Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
SQL
Загружено:
Hariprasad Reddy GИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SQL
Загружено:
Hariprasad Reddy GАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SQL
* SQL
is a standard computer language for accessing and manipulating databases.
What is SQL?
SQL SQL SQL SQL SQL SQL SQL SQL SQL stands for Structured Query Language allows you to access a database is an ANSI standard computer language can execute queries against a database can retrieve data from a database can insert new records in a database can delete records from a database can update records in a database is easy to learn
SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML):
SELECT - extracts data from a database table UPDATE - updates data in a database table DELETE - deletes data from a database table INSERT INTO - inserts new data into a database table
SQL Data Definition Language (DDL):
CREATE TABLE - creates a new database table ALTER TABLE - alters (changes) a database table DROP TABLE - deletes a database table CREATE INDEX - creates an index (search key) DROP INDEX - deletes an index
SQL Data Control Language (DCL): Grant Revoke Rollback Commit
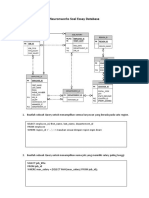
Way of procedure to create database and table (database name is vel and table name is murugan): First we have to create database Ex; Create database vel; Then use that database
Ex; Use vel; And then we have to create table Ex; Create table murugan (id int, name varchar (20), city varchar (20)); After create table we have to insert values Ex; Insert into murugan values (1,velmurugan,cuddalore); If we want see that tables then we have to use following queries Ex; Select * from murugan;
Id 1
Name Velmurugan
City cuddalore
If you want to add more than two tables then We should using like following queries Ex; Insert into murugan values (2,balaji,cuddalore), (3,suresh,cuddalore), (4,selvi,chennai), (5,sam, pondy); Then you want see that table Ex; Select*from murugan;
Id 1 2 3 4 5
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai pondy
Select statement: If you want see id no: 2 only means then we have to use Ex; Select id from murugan;
Id 1 2 3 4 5
If you want to see more than two fields, for example consider in name, city field. Then Ex; Select name, city from murugan;
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai pondy
In city field cuddalore comes three times if we want to see the city without difference then we have to use Distinct statement; Ex; Select distinct city from murugan;
City Cuddalore Chennai pondy
Where clause : If we want to find out particularly city=cuddalore then Ex;
Select * from murugan where city=cuddalore;
Id 1 2 3
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore
Condition cause (<,>, <=,>=, <> (not equal)): If you want to find out less than and more than from numeric field i.e. id then Ex; Select * from murugan where id<3;
Id 1 2
Name Velmurugan Balaji
City Cuddalore Cuddalore
Ex; Select * from murugan where id>3;
Id 4 5
Name Selvi Sam
City Chennai pondy
Ex; Select * from murugan where id <=3;
Id 1 2 3
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore
Ex; Select * from murugan where id >=3;
Id 3 4 5
Name Suresh Selvi Sam
City Cuddalore Chennai pondy
If we want find out without city=cuddalore then Ex; Select * from murugan where city<>cuddalore;
Id 4 5
Name Selvi Sam
City Chennai pondy
Like conditions: If we want to find out the city with first letter then Ex; Select * from murugan where city like c%;
Id 1 2 3 4
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai
If we want to find out the name with last letter then
Ex; Select * from murugan where name like %i;
Id 2 4
Name Balaji Selvi
City Cuddalore Chennai
If we want to find out the city with first two letters then Ex; Select * from murugan where city like %cu%;
Id 1 2 3
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore
Insert into statements: If we want insert the datas only for specified columns then Ex; Insert into murugan (id, city) values (7,vadalur); Then Select * from murugan;
Id 1 2 3 4 5 7
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam NILL
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai Pondy vadalur
Update statment : If we want to update the datas for empty columns then Ex; Update murugan set name=barani where id=7;
Id 1 2 3 4 5 7
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam barani
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai Pondy vadalur
If we want update more than one column then Ex; Update murugan set id=6, city=Salem where name=barani;
Id 1 2 3 4 5 6
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam barani
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai Pondy Salem
