Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Form 5 Nutrition
Загружено:
JoycelinaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Form 5 Nutrition
Загружено:
JoycelinaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
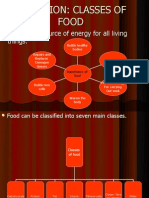
Chapter 2 1. There are 7 main classes of food, namely : 2.
A balanced diet is food that contains all the classes of food in the right ratio and quality to maintain good health. 3. Calorific value is __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. It is measured in ______________(cal) or __________(J) by using Bomb Calorimeter. Type of food Margerine Butter Groundnuts Chocolate milk Cake Sugar (white) Cornflakes Rice White Bread Chicken Potato (boiled) Milk Cabbage (steamed) Calories (kJ) 32.2 31.2 24.5 24.2 18.0 16.5 15.3 15.0 10.6 7.7 6.6 3.3 2.7 0.34
Meal TIme Breakfast 100g of cornflakes 100g of eggs 200g of milk Lunch 250g of rice 200g of chicken 200g of cabbage Tea time 50g of cakes 150g of nuts 10g of sugar Dinner 200g of rice 200g of chicken 50g of eggs 50g of potatoes
Calculation
Total Calories (kJ)
Total
Factors Affecting the Calories Requirement 1. Age 2. Gender 3. Occupation/Physical Activities 4. Body Size 5. Climate 6. Body Health HEALTH PROBLEMS AND EATING HABITS 1. Malnutrition = is diet which contains insufficient of nutrients. Deficiency in Protein DIsease Symptoms Retarded Growth, swollen tummy, loss of appetite, diarrhoea Pale because of lack of haemoglobin the blood Fatigue, irritability, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances, abdominal discomfort, a burning sensation in the feet that is particularly severe at night, and pain, weakness and wasting of muscles in the leg Swelling of the thyroid gland Thin, too weak to do work Soft bones and teeth, teeth decay easily, head becomes bigger and chest shrink Bleeding of gums Bruises like a chain form around the neck Night vision is very weak
Iron Vitamin B
Iodine Carbohydrate Vitamin D, Calcium
Vitamin C Vitamin B Vitamin A 2. Bad eating habits will lead to -
3. Obesity = extra calories which form fats because of overeating Obesity Diseases High blood pressure Diabetes Mellitus Gout Cholesterol Excessive intake of
FOOD Carbohydrates a. Starch b. Glucose c. Cellulose/fibre Protein (Amino acids) Fats
DEFICIENCY Underweight/marasmus Coma Constipation Kwashiorkor Underweight, vitamins such as A, D, E, K cannot be dissolved FUNCTION Maintains healthy skin and eyesight Needed in cellular respiration, maintains a healthy nervous system Wounds heal faster, healthy skin and gums, prevent spreading of diseases Help clotting of blood, help body to absorb calcium, can be formed by our skin when expose to ultraviolet(UV) light Maintain the reproductive system Clotting of blood FUNCTION Formation of bones, teeth and clotting of blood Formations of bones and teeth Build up plasma To prevent goiter Build haemoglobin in red blood cells
EXCESSIVE
Change into urea by liver
VITAMINS A B
DEFICIENCY
E K MINERALS Calcium Phosphorus Sodium Iodine Iron
DEFICIENCY
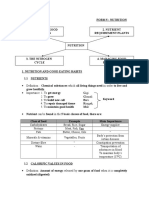
NUTRIENTS REQUIREMENTS OF PLANTS Nutrients needed by plants 1. Macronutrients and micronutrients MACRONUTRIENTS Are nutrients needed in large quantities for growth FUNCTION EFFECT OF DEFICIENCY
NUTRIENT Nitrogen
Potassium
Calcium
Sulphur
Magnesium
Phosphorus
Carbon
MICRONUTRIENTS Are nutrients needed in small quantities FUNCTION
NUTRIENTS Boron
Molybdenum
Zinc
Manganese
Copper
Iron
THE NITROGEN CYCLE AND ITS IMPORTANCE 1. Nitrogen is important for synthesis of protein. 2. Though nitrogen stands about 78% in our atmosphere but they could not be used by plants and animals directly. 3. Plants get nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate ions. 4. Nitrogen is recycled in nature through the nitrogen cycle.
