Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Guidelines Categorized by Profile: Media Models
Загружено:
Elizabeth ArosteguiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Guidelines Categorized by Profile: Media Models
Загружено:
Elizabeth ArosteguiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Web Site Design Profiles: Guidelines by Profile
Guidelines Categorized by Profile
If you're designing for this audience, you probably don't need guidelines.
Kevin Benko: The Square Peg
Use color, imagery and backgrounds to set a mood and evoke a response in your audience. Adopt media models that evoke responses in your audience similar to the ones you want them to have for your site. Use links for suspense, aesthetic unity, branching storylines and annotations. (Jorn) Be sure the audience will experience what you intend.
q
Mars Attacks: The Movie
The Spot
Test your page on multiple browsers and platforms, and over a 14.4 modem. Use a Web-safe palette to index images so that they give the same impression on both PC and Macintosh computers. Pay attention to the experience audiences will have watching your pages load; not just the experience of seeing them after they are loaded.
file:///F|/ztemp/design_guideline/guidelines.html (1 of 8)15.02.2005 22:16:33
Web Site Design Profiles: Guidelines by Profile
Use the simplest and most direct layout possible.
r
Yahoo! Main Page
Limit the number of heading sizes, font sizes and colors, font treatments, embedded lists and clarifying graphical elements (decorative bullet points and horizontal bars) to the smallest number for which a distinct and justifiable purpose may be stated. Use your limited number of typographic cues (font sizes, font treatments, heading sizes), spatial cues (embedded lists) and graphical cues (bullet points and decorative bars) consistently throughout the site. Use BLOCKQUOTE tags and tables to limit the width of text blocks and improve readbility.
Use the simplest and most direct structure possible.
r
r r
Keep content as high in the hierarchy as possible -- create "shallow" structures. Rule of Thumb: Limit your discrete hierarchical levels to four. When a "shallow" structure results in more than 7 - 10 major choices, group the choices into a perceptually smaller number. Provide links back to your home page on all lower levels. Present coherent documents as wholes (REES), but keep them under 32K (JORN) or under 5 screens long (LYNCH). Pare down text. Even when you have a lot of information, rewrite text to be as concise as possible.
Consider every graphic critically for its information value.
r
Use only "content critical" graphics -- images that convey or support the primary content of your site. Test on several platforms with different browsers to be sure your graphics are clear enough on screen to be accurately interpreted.
file:///F|/ztemp/design_guideline/guidelines.html (2 of 8)15.02.2005 22:16:33
Web Site Design Profiles: Guidelines by Profile
Make a clear distinction between what is content and Harley Davidson what is not. Home Page s Make buttons look like buttons and non-buttons not look like buttons. s Make buttons that lead to content look different than ones that don't. s Use consistent layout for the content segments of the site.
Make sure the graphical treatment of your pages (background images and colors, large graphics, alternate colors of text, animated images) doesn't interfere with the readability of content-bearing text and graphics.
Don't give the impression that your site holds more content than it does. r Except for navigation, link everything only once (the first time a word or phrase occurs -- not every time). r Don't chop content into tiny chunks on many separate pages. Even if the site contains a small amount of content relative to the entertainment, or affective portions, group it together or provide an optional link where it is all accessible in one place.
Use graphics to create a visual identity and sustain it throughout the site. r Use small graphics and buttons to build site identity and a smaller "signature graphic" for lower level pages that can double as a button to return to the main page. r Make sure that the images used for identity convey an appropriate message about you and your site. Be careful to avoid media models that do not match the identity you want for your site. r Use few enough colors in your identity graphics that your site has an identifiable color scheme, and sustain the color scheme throughout the site.
First Monday: Peerreviewed Journal on the Internet
Thinkshop Noblesville School District
Use a grid-based layout for the site.
file:///F|/ztemp/design_guideline/guidelines.html (3 of 8)15.02.2005 22:16:33
Web Site Design Profiles: Guidelines by Profile
Supply text alternatives for all graphic elements in the site, and use very few text treatments (bold, italic, heading sizes). Too many typographic treatments add visual noise to pages that also display small graphics.
Use graphics to create a visual identity and sustain it throughout the site.
q
Use small graphics and buttons to build site identity and a smaller "signature graphic" for lower level pages that can double as a button to return to the main page. Toad Head Make sure that the images used for identity convey an appropriate message about you and your site. Be careful to avoid media models that do not match the identity you want for your site. Use few enough colors in your identity graphics that your site has an identifiable color scheme, and sustain the color scheme throughout the site.