Delete statment : If we want to delete that particular column from table then Ex; Delete from murugan where id=6;
Id 1 2 3 4 5
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai pondy
If we want to delete overall table then Ex; Delete from murugan; Or Delete * from murugan; Order by clause: If we want to see the name and city in alphabetical order then Ex; Select name, city from murugan order by name, city;
Name Balaji Sam Selvi Suresh Velmurugan
City Cuddalore Pondy Chennai Cuddalore Cuddalore
The above format we can use another model like (asc (ascending order), desc (descending order)) Ex; Select name, city from murugan order by name asc, city desc; And or clause: The AND operator displays a row if ALL conditions listed are true. Ex; Select * from murugan where id=3 and city=cuddalore;
Id 3
Name Suresh
City Cuddalore
The OR operator displays a row if ANY of the conditions listed are true. Ex;
Select * from murugan where id=3 or city=cuddalore;
Id 1 2 3
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh
City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore
You can also combine AND and OR (use parentheses to form complex expressions): Ex; Select * from murugan where (id=3 and city=cuddalore) and id=3;
Id 3 Name Suresh City Cuddalore
In clause: If we want to see that selected datas it can be two or three then Ex; Select * from murugan where name in (balaji,selvi);
Id 2 4
Name Balaji Selvi
City Cuddalore Chennai
Between .And clause: The BETWEEN ... AND operator selects a range of data between two values. These values can be numbers, text, or dates. Ex; Select * from murugan where id between 2 and 5;
Id Name City
2 3 4 5
Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam
Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai pondy
Ex; Select * from murugan where id not between 2 and 5;
Id 1 Name Velmurugan City cuddalore
Aliases clause: If we want to change the table name and column name then we have to use alias clause If you want change column name then Ex; Select id as userid, name as employeename from murugan;
Userid 1 2 3 4 5 employeename Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam
If you want change the table name of particular column of table then Ex; Select name, city from murugan as balaji;
Name Velmurugan Balaji Suresh Selvi Sam City Cuddalore Cuddalore Cuddalore Chennai pondy
The above table name is balaji.
Вам также может понравиться
- Performance Report SummaryДокумент13 страницPerformance Report SummaryHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- POSTMAN Complete Reference Guide For API TestingДокумент6 страницPOSTMAN Complete Reference Guide For API TestingHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Performance Test Report: Cycle 1Документ40 страницPerformance Test Report: Cycle 1Hariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- ChaduvuinnerДокумент4 страницыChaduvuinnerHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Here Was A Dog Called ElleotДокумент1 страницаHere Was A Dog Called ElleotHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- ATP Transacction Flow ProcessДокумент1 страницаATP Transacction Flow ProcessHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Here Was A Dog Called ElleotДокумент1 страницаHere Was A Dog Called ElleotHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Vbscript: Vbscipt User'S Guide Vbscript Langauge ReferenceДокумент331 страницаVbscript: Vbscipt User'S Guide Vbscript Langauge Referenceanon_987603882Оценок пока нет
- Test Case Path Test Case Name Test DescriptionДокумент9 страницTest Case Path Test Case Name Test DescriptionHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- User Scenario 1: Identifying The UI (When The User Logs As Just A PPD and Not and LEP With Only User Role)Документ45 страницUser Scenario 1: Identifying The UI (When The User Logs As Just A PPD and Not and LEP With Only User Role)Hariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- QTP Technical QuestionsДокумент14 страницQTP Technical Questionskarthick_49Оценок пока нет
- VBScripting For QTPДокумент78 страницVBScripting For QTPAmardeep KumarОценок пока нет
- VB Script General ExamplesДокумент12 страницVB Script General ExamplesHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- User Scenario 1: Identifying The UI (When The User Logs As Just A PPD and Not and LEP With Only User Role)Документ45 страницUser Scenario 1: Identifying The UI (When The User Logs As Just A PPD and Not and LEP With Only User Role)Hariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- VB Script General ExamplesДокумент12 страницVB Script General ExamplesHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Scenario 3 Navigate From A Page To OtherДокумент144 страницыScenario 3 Navigate From A Page To OtherHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- VBScript in QTPДокумент30 страницVBScript in QTPsachxn100% (22)
