Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Corporate Finance - Formulas
Загружено:
Abhijit PanditАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Corporate Finance - Formulas
Загружено:
Abhijit PanditАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
==================================Capital Structure====================================
1. Total risk of equity shareholders = ROE
2. Business risk = ROE (u)
3. Financial risk = ROE - ROE (u)
Without Corporate Taxes;
[V(lev) = market value of a leveraged company, V(unlev) = market value of an unleveraged company,
Ko = weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of a leveraged company, Keu = cost of equity of an
unleveraged company, EBIT = earnings before interest and tax]
[Ko = overall capitalization rate (WACC), Ke = cost of equity capital, Kd = cost of debt, We =
proposition of equity in total capital, Wd = proposition of debt in total capital, E = amount of
equity capital, D = amount of debt capital]
4. V(lev) = V(unlev) = EBIT / Ko = EBIT / Keu
5. Ke = Ko + (Ko Kd) * D/E
With Corporate Taxes (t);
[Vu = value of unlevered company, Keu = cost of equity of unlevered company, t = corporate tax rate]
[V(lev) = market value of levered company, Vu = market value of unlevered company, D = market
value of debt, t = corporate tax rate]
[Ke = cost of equity of levered company, Keu = cost of equity of unlevered company, Kd = cost of debt,
D/E = debt equity ratio, t = corporate tax rate]
6. Vu = EBIT*(1-t) / Keu
7. V(lev) = Vu + Dt
8. Ke = Keu + (Keu Kd) * D/E * (1-t)
9. V(lev) = D + E
10. WACC = We * Ke + Wd * Kd * (1 t)
==================================Personal Tax====================================
11. A stockholder receives the net amount = (1-TC) x (1-TS)
12. The bondholder receives = (1-TB)
13. If T
S
= T
B
then the firm should be financed primarily by debt (avoiding double tax).
14. The firm is indifferent between debt and equity when: (1-T
C
) x (1-T
S
) = (1-T
B
)
15. Tax advantage of debt is positive when:
(1-T
C
) x (1-T
S
) < (1-T
B
)
16. Tax advantage of debt is negative when:
(1-T
C
) x (1-T
S
) > (1-T
B
)
17. Vu = EBIT * (1-T
C
)* (1-T
S
) / Keu
18.
19. EBIT Interest = EBT; EBT Taxes = EAT; EAT Preference Div = Earnings avail = EPS * No of Shares
D *
) T (1
) T (1 * ) T (1
1 V V
B
S C
U L
+ =
==================================
[Po =Current value of the equity share; Do=Dividend per share paid at time 0; g=Constant rate of
growth of dividends; Ke = Cost of the retained earnings
1. Ke = Do*(1+g) /Po + g
[gr = Rapid growth rate of dividend during the first n years; gn =Normal growth rate of dividend
continuously for ever; Pn = Share price at the end of n years]
2. Pn = Do*(1+gr)^n*(1+gn) / (Ke
3. Po = Do*(1+gr) / (1+Ke) + Do*(1+gr)^2 / (1+Ke)^2 + .
[E(Rs) = Expected rate of return of the security; Rf= Risk
return of the market; s = Beta co
4. E(Rs) = Rf + s [E(Rm) Rf]
5. E(Rs) = Rf + s [E(Rm) Rf]
6.
=====Cost of Equity========
7. Net proceeds = Po (1 f).
8. Cost of the new equity
9. Adjustment for flotation costs
=====Cost of Preference Capital
10. Kp = D / [Po*(1-f)]
11. Kat= (1-t) * Kbt
[We = Proportion of equity in the total capital; Wp = preference shares; Wd = debt ; Ke = Cost
of retained earnings / external equity; Kp = Cost of preference capital; Kd = Pre
t=corporate tax rate; We + Wp + Wd = 1.0
12. WACC = We * Ke + Wp * Kp
13. With constant D/E ratio;
14. With constant amount of D
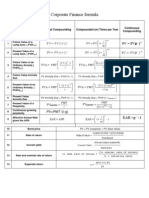
===============================
FV = C
0
(1 + r)
C
0
is cash flow today (time zero),r is the appropriate interest rate.