National Center for Missing & Exploited Children
Establish different treatments for the "content heavy" and "affect heavy" portions of the pages and/or the site.
When in doubt, err on the side of content. Universal WEB Guidelines Discriminate between what's amusing or informative and Samples what's distracting. Eliminate the distractions.
q
Blinking text and animated images are the visual equivalent of tugging repeatedly on someone's sleeve -after you've first gotten their attention the continued tugging can get pretty annoying. Find someone who has no stake in your site and no hesitation about giving you bad news. Ask that person to make your animated/ blinking page their browser "home page" for a week and then ask them whether or not the moving parts of it are distracting. Make pages viewable without adjustment beyond the
file:///F|/ztemp/design_guideline/guidelines.html (4 of 8)15.02.2005 22:16:33
Web Site Design Profiles: Guidelines by Profile
default window size of most browsers (no wider than 472 pixels and critical information viewable within 325 - 350 pixels vertically). "Under construction" notices and repeated exhortations to "Check out ..." this and that are verbal distractions. Unless your site is a parody of Web jargon, don't make it sound like one. Waiting for pages to load is a distraction, no matter what other expectations your audience may have. If your site has an All Affect profile you won't eliminate your large image files but you should employ every trick you can to lower wait times for your pages.
Instill confidence in your primary audience.
q
Provide update information so that people know when someone last changed the page. Provide valid contact information so that people know where to ask questions and so that they know who is behind the experience/information they are getting. Visual design is susceptible to the equivalent of misspellings, inaccuracies and grammatical errors. Check for: r stray pixels, r images that didn't get processed properly for transparency or indexed color, r misspelled words in image files (very common since most graphics programs don't provide spell checking), r images loaded into the wrong file name so that they don't match the text or are mislabelled, or r graphics that give unintended effects when they are seen next to each other (strange color combinations, a person in one image appearing to point to someone else, the semantic content of images producing unintended juxtapositions).
Provide for users with low-end systems and browsers unless you have hard data showing that your primary audience has the same capabilities you do.
file:///F|/ztemp/design_guideline/guidelines.html (5 of 8)15.02.2005 22:16:33
Web Site Design Profiles: Guidelines by Profile
q
Use ALT tags to show text when images do not load or will not display. Warn users when links lead to large image or media files or graphics-intensive pages and sites. Try your pages out in a text-only browser so you know what kind of experience they are giving to that audience.
Following Media Models "Media models" are recognizable combinations of color, imagery, layout and graphical treatment that people are used to seeing in advertising, television shows, movies, video games and other media. People associate different models with the messages they are used to getting in those forms ... black and white photographs accompanied by closely set text in narrow columns is a simple model associated with newspapers, so the use of these elements in combination may suggest journalism, accuracy of fact, realism and authenticity.
The New York Times.
By observing the components of media models you can adopt their "looks" and use them to encourage the response you want from your audience. Remember that people seek out different media models as cues to the experiences they will get, and they are not always in the mood to have the same kind of experience. An investment analyst may repond positively to the clean, open layout and rich accent detail in an expensive hobbyist magazine when she is pursuing her interest in philately, but seek out garish purple-and-pink color schemes accompanied by outsized, ornate fonts and baroque curliques when she is looking for an entertaining romance story to read over the weekend.
Have a Look at Swedish Stamps.
Romance Web go back to the All Affect model
Avoiding Media Models "Media models" are recognizable combinations of color, imagery, layout and graphical treatment that people are
file:///F|/ztemp/design_guideline/guidelines.html (6 of 8)15.02.2005 22:16:33
Web Site Design Profiles: Guidelines by Profile
used to seeing in advertising, television shows, movies, video games and other media. People associate different models with the messages they are used to getting in those forms ... grainy black and white photographs accompanied by closely set text in narrow columns is a simple model associated with newspapers, so the use of these elements in combination may suggest to an audience journalism, accuracy of fact, realism and authenticity. If you have ever been to a toy store with a 10-12 year old boy you may have noticed that it is almost impossible to get him to go down the "pink aisle" where all the dolls are displayed, but that he has an unerring eye for the strong color combinations typical of video game displays. When you are planning the visual identity for a site you can't afford to use a media model that inadvertently offends or disinterests your audience.
Barbie Collectibles.