Вам также может понравиться
- Wjec Eduqas Level 1 /2 Hospitality and Catering Unit 2: Guide To Completing The Unit 2 CourseworkДокумент36 страницWjec Eduqas Level 1 /2 Hospitality and Catering Unit 2: Guide To Completing The Unit 2 CourseworkEve InacioОценок пока нет
- A Healthy DietДокумент20 страницA Healthy DietsunoyebimpeОценок пока нет
- TLE 322 Chapter 5 NewДокумент9 страницTLE 322 Chapter 5 NewKrizzia Gladys Mae JuanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 NuritionДокумент54 страницыChapter 2 NuritionteacherYatie82Оценок пока нет
- Nutrition: Classes of Food: Food Is The Source of Energy For All Living ThingsДокумент36 страницNutrition: Classes of Food: Food Is The Source of Energy For All Living ThingsSuria SawalОценок пока нет
- Lesson - 1 Human NutritionДокумент21 страницаLesson - 1 Human NutritionJesus saves youОценок пока нет
- SSU0013 Basic Science Molecules of Life and NutritionДокумент35 страницSSU0013 Basic Science Molecules of Life and NutritionMuhammad SyamimОценок пока нет
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course Questions SolutionsДокумент111 страниц2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course Questions SolutionsVan halenОценок пока нет
- 2223 Level M Biology Course Questions - Solutions UpdatedДокумент129 страниц2223 Level M Biology Course Questions - Solutions UpdatedFreddy BotrosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ8 страницChapter 2Abhinaba PaulОценок пока нет
- Lecture9 GEST1007 2022 ClassДокумент30 страницLecture9 GEST1007 2022 Classa28437938Оценок пока нет
- THesisДокумент13 страницTHesismahoojhaaseОценок пока нет
- 7.1 7.2 Animal Nutrition Alimentary CanalДокумент6 страниц7.1 7.2 Animal Nutrition Alimentary CanalgesОценок пока нет
- Food and Nutrition Revision NotesДокумент9 страницFood and Nutrition Revision NotesNiamh Marie McCarville100% (3)
- Animal NutritionДокумент15 страницAnimal NutritionDewan Anisha IslamОценок пока нет
- Sports &nutrition 12thДокумент4 страницыSports &nutrition 12thPavitra Kumar JainОценок пока нет
- A Balanced Diet and Nutrition: The Nutritional FunctionДокумент4 страницыA Balanced Diet and Nutrition: The Nutritional FunctionAnonymous iOaluenhОценок пока нет
- 6 HBДокумент6 страниц6 HBMonkey LoverОценок пока нет
- Biology Level M Couse Questions SolutionДокумент71 страницаBiology Level M Couse Questions SolutionMyNameIsYeetОценок пока нет
- Also Know The Good Food Sources of Each Type of NutrientДокумент28 страницAlso Know The Good Food Sources of Each Type of NutrientOctaviano SimonОценок пока нет
- Best Keto Dessert Diet Cookbook: The Easy Way to Cut Down on Carbs and Then Obtain a Sufficient Protein and NutrientОт EverandBest Keto Dessert Diet Cookbook: The Easy Way to Cut Down on Carbs and Then Obtain a Sufficient Protein and NutrientОценок пока нет
- Commit To Be Fit: Wellness Comes From Healthy Diet and ExerciseДокумент37 страницCommit To Be Fit: Wellness Comes From Healthy Diet and ExerciseGary TengОценок пока нет
- Diet-The Vital NutrientsДокумент32 страницыDiet-The Vital Nutrientsevelin.szaboОценок пока нет
- Vitamin DДокумент38 страницVitamin DPriya BhirmanОценок пока нет
- NUTRITIONДокумент5 страницNUTRITIONDesy Ayu SukmaОценок пока нет
- The Ketogenic Diet Cookbook: The Complete Guide To Healthy Low Carb And High Fat Keto RecipesОт EverandThe Ketogenic Diet Cookbook: The Complete Guide To Healthy Low Carb And High Fat Keto RecipesОценок пока нет
- Diet and Growth PPT Grade 7Документ21 страницаDiet and Growth PPT Grade 7redwannawazОценок пока нет
- Quick Keto Meals: Easy Ketogenic Cooking In 30 Minutes Or LessОт EverandQuick Keto Meals: Easy Ketogenic Cooking In 30 Minutes Or LessОценок пока нет
- Module 3Документ33 страницыModule 3Saalif RahmanОценок пока нет