FV = C
0
(1 + r)
T..
T is the number of periods over which the cash is invested.
NPV = Cost + PV
Continuous Compounding, FV =
==================================Cost of Capital====================================
e equity share; Do=Dividend per share paid at time 0; g=Constant rate of
Ke = Cost of the retained earnings]
Constant Dividend Growth Model
= Rapid growth rate of dividend during the first n years; gn =Normal growth rate of dividend
continuously for ever; Pn = Share price at the end of n years]
gn) Two Stage Growth Model
*(1+gr)^2 / (1+Ke)^2 + . + Do*(1+gr)^n / (1+Ke)^n +Pn / (1+Ke)^n
Using Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) approach
[E(Rs) = Expected rate of return of the security; Rf= Risk-free rate of return; E(Rm) = Expected rate of
Beta co-efficient of the security]
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) Approach
or, E(Rs) = (1-s) Rf + s E(Rm)
. [Po = Gross amount received per share; f =Percent floatation costs.]
= Cost of the existing equity + Adjustment for the flotatio
= Do*(1+g)*f / [Po*(1-f)]
=====Cost of Preference Capital========
[Kp = Cost of Preference share capital; D = Annual dividend]
[Kat=post-tax cost; Kbt=pre-tax cost; t=corporate income tax rate.]
[We = Proportion of equity in the total capital; Wp = preference shares; Wd = debt ; Ke = Cost
of retained earnings / external equity; Kp = Cost of preference capital; Kd = Pre
We + Wp + Wd = 1.0]
+ Wp * Kp + Wd * Kd * (1-t)
(equity) = (asset) (1+D/E)
(equity) = (unlevered firm) [1+(1-t)*D/E]
===============================Discounted Cash Flow==================================
is cash flow today (time zero),r is the appropriate interest rate.
T is the number of periods over which the cash is invested. ; e is a transcendental number approximately equal to 2.718.
= C
0 .
e
rT
2
2
) (
) , (
M
i
M
M i
R Var
R R Cov
= =
r
C
PV
+
=
1
1
C FV =
====================================
e equity share; Do=Dividend per share paid at time 0; g=Constant rate of
Constant Dividend Growth Model
= Rapid growth rate of dividend during the first n years; gn =Normal growth rate of dividend
+ Do*(1+gr)^n / (1+Ke)^n +Pn / (1+Ke)^n
Using Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) approach
free rate of return; E(Rm) = Expected rate of
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) Approach
f =Percent floatation costs.]
+ Adjustment for the flotation costs
[Kp = Cost of Preference share capital; D = Annual dividend]
t=corporate income tax rate.]
[We = Proportion of equity in the total capital; Wp = preference shares; Wd = debt ; Ke = Cost
of retained earnings / external equity; Kp = Cost of preference capital; Kd = Pre-tax cost of debt;
==================================
is cash flow today (time zero),r is the appropriate interest rate.
e is a transcendental number approximately equal to 2.718.