- Datastage Interview QuestionsДокумент22 страницыDatastage Interview Questionsanilsoft.comОценок пока нет
- Application KeywordДокумент15 страницApplication KeywordHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- User GuideДокумент174 страницыUser Guidemanojinfa9Оценок пока нет
- FiltersДокумент1 страницаFiltersHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Seleniul ContentsДокумент3 страницыSeleniul ContentsHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Application KeywordДокумент15 страницApplication KeywordHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- User GuideДокумент174 страницыUser Guidemanojinfa9Оценок пока нет
- InformaticaДокумент3 страницыInformaticaChandrasekar VempalleeОценок пока нет
- Test Case Path Test Case Name Test DescriptionДокумент9 страницTest Case Path Test Case Name Test DescriptionHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Informatica QuestionnaireДокумент79 страницInformatica Questionnairelokeshscribd186Оценок пока нет
- Seleniul ContentsДокумент3 страницыSeleniul ContentsHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- Seleniul ContentsДокумент3 страницыSeleniul ContentsHariprasad Reddy GОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Install OA Framework jDeveloperДокумент11 страницInstall OA Framework jDeveloperendalОценок пока нет
- MySQL Database and Image Storage in JavaДокумент4 страницыMySQL Database and Image Storage in JavaPutraOrionОценок пока нет
- Why Redundancy and Replication?Документ5 страницWhy Redundancy and Replication?avcОценок пока нет
- Use Firebug to collect source code and identify server-side technologiesДокумент16 страницUse Firebug to collect source code and identify server-side technologiesAbdullah Mirza100% (1)
- Literature Review On System Development Life CycleДокумент7 страницLiterature Review On System Development Life Cyclegvznen5kОценок пока нет
- Starting Out With Java-Gaddis NotesДокумент2 страницыStarting Out With Java-Gaddis NotesThomas NgoОценок пока нет
- Test DiskДокумент67 страницTest DiskkarlheinzeОценок пока нет
- The 6 Annual Data Report: B2B MarketingДокумент13 страницThe 6 Annual Data Report: B2B MarketingSean TanОценок пока нет
- IT4IT Definitions and SymbolsДокумент2 страницыIT4IT Definitions and SymbolsLuis Alberto Lamas LavinОценок пока нет
- Catalyst Plug-In For SAP HANAДокумент34 страницыCatalyst Plug-In For SAP HANANeoОценок пока нет
- 70 346 QuestionsДокумент19 страниц70 346 QuestionsMelania UzunОценок пока нет
- Techrefvol2 PDFДокумент482 страницыTechrefvol2 PDFRachidAbdallahОценок пока нет
- Ccs K Study GuideДокумент35 страницCcs K Study Guidedeals4kbОценок пока нет
- Spring Certification 4.2 Mock ExamДокумент26 страницSpring Certification 4.2 Mock ExamEdyBОценок пока нет
- MIT203 - Advanced System Design and ImplementationДокумент5 страницMIT203 - Advanced System Design and ImplementationRedan JonnaОценок пока нет
- List of All Published Articles by Learn SAP Tips (As of 3rd Jan 2016)Документ5 страницList of All Published Articles by Learn SAP Tips (As of 3rd Jan 2016)Anupa Wijesinghe100% (3)
- Scrap Website With Python Free Code CampДокумент6 страницScrap Website With Python Free Code CampusmvandeОценок пока нет
- Ch3 Network ImplementationДокумент132 страницыCh3 Network ImplementationtsibiОценок пока нет
- Backend Assignment - Dream11Документ2 страницыBackend Assignment - Dream11Priyanka mestryОценок пока нет
- SRC SCHUMACK GDS2-3.00 Lib GDS2.PmДокумент46 страницSRC SCHUMACK GDS2-3.00 Lib GDS2.PmYongchang HuangОценок пока нет
- Ditya Felix - Essay DatabaseДокумент9 страницDitya Felix - Essay Databasenija100% (1)
- Racking Up Office 365 Sales: A Step-By-Step Guide To Reselling Office 365 For Vars & MspsДокумент35 страницRacking Up Office 365 Sales: A Step-By-Step Guide To Reselling Office 365 For Vars & MspsJawan StarlingОценок пока нет
- Dynamic File GenerationДокумент24 страницыDynamic File GenerationetlvmaheshОценок пока нет
- Win License HelpДокумент273 страницыWin License HelpmetanirvanaОценок пока нет
- Good - PWC Services OfferДокумент28 страницGood - PWC Services OffermanishОценок пока нет
- SafeNet Ikey4000 PB (En) WebДокумент2 страницыSafeNet Ikey4000 PB (En) WebbasharaccountОценок пока нет
- CV François La Haye Data Analyst 1.3Документ2 страницыCV François La Haye Data Analyst 1.3FrançoisAmaniОценок пока нет
- USMTGUI User GuideДокумент11 страницUSMTGUI User GuideNguyen Hoang AnhОценок пока нет
- Rabbit MQ y Symfony2Документ81 страницаRabbit MQ y Symfony2Cristhian FernándezОценок пока нет
- Transaction Control Transformation: Informatica Complete Reference Informatica Complete ReferenceДокумент8 страницTransaction Control Transformation: Informatica Complete Reference Informatica Complete ReferenceRavi Chandra Reddy MuliОценок пока нет