Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transfusion RXN
Загружено:
Nikki AngОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Transfusion RXN
Загружено:
Nikki AngАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
BBGuy.
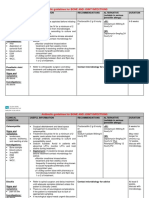
org Reaction Summary Chart; 2011, Joe Chaffin, MD Updated 08/2011 ACUTE FEBRILE REACTIONS (during or <24 hrs from transfusion; presenting with fever) Reaction/Incidence Presentation; Diagnosis Common Mechanism Treatment Prevention
Acute Hemolytic (AHTR); 1:76,000, 1 in 1.8 million are fatal Febrile Nonhemolytic (FNHTR); < 1% Bacterial Contamination (Septic reaction); 1:3000 PLTS (much lower reactions) Transfusion-related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI); 1:1300-1:5000 Fever/chills, back/flank pain, HGBemia/uria, bleeding, DIC; clerical errors, free HGB, repeat x-match Fever/chills only (>1 C/2oF); negative workup Rapid high fever, rigors, shock, GI symptoms; gram stain (50%), culture is conclusive Acute lung injury <6 hours after transfusion. Bilateral CXR infiltrates, hypoxemia. No cardiac dysfunction. Difficult; donor HLA/HNA abs, consensus criteria ABO-incompatible red cells given to patient (rarely from incompatible plasma hemolyzing patient RBCs) Accumulated cytokines (IL-6, TNF); HLA antibodies Bacteria in donors blood or through collection site 1. Transfused anti-HLA and/or anti-HNA Abs activate PMNs or 2. Endothelial activation and PMN lung sequestration, then activation by blood substances Pressure and volume support, fluids, diuretics if necessary (urine output > 1 mL/Kg/hr); may need PLT/FFP/Cryo if DIC Antipyretics; meperidine if chills are violent As for sepsis; antibiotics and pressure support as necessary Aggressive supportive care (may include intubation); most resolve but close to 20% fatal Careful attention to detail and processes
Leukoreduction. Pretransfusion antipyretics used but may not work. Donor Center precautions, possible leukoreduction contribution Preferential male plasma use for decreased HLA/HNA antibodies. HLA antibody screening of female PLT donors. If + antibodies in implicated donor, donor should be deferred
Reaction
ACUTE AFEBRILE REACTIONS (during or <24 hrs from transfusion; presenting WITHOUT fever) Presentation/Diagnosis Common Mechanism Treatment Prevention
Localized or diffuse hives/redness Severe hypotension very early in transfusion, GI symptoms, rare fever; anti-IgA, check IgA levels Similar to anaphylactic, often milder Dyspnea, hypoxia during or after transfusion; +/- inc BNP, JVD, hypertension Chills IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to transfused protein Recipient IgA deficiency with anti-IgA antibodies, haptoglobin deficiency Milder IgA deficiency, also those on ACE inhibitors with LR filters or plasma exchange Cardiopulmonary disease with too rapid blood infusion; very old and very young most at risk As for febrile nonhemolytic; fever blocked by antipyretic Antihistamines Epinephrine (0.2-0.5 mL of 1:1000 given IM or SC; use IV if necessary), pressure support As for anaphylactic Diuretics, slow infusion Meperidine if chills are violent Pretransfusion antihistamine; may wash product if necessary IgA deficient products (washed or from deficient donor) If associated with mild IgA deficiency, IgA deficient products Divide products into aliquots, slow infusion, monitor I/Os As for febrile nonhemolytic
Urticarial (mild allergic reaction); 1-3% Anaphylactic (severe allergic reaction); 1:20,000-50,000 Anaphylactoid; rare Transfusion associated circulatory overload (TACO); 1:350-5000 reported Premedicated Febrile
Reaction
Delayed Hemolytic (DHTR); 1:2500-11,000 TA-GVHD; Risk varies widely by locale
DELAYED FEBRILE REACTIONS (>24 hrs from transfusion; presenting with fever) Presentation/Diagnosis Common Mechanism Treatment Prevention
Fever, anemia > 1 week after transfusion; +DAT, hyperbili, new antibody (Jk, Fy, K especially) Fever, diarrhea, skin rash Anamnestic response to reexposure to red cell antigen; rarely 1o response Cellular immune response by transfused T-lymphocytes vs host Supportive; as for acute hemolytic if severe Supportive, immunosuppress; usually in vain Previous records (honor previous antibodies), patient history, some use ID tags/cards Irradiation of cellular products transfused to at-risk recipients
Reaction
Post-transfusion Purpura (PTP);1:24,000 Iron Overload
DELAYED AFEBRILE REACTIONS (>24 hrs from transfusion; presenting WITHOUT fever) Presentation/Diagnosis Common Mechanism Treatment Prevention
Dec PLTS +/- bleeding 1 week after transfusion (RBCs +/- PLTs); clinical dx, platelet antibodies Liver, pancreas, cardiac dysfx Recipient antibody vs. absent antigen (HPA-1a 70%) Iron deposition from multiple Tx IVIG 1st choice; avoid platelet transfusion Deferoxamine Antigen-negative platelet transfusions Judicious transfusion