T m
m
r
C
+ 1
0
Perpetuity
Growing
Perpetuity
Annuity
Growing
Annuity
T
T
r
g C
r
g C
r
C
PV
) 1 (
) 1 (
) 1 (
) 1 (
) 1 (
1
2
+
+
+ +
+
+
+
+
=
L
1
1
]
1
|
|
\
|
+
+
=
T
r
g
g r
C
PV
) 1 (
1
1
T
r
C
r
C
r
C
r
C
PV
) 1 ( ) 1 ( ) 1 ( ) 1 (
3 2
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
= L
+
=
T
r r
C
PV
) 1 (
1
1
L +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
=
3
2
2
) 1 (
) 1 (
) 1 (
) 1 (
) 1 ( r
g C
r
g C
r
C
PV
g r
C
PV
=
L +
+
+
+
+
+
=
3 2
) 1 ( ) 1 ( ) 1 ( r
C
r
C
r
C
PV
r
C
PV =
Вам также может понравиться
- Exam Prep for:: Business Analysis and Valuation Using Financial Statements, Text and CasesОт EverandExam Prep for:: Business Analysis and Valuation Using Financial Statements, Text and CasesОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionОт EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (8)
- Finance Cheat SheetДокумент4 страницыFinance Cheat SheetRudolf Jansen van RensburgОценок пока нет
- CheatSheet (Finance)Документ1 страницаCheatSheet (Finance)Guan Yu Lim100% (3)
- Kelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Документ2 страницыKelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Kelly Koh100% (4)
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetДокумент4 страницыCorporate Finance Formula Sheetogsunny100% (3)
- CorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2Документ2 страницыCorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2subtle69100% (4)
- BF2201 Cheat Sheet FinalsДокумент2 страницыBF2201 Cheat Sheet Finalssiewhong93100% (1)
- Overview of Financial Management Concepts and ToolsДокумент4 страницыOverview of Financial Management Concepts and ToolsPeixuan Zhuang100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet Corporate - FinanceДокумент2 страницыCheat Sheet Corporate - FinanceAnna BudaevaОценок пока нет
- Fnce 100 Final Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыFnce 100 Final Cheat SheetToby Arriaga100% (2)
- Corporate Finance Math SheetДокумент19 страницCorporate Finance Math Sheetmweaveruga100% (3)
- Cheat Sheet Final - FMVДокумент3 страницыCheat Sheet Final - FMVhanifakih100% (2)
- Cheat Sheet - AccountingДокумент2 страницыCheat Sheet - AccountingJeffery KaoОценок пока нет
- Equation Formula: 1 1 FV PMT 1Документ3 страницыEquation Formula: 1 1 FV PMT 1JMSB09Оценок пока нет
- Cheat Sheet - EXAM Version - BARBARAДокумент2 страницыCheat Sheet - EXAM Version - BARBARAJosé António Cardoso RodriguesОценок пока нет
- FMV Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаFMV Cheat SheetAyushi SharmaОценок пока нет
- Midsem Cheat Sheet (Finance)Документ2 страницыMidsem Cheat Sheet (Finance)lalaran123Оценок пока нет
- Corporate FinanceДокумент19 страницCorporate FinanceBilal Shahid100% (4)
- Formula Sheet Corporate Finance (COF) : Stockholm Business SchoolДокумент6 страницFormula Sheet Corporate Finance (COF) : Stockholm Business SchoolLinus AhlgrenОценок пока нет
- Fin Cheat SheetДокумент3 страницыFin Cheat SheetChristina RomanoОценок пока нет
- Session 2 - Doing VC Deals - Lecture Presentation Slides IM 5 Mar 12Документ58 страницSession 2 - Doing VC Deals - Lecture Presentation Slides IM 5 Mar 12Henry So E Diarko100% (1)
- CheatДокумент1 страницаCheatIshmo KueedОценок пока нет
- Finance ProblemSets11Документ323 страницыFinance ProblemSets11Stefan CN100% (2)
- The Ultimate Financial Management Cheat SheetДокумент3 страницыThe Ultimate Financial Management Cheat SheethazimОценок пока нет
- Accounting Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыAccounting Cheat Sheetanoushes1100% (2)
