Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Numerical Protection
Загружено:
Raj Kumar PrajapatiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Numerical Protection
Загружено:
Raj Kumar PrajapatiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Re: 50/51G and 50/51N 50 a IEEE Device number defined as an "Instantaneous over current relay, or rate-ofrise relay that
functions instantaneously on an excessive value of current, or on an excessive rate of current rise, thus indication a fault in the apparatus of circuit being protected. Device 51 is an AC time over current relay which is a relay with either a definite or inverse time characteristic that functions when the current in the AC circuit exceeds a Predetermined value. 'G'=Generator, or ground 'N'=Network, or neutral Suffix "N" generally used in reference to "G" for devices connected in the secondary neutral current transformers, or in the secondary of a current transformer whose primary winding is located in the neutral of a machine or power transformer, except in the case of transmission line relaying, where the suffix "G" is more commonly used for those relays which operate on ground fault. The actual protective relay being applied would most likely be in the "CO" relay family used with a suitable sized CT on the neutral. However, the selection as well as the setting values of the device would be the responsibility of a electrical engineering consultant who has experience in protective relaying and distribution system coordination.
Current transformers are used to transform high currents to standardized values for control equipment as relays and meters. The primary winding in a current transformer is incorporated in the line and carries the current flowing in the network. The magnitude of the secondary current is dependent of the ratio of the transformer. A current transformer (CT) is a type of instrument transformer designed to provide a current in its secondary winding proportional to the alternating current flowing in its primary. They are commonly used in metering and protective relaying in the electrical power industry where they facilitate the safe measurement of large currents, often in the presence of high voltages. The current transformer safely isolates measurement and control circuitry from the high voltages typically present on the circuit being measured. The most common design of CT consists of a length of wire wrapped many times around a silicon steel ring passed over the circuit being measured. The CT's primary circuit therefore consists of a single 'turn' of conductor, with a secondary of many hundreds of turns. The CT acts as a constant-current series device with an apparent power burden a fraction of that of the high voltage primary circuit. Hence the primary circuit is largely unaffected by the insertion of the CT. Usage Current transformers are used extensively for measuring current and monitoring the operation of the power grid. The CT is typically described by its current ratio from primary to secondary. Often, multiple CTs are installed as a "stack" for various uses (for example, protection devices and revenue metering may use separate CTs). Similarly potential transformers are used for measuring voltage and monitoring the operation of the power grid.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- TestingДокумент14 страницTestingRaj Kumar PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- 220kv Switch Yard View and Equipment FunctionsДокумент3 страницы220kv Switch Yard View and Equipment FunctionsRaj Kumar Prajapati100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Vacuum CBДокумент8 страницVacuum CBAntra ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- ILFS PresentationДокумент21 страницаILFS PresentationmeghanahariОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Substation ReliabilityДокумент19 страницSubstation ReliabilitypsenergiaОценок пока нет
- Specification Substation AutomationДокумент258 страницSpecification Substation Automationmspd2003100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Over CurrentДокумент5 страницOver Currentanon-6056Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Work Breakdown StructureДокумент9 страницWork Breakdown StructureArif ForhadОценок пока нет
- Ohms LawДокумент5 страницOhms LawRaj Kumar PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- Basic Electrical ConceptsДокумент4 страницыBasic Electrical ConceptsRaj Kumar PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Project Management 2: Chu Eu HoДокумент44 страницыProject Management 2: Chu Eu HoGanesh BorkarОценок пока нет