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Grief Death and Dying HandoutДокумент8 страницGrief Death and Dying HandoutNikki AngОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Biddis Disease and DictatorshipДокумент5 страницBiddis Disease and DictatorshipNikki AngОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11th Edition: Guyton & HallДокумент40 страницTextbook of Medical Physiology, 11th Edition: Guyton & HallNikki AngОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Lymphatics TableДокумент5 страницLymphatics TableNikki AngОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Psicoterapia Interpersonal en El Tratamiento de La Depresión MayorДокумент11 страницPsicoterapia Interpersonal en El Tratamiento de La Depresión MayorAndrea MiñoОценок пока нет
- Lifewater LatrineDesignandConstruction ManualДокумент270 страницLifewater LatrineDesignandConstruction ManualDelovan CheikhoОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- SCAI Shock Classification DeckДокумент22 страницыSCAI Shock Classification DeckJimmy JimmyОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- CPR Memo 1Документ2 страницыCPR Memo 1api-509697513Оценок пока нет
- Criterios de Elegibilidad de ACOДокумент88 страницCriterios de Elegibilidad de ACOquimegiОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- DR - Kavita Priya Iicm 1Документ68 страницDR - Kavita Priya Iicm 1Kavita PriyaОценок пока нет
- PharmДокумент16 страницPharmEi SetteОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Anatomia Clitoris Orgasmo Femenina PDFДокумент12 страницAnatomia Clitoris Orgasmo Femenina PDFJaviMéndezОценок пока нет
- Anaemia: by Swaathi R Final Year MbbsДокумент33 страницыAnaemia: by Swaathi R Final Year MbbsGopi NathОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Sharma Et Al-2016-Journal of Applied MicrobiologyДокумент11 страницSharma Et Al-2016-Journal of Applied MicrobiologyJoanaОценок пока нет
- Bioethics OutlineДокумент30 страницBioethics OutlineJason KeithОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Cae Open Cloze PhobiasДокумент3 страницыCae Open Cloze PhobiasValéria DuczaОценок пока нет
- Kevin Chen - Book Review: Scientific Qigong Exploration: The Wonders and Mysteries of Qi by Lu, ZuyinДокумент6 страницKevin Chen - Book Review: Scientific Qigong Exploration: The Wonders and Mysteries of Qi by Lu, ZuyinSonyRedОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Antibiotic Guidelines For BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONSДокумент3 страницыAntibiotic Guidelines For BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONSKhurram NadeemОценок пока нет
- Health As Expanding ConsciousnessДокумент8 страницHealth As Expanding ConsciousnessJun ManОценок пока нет
- Perdev ReviewerДокумент9 страницPerdev ReviewerPretut VillamorОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Pedia ReviewerДокумент27 страницPedia ReviewerEvangeline GoОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Brief History of Makabali HospitalДокумент1 страницаBrief History of Makabali Hospitalpaulo_070390100% (1)
- Emotionally Focused Therapy (Eft) and Emotionally Focused Family Therapy (Efft) : A Challenge/opportunity For Systemic and Post-Systemic TherapistsДокумент5 страницEmotionally Focused Therapy (Eft) and Emotionally Focused Family Therapy (Efft) : A Challenge/opportunity For Systemic and Post-Systemic TherapistsEFTcouplesОценок пока нет
- Blanche GrubeДокумент21 страницаBlanche GrubesangroniscarlosОценок пока нет
- Tesis vITAMIN C CONTENT IN FRUITSДокумент24 страницыTesis vITAMIN C CONTENT IN FRUITSHema JothyОценок пока нет
- Symptoms of Sexual DisordersДокумент5 страницSymptoms of Sexual DisordersJham ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠ CapulongОценок пока нет
- 06 Senior Citizen PolicyДокумент26 страниц06 Senior Citizen PolicyJaimson FrancisОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- CPD Questions For Volume 21 Issue 3Документ4 страницыCPD Questions For Volume 21 Issue 3KeeranmayeeishraОценок пока нет
- Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Guide:Dr Suchitra Dashjohn Speaker: DR Madhusmita BeheraДокумент20 страницCerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Guide:Dr Suchitra Dashjohn Speaker: DR Madhusmita Beheraasish753905Оценок пока нет
- MAN ParaTitle-Manuscript - Grace-EpresДокумент80 страницMAN ParaTitle-Manuscript - Grace-EpresSevered AppleheadОценок пока нет
- Review Shows EGb 761 Optimizes Standards of Life For Tinnitus PatientsДокумент2 страницыReview Shows EGb 761 Optimizes Standards of Life For Tinnitus PatientsTotoDodongGusОценок пока нет
- Fibula Stress Fractures: A Treatment Review: Iftach Hetsroni, MD, and Gideon Mann, MDДокумент3 страницыFibula Stress Fractures: A Treatment Review: Iftach Hetsroni, MD, and Gideon Mann, MDJamaluddin HaikhahОценок пока нет
- Introduction Definition: Types of PacemakersДокумент8 страницIntroduction Definition: Types of PacemakersPrasann RoyОценок пока нет
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus (HNP)Документ21 страницаHerniated Nucleus Pulposus (HNP)Kaye100% (1)