- Balance of Payments:: Chapter Objectives & Lecture Notes FINA 5500Документ27 страницBalance of Payments:: Chapter Objectives & Lecture Notes FINA 5500Anonymous H0SJWZE8100% (1)
- Summary - Corporate Finance Beck DeMarzoДокумент54 страницыSummary - Corporate Finance Beck DeMarzoAlejandra100% (2)
- DCF Intrinsic ValuationДокумент38 страницDCF Intrinsic ValuationKritika KoulОценок пока нет
- FIN6215-Cheat Sheet BigДокумент3 страницыFIN6215-Cheat Sheet BigJojo Kittiya100% (1)
- Cfa Level I - Us Gaap Vs IfrsДокумент4 страницыCfa Level I - Us Gaap Vs IfrsSanjay RathiОценок пока нет
- Cheat Sheet For Financial AccountingДокумент1 страницаCheat Sheet For Financial Accountingmikewu101Оценок пока нет
- Accounting Cheat Sheet FinalsДокумент5 страницAccounting Cheat Sheet FinalsRahel CharikarОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance Cheat SheetДокумент3 страницыCorporate Finance Cheat Sheetdiscreetmike50Оценок пока нет
- 3 - FCF CalculationДокумент2 страницы3 - FCF CalculationAman ManjiОценок пока нет
- Practice MidtermДокумент8 страницPractice MidtermghaniaОценок пока нет
- Cohen Finance Workbook FALL 2013Документ124 страницыCohen Finance Workbook FALL 2013Nayef AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Intl Finance Cheat SheetДокумент6 страницIntl Finance Cheat Sheetpradhan.neeladriОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance FormulasДокумент3 страницыCorporate Finance FormulasMustafa Yavuzcan83% (12)
- Corporate FinanceДокумент24 страницыCorporate Financeapi-3719687100% (3)
- Financial Modeling and Analysis 3Ed-LibreДокумент14 страницFinancial Modeling and Analysis 3Ed-LibremjcstimsonОценок пока нет
- Managerial Accounting Mid-Term Cheat SheetДокумент6 страницManagerial Accounting Mid-Term Cheat SheetĐạt Nguyễn100% (1)
- Atlassian 3 Statement Model CompleteДокумент24 страницыAtlassian 3 Statement Model CompleteShrey JainОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance Cheatsheet Zhiwei NewДокумент2 страницыCorporate Finance Cheatsheet Zhiwei NewZaggie NgОценок пока нет
- Technical Finance Interview Prep (Student)Документ261 страницаTechnical Finance Interview Prep (Student)fernando.torrealbatesiОценок пока нет
- Handout # 1 Solutions (L)Документ10 страницHandout # 1 Solutions (L)Prabhawati prasadОценок пока нет
- Finance Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыFinance Cheat SheetMarc MОценок пока нет
- Dividend Discount and Residual Income Models ExplainedДокумент2 страницыDividend Discount and Residual Income Models ExplainedMohammad DaulehОценок пока нет
- Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыCheat SheetDimana Dollo100% (1)
- Capital Structure and Cost of CapitalДокумент3 страницыCapital Structure and Cost of CapitalAbhijit PanditОценок пока нет
- FIN 401 - Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыFIN 401 - Cheat SheetStephanie NaamaniОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetДокумент9 страницCorporate Finance Formula SheetWilliamОценок пока нет
- Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceДокумент6 страницFormulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceNaeemОценок пока нет
- Financial Management - Formula SheetДокумент8 страницFinancial Management - Formula SheetHassleBustОценок пока нет
- R) (1 CF ...... R) (1 CF R) (1 CF CF NPV: Invesment Initial NPV 1 Invesments Initial Flows Cash Future of PVДокумент9 страницR) (1 CF ...... R) (1 CF R) (1 CF CF NPV: Invesment Initial NPV 1 Invesments Initial Flows Cash Future of PVAgnes LoОценок пока нет
- CFA Formula Cheat SheetДокумент9 страницCFA Formula Cheat SheetChingWa ChanОценок пока нет
- Cost of CapitalДокумент31 страницаCost of CapitalMadhuram Sharma100% (1)
- Accounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionОт EverandAccounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (8)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)От EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Рейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (17)
- Geneva IntrotoBankDebt172Документ66 страницGeneva IntrotoBankDebt172satishlad1288Оценок пока нет
- Victor's Letter Identity V Wiki FandomДокумент1 страницаVictor's Letter Identity V Wiki FandomvickyОценок пока нет
- Course Syllabus: Aurora Pioneers Memorial CollegeДокумент9 страницCourse Syllabus: Aurora Pioneers Memorial CollegeLorisa CenizaОценок пока нет
- Lec - Ray Theory TransmissionДокумент27 страницLec - Ray Theory TransmissionmathewОценок пока нет
- Civil Aeronautics BoardДокумент2 страницыCivil Aeronautics BoardJayson AlvaОценок пока нет
- Tyron Butson (Order #37627400)Документ74 страницыTyron Butson (Order #37627400)tyron100% (2)
- Mayor Byron Brown's 2019 State of The City SpeechДокумент19 страницMayor Byron Brown's 2019 State of The City SpeechMichael McAndrewОценок пока нет
- CORE Education Bags Rs. 120 Cr. Order From Gujarat Govt.Документ2 страницыCORE Education Bags Rs. 120 Cr. Order From Gujarat Govt.Sanjeev MansotraОценок пока нет
- Asian Construction Dispute Denied ReviewДокумент2 страницыAsian Construction Dispute Denied ReviewJay jogs100% (2)
- Wind EnergyДокумент6 страницWind Energyshadan ameenОценок пока нет
- Benchmarking Guide OracleДокумент53 страницыBenchmarking Guide OracleTsion YehualaОценок пока нет
- Case Study 2 F3005Документ12 страницCase Study 2 F3005Iqmal DaniealОценок пока нет
- ZOOLOGY INTRODUCTIONДокумент37 страницZOOLOGY INTRODUCTIONIneshОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Succession-1Документ8 страницIntroduction To Succession-1amun dinОценок пока нет
- Chill - Lease NotesДокумент19 страницChill - Lease Notesbellinabarrow100% (4)
- Safety QualificationДокумент2 страницыSafety QualificationB&R HSE BALCO SEP SiteОценок пока нет
- ITSCM Mindmap v4Документ1 страницаITSCM Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallОценок пока нет
- ADSLADSLADSLДокумент83 страницыADSLADSLADSLKrishnan Unni GОценок пока нет
- NEW CREW Fast Start PlannerДокумент9 страницNEW CREW Fast Start PlannerAnonymous oTtlhP100% (3)
- Improvements To Increase The Efficiency of The Alphazero Algorithm: A Case Study in The Game 'Connect 4'Документ9 страницImprovements To Increase The Efficiency of The Alphazero Algorithm: A Case Study in The Game 'Connect 4'Lam Mai NgocОценок пока нет
- High Altitude Compensator Manual 10-2011Документ4 страницыHigh Altitude Compensator Manual 10-2011Adem NuriyeОценок пока нет
- Department Order No 05-92Документ3 страницыDepartment Order No 05-92NinaОценок пока нет
- DSA NotesДокумент87 страницDSA NotesAtefrachew SeyfuОценок пока нет
- Advance Bio-Photon Analyzer ABPA A2 Home PageДокумент5 страницAdvance Bio-Photon Analyzer ABPA A2 Home PageStellaEstel100% (1)
- Micromaster 430: 7.5 KW - 250 KWДокумент118 страницMicromaster 430: 7.5 KW - 250 KWAyman ElotaifyОценок пока нет
- 50TS Operators Manual 1551000 Rev CДокумент184 страницы50TS Operators Manual 1551000 Rev CraymondОценок пока нет
- 1LE1503-2AA43-4AA4 Datasheet enДокумент1 страница1LE1503-2AA43-4AA4 Datasheet enAndrei LupuОценок пока нет
- International Convention Center, BanesworДокумент18 страницInternational Convention Center, BanesworSreeniketh ChikuОценок пока нет
- GS Ep Cor 356Документ7 страницGS Ep Cor 356SangaranОценок пока нет
- Resume Ajeet KumarДокумент2 страницыResume Ajeet KumarEr Suraj KumarОценок пока нет