- Components of Food Q&A Work Done Today 13th May PDFДокумент44 страницыComponents of Food Q&A Work Done Today 13th May PDFPradeepKanwarОценок пока нет
- Ketogenic Snack Kitchen with Metabolism Diet and Apple Cider Vinegar UsesОт EverandKetogenic Snack Kitchen with Metabolism Diet and Apple Cider Vinegar UsesОценок пока нет
- As The Food Vehicle NutrientsДокумент4 страницыAs The Food Vehicle Nutrients4gen_7Оценок пока нет
- Keto Diet: 60 Amazing High-Fat/Low-Carb Keto Recipes and 7-Day Ketogenic Meal Plan for Weight Loss and Healthy LifeОт EverandKeto Diet: 60 Amazing High-Fat/Low-Carb Keto Recipes and 7-Day Ketogenic Meal Plan for Weight Loss and Healthy LifeОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Sports &-Nutrition 2Документ38 страницCH 5 Sports &-Nutrition 2kartikeyakushwaha046Оценок пока нет
- About Soaps: Chemistry: Soaps and DetergentsДокумент82 страницыAbout Soaps: Chemistry: Soaps and DetergentsGeethjvbОценок пока нет
- Components of FoodДокумент3 страницыComponents of FoodRAndy rodelas100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Grade-12Документ5 страницChapter 5 Grade-12umamahfarooq75Оценок пока нет
- LasagnaДокумент13 страницLasagnaapi-552730267Оценок пока нет
- THesisДокумент21 страницаTHesismahoojhaaseОценок пока нет
- CH-2 Class 12 (1) PDFДокумент48 страницCH-2 Class 12 (1) PDFAshok KumarОценок пока нет
- NUTRITIONДокумент11 страницNUTRITIONVANGAWA JOHNОценок пока нет
- Human Nutrition NotesДокумент7 страницHuman Nutrition Notesirumfatimakhlaq2008Оценок пока нет
- Ketogenic Diet with Apple Cider Vinegar for Beginners: Weight Loss with Easy Low-Carb Dessert RecipesОт EverandKetogenic Diet with Apple Cider Vinegar for Beginners: Weight Loss with Easy Low-Carb Dessert RecipesОценок пока нет
- B.inggris FdanadaДокумент6 страницB.inggris Fdanadaegafadelia fadeliaОценок пока нет
- NSC 310 Disease Conditions Excess and DeficiencyДокумент4 страницыNSC 310 Disease Conditions Excess and DeficiencyPreciousОценок пока нет
- Optimizing Nutrition for Weight Loss: A Comprehensive GuideОт EverandOptimizing Nutrition for Weight Loss: A Comprehensive GuideОценок пока нет
- TengG WB10 FinalДокумент117 страницTengG WB10 FinalScott BurtonОценок пока нет
- Dentifying THE Rinciples OF UtritionДокумент30 страницDentifying THE Rinciples OF UtritionIon Logofătu AlbertОценок пока нет
- A 7-Day Keto Cookbook: A Complete Guide to Weight Loss and a Healthier LifestyleОт EverandA 7-Day Keto Cookbook: A Complete Guide to Weight Loss and a Healthier LifestyleОценок пока нет
- SportssssДокумент2 страницыSportssssKisha KhuranaОценок пока нет
- Healthy EatingДокумент63 страницыHealthy EatingMahesh ManeОценок пока нет
- AyalaM WBFinalДокумент20 страницAyalaM WBFinalMarinaeayalaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Form 5 ScienceДокумент9 страницChapter 2 Form 5 ScienceSubashini Muniandy100% (1)
- Before You Do Keto Diet: Do’s and Don’ts of Keto for BeginnersОт EverandBefore You Do Keto Diet: Do’s and Don’ts of Keto for BeginnersОценок пока нет
- EthicДокумент14 страницEthicJoycelinaОценок пока нет
- HBET1103 Christina Teh 880326015084001Документ12 страницHBET1103 Christina Teh 880326015084001JoycelinaОценок пока нет
- Listening and Speaking AssignmentДокумент30 страницListening and Speaking AssignmentJoycelinaОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 - The Fall of MalaccaДокумент1 страницаTopic 1 - The Fall of MalaccaJoycelinaОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 - The Fall of MalaccaДокумент1 страницаTopic 1 - The Fall of MalaccaJoycelinaОценок пока нет
- The Influence of Schema Theory On Foreign Language Reading ComprehensionДокумент9 страницThe Influence of Schema Theory On Foreign Language Reading ComprehensionJoycelinaОценок пока нет
- Clinic by Alissa QuartДокумент4 страницыClinic by Alissa QuartOnPointRadioОценок пока нет