- 220kV GIS Tech Spec - TrackДокумент42 страницы220kV GIS Tech Spec - Trackaravind_k104100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- L-26 (TB) Three Phase TransformerДокумент16 страницL-26 (TB) Three Phase Transformervelisbar100% (1)
- 400KV Substion AP TranscoДокумент256 страниц400KV Substion AP TranscoRaj Kumar PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Construction Manual For Sub-StationsДокумент150 страницConstruction Manual For Sub-Stationspankaj_electrical0% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Protection PrimerДокумент61 страницаProtection Primertushar ddigheОценок пока нет
- IEC 61850 StandardДокумент2 страницыIEC 61850 StandardRaj Kumar PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- SDCK CD Ies 01 (Rev B)Документ125 страницSDCK CD Ies 01 (Rev B)Narada HerathОценок пока нет
- Sap MM LSMWДокумент18 страницSap MM LSMWMani balan100% (1)
- STN Cat Novelties Vol.i 2023Документ89 страницSTN Cat Novelties Vol.i 2023ruba herbawiОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Sad Thesis Guidelines FinalsДокумент13 страницSad Thesis Guidelines FinalsJes RamosОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- GaN technology powers bright LEDsДокумент13 страницGaN technology powers bright LEDsluciowwОценок пока нет
- Zener DataДокумент2 страницыZener Dataapi-27149887Оценок пока нет
- Thinking ForthДокумент311 страницThinking ForthCristianОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Catalog Advantys AS-I IP20-IP67 - 803510 - DIA3ED2040909EN - 200408Документ30 страницCatalog Advantys AS-I IP20-IP67 - 803510 - DIA3ED2040909EN - 200408Jean MarzanОценок пока нет
- Physics Lab ReportДокумент2 страницыPhysics Lab ReportFelix SonsunОценок пока нет
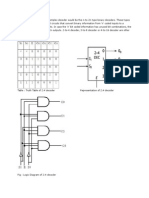
- 2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesДокумент6 страниц2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesPavithraRamОценок пока нет
- Simucube 2 Quick Release GuideДокумент7 страницSimucube 2 Quick Release Guideemyrs12Оценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Propeller DesignДокумент74 страницыPropeller DesignBambang Teguh Setiawan75% (4)
- Iraqi Code for Reinforced Concrete StructuresДокумент71 страницаIraqi Code for Reinforced Concrete Structuresmamandawe50% (2)
- Smart Access 1105Документ12 страницSmart Access 1105Gerson Freire De Amorim FilhoОценок пока нет
- Civil 3 8sem PDFДокумент43 страницыCivil 3 8sem PDFG0utham100% (1)
- Design of A Fluidized Drum GranulatorДокумент6 страницDesign of A Fluidized Drum GranulatorditchcheОценок пока нет
- List of Linkages2016Документ74 страницыList of Linkages2016engrwho0% (1)
- Diffraction of Laser Beam Using Wire Mesh, Cross Wire and GratingДокумент2 страницыDiffraction of Laser Beam Using Wire Mesh, Cross Wire and GratingPriyesh PandeyОценок пока нет
- Biogas Calculator TemplateДокумент27 страницBiogas Calculator TemplateAlex Julian-CooperОценок пока нет
- Strength and Insulating Properties of Building Blocks Made From Waste MaterialsДокумент7 страницStrength and Insulating Properties of Building Blocks Made From Waste Materialsmjrobust05Оценок пока нет
- Product Design Recommended Reading ListДокумент3 страницыProduct Design Recommended Reading ListSai Prasath100% (1)
- Strength of Pressure Vessels With Ellipsoidal HeadsДокумент8 страницStrength of Pressure Vessels With Ellipsoidal Headsنصرالدين ادريسОценок пока нет
- Failure Analysis of Syngas Bypass Line Rupture inДокумент11 страницFailure Analysis of Syngas Bypass Line Rupture inshahgardezОценок пока нет
- Hino 500S Catalog LR PDFДокумент8 страницHino 500S Catalog LR PDFZulОценок пока нет
- Minor Project Report On Efficiency Improvement of A Combined Cycle Power PlantДокумент40 страницMinor Project Report On Efficiency Improvement of A Combined Cycle Power PlantArpit Garg100% (1)
- Suvarnabhumi Airport Trial OperationДокумент4 страницыSuvarnabhumi Airport Trial Operationfwmching0% (1)
- Lab Sheet - Infiltration TestДокумент8 страницLab Sheet - Infiltration TestDINAMARIANASAMUJI0% (1)
- Lec 958975Документ19 страницLec 958975Rajasekar PichaimuthuОценок пока нет
- January2016page1to36 Layout 1Документ36 страницJanuary2016page1to36 Layout 1c737Оценок пока нет
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionОт EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)