Engage. go back to the High Content model
References Web references Art and the Zen of Web Sites, Tony Karp, TLC Systems Corp. Design Issues and Conventions for Web Pages, Elizabeth Boling and Sonny Kirkley, Indiana University. Elements of HTML Style, J.K. Cohen, University of California. HyperContent, HyperJunk: Hypertext theory as if the WWWeb matters , Jorn Barger. Indiana University Basics of Web Design, Indiana University. Style Guide, Gareth Rees, University of Cambridge. Guide to Web Style, Rick Levine, Sun Microsystems, Inc. WSC Style Guide for Online Hypertext, Tim Berners-Lee, World Wide Web Consortium. Web Style Manual, Patrick Lynch, Yale Center for Advanced Instructional Media.
file:///F|/ztemp/design_guideline/guidelines.html (7 of 8)15.02.2005 22:16:33
Web Site Design Profiles: Guidelines by Profile
Print references Niederst, J. & Freedman, E. (1996). Designing for the Web: Getting started in a new medium. Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly. (See O'Reilly for a description of this book.) Waters, C. (1996). Web concept and design: A comprehensive guide for creating effective Web sites. Indianapolis, IN: New Riders. (See typo.com for an overview of this book.) back to the top of the page
AECT 1997 Conference, Albuquerque, NM Elizabeth Boling, Kurt Squire, Sonny Kirkley Indiana University Last updated 7 January 1997 URL: http://www.indiana.edu/~iirg/ARTICLES/AECT97/guidelines.html
file:///F|/ztemp/design_guideline/guidelines.html (8 of 8)15.02.2005 22:16:33
Вам также может понравиться
- Ux Myths Poster EngДокумент32 страницыUx Myths Poster EngPaskualОценок пока нет
- Empowerment Technology Week 5-6Документ17 страницEmpowerment Technology Week 5-6Sonia Agustin100% (2)
- Exterro FTK 7.5.1-User GuideДокумент612 страницExterro FTK 7.5.1-User GuideMuhammad ZulkhairiОценок пока нет
- Angels in America A Gay PDFДокумент1 страницаAngels in America A Gay PDFGabriel Castillo0% (1)
- Bambang Ali Basyah Sarif Coe, KfupmДокумент33 страницыBambang Ali Basyah Sarif Coe, Kfupmmido2266100% (1)
- 65 Web Design Terms You Should Know EbookДокумент14 страниц65 Web Design Terms You Should Know EbookTuggОценок пока нет
- The Seven Deadly Sins of Powerpoint PresentationsДокумент5 страницThe Seven Deadly Sins of Powerpoint PresentationsNiranjan Kumar DasОценок пока нет
- NEU Web Technologies End of Module ProjectДокумент4 страницыNEU Web Technologies End of Module ProjectNguyễn DatОценок пока нет
- How To Create 5 Fabulous Infographics FinalДокумент6 страницHow To Create 5 Fabulous Infographics FinalKreiton SitorusОценок пока нет
- How To Win in A Digital EconomyДокумент6 страницHow To Win in A Digital EconomyAntonio SОценок пока нет
- How To Create InfographicsДокумент6 страницHow To Create InfographicsRahul AroraОценок пока нет
- How to Create Five Fabulous Infographics in PowerPointДокумент6 страницHow to Create Five Fabulous Infographics in PowerPointhpdefalconОценок пока нет
- Re-Designingandopensourcingourportfoliowebsite FinaldraftДокумент14 страницRe-Designingandopensourcingourportfoliowebsite Finaldraftapi-317127031Оценок пока нет
- Intelligent Web Design TechniquesДокумент40 страницIntelligent Web Design TechniquesEkle Onoja WilliamsОценок пока нет
- TipsДокумент7 страницTipsMaster EjОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three Web Page Design Issues: Users Are ScannersДокумент6 страницChapter Three Web Page Design Issues: Users Are ScannersEfoy TechОценок пока нет
- Basics of Web DesignДокумент8 страницBasics of Web DesignUsman JuniorОценок пока нет
- L8 Basic Webpage CreationДокумент40 страницL8 Basic Webpage CreationMikhaila FernandezОценок пока нет
- Tips For Making Effective PowerPoint PresentationsДокумент6 страницTips For Making Effective PowerPoint PresentationsHilario Domingo ChicanoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5.1: Slide Design and Elements, and Animation and MediaДокумент7 страницLesson 5.1: Slide Design and Elements, and Animation and MediabeeeeeОценок пока нет