- Urine Case 2010-2Документ9 страницUrine Case 2010-2hendra_darmawan_4Оценок пока нет
- Project Proposal: A. Project Tittle: "Operation Cleanliness"Документ8 страницProject Proposal: A. Project Tittle: "Operation Cleanliness"Mike Avila100% (1)
- 2022 India Accessibility Standards and Guidelines For Civil Aviation - EnglishДокумент110 страниц2022 India Accessibility Standards and Guidelines For Civil Aviation - EnglishDisability Rights AllianceОценок пока нет
- 1053-Article Text-2175-1-10-20230227Документ8 страниц1053-Article Text-2175-1-10-20230227inОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4: Roadway Lighting Evaluation And: DesignДокумент12 страницExperiment 4: Roadway Lighting Evaluation And: DesignEdogawa ConanОценок пока нет
- Public Opinion On Idea of Digitalising Rural CommunityДокумент11 страницPublic Opinion On Idea of Digitalising Rural CommunityINSTITUTE OF LEGAL EDUCATIONОценок пока нет
- CCL-81 Product Sheet - VeroДокумент5 страницCCL-81 Product Sheet - VeroKrishnan KrishnanОценок пока нет
- The Adult Psychodiagnostic Chart 2012 1.7 PDFДокумент3 страницыThe Adult Psychodiagnostic Chart 2012 1.7 PDFMF LeblancОценок пока нет
- Business Plan SampleДокумент14 страницBusiness Plan SampleErvin Evangelista100% (1)
- Effectiveness of Maitland vs. Mulligan Mobilization Techniques in (Ingles)Документ4 страницыEffectiveness of Maitland vs. Mulligan Mobilization Techniques in (Ingles)mauricio castroОценок пока нет
- SRM04-05 On A Silver PlatterДокумент37 страницSRM04-05 On A Silver PlatterBrandon Dempe100% (1)
- BiotechnologyДокумент39 страницBiotechnologyChrystal Kyla SalengaОценок пока нет
- Logistics Management Plan FormatДокумент10 страницLogistics Management Plan FormatAnna BelleОценок пока нет
- Med Tech LawsДокумент78 страницMed Tech LawsMarie LlanesОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Phinma University of PangasinanДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan: Phinma University of PangasinanShaira De La CruzОценок пока нет
- Owner's Manual: Ironman TRIAD TreadmillДокумент34 страницыOwner's Manual: Ironman TRIAD Treadmilljtaylor888Оценок пока нет
- Darrells ResumeДокумент5 страницDarrells Resumeapi-273253154Оценок пока нет
- Normal GFR in ChildДокумент8 страницNormal GFR in ChildbobbypambudimdОценок пока нет
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Teaching Strategies Knowledge Regarding Drug Calculation Among B.Sc. N Students in Selected College at ChennaiДокумент3 страницыA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Teaching Strategies Knowledge Regarding Drug Calculation Among B.Sc. N Students in Selected College at ChennaiEditor IJTSRDОценок пока нет
- Periodontal AbscessДокумент27 страницPeriodontal AbscessAhmed Tawfig GamalОценок пока нет
- Agri SBA (Broiler)Документ20 страницAgri SBA (Broiler)Shanti KissoondyalОценок пока нет
- BA 89402175 001100 Innopack EN 00 PDFДокумент293 страницыBA 89402175 001100 Innopack EN 00 PDFBruno GiffoniОценок пока нет
- Kardiomed-700-User ManualДокумент87 страницKardiomed-700-User ManualJulia TimakovaОценок пока нет
- Baby Led-WeaningДокумент7 страницBaby Led-WeaningsophieОценок пока нет
- DebateДокумент12 страницDebate•Kai yiii•Оценок пока нет
- Jeehp 12 06Документ4 страницыJeehp 12 06Sohini KhushiОценок пока нет
- Recent EMF Papers PDFДокумент394 страницыRecent EMF Papers PDFAndi Kurniawan100% (1)
- Using Disinfectants and Gels: ATL Ultrasound P.O. Box 3003 Bothell, WA 98041-3003 USA 4700-0249-18 Rev A June 2001Документ73 страницыUsing Disinfectants and Gels: ATL Ultrasound P.O. Box 3003 Bothell, WA 98041-3003 USA 4700-0249-18 Rev A June 2001Foued MbarkiОценок пока нет
- Disaster Readiness Risk Reduction: Quarter 2-Module 13: DRR-related Laws and PoliciesДокумент16 страницDisaster Readiness Risk Reduction: Quarter 2-Module 13: DRR-related Laws and PoliciesUel Cabz LaquihonОценок пока нет