo de Cori, Creatina Fosfato y Ciclos Energéticos Del MúsculoДокумент39 страницMI - 11 - Ciclo de Cori, Creatina Fosfato y Ciclos Energéticos Del MúsculoANDRÉS FELIPE VALDERRAMA BAEZОценок пока нет
- Conference 1 - BiochemistryДокумент12 страницConference 1 - BiochemistryJoicey CatamioОценок пока нет
- Vitamin D and Calcium Role in Cardiac Muscle MetabolismДокумент19 страницVitamin D and Calcium Role in Cardiac Muscle MetabolismMariela AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Bio Notes 1Документ180 страницBio Notes 1JyNadarilОценок пока нет
- AST and ALTДокумент7 страницAST and ALTTrisha NavarceОценок пока нет
- Enzymology Definitions and TerminologyДокумент23 страницыEnzymology Definitions and TerminologyCalvin Yeow-kuan ChongОценок пока нет
- Changes in Cardiac Metabolism: A Critical Step From Stable Angina To Ischaemic CardiomyopathyДокумент6 страницChanges in Cardiac Metabolism: A Critical Step From Stable Angina To Ischaemic CardiomyopathyazizhaОценок пока нет
- Answers of Exam Ques.Документ3 страницыAnswers of Exam Ques.Sonali SehrawatОценок пока нет
- Atp AdpДокумент8 страницAtp AdpChristian Jay AspacioОценок пока нет
- Mitochondrial Creatine Kinase in Human Health andДокумент18 страницMitochondrial Creatine Kinase in Human Health andlindaОценок пока нет
- Energy Metabolism of The Heart Under Different PathophysiologicalДокумент27 страницEnergy Metabolism of The Heart Under Different PathophysiologicalAmanuel MaruОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of Cardiovascular System: Agnes O. KwenangДокумент70 страницBiochemistry of Cardiovascular System: Agnes O. KwenangAdi Surya SyamОценок пока нет
- Na/K-ATPase Role in Calcium Signaling MicrodomainsДокумент10 страницNa/K-ATPase Role in Calcium Signaling MicrodomainsKrisha 21BBT0145Оценок пока нет
- Creatine Kinase: Amy WardДокумент33 страницыCreatine Kinase: Amy WardYondri Mandaku TasidjawaОценок пока нет
- 8- Physical and Phsyiological Factors in Sport (1)Документ28 страниц8- Physical and Phsyiological Factors in Sport (1)ganesh raoОценок пока нет
- Muscle MetabolismДокумент17 страницMuscle MetabolismAlejandro EVОценок пока нет
- Adenosine TriphosphateДокумент2 страницыAdenosine TriphosphateThanh NguyenОценок пока нет
- What Is Energy CouplingДокумент16 страницWhat Is Energy Couplingjoei ArqueroОценок пока нет
- Burn Injury Decreases Myocardial Na-K-Atpase Activity: Role of PKC InhibitionДокумент9 страницBurn Injury Decreases Myocardial Na-K-Atpase Activity: Role of PKC InhibitionChristine Notoningtiyas SantosoОценок пока нет
- ATP: The Energy Currency of the CellДокумент12 страницATP: The Energy Currency of the CellCielo PepitoОценок пока нет
- 3 - Energy System and The Overall Metabolic RegulationДокумент41 страница3 - Energy System and The Overall Metabolic RegulationmeralОценок пока нет
- NHE3 ZIjian XieДокумент9 страницNHE3 ZIjian Xienilberto2Оценок пока нет
- A Level Biology: Alevelbiology - Co.ukДокумент11 страницA Level Biology: Alevelbiology - Co.ukg8yd7q9cnmОценок пока нет
- Clinical EnzymologyДокумент23 страницыClinical EnzymologyKishore KaranОценок пока нет
- Science 9 q1w7Документ9 страницScience 9 q1w7seanfelix07102009Оценок пока нет
- Gluconeogenisis.Документ21 страницаGluconeogenisis.Shivanand MaliОценок пока нет
- BIO3420.2010.5Muscle Part 2 06oct10 2Документ27 страницBIO3420.2010.5Muscle Part 2 06oct10 2aemilianneОценок пока нет
- Edexcel Biology A2 Core Practical WorkbookДокумент5 страницEdexcel Biology A2 Core Practical WorkbookHayamMohamedОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of MuscleДокумент68 страницBiochemistry of MuscleWisnu KuncoroОценок пока нет
- Cardio Vas LarДокумент13 страницCardio Vas LarKathrine SiahaanОценок пока нет
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances WordДокумент1 страницаFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances WordTel SisonОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology For Small Gestational Age InfantДокумент4 страницыAnatomy and Physiology For Small Gestational Age InfantTel SisonОценок пока нет
- Aspartate TransaminaseДокумент2 страницыAspartate TransaminaseTel SisonОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology For Small Gestational Age InfantДокумент4 страницыAnatomy and Physiology For Small Gestational Age InfantTel SisonОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology For Small Gestational Age InfantДокумент4 страницыAnatomy and Physiology For Small Gestational Age InfantTel SisonОценок пока нет
- Indications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnДокумент1 страницаIndications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnTel SisonОценок пока нет
- General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level ExaminationДокумент20 страницGeneral Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level ExaminationMaggie NgОценок пока нет
- Kizen Training 12 Week Strength and Fat Loss ProgramДокумент20 страницKizen Training 12 Week Strength and Fat Loss Programjoey100% (1)
- Structure of Blood Vessels - StationsДокумент6 страницStructure of Blood Vessels - StationsRamya MalariniОценок пока нет
- Induced Lactation ANR SlidesДокумент11 страницInduced Lactation ANR Slidesjohn cageОценок пока нет
- Reflex Testing Methods For Evaluating C.N.S. Development - Anna's ArchiveДокумент78 страницReflex Testing Methods For Evaluating C.N.S. Development - Anna's ArchiveBrain AngОценок пока нет
- Before Diving Make A Complete Dive Plan Together & Estimate Sea ConditionsДокумент8 страницBefore Diving Make A Complete Dive Plan Together & Estimate Sea ConditionsMike LuckyОценок пока нет
- IB Psychology HL Biological LOAДокумент11 страницIB Psychology HL Biological LOAgfore3Оценок пока нет
- The Wolbam Destiny 6Документ12 страницThe Wolbam Destiny 6Michael WolfsonОценок пока нет
- Dr. Sak Indriyani, Spa, Mkes: Department of Child Health Rsu MataramДокумент48 страницDr. Sak Indriyani, Spa, Mkes: Department of Child Health Rsu MataramMuhammad Bilal Bin AmirОценок пока нет
- How Gases Are Transported in the BloodДокумент22 страницыHow Gases Are Transported in the BloodAiza AyazОценок пока нет
- Fantasy/Imagination: Patti M. ValkenburgДокумент3 страницыFantasy/Imagination: Patti M. ValkenburgalbertoadalidОценок пока нет
- Veta 3 - Datasheet - ENG - 20210315Документ2 страницыVeta 3 - Datasheet - ENG - 20210315JuanОценок пока нет
- Classification and Types of StrokeДокумент11 страницClassification and Types of StrokeJose Enrique OrtizОценок пока нет
- Group 6 Part 1 Review of The Aging of Physiological System Notes Part 1Документ7 страницGroup 6 Part 1 Review of The Aging of Physiological System Notes Part 1Crissan Jejomar AbanesОценок пока нет
- Myasthenia GravisДокумент3 страницыMyasthenia GravisfsОценок пока нет
- ACOSTA, Joyce Ara, SBAR 3 (In Good Condition)Документ2 страницыACOSTA, Joyce Ara, SBAR 3 (In Good Condition)Joyce Ara Tumbaga AcostaОценок пока нет
- CARDIOVASCULAR - SYSTEM Group No.3 MODULEДокумент12 страницCARDIOVASCULAR - SYSTEM Group No.3 MODULEDavid Paul LanuzaОценок пока нет
- Aip Summer 2017 PDFДокумент116 страницAip Summer 2017 PDFShibli KushtiaОценок пока нет
- Pathomorphology Final ExamДокумент262 страницыPathomorphology Final ExamMann SarwanОценок пока нет
- Haemorrhage & ShockДокумент22 страницыHaemorrhage & ShockAmiОценок пока нет
- DIPIRO Gagal GinjalДокумент19 страницDIPIRO Gagal Ginjalselfa louhenapessyОценок пока нет
- Enls V 4 0 Protocol Coma FinalДокумент16 страницEnls V 4 0 Protocol Coma Finalsucipto suciptoОценок пока нет
- TonsillectomyДокумент27 страницTonsillectomyRho Vince Caño MalagueñoОценок пока нет
- Circulatory System Peer Assessment: Examiner's NotesДокумент4 страницыCirculatory System Peer Assessment: Examiner's NotespkrajenpillaygmailcomОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Biomolecules and Cellular ComponentsДокумент18 страницIntroduction to Biomolecules and Cellular ComponentsM Nur M. MahmudОценок пока нет
- Nephrology Block Ia. History: A. InformantДокумент4 страницыNephrology Block Ia. History: A. InformantKatherine FabrosОценок пока нет
- Nice Guideline NstemiДокумент23 страницыNice Guideline NstemiKhondoker SayeedОценок пока нет
- Biographic Data: AdolescentДокумент4 страницыBiographic Data: AdolescentHanna GardoqueОценок пока нет
- Dental and anesthesia procedures and equipmentДокумент56 страницDental and anesthesia procedures and equipmentVijay RanaОценок пока нет
- Understanding CLL: A Guide For Patients Who Want To Take Charge of Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding CLL: A Guide For Patients Who Want To Take Charge of Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaNakul Singh ParkwayIndiaОценок пока нет