- Infographic AssignmentДокумент5 страницInfographic Assignmentnael94Оценок пока нет
- Q4-Module-3Документ20 страницQ4-Module-3Krd lyricОценок пока нет
- Online Creation Tools and Web Design PrinciplesДокумент13 страницOnline Creation Tools and Web Design PrinciplesKyla Grace BedisОценок пока нет
- Architecture Presentation BoardДокумент26 страницArchitecture Presentation BoardHealthene Joy Familara AlesnaОценок пока нет
- Week 6Документ8 страницWeek 6John Denver De la CruzОценок пока нет
- Imaging and Design For The Online Environment: Prepared By: Ms. Erica V. SalisodДокумент18 страницImaging and Design For The Online Environment: Prepared By: Ms. Erica V. SalisodRenie FedericoОценок пока нет
- Graphics and Video CreationsДокумент63 страницыGraphics and Video CreationsAMAN SОценок пока нет
- UX Module 07 Week 003Документ105 страницUX Module 07 Week 003Duas RuasОценок пока нет
- Web Design Principles ChecklistДокумент5 страницWeb Design Principles Checklistp_caracenaОценок пока нет
- Web Design PrinciplesДокумент46 страницWeb Design PrinciplesjenniferespanolОценок пока нет
- How To Make A Poster Eye-Catching and EffectiveДокумент9 страницHow To Make A Poster Eye-Catching and Effectiveeljay gomezОценок пока нет
- Ch. 2 Web DesignДокумент17 страницCh. 2 Web Designpriyanimbhorepatil20Оценок пока нет
- How To Create 5 Fabulous Infographics v4Документ6 страницHow To Create 5 Fabulous Infographics v4Wilkens JM SantosОценок пока нет
- How To Create 5 Fabulous InfographicsДокумент6 страницHow To Create 5 Fabulous InfographicsGajendra Singh SisodiaОценок пока нет
- Tips For Making Effective Powerpoint PresentationsДокумент6 страницTips For Making Effective Powerpoint PresentationsJyotishree PandeyОценок пока нет
- Tips and TricksДокумент7 страницTips and TricksRamesh ChandraОценок пока нет
- Inclusive Design PatternsДокумент313 страницInclusive Design PatternsmistiОценок пока нет
- Inclusive Design PatternsДокумент313 страницInclusive Design PatternsLevente Kiraly100% (2)
- 10 Design Principles ExamplesДокумент17 страниц10 Design Principles ExamplesAbinav NatarajanОценок пока нет
- 21 Unique Web Design Trends For 2021 Webflow BlogДокумент1 страница21 Unique Web Design Trends For 2021 Webflow Bloggpzq29nwrtОценок пока нет
- Tzul - Exp22 - Word - Ch04 - ML1 - Design (1) 2Документ9 страницTzul - Exp22 - Word - Ch04 - ML1 - Design (1) 2muhammadaboubakker1122Оценок пока нет
- Internet and E-BusinessДокумент83 страницыInternet and E-BusinessRobert LancerОценок пока нет
- Module 9Документ20 страницModule 9Leonora CidОценок пока нет
- ESL Brains Web Design Trends TV 2833Документ5 страницESL Brains Web Design Trends TV 2833antonina.1989Оценок пока нет
- TerminologiesДокумент43 страницыTerminologiesAileen P. de LeonОценок пока нет
- 8.nature and Purposes of Online PlatformsДокумент26 страниц8.nature and Purposes of Online PlatformsRyan Rojas RicablancaОценок пока нет
- Web Page DesignДокумент19 страницWeb Page DesignSabel Ross CaliliwОценок пока нет
- MoodBoard Vs StoryBoardДокумент1 страницаMoodBoard Vs StoryBoardchihiroОценок пока нет
- Printed Media 3Документ3 страницыPrinted Media 3Maricar SabilalaОценок пока нет
- Digital Design in ActionДокумент31 страницаDigital Design in Actionsaeed farragОценок пока нет
- Digital Design in Action - Creative Solutions For DesignersДокумент249 страницDigital Design in Action - Creative Solutions For DesignersSANDEEP STH100% (4)
- Poster-Making 101: An Important Note About The Poster Printers at BatesДокумент14 страницPoster-Making 101: An Important Note About The Poster Printers at BatesAriZonaFlavorОценок пока нет
- JAVASCRIPT para IniciantesДокумент30 страницJAVASCRIPT para IniciantesJennifer ReisОценок пока нет
- Technical Vocational Livelihood: Brief IntroductionДокумент8 страницTechnical Vocational Livelihood: Brief IntroductionJericho del rosarioОценок пока нет
- Unit 5: Create Meaningful Graphics, Icons and ImagesДокумент15 страницUnit 5: Create Meaningful Graphics, Icons and ImagesSai Venkat GudlaОценок пока нет
- REF - Design SkillsДокумент38 страницREF - Design SkillsSteve BoyesОценок пока нет
- PC Chapter 6Документ10 страницPC Chapter 6Jemie Cortillo100% (1)
- R Data Visualization Cookbook Sample ChapterДокумент25 страницR Data Visualization Cookbook Sample ChapterPackt PublishingОценок пока нет
- IA Etech11 Week 5Документ21 страницаIA Etech11 Week 5Lhyanne100% (1)
- 18 of The Best Personal Websites Weve Ever SeenДокумент18 страниц18 of The Best Personal Websites Weve Ever SeenPeter LostОценок пока нет
- Howtonotsuckonline PosterДокумент1 страницаHowtonotsuckonline PosterElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- University Computer Systems Security PolicyДокумент2 страницыUniversity Computer Systems Security PolicyElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Don't Take Design Critique As An Insult - UX CollectiveДокумент5 страницDon't Take Design Critique As An Insult - UX CollectiveElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- 10 Commandments For UI Design - UX Collective PDFДокумент11 страниц10 Commandments For UI Design - UX Collective PDFElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- What Makes A Design Seem IntuitiveДокумент8 страницWhat Makes A Design Seem IntuitiveElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- GIRAFAДокумент1 страницаGIRAFAElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Usability Testing Reveals OPAC IssuesДокумент18 страницUsability Testing Reveals OPAC IssuesElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Usability Testing of An Academic Library Web: Site: A Case StudyДокумент12 страницUsability Testing of An Academic Library Web: Site: A Case StudyElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Tony Spaeth: IdentityДокумент8 страницTony Spaeth: IdentityElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- CaballoДокумент1 страницаCaballoElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- What Makes A Design Seem IntuitiveДокумент8 страницWhat Makes A Design Seem IntuitiveElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Improving Your Skills in Usability Testing: CHI 2002 TutorialДокумент18 страницImproving Your Skills in Usability Testing: CHI 2002 TutorialElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- TetraДокумент1 страницаTetrackyt521Оценок пока нет
- Logo Critique SpiralsДокумент34 страницыLogo Critique SpiralsElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Logo Identity ChecklistДокумент1 страницаLogo Identity ChecklistElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
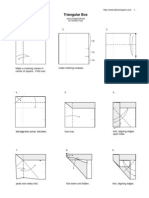
- Triangular Box: Make A Marking Crease in Center of Square. Fold Over. Make Marking Creases. Fold Down To First CreaseДокумент3 страницыTriangular Box: Make A Marking Crease in Center of Square. Fold Over. Make Marking Creases. Fold Down To First CreaseElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- How To Become A Creative GeniusДокумент19 страницHow To Become A Creative GeniusElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Trad Page1Документ1 страницаTrad Page1ckyt521100% (2)
- Trad Page2Документ1 страницаTrad Page2ckyt521Оценок пока нет
- Printstop - Com Publishing TipzДокумент19 страницPrintstop - Com Publishing TipzElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Monitor Calibration: by Thomas NiemannДокумент6 страницMonitor Calibration: by Thomas NiemannmrrwhoОценок пока нет
- SpidersДокумент3 страницыSpidersElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Platinum RectangleДокумент2 страницыPlatinum Rectangleapi-3834843Оценок пока нет
- Market Share 02Документ1 страницаMarket Share 02Elizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Memo From Walt DisneyДокумент10 страницMemo From Walt DisneyElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Top100 Advertising OrgzДокумент2 страницыTop100 Advertising OrgzElizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Nike's Just Do It - CampaignДокумент3 страницыNike's Just Do It - Campaignapi-371600250% (2)
- Business tCA Campaign Plan TemplateДокумент3 страницыBusiness tCA Campaign Plan TemplateAmar_IbsОценок пока нет
- Ad 4 Results V3Документ164 страницыAd 4 Results V3Elizabeth ArosteguiОценок пока нет
- Java Inner Class (Nested Class) PDFДокумент4 страницыJava Inner Class (Nested Class) PDFKajal SinghОценок пока нет
- Replacement, AMC & Warranty Management Solution - TallyWarmДокумент12 страницReplacement, AMC & Warranty Management Solution - TallyWarmMilansolutionsОценок пока нет
- Install PDFДокумент18 страницInstall PDFreferenceref31Оценок пока нет
- Amendment57 HCДокумент4 страницыAmendment57 HCMengistu TayeОценок пока нет
- 2.DataTypes Control Statements OperatorsДокумент42 страницы2.DataTypes Control Statements OperatorsKolachalama MythiliОценок пока нет
- Android Security ArchitectureДокумент9 страницAndroid Security ArchitectureSomayeh SeidoonОценок пока нет
- Database PL SQL Packages and Types ReferenceДокумент4 982 страницыDatabase PL SQL Packages and Types ReferenceAna BorobioОценок пока нет
- Tor Active LinksДокумент38 страницTor Active LinksshangОценок пока нет
- 100 Cool Mainframe TipsДокумент15 страниц100 Cool Mainframe Tipskishore21kОценок пока нет
- After You Will Open The VirtualДокумент3 страницыAfter You Will Open The VirtualStanley EhizОценок пока нет
- Guide To Linux File Command MasteryДокумент23 страницыGuide To Linux File Command MasteryAnbao ChengОценок пока нет
- Catalyst 8000 Edge Platforms Family: Accelerate Your Journey To The CloudДокумент40 страницCatalyst 8000 Edge Platforms Family: Accelerate Your Journey To The CloudAlonso Sal y RosasОценок пока нет
- CДокумент161 страницаCMano HaranОценок пока нет
- SAS Certified Base Programmer For SAS 9 - A00-211 - DumpsДокумент30 страницSAS Certified Base Programmer For SAS 9 - A00-211 - Dumpsmukesh75% (36)
- Emr Specification V4.1a - Appendix F - Mar082013 v1Документ33 страницыEmr Specification V4.1a - Appendix F - Mar082013 v1marcpitreОценок пока нет
- GL200 SMS Protocol V102 Decrypted.100130920 PDFДокумент28 страницGL200 SMS Protocol V102 Decrypted.100130920 PDFCezaryОценок пока нет
- ISTQB-Full-Practice-Test-ISTQB - Guru-03 - Unlocked 40 SoruДокумент12 страницISTQB-Full-Practice-Test-ISTQB - Guru-03 - Unlocked 40 SoruErdoğan HizanОценок пока нет
- Ail 605 Assignment 3 Empress Searight Multimedia Project ToolsДокумент5 страницAil 605 Assignment 3 Empress Searight Multimedia Project ToolsEmpress SearightОценок пока нет
- Leica DX Manager FLY 850605 0320 en LRДокумент2 страницыLeica DX Manager FLY 850605 0320 en LRAndré OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Gpsmap 580/585: Chartplotter/Combo Fishfinder Owner's ManualДокумент98 страницGpsmap 580/585: Chartplotter/Combo Fishfinder Owner's ManualfattaharisОценок пока нет
- Detect Fraudulent Water Customers Using Data MiningДокумент36 страницDetect Fraudulent Water Customers Using Data MiningSaikiran MamidiОценок пока нет
- Rapidshare Download LinksДокумент4 страницыRapidshare Download LinksyayayalОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Computer Technology on Accounting Systems and EmploymentДокумент12 страницThe Impact of Computer Technology on Accounting Systems and Employmentafqhs100% (1)
- Dell PowerEdge R520Документ2 страницыDell PowerEdge R520Illiana CassaniОценок пока нет
- Sergio Ananias O. English CVДокумент1 страницаSergio Ananias O. English CVSergio AnaniasОценок пока нет
- Database Design Theory: Introduction To Databases CSCC43 Winter 2012 Ryan JohnsonДокумент15 страницDatabase Design Theory: Introduction To Databases CSCC43 Winter 2012 Ryan JohnsonwuvesevarОценок пока нет
- All Chapter Exercise of VBДокумент50 страницAll Chapter Exercise of VBephrem mollaОценок пока нет
- User Manual: HAT560N Series (HAT560N/HAT560NB) Ats ControllerДокумент29 страницUser Manual: HAT560N Series (HAT560N/HAT560NB) Ats ControllercarderinОценок